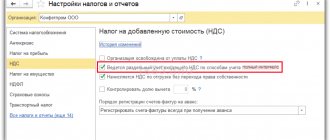
In accordance with paragraph 3 of the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when exporting and importing goods, performing work, providing services (Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union) when exporting goods from the territory of one EAEU member state to territory of another EAEU member state:
- a zero VAT rate is applied when submitting to the tax authority the documents provided for in paragraph 4 of the Protocol;
- the right to tax deductions is exercised in a manner similar to that provided for by the legislation of the EAEU member state in relation to goods exported outside the EAEU.
If non-commodity goods are shipped for export to EAEU member states:
- the deduction of the presented amount of VAT is carried out in the generally established manner, i.e., similar to the deduction for goods (work, services), property rights acquired for the implementation of transactions subject to VAT at rates of 18% and 10% (clause 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) ;
- The taxpayer does not have the obligation to determine the amount of VAT relating to goods (work, services), property rights acquired for the production and (or) sale of goods using a 0% rate, i.e. there is no obligation to maintain separate accounting (paragraph 2 p. 10, Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Receipt of payment for goods sold (operation 4.1 “Receipt of payment from buyer”) in the 1C: Accounting 8 version 3.0 program is reflected using the document Receipt to current account with the transaction type Payment from buyer, which is generated in the following ways:
- based on the document Invoice for payment to the buyer (section Sales - subsection Sales - journal of documents Invoices to buyers);
- by adding a new document to the Bank statements list (section Bank and cash desk - subsection Bank - document journal Bank statements).
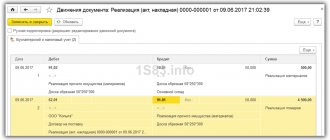
As a result of posting the document, the following accounting entry is entered into the accounting register:
Debit 51 Credit 62.01 - for the amount of payment received, which is 600,000.00 rubles.
A 0% VAT rate can be applied by a taxpayer-exporter if, within 180 calendar days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods, the validity of its application is confirmed by submitting a VAT return and a set of supporting documents to the Federal Tax Service (see above).
When selling goods provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the moment for determining the tax base is the last day of the quarter in which the full package of supporting documents is collected (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's consider the procedure for reflecting in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, confirmation of the VAT rate of 0% within 180 calendar days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods in the case of the sale of non-commodity goods for export to the EAEU countries.
In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 1 of the Protocol on Goods, to confirm the validity of the application of the zero VAT rate by the taxpayer of the CU member state from whose territory the goods were exported, the following documents (copies thereof) are submitted to the tax authority simultaneously with the tax return:
- agreements (contracts) with amendments (additions and annexes) to them, on the basis of which the export of goods is carried out;
- application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes, drawn up in the form established by the Protocol on the exchange of information in electronic form between the tax authorities of the member states of the Customs Union on the paid amounts of indirect taxes dated December 11, 2009 (Appendix 1), with a mark from the tax authority of the state — a member of the Customs Union into whose territory goods are imported, on the payment of indirect taxes (exemption or other procedure for fulfilling tax obligations). It should be noted that by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 30, 2012 N ММВ-7-6/, the electronic format of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes by Russian taxpayers was approved;
- transport (shipping) documents provided for by the legislation of the CU member state, confirming the movement of goods from the territory of one CU member state to the territory of another CU member state.
- other documents provided for by the legislation of the CU member state from whose territory the goods were exported. Such documents may be required, for example, in the case of selling goods through an intermediary (Clause 2 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They can be a commission agreement, a commission agreement or an agency agreement, reports from the intermediary on the performance of his duties, etc.
The exporter must provide the above documents to the tax authority within 180 calendar days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 1 of the Protocol on Goods, the date of shipment is the date of the first drawing up of the primary accounting document issued to the buyer of goods or the first carrier, or the date of issuance of another mandatory document provided for by the legislation of the CU member state for VAT payers.
According to the explanations of the regulatory authorities, set out in Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 11, 2013 N 03-07-13/1/26980 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 13, 2011 N KE-4-3 / tax base for goods sold to countries TS is determined on the last day of the quarter in which the full package of documents necessary to confirm the zero VAT rate is collected (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, if documents are collected within 180 calendar days from the date of shipment (transfer) of goods, they should be submitted to the inspection along with a declaration for the quarter in which they were collected.
