Home — Documents
- Fill in column 2
- Fill in column 3
- Fill out column 7
- Fill in column 10
The question of how to fill out a particular document (declaration lines) is perhaps the most discussed in accounting forums. Therefore, from time to time we pay attention to it on the pages of our magazine. Today we’ll talk about the algorithm for filling out the purchase book for organizations importing goods from EAEU member countries.
Note. Countries participating in the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU): Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan.
The rules for maintaining a purchase book used in calculations of value added tax (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) were approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137 (Appendix 4). Despite the fact that the procedure for filling out each of the lines (columns) is spelled out in detail, accountants have reasonable questions.
Fill in column 2
For example, in column 2 “Code of the type of operation” the code of the type of operation must be indicated according to the list approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. However, this list has not yet been approved. Tax authorities advise using the following codes to fill out this column:
- approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 14, 2012 N ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices (codes from 01 to 13);
- recommended by the Federal Tax Service in Letter dated January 22, 2015 N GD-4-3/ [email protected] (codes 16 to 28).
The last of these documents proposes that in the case of importing goods from EAEU member countries, in column 2, indicate code 19, which corresponds to the operation “Import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation and other territories under its jurisdiction from the territory of the states of the Eurasian Economic Union.”
Fill in column 3
The next column, which is difficult to fill out, is column 3 “Number and date of the seller’s invoice.” The rules establish that when reflecting in the purchase book the amount of VAT paid when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, column 3 indicates the number of the customs declaration for goods imported into the territory of the Russian Federation. When importing into the territory of the Russian Federation from the territory of a member state of the Customs Union of goods in respect of which VAT is collected by tax authorities in accordance with the Agreement on the principles of collection of indirect taxes for the export and import of goods, performance of work, provision of services in the Customs Union of January 25, 2008 . and the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes and the mechanism for monitoring their payment when exporting and importing goods in the Customs Union of December 11, 2009, in column 3 of the purchase book the number and date of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes with marks from the tax authorities are indicated on payment of value added tax.
Note. The Agreement and Protocol mentioned in the Rules became invalid as of 01/01/2015 (that is, from the date of entry into force of the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union of 05/29/2014).
Despite the fact that this norm contains references to documents that have become invalid, it continues to apply: organizations importing goods from EAEU member countries must reflect in column 3 the number and date of the application for the import of goods and the payment of indirect taxes with marks from the tax authorities on the payment of VAT .
Where do you get these details from? In clause 8.1.3 of the Methodological Recommendations for maintaining the information resource “EAEU-Exchange” (Approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04/08/2015 N ММВ-7-15 / [email protected] ) it is stated that the registration number is assigned to the application automatically and cannot be edited . The structure of the registration number is a 16-digit digital code consisting of a sequence of numbers.
From left to right, the code states the following:
- code of the tax authority that assigned the registration number (NNNN);
- date of registration of the application (DDMMYYYY);
- serial number of the registration record during the day (XXXX).
Thus, column 3 reflects the registration number of the application corresponding to this structure. It is not necessary to indicate the date of filling out the application, since the 16-digit code already contains the date of registration of the application (similar explanations are given in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 21, 2016 N ED-4-15 / [email protected] ).
For reference. A taxpayer who is an importer of goods from member states of the EAEU, along with a tax return, submits an application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes on paper (in four copies) and in electronic form or in electronic form, certified by an electronic digital signature. When submitting an application in electronic form, certified by an electronic digital signature, the taxpayer does not need to contact the tax authority for a tax payment stamp, since this is done automatically (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 1, 2015 N ZN-4-17 / [email protected] ) .
The Russian Ministry of Finance provided clarification on how to indicate in column 15 of the purchase book the cost of goods imported into the Russian Federation. According to the financial department, it should reflect the customs value of imported goods, increased by the amount of customs duties, excise taxes on excisable goods and the amount of VAT.
Let us briefly remind you about the payment of VAT when importing goods into the Russian Federation.
VAT on import of goods
Operations for the import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation and other territories under its jurisdiction are recognized as subject to VAT taxation (clause 2 of article 11, subclause 4 of clause 1 of article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Goods in this case are movable property, including storage media, securities and (or) currency values, traveler's checks, electrical and other types of energy, as well as other moveable things. VAT on imported goods is a customs payment.
In case of import of goods, all importers are VAT payers. These include organizations and individual entrepreneurs:
— located on the general taxation system;
— switched to the simplified tax system (clauses 2, 3 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
— paying UTII (clause 4 of article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
— paying the Unified Agricultural Tax (clause 3 of Article 346.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
— exempt from VAT (clause 3 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, taxation is carried out in a manner that depends on the chosen customs procedure (clause 1 of Article 151 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In particular, full VAT is charged when goods are placed under customs procedures:
— release for domestic consumption (subclause 1, clause 1, article 151 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
— processing for domestic consumption (subclause 7, clause 1, article 151 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, tax rates of 10 percent and 18 percent are applied, depending on the type of goods (clause 5 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The tax base is calculated as the sum of the customs value of these goods subject to payment of customs duties and excise taxes (for excisable goods). In this case, the tax base is established separately for each group of goods of the same name, type and brand imported into the territory of the Russian Federation (clauses 1, 3 of Article 160 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Import VAT documents
Information on the calculation of customs duties (rates and amounts of calculated customs duties, taxes, customs fees, as well as the application of benefits for the payment of customs duties) is indicated in the customs declaration for goods.
In addition, the importer fills out a purchase ledger. The rules for maintaining a purchase book are established by Appendix 4 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
The following entries will be reflected in the purchase ledger:
- in column 1 - the serial number of the invoice information record;
- in column 2 - code of the type of operation. When importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation in the customs procedure of release for domestic consumption, code 20 is used (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 22, 2015 No. GD-4-3 / [email protected] );
- in column 3 - the serial number and date of the seller’s invoice. When reflecting in the purchase book the amount of VAT paid when importing goods, column 3 indicates the number of the customs declaration;
- in column 7 - details of payment documents on the actual payment of VAT to the customs authority;
- in column 8 - the date of acceptance of goods for registration;
- in column 9 - the name of the seller;
- in column 15 - the Rules do not have a special rule explaining the procedure for filling out this column when importing goods. Therefore, the Russian Ministry of Finance believes that the amount that consists of the customs value of goods, customs duties and VAT specified in the customs declaration should be reflected here;
- in column 16 - the amount of VAT paid to the customs authority when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation.
Example. Filling out a purchase book when importing goods into the Russian Federation (import).
On March 10, 2016, the organization imports a consignment of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation under the customs procedure “release for domestic consumption.” The seller is LLL. The customs value of the consignment is 60,000 euros. On the same day, the organization carried out customs clearance.
The exchange rate of the Bank of Russia on the date of acceptance of the customs declaration (conditionally) is 80.00 rubles/euro.
The customs value in rubles is 4,800,000 rubles. (60,000 euros x 80.00 rubles/euro).
The customs duty rate for these goods is 15 percent.
Customs payments will be:
— customs clearance fee — 7,500 rubles. — transferred by payment order dated March 10, 2016 No. 123;
— customs duty — 720,000 rubles. (RUB 4,800,000 x 15%) - listed as of March 10, 2016 No. 124;
— VAT — 993,600 rub. ((RUB 4,800,000 + RUB 720,000) x 18%) - transferred by payment order No. 125 dated March 10, 2015.
What a fragment of the purchase book will look like is shown in the table.
Table. Filling out the purchase book when importing
When VAT is not charged
In conclusion, we would like to remind you that certain categories of goods are exempt from VAT when imported. Their list is given in Article 150 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Among them:
— medical products, as well as raw materials and components for their production (according to the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 30, 2015 No. 1042);
— technological equipment (including components and spare parts for it), analogues of which are not produced in the Russian Federation (according to the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 30, 2009 No. 372);
— consumables for scientific research, analogues of which are not produced in the Russian Federation (according to the list approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 24, 2014 No. 1096).
Fill out column 7
According to the Rules, in column 7 “Number and date of the document confirming payment of tax” the following is indicated:
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation - details of documents confirming the actual payment of VAT to the customs authority;
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation from the territory of a member state of the Customs Union - details of documents confirming payment of VAT to the tax authority.
For reference. Collection of indirect taxes on goods imported into the territory of one EAEU member state from the territory of another EAEU member state is carried out by the tax authority of the member state into whose territory the goods were imported, at the place of registration of taxpayers - owners of goods (clause 13 of Appendix 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union).
Since the Rules do not contain special provisions on the details of which documents should be given in column 7 when importing goods from states included in the EAEU, but taking into account the fact that the tax is paid to the tax authority, this column should reflect the details of documents confirming payment of VAT to the tax authority. That is, in this column you should indicate:
- or the number of the payment slip by which the tax is transferred to the budget;
- or details of the decision on offset of VAT amounts - if the obligation to pay tax is fulfilled by the taxpayer by carrying out an offset of VAT amounts by the tax authority (if the taxpayer has overpaid (collected) amounts of taxes).
"1C: Accounting 8" (rev. 3.0). Reflection of VAT on import transactions in accounting and reporting (+ video)
How to reflect VAT paid at customs when importing imported goods into Russia in the 1C: Accounting 8 version 3.0 program?
A taxpayer importing imported goods into the territory of the Russian Federation must configure the program functionality accordingly (section Main
–
Functionality
,
Inventory tab,
Imported goods
flag ).
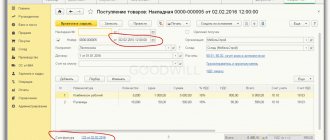
The receipt of imported goods in the program is registered using the document Receipt (act, invoice)
with the transaction type
Goods
. The following data is entered into the tabular part of the document:
- in the Nomenclature
- the name of the purchased imported goods; - quantity and price of goods in the contract currency;
- accounting account for purchased goods;
- in the field Customs declaration number
- the number of the customs declaration on the basis of which the goods were released for domestic consumption; - in the Country of origin
- the country of origin of the imported goods; - in the % VAT
the value
Without VAT
, since the amount of value added tax is not presented by the foreign supplier, but is paid to the customs authority as part of the customs payment; - The VAT accounting method
field (for users who maintain separate VAT accounting) is not filled in, since information about the amounts and method of accounting for VAT paid to the customs authority will be entered further using the
import customs declaration
.
If an advance payment for goods was made to a foreign supplier, then the cost of purchased imported goods in relation to the credited advance payment will be calculated at the rate on the day of the advance payment.
The import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation is recognized as an object of VAT taxation, while the VAT tax base is determined as the sum of the customs value of these goods and the customs duty payable. The obligation to pay VAT arises for the organization from the moment the customs declaration is registered by the customs authority. VAT is payable in rubles until the goods are released in full.
Accounting for customs duties in the program is registered using the customs declaration document for imports
(
Purchases
), which is entered on the basis of the document
Receipt (act, invoice)
.
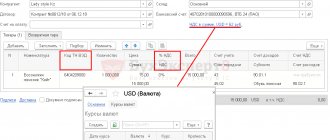
In the new customs declaration document for import
on the
Main
indicate:
- in the fields from
and
Customs declaration number
- the date and number of the customs declaration; - in the Customs
- the name of the customs authority that carried out the registration; - in the Deposit
- details of the document (agreement with the customs authority) for the transfer of advance customs payment (the type of agreement should take the value
Other
); - in the Customs duty
- the amount of customs duty; - in the field Account for settlements with customs
- account 76.09 “Other settlements with various debtors and creditors”.
On the CCD Sections
document
for import,
the customs value of the goods will be automatically filled in at the top of the table (please note that in the
customs declaration document for import
, created on the basis of the
Receipt document (act, invoice)
, the customs value of the goods will be reflected in the same currency as in document
Receipