In accordance with Article 217 of the Tax Code (TC) of the Russian Federation, not all income of individuals is subject to personal income tax (personal income tax). It is calculated as a percentage of a person’s total income, and various property or social deductions may apply. The income from which tax is withheld can be expressed in any form: monetary, in kind, in the form of material benefits, and others.
Questions and Answers Do I need to pay income tax on gifts?
Tax will have to be paid on income:
- from the sale of property owned for less than 3 years or 5 years; — from renting out property; - from whom tax agents (organizations that are the source of this income for a person) did not collect tax; — in the form of insurance payments upon the occurrence of an insured event; — from any sources located outside of Russia; — in the form of various kinds of winnings (lottery, prize draws); - from salary; — from dividends and interest; — from remuneration under civil contracts; - from deposits and deposits. This will not affect standard deposits. The tax-free deposit rate in 2021 will remain at the level of the “Central Bank Key Rate + 5%” formula. If the profit exceeds the value of this formula (which is 12.5%), then you will have to pay tax. A contribution to mutual funds under trust management may well exceed 12.5%, then you will also have to pay tax (if you own the share for less than 3 years);
— from a non-state pension (clause 2 of Article 213.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); — from the use of copyright or related rights in Russia; — from the use of any vehicles in connection with transportation to and/or from Russia or within its borders; - from other income received by the taxpayer as a result of his activities in Russia.
Article on the topic
Are you ready to pay more taxes for the sake of doctors and teachers?
General taxation system
The general taxation system (OSNO, OSN, traditional, basic) is a tax regime that is automatically assigned to all individual entrepreneurs and organizations after their creation (except for cases where an application for transition to one of the special regimes was submitted along with registration documents).
OSN is the most difficult tax regime in terms of tax payment and reporting. As a rule, the general regime is used by those entrepreneurs and organizations that for some reason cannot be subject to other taxation systems (for example, due to a large number of employees or income exceeding the available limits).
Read more about the general taxation system.
1.1. General provisions
Such famous pre-revolutionary historians as D.I. turned to the study of the history of taxation in Russia. Ilovaisky, N.M. Karamzin, V.O. Klyuchevsky, S.M. Soloviev, I.G. Pryzhov, V.N. Tatishchev and others, as well as venerable economists: E.Ya. Bretel, I.Ya. Gorlov, V.P. Dyachenko, P.I. Lyashchenko, I.Kh. Ozerov, V.N. Tverdokhlebov and others.
Among lawyers, to one degree or another, these issues were studied by S.V. Zavadsky, B.P. Raspopov, G.F. Shershenevich, A.F. Kislyakovsky, F.V. Taranovsky and others. In addition, of the pre-revolutionary books on law that have come down to us, chronologically the earliest is the collection of church law “Nomocanon” published in Kyiv in 1624, which contains, among other things, provisions on obligatory payments in favor of churches.
In modern science, certain periods in the history of taxation and tax law are considered in the works of M. Boulanger, A.V. Bryzgalina, I.S. Zuikova, L.V. Zuikova, A.D. Melnik, A.A. Tedeeva, V.A. Timoshenko, Yu.P. Titova, A.V. Tolkushkina, I.V. Toropitsyna, D.G. Blueberries, etc.
By level of legislative power
The fundamental classification of taxes in the Russian Federation is the fragmentation of fiscal payments by levels of government, which are empowered to establish exclusive norms and rules of taxation for a specific fee.
In simple terms, the terms of calculation and payment for each tax payment can be regulated. The person who approves these rules determines the main types of taxes in Russia.
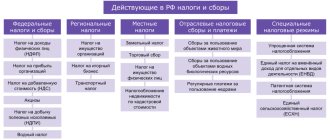
According to the level of legislative power, tax classification is briefly divided into three levels. Let us define these concepts and types of taxes and fees in the Russian Federation:
- Federal. They are established exclusively by the Government of the Russian Federation and enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Cannot be adjusted by regional or municipal authorities. For example: VAT, personal income tax, on corporate profits.
- Regional. They are regulated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but the rights to regulate norms, rates, periods and other tax rules are transferred to the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. For example: transport, gambling, property of organizations.
- Municipal or local. General rules of taxation are established in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but are detailed by local authorities, for example, administrations of municipalities or rural settlements. For example: land, for the property of citizens.
This tax system (classification of taxes and fees) is not the only one. Consider the following groupings.
New taxes from 2021
Personal income tax on bond coupons.