In accordance with paragraph. 2 p. 1 art. 1 of the Protocol on Goods, when exporting goods from the territory of one CU member state to the territory of another CU member state, the taxpayer has the right to tax deductions in a manner similar to that provided for by the legislation of the CU member state applied to goods exported from the territory of this state beyond TS.
Clause 3 art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes a special procedure for deducting VAT in relation to operations for the sale of goods for export, according to which such a deduction is made at the time of determining the tax base under Art. 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, namely on the last day of the quarter in which documents confirming the zero rate were collected.
Operations for the export of goods to Belarus are reflected in the relevant sections of the VAT declaration, the form and procedure for filling which are approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 15, 2009 N 104n. (as amended on April 21, 2010). The declaration is submitted no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired quarter (Article 163, paragraph 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
RESTORATION OF EXPORT VAT. CLARIFICATIONS OF THE RUSSIAN MINISTRY OF FINANCE
Accounting for export transactions in 1C 8.3 Accounting - step-by-step instructions
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
The organization entered into an export contract with a foreign buyer LadystyleKz (Kazakhstan) for the supply of non-raw materials in the amount of 15,000 USD.
On February 15, the products “Kate” women’s sandals (1,000 pairs) worth 15,000 USD were exported to the buyer LadystyleKz.
In accordance with the contract, the transfer of ownership of the goods occurs at the moment the goods are transferred by the carrier to the buyer's warehouse. Delivery basis - DAP Almaty.
On February 18, the products were delivered to the buyer’s warehouse.
On February 20, the buyer of Ladystyle Kz transferred 100% postpayment for goods in the amount of 15,000 USD.
Conditional courses for example design:
- February 15, the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is 62.00 rubles/USD;
- February 18, the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is 63.00 rubles/USD;
- On February 20, the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation was 69.00 rubles/USD.
Let's look at the step-by-step instructions for processing export operations in 1C 8.3. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Sales of finished products for export (EAEU) | |||||||
| Shipment of finished products for export | |||||||
| February, 15 | 45.02 | 43 | 258 356,16 | 258 356,16 | 258 356,16 | Shipment of finished products | Sales (act, invoice) - Shipment without transfer of ownership |
| Issuance of export invoices in foreign currency (VAT rate 0%) | |||||||
| February, 15 | — | — | 15 000 | Issuing invoices for shipment in foreign currency (VAT rate 0%) | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| Sales of shipped products | |||||||
| 18th of Febuary | 62.21 | 90.01.1 | 945 000 | 945 000 | 945 000 | Revenue from product sales | Sales of shipped goods |
| 90.02.1 | 45.02 | 258 356,16 | 258 356,16 | 258 356,16 | Write-off of product costs | ||
| Receipt of payment from a foreign buyer | |||||||
| February 20th | 52 | 62.21 | 1 035 000 | 1 035 000 | Receipt of payment from a foreign buyer to a transit account | Receipt to the bank account - Payment from the buyer | |
| 62.21 | 91.01 | 90 000 | 90 000 | 90 000 | Revaluation of receivables in foreign currency | ||
| Submission of a statistical report to the Federal Customs Service in electronic form | |||||||
| 28th of February | — | — | 15 000 | Submission of a statistical report to the Federal Customs Service in electronic form | Regulated report - Statistical form of accounting for the movement of goods | ||
For the beginning of the example, see the publication:
- Purchase of materials for production of products
Find out about the release of products with the write-off of materials according to specifications (without the subconto Products)
Regulatory regulation
When exporting, a 0% VAT rate is applied, which must be confirmed. To do this, you should collect a package of documents and submit it simultaneously with the VAT return to the Federal Tax Service.
Please note that exports to the EAEU countries (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan) differ from shipments to non-CIS countries. The main regulatory document when working with partners from the EAEU is the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union dated May 29, 2014 (EAEU Treaty).
Taxation of export transactions is regulated by:
- Appendix No. 18 to the EAEU Treaty - the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when exporting and importing goods, performing work, and providing services (EAEU Protocol).
- The Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the part that is not regulated by the EAEU Protocol, as well as in cases where the Protocol makes reference to local legislation.
The moment of transfer of risks from the seller to the buyer according to Incoterms (Incoterms) and the moment of transfer of ownership of goods should not be confused.
The contract must indicate the moment of transfer of ownership, because according to this date:
- the asset is registered with the buyer;
- the buyer becomes indebted to the supplier for payment;
- Revenue in foreign currency is recalculated into rubles if there has been no prepayment.
When exporting non-commodity goods, there are different procedures for applying input VAT deductions depending on when they were purchased:
- until 07/01/2016 - VAT deduction at the time of confirmation of the 0% rate or not confirmation of it, if 180 days have passed for collecting documents, separate VAT accounting is maintained;
- from 07/01/2016 - VAT is deducted in the general manner; separate VAT accounting is not maintained (Federal Law dated 05/30/2016 N 150-FZ).
We will consider the export of non-commodity goods that were purchased and sold after 07/01/2016.
Is separate VAT accounting required when exporting to the EAEU in 1C?
Conditions Rate
| When selling telecommunication services | 25% |
| When selling crop products, wild products, beekeeping, livestock and fish farming produced on the territory of the Republic of Belarus. | 10% |
| When importing and (or) selling food products and goods for children according to the list approved by the President. | |
| When selling goods at regulated retail prices, including VAT. | 16.67% and 9.09% |
| When importing precious stones to Belarus from CU member countries for production purposes. | 0,5% |
| When selling (exporting) goods and services outside the country (Chapter 12, Article 102 of the Tax Code). | 0% |
VAT is transferred to the Belarusian state budget:
- Legal entity. These include organizations registered and conducting economic activities in Belarus, including foreign ones.
- Trustees for turnover arising from the disposal of the trustor's property in his favor.
- An individual entrepreneur whose quarterly revenue exceeds 40 thousand euros at the National Bank exchange rate. If desired, the individual entrepreneur can pay a percentage of the added value for any amount of revenue.
- Individuals with products imported into the country.
Legal entities from other countries operating in Belarus, but not registered with the tax authorities and not opening a branch, do not pay tax. In such a situation, a percentage of the added value is paid by those Belarusian organizations that purchase goods from a foreign legal entity.
The tax is imposed on the added value that arises during the sale of property rights or services within the country. This includes:
- free transfer of rights or goods;
- exchange;
- pledges and compensation;
- transfer of rental objects, leased items;
- transfer under a loan agreement of goods in the form of things;
- transfer of rights to intellectual property;
- import to Belarus;
- sale of the debtor's property during enforcement proceedings.
Added value is not paid for:
- Medicines, products and services in the field of medicine. Their list is approved by the head of state. The exemption does not apply to non-therapeutic cosmetology.
- Social services of government organizations, as well as non-profit non-governmental legal entities working in the format of stationary social services.
- Meals for students of educational institutions.
- Cultural services from the list approved by the head of the country.
- Arrangement of funerals and sale of ritual accessories: tombstones, fences, etc.
- Housing and communal services and maintenance services for individuals.
- Artworks of folk crafts.
When determining the amount of tax, one of the main points is the tax deduction. You can understand what this is using the example of reselling a product.
VAT is added to the sales price, but since the product has already been sold once, the previous seller has already allocated tax on it.
In such a situation, the previously allocated VAT is deducted from the amount contained in the sales price. This is called a tax deduction. Three categories of amounts are subtracted:
- tax imposed on a payer buying from a seller who is himself the payer;
- VAT already paid when importing products from abroad;
- tax paid at the time of purchase from foreign legal entities not registered with the Belarusian tax office.
Sometimes the deduction may be greater for the next payer than the value added tax itself. In such a situation, the payer does not owe anything to the budget, and the difference between all deductions and the final amount of VAT is returned.
Export of finished products in 1C 8.3
In our example, the transfer of ownership of finished products occurs not at the time of shipment, but at the time of delivery of the product to the buyer’s warehouse. Such a shipment is formalized by the document Sales (acts, invoice) transaction type Shipment without transfer of ownership in the section Sales - Sales - Sales (acts, invoices) - button Sales - Shipment without transfer of ownership).
Let's look at the features of filling out the Implementation document (act, invoice) following an example.
Document header
- Counterparty is a foreign buyer with whom a contract has been concluded. Selected from the Contractors directory.
When entering the Contractors of a buyer from the Eurasian Economic Union into the directory, you must provide the following data: PDF
- Country of registration - select KAZAKHSTAN from the drop-down list. Important for auto-filling the tabular part of the document Implementation (act, invoice) ;
- Tax number;
- Reg. number ;
- The TIN is filled out only for a foreign company that has registered for tax purposes in the Russian Federation. This is not our case.
- Agreement is a contract under which mutual settlements are carried out with a foreign buyer.
The agreement with the buyer in foreign currency must be completed as follows:
- Type of agreement - With the buyer ;
- Price in - USD , i.e. the currency in which the contract was concluded;
- Payment in - switch USD , i.e. payment currency.
In the Prices form in the document, the exchange rate is set from the Currency on the date of the document Sales (deed, invoice) .
Tabular part of the document
On the Products , information about the products being shipped is indicated (name, quantity, price, VAT rate, as well as accounting accounts, HS code, item group in the Subconto ):
- Nomenclature - products shipped to a foreign buyer are selected from the Nomenclature .
For goods (products) intended for export, be sure to fill out the following field in the nomenclature card:
- Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign , according to the Decision of the Council of the Eurasian Economic Commission dated July 16, 2012 N 54 - if the product (product) is a raw material , then the card with the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity code should have the Commodity Commodity .
The unit of measurement of the nomenclature must correspond to that established by law for a given HS code. In our example, the Unit is par .
This is important for filling out the report Statistical form for recording the movement of goods (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 19, 2020 N 891). The upload file is checked, among other things, for the correctness of the unit of measurement of the item according to the HS code.
- Commodity nomenclature code - the product code can be entered manually by selecting from the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity Classifier or pre-filled in the item card. Then the value will be inserted into documents automatically.
- Price and Amount - the columns are filled in in currency, since the agreement was concluded in USD.
- % VAT - 0% , the VAT rate applied when selling goods for export.
- Transfer account - account 45.02 “Finished products shipped” is used to reflect movements of shipped finished products when the proceeds from their sale are not immediately recognized in accounting. In our example, this is due to the fact that ownership of the goods does not pass from the seller to the buyer at the time of shipment.
a member country of the EAEU is selected in the Counterparty card in the Country of Registration the following columns will be automatically filled Sales document (act, invoice)
- % VAT with a value of 0%;
- The HS code is a code from the nomenclature card.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 45.02 Kt - shipment of finished products without transfer of ownership at actual cost.
The document is filled out in the currency based on the contract. The amounts in the entries are reflected in rubles. This is due to the fact that accounting in the Russian Federation is carried out in rubles. The value of assets or liabilities in foreign currency is subject to conversion into rubles (clause 4 of PBU 3/2006).
Revenue in accounting and accounting records has not yet been recognized, since there is no transfer of ownership of the products from the seller to the buyer (clause 12 of PBU 9/99, clause 3 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax base for VAT in foreign currency is recalculated into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment, i.e., the preparation of the first primary document addressed to the buyer (clause 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 of the EAEU Protocol).
Control
Calculation of the tax base for VAT
Documenting
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, including the document for the sale of goods. In 1C, for internal document flow, a consignment note in the TORG-12 form is used.
The form can be printed by clicking the Print button – Consignment note (TORG-12) of the Sales document (act, invoice) . PDF
As a rule, a foreign buyer is issued:
- invoice-proforma;
- invoice;
- invoice (VAT-invoice), etc.
Documents are prepared with translation into a foreign language. Such forms are not implemented in 1C and can be modified independently.
Documents for the tax authorities for export to Belarus 2021
Belarus is forming a Customs Union together with Armenia, Kyrgyzstan and Russia. Conducting transactions within its framework is guided by a whole list of rules. The process follows clear legal requirements:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- 150-FZ dated May 30, 2021;
- Treaty of the Eurasian Union.
The absence of customs control simplifies the export procedure, but there are many nuances of legislation without which it cannot be carried out. Registration of documents and compliance with regulations is a mandatory requirement. By contacting us, you receive qualified assistance and do not have to delve into all the details. We guarantee prompt resolution of any issues.
The exporter is entitled to the deduction only after submitting documentation. For these purposes, you need to hurry up with collecting them and make sure that everything is done correctly the first time.
We come to the rescue when the client wants to refuse partially or completely from independently processing exports within the Customs Union.
Registration of export to Belarus
requires the preparation of an extended package of documents:
- Transaction passport;
- Foreign economic contract (copy);
- Accompanying documents (TORG-12 waybills, invoices, waybills);
- Applications for payment of indirect taxes (from the importer);
- Statistical form.
The last document is submitted to the tax office by the 10th day of the next month. Do you think this is difficult and don’t know what to do in a particular situation? Contact us! We have experience in conducting foreign trade transactions, and we can really help. We simplify the export process and guarantee results!
We have prepared a guide for those who are engaged or planning to import goods.
The contract must indicate:
1. The maximum amount for which you can make deliveries under this agreement.
Please note: the amount is not the delivery, but the contract itself. For example, if you have a non-one-time contract for one delivery, then further shipments should not exceed the amount specified in the contract.
2. Terms of payment (prepayment, partial prepayment or payment within X days from the date of receipt of the goods).
If you have prepaid under the contract, then the goods must arrive within 60 calendar days (Decree 178).
Accordingly, if you do not have time to pay, take care in advance of the National Bank’s permission to extend your transaction.
Another sore spot for many importers is control marks.
A control mark (KZ) is a sign confirming the legality of import into the territory of Belarus or production of goods on its territory.
Allows you to control the volume of import and production of goods subject to marking with such marks.
To determine whether you need control marks, you need to look at the name of the product and the HS code. If your product is on the list, you need to purchase a KZ.
At the end of the quarter, do not forget to submit reports to the Internal Revenue Service at the place of registration:
1. Report on the use of control (identification) marks.
2. Report on the volume of production, import, sale, use of goods marked with control (identification) marks, the forms of which are established by Resolution No. 32 of 08/09/2011.
When importing goods from a country that is a member state of the EAEU, you must have the following documents:
Keep in mind that if your foreign counterparty is a VAT payer, then he registers the goods with a VAT rate of 0%; if he is not, then with the “No VAT” rate.
The deadline for filing a statistical customs declaration (STD) is 7 working days from the date of delivery.
Please note that the STD is submitted only if the amount of the contract under which you delivered the goods is more than € 1000 (namely the contract, not the delivery)
Everyone pays VAT when importing goods, regardless of whether the importer is a VAT payer when selling goods on the territory of Belarus or he applies special tax regimes without paying VAT:
The tax base is determined on the date of registration of imported goods with an organization (individual entrepreneur).
When importing goods into the Republic of Belarus, you are required to provide the following documents to the Internal Revenue Service:
1. Completed application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes (they are submitted to the Tax Inspectorate along with copies of documents confirming delivery).
If your supplier is a VAT payer, then the application is made in 4 copies:
- For Internal Revenue Service
- For you
- And you must return 2 copies to your supplier within 180 days from the date of delivery so that he does not have any obligation to pay VAT
Often foreign counterparties reduce the period within which you must submit an application, so read the agreement carefully!
If your supplier is not a VAT payer, then the application is made in 2 copies (for the Tax Inspectorate and for you).
2. Submit a VAT return, section 2, by the 20th day of the month following the reporting month.
You must also pay import VAT by the 20th day of the month following the import of the goods.
3. As for the ESCHF for VAT, now there is nowhere without them: when importing goods from abroad, the importer also needs to send them. Regardless of whether you are a VAT payer or not, you must submit an ESCHF after submitting an application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes.
Issuance of export invoices in foreign currency (VAT rate 0%)
Despite the fact that a Russian invoice is not required for a foreign buyer and ownership of the products has not yet been transferred, the organization is obliged to draw up an invoice for export sales according to the general rules no later than 5 days from the date of shipment (clause 3 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , clause 17 of the Rules for maintaining a sales book, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137).
It is allowed to draw up not only the SF, but also the UPD (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 07/06/2016 N ED-4-15/12070).
An invoice for shipped export goods is issued using the Issue an invoice at the bottom of the Sales document (act, invoice) .
The Invoice document issued is automatically filled with data from the Sales document (act, invoice) . Operation type code – “01” Sales of goods, works, services...”.
The invoice was issued in foreign currency, since the transaction is expressed in foreign currency (Clause 7, Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
If the SF is not transferred to a foreign buyer, then the Checked (transferred to the counterparty) can be left unchecked. The presence of a checkbox is for reference information; it does not affect the movement of the document and the filling out of the purchase and sales books.
SF with a VAT rate of 0% does not by default enter the sales book simultaneously with sales, as happens when shipping on the domestic market. But only at the time of determining the tax base for VAT for export, if (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- export confirmed within / later than 180 days - on the last day of the quarter in which supporting documents were collected;
- export is not confirmed within 180 days - on the last day of the quarter in which the sale took place.
The moment of determining the tax base for VAT is not specified in the EAEU Protocol, therefore, on this issue one should be guided by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of the EAEU Protocol, clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the Northern Federation, for shipment to the EAEU, it is necessary to indicate the HS code in column 1a “Product type code” (clause 15, clause 5, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 7, 2016 N 03-07-11/58589). PDF The data will be filled in automatically if the HS code was previously indicated in the nomenclature card and in the tabular part of the Sales document (act, invoice) in the HS Code .
The document does not generate postings according to BU and NU.
Documenting
The Invoice form was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 N 1137. It can be printed by clicking the Print document Invoice or Sales (act, invoice ) button. PDF
VAT on export to Belarus
How to confirm the zero rate, which sections to fill out in the declaration, if the cameral passed without documents, do they need to be sent? These were the questions asked by one of the listeners of our webinars - so far only a theorist in export issues. We answer in order.
Question: OSNO LLC exports goods to Belarus.
- which sections of the value added tax declaration must be completed upon initial shipment;
- what sections of the value added tax declaration must be completed in the quarter of receipt of the full set of documents for the export transaction (within 180 days);
- How exactly are documents to confirm the 0% rate provided to the tax authority within 180 calendar days (by informal letter?);
- If more than 3 months have passed since the date of submission of the value added tax declaration, which displays the amount of VAT tax on line 020 (030) of Section 4 without providing the documents themselves, a desk audit was carried out and no demands were received, then everything is fine?
Answer:
In the quarter when goods are shipped for export, including to the countries of the EAEU (Belarus), and documents confirming the right to apply the 0% rate have not yet been collected, indicators associated with such shipment are not reflected in the VAT return.
At the same time, you have the right, if you exported a non-commodity product , to claim VAT tax deductions for goods, works, services associated with this operation (paragraph 3, clause 3, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, you do not keep separate records of “input” VAT on exports, but take it into account in the general manner in conjunction with other amounts of VAT, which you accept for deduction immediately after receiving invoices and accepting the received goods, works, and services for accounting.
If you export raw materials , then the procedure for applying tax deductions is different. They can be declared only after confirmation of the 0% rate (collection of the appropriate package of documents). This procedure is provided for in paragraph 1, paragraph 3, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The list of codes for types of raw materials was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 18, 2018 No. 466.
Filling out the declaration
When submitting a VAT return for the quarter, which contains a set of documents confirming the zero VAT rate, you must fill out section 4 of the VAT return.
- Line 020 of section 4 of the declaration shows the tax base (the cost of the exported goods).
- Line 030 (tax deductions) is filled in only if a commodity is exported. You declare in it deductions associated with the production or purchase of this product, as well as its sale.
The rules for filling out lines 020 and 030 of the VAT Declaration are established by clauses 41.2 and 41.3 of the Procedure for filling out the VAT return, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
If a non-commodity product was exported, then line 030 of section 4 of the VAT return does not need to be filled out. Only line 020 is filled in. Tax deductions for raw materials must be declared in section 3 of the declaration in the general manner provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 171, art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 31, 2017 No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
About documents
When you submit a declaration with completed section 4 to the tax authority, documents confirming the fact of export of goods to Belarus must be submitted at the same time (paragraph 21, clause 3 of the Procedure for filling out a VAT return). Documents confirming the right to apply the 0% rate are an appendix to the tax return and the number of sheets of the appendix must be reflected in the corresponding indicator of the title page (clause 30 of the Procedure for filling out the VAT return).
The current Procedure for filling out a VAT return does not establish how the application (documents confirming the 0% rate) should be sent to the tax authority. However, the Procedure for filling out a VAT return states that these documents must be sent simultaneously with the tax return. Therefore, supporting documents should be sent by mail on the same day as the declaration itself in electronic form via telecommunication channels. Or you can submit these documents to the tax authority in person on the same day.
You can contact your tax office in order to agree on another method of transferring these documents attached to the declaration.
You have the right to apply a zero VAT rate and declare it in your VAT return (section 4) only if you have submitted supporting documents to the tax authority. This is provided for in clause 3 of the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes (Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the EAEU).
Therefore, the fact that the tax authority did not request documents from you within three months does not mean that the tax authority accepted the declaration without comments.
Perhaps the information about the desk audit that was carried out did not reach you, or there are some other reasons related to your failure to receive information about violations committed during the preparation of this declaration.
Sales of shipped products
Sales of shipped products for export in 1C 8.3 Accounting is prepared with the document Sales of shipped goods in the Sales – Sales – Sales of shipped goods section – Create button.
The document reflects the transfer of ownership of goods based on a previously completed shipment. It is convenient to enter it on the basis of the document Sales (deed, invoice) type of operation Shipment without transfer of ownership .
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Sales of shipped goods using the example.
- Number - the serial number of the document in 1C, assigned automatically when saving the document;
- from - the date of transfer of ownership of the product from the seller to the buyer under the contract. In our example, the date the carrier transfers the goods to the buyer’s warehouse;
- A shipment document is a Sales document (act, invoice) , which was previously issued for the shipment of products without transfer of ownership.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 90.02.1 Kt 45.02 - write-off of production costs;
- Dt 62.21 Kt 90.01.1 - revenue from sales of products, where: the unpaid portion is assessed at the exchange rate on the date of sale from the Currency .
Control
Calculation of the ruble amount of revenue from the sale of finished products for export.
Please note that revenue in foreign currency is converted into rubles at the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of recognition of income, i.e., sale, but the rate also depends on the payment procedure.
In our example there was no prepayment. Revenue in accounting and accounting records is calculated at the exchange rate on the date of sale (clause 9 of PBU 3/2006; clause 8 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax base for VAT
According to the legislation, the tax base for VAT in foreign currency is recalculated into rubles at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment (clause 5 of the EAEU Protocol), the rate on the date of transfer of ownership is not taken into account. Therefore, revenue in accounting and NU may differ from the tax base for VAT.
When converting revenue from foreign currency into rubles for:
- BU and NU rate is applied by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of the advance and on the date of sale (transfer of ownership) (clause 9 of PBU 3/2006, clause 8 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- To calculate the tax base for VAT, only the exchange rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment (transfer) of goods is used (clause 3 of Article 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax base for VAT is determined at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of shipment, so it will differ from the sales amount in accounting and tax accounting in ruble equivalent if:
- there was an advance payment;
- the date of transfer of ownership does not coincide with the date of shipment.
In our example, there was no prepayment, and the revenue in accounting and accounting records does not coincide with the VAT tax base because the USD exchange rate is different on the date:
- shipments - 62 rubles;
- sale (transfer of ownership of products) - 63 rubles.
Income tax return
In the income tax return:
Revenue from the sale of finished products for export is reflected in the income from sales:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 1:
- page 010 “Proceeds from sales - total”, including: page 011 “revenue from sales of goods (works, services) of own production.” PDF
Learn more about Setting up Accounting Policies in NU
The cost of finished products sold is reflected in direct expenses:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2:
- page 010 “Direct costs related to goods sold...”. PDF
Receipt of payment from a foreign buyer
In our example, postpayment is made. At the time of sale, a receivable from the foreign buyer was formed under Dt 62.21, calculated as of the date of transfer of ownership.
At the moment the buyer repays the debt under the contract in foreign currency, the receivables are revalued at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the day of payment (clause 7 of PBU 3/2006, clause 8 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a result, exchange rate differences arise.
Receipt of payment from a foreign buyer is registered with the document Receipt to current account transaction type Payment from buyer in the Bank and cash desk section – Bank – Bank statements – Receipt button.
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Receipt to a current account using our example.
Bank accounts must first be filled out : information about the Organization's currency account to which payment is received from the buyer must be entered.
Payment in foreign currency is credited to a transit foreign currency account.
In our example, settlements under the contract are carried out in foreign currency. PDF As a result of selecting such an agreement in the Receipt to Current Account , settlement accounts with the buyer are automatically set in the field:
- Settlement account - 62.21 “Settlements with buyers and customers (in foreign currency)”;
- Advances account - 62.22 “Calculations for advances received (in foreign currency).”
Since payment by the buyer is made in foreign currency, the document states:
- Bank account - a transit currency account in USD, into which funds are received from the buyer;
- Accounting account - “Currency accounts”, is installed automatically when selecting a foreign currency bank account;
- Amount - payment amount in currency according to the bank statement;
- VAT rate — 0%.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt Kt 62.21 - receipt of postpayment from the buyer to the transit currency account;
- Dt 62.21 Kt 91.01 - revaluation of receivables in foreign currency.
Control
Calculation of exchange rate differences when revaluing accounts receivable
Income tax return
In the income tax return:
Positive exchange rate differences are reflected in non-operating income: PDF
- Sheet 02 Appendix No. 1 page 100 “Non-operating income.”
Submission of a statistical report to the Federal Customs Service in electronic form
When exporting to the EAEU, the Organization is obliged to submit to the Federal Customs Service (Federal Customs Service) a statistical form for recording the movement of goods (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of June 19, 2020 N 891).
The statistical form in the Federal Customs Service is drawn up using the regulated report Statistical form for accounting for the movement of goods in the section Reports - 1C-Reporting - Regulated reports - the Create button - the All tab - the By Recipients folder - the Federal Customs Service folder.
The report is filled out manually by exporters. PDF
The report period must be selected before the report is recorded. If an incorrect period is selected, you must close the report without saving it and then create a new one.
Yellow cells are filled in manually. Data in green cells is calculated automatically based on the information entered into the report.
After filling out the Statistical form for accounting for the movement of goods, you should Write it down , then using the appropriate buttons, the report can be:
- unload,
- check the unloading,
- type,
- send to the Federal Customs Service.
The statistical form is submitted to the customs authorities by the 10th day of the month following the month of shipment or receipt of goods. It can be downloaded from 1C and sent from your personal account on the FCS portal
For failure to submit or untimely submission of a statistical form for recording the movement of goods to the Federal Customs Service, a fine will be charged (Administrative Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 19.7.13):
- for officials - from 10,000 rubles. up to 15,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 20,000 rubles. up to 50,000 rub.
Calculation of VAT when exporting non-commodity goods to the EAEU
Next, using an example, we will consider different options for calculating VAT on the export of non-commodity goods that were purchased and sold starting from 07/01/2016.
The calculation of VAT on export supplies of non-commodity goods in 1C will differ depending on whether the 0% VAT rate is documented within 180 days or not.
Export confirmed within 180 days
Export not confirmed within 180 days
Previously unconfirmed exports were confirmed later than 180 days
Export of goods to Belarus: zero VAT rate
You need to export goods to Belarus. Do you know that there should be a zero VAT rate, but you have no idea how this is shown in accounting and what documents are needed to confirm the 0% rate? Exporting goods to Belarus has a number of features that arise during customs clearance. Since the Republic of Belarus is part of the EAEU, a zero rate is applied.
Zero VAT rate
The application of the zero VAT rate is carried out when carrying out an export operation and providing a certain package of documents. To confirm the 0 VAT rate, the exporting company must confirm the fact of export of goods and payment of indirect taxes for goods in Belarus.
Documents provided to the tax office:
1. VAT return 2. contract with specifications with a Belarusian company for the supply of goods 3. bank statement confirming the receipt of money into the account of the Russian company from the Belarusian buyer 4. copies of transport documents 5. third copy of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes , with a note from the Belarusian tax office that the buyer paid VAT.
It is important that this mark confirms the zero VAT rate.
All of the above documents must be collected and submitted to the tax office within 180 calendar days.
After the export delivery has been completed, the tax service carries out a desk audit within 3 months from the date of filing the declaration.
will help when exporting goods to Belarus. We offer a package. In this scheme of work, on your instructions and on our own behalf, we will export goods to Belarus. By using it you will avoid checks by tax and customs services.
The work scheme is simple for both the Russian supplier and the Belarusian buyer:
- Your company issues an invoice to us for the goods including VAT;
- We add the cost of our services to the invoice and reissue it to the Belarusian company;
- After agreeing on the price, we conclude a Russian contract with you, and a contract with the counterparty from Belarus;
- As soon as the client transfers money to us for the goods, we transfer it to you;
- We pick up the goods from your warehouse, carry out customs clearance and deliver to Belarus;
- We exchange original documents.
Why should you contact us?
- We provide comprehensive services for the supply of goods
- We have been successfully cooperating with companies around the world in the field of foreign trade for more than 3 years.
- We employ highly qualified specialists in foreign trade and customs clearance
- We always offer the best option for work and take an individual approach to solving our clients’ problems.
- We always protect the interests of our clients
Get advice on your delivery right now by calling +7 or leave a request on the website, and our specialists will contact you.