From 2021, the broker will automatically withhold 13% from coupons on all bonds. Previously, income, for example, received from federal loan bonds, was exempt from tax. So, if in 2021 you receive coupons worth 20,000 rubles on bonds, the broker will automatically withhold 2,600 rubles. Personal income tax on income exceeding 5 million rubles per year. If during the year a person’s total income from salary, investments, real estate rental, etc. exceeds 5 million rubles, then a 15% tax will be taken from the excess amount. For example, a person earned 8 million rubles in a year. On an amount up to 5 million rubles, he will pay tax at a rate of 13% - 650,000 rubles, and on the remaining 3 million - at a rate of 15% - 450,000 rubles. That is, only 1.1 million rubles. There are exceptions to this. A rate of 13%, regardless of the amount of income, will be applied, for example, when selling an expensive apartment or an expensive car.
Read on topic: Income tax increased to 15%. Who can not pay it
Personal income tax on deposits. Since 2021, Russia has introduced a tax on deposits exceeding 1 million rubles, but in fact it will only begin to be taken from 2022. The tax will be taken on income that exceeds the amount of income from 1 million rubles, multiplied by the key rate of the Central Bank. As of February 2021, the Central Bank rate is 4.25%, which means that income in the amount of 42,500 rubles will not be taxed. For example, if you invest 1 million rubles at 5%, you can earn 50,000 rubles, of which 42,500 rubles are tax-free, and the remaining 7,500 rubles are taxed. On the last amount you need to pay 13%, that is, 975 rubles.
Read on topic: Instructions: how the new tax on deposits will work
Simplified taxation system
The simplified tax system (USNO, simplified tax system, simplified tax system) is a special tax regime, which is most often the most profitable for paying taxes and maintaining records. Compared to other special regimes, a much larger number of types of business activities fall under the simplified tax system.
Using the simplified tax system, entrepreneurs and organizations pay only one tax in accordance with their pre-selected tax base (6% of income or 15% of income reduced by the amount of expenses).
Read more about the simplified taxation system.
PSN
This type of special taxation can only be applied by individual entrepreneurs. To use it, you must purchase a patent for the relevant type of activity. PSN can be combined with any other taxation system. Purchasing a patent replaces the need to pay VAT and personal income tax.
The cost of a patent will be calculated by the Federal Tax Service upon its issuance. But you can first make a calculation on the official service of the Federal Tax Service.
There are restrictions on the use of PSN:
- number of employees - no more than 15 people;
- annual income from activities on PSN - no more than 60 million rubles.
Combination of taxation systems
The patent tax system (PTS) is a special tax regime that can only be applied by individual entrepreneurs, while the average number of employees should not exceed 15 people.
Using PSN, an individual entrepreneur receives the right to buy patents (one for each) for certain types of activities (usually the provision of household services to the population and retail trade).
When calculating the value of a patent, the amount of actual income received does not matter. The tax on PSN is calculated based on the potential income that can be received, which is established by the laws of the constituent entities of Russia.
Read more about the patent tax system.
The vast majority of individual entrepreneurs and organizations during their activities use only one of the above tax regimes, however, the law does not prohibit the combination of some taxation systems (which you can see in this table).
We suggest you read: Income tax is paid to which budget - Open a business
In this system, all obligations are divided into two large groups: direct and indirect. Let us define the concepts of these types of taxes and fees in the Russian Federation.
Direct are those fiscal fees that are calculated directly to the income or value of the taxpayer’s property. Moreover, settlements with budgets are carried out exclusively at the expense of the payer himself, that is, at the expense of his own income, funds, and money. For example: personal income tax, property, land, transport.
Indirect are those fees that are levied on the consumer of a product, work or service and represent a special markup on the cost. In this case, companies that pay indirect fiscal payments act as tax agents between consumers and the state, since they are the ones who calculate and pay funds to the budget. For example: VAT or excise taxes.
The current tax system of the Russian Federation provides for the classification of taxes and fees according to numerous criteria. We discussed the key groups above. We present the remaining distinctions in the form of a table.
| Grouping criterion | Subspecies name | Description of tax classification criteria with examples |
| By subject of taxation | Property Profitable Rental Consumption Exceptional | Grouped by object of taxation. For example, property payments are calculated from a specific type of property owned by the taxpayer. Income - from a certain type of income, an exhaustive list of which is regulated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
| By purpose | Are common Target | The distinction depends on the purpose of the payment. Thus, for general collections a single, common goal is established - replenishing the state budget. Targeted payments are sent to the budget for specific purposes. For example, transport is sent to the road reconstruction fund. |
| By calculation methods | Solid | Transport (the rate is set depending on the power of the car). |
| Proportional | Personal income tax, VAT (as a percentage of the taxable base). | |
| Stepped | Insurance premiums (the rate changes when the volume of the fiscal base changes). | |
| Fixed | UTII (in a fixed amount, does not change when the object of taxation increases or decreases). | |
| By accounting source of payment | From proceeds | STS "Income". |
| From salary | Personal income tax, insurance premiums. | |
| Attributable to financial result | For the property of organizations. | |
| Attributable to the cost of finished products | Transport, insurance premiums, personal income tax. | |
| Calculated from gross profit | For the profits of organizations. |
How to pay tax: TOP 6 best ways!
Payers of personal income tax from wages, faced with the need to pay taxes on their own, often experience difficulties. We bring to your attention 6 convenient ways to pay taxes.
Method 1. Bank cash desk.
It’s convenient because a professional will do all the work for you. You just need to provide payment details and a passport. The payer receives a payment order marked by the bank and can be completely calm. The disadvantages are that sometimes you have to wait in a long line. It is convenient to generate details through your personal account.
Method 2. Payment terminal.
With it, of course, you can only pay some taxes. For example, transport. But quickly, without queues, in any convenient place. The only significant drawback is the relatively high commission. Some terminals simply charge extortionate fees for payments.
Method 3. Taxpayer’s personal account.
Using your personal account, you can not only find out all the necessary information, but also pay taxes. The only drawback is that payments are supported using cards opened in FTS partner banks, and their number is not large (about 13). It is worth noting that the tax office cooperates with almost all major banks.
Method 4. Internet banking.
You can pay through Internet banking of any bank in the Russian Federation. The main thing is that there is money in the card account. Fill out the payment order and then pay. That is, you independently perform the function of a cashier. By the way, for some types of taxes, payment orders are generated automatically.
Method 5. Intermediary sites.
Quite a lot of intermediary sites have appeared that offer to act as a payment operator. Most often this applies to transport tax; on the same sites you can easily check the debt according to the TIN. If you have a notice from the tax office, then enter the UIN number in the appropriate field. In just a couple of seconds, your debt and fields for entering card details will be displayed on the screen. The disadvantage of this method is the need to enter secret data on a dubious site.
Method 6. Electronic wallets.
Electronic payment systems such as Qiwi, YaD, WebMoney and others allow you to pay any tax without any problems. At the same time, in the wallet you will find the function described in the previous paragraph, that is, searching for debt by UIN number from the notification. This eliminates the need to enter details manually. But if you do not have a notification, but only details, then you can still pay through an electronic wallet using “payment to free details”. This function is currently available in all electronic payment systems.
How to pay tax is up to you! The main thing is to be careful when specifying the recipient's details and entering sensitive payment card data. And here is another interesting article on this topic: “Paying taxes for individuals: how to do it quickly?”
By taxpayer status
Types of taxes and methods of their classification by category of payers are as follows:
- For individuals. These are the payments for which ordinary citizens are taxpayers. And not only citizens of our country, but also representatives of foreign states who receive income or own property in Russia. Note that this group should also include obligations provided for individual entrepreneurs. For example: personal income tax on the property of individuals.
- For legal entities. Fiscal encumbrances that are paid exclusively by companies, organizations or firms that have the status of a “legal entity”. For example: fees, taxes of an enterprise (types of taxes in the Russian Federation, table below) on profit and property.
- Mixed payments are those amounts that are required to be paid by all categories of taxpayers, regardless of their status. For example: VAT, excise taxes. This category of fiscal obligations also includes payments to the budget under simplified taxation systems. For example: payment of unified agricultural tax, UTII, simplified tax system or PNS. Such obligations are provided for both legal entities and individual entrepreneurs.
Excise taxes
An indirect tax deduction, such as excise duty, is paid on the sale of goods such as gasoline, alcohol, cigarettes, and cars with a capacity of more than 90 horsepower. In most cases, excise taxes are included in the price of products. Thus, the price of gasoline includes an excise tax of 22% and additional taxes of more than 20%, which consist of a mineral extraction tax (17%) and others.
Excise tax rate on alcohol per liter:
- 418 rubles for products that contain less than 9% ethyl alcohol;
- 523 rubles for products that contain more than 9% ethyl alcohol;
- 18 rubles for fruit and berry wines;
- 5 rubles for wines that indicate geographical location;
- 21 rubles for cider and mead;
- 14 rubles for sparkling wines indicating geographical location;
- 21 rubles for beer that contains no more than 8.6% ethyl alcohol;
- 39 rubles for beer that contains more than 8.6% ethyl alcohol.
Excise tax is paid by legal entities, individual entrepreneurs, exporters and importers. In essence, the amount of indirect tax is included in the price of the product for the consumer. The state establishes an excise tax to increase the budget and control certain types of products. The excise tax is planned to increase in 2021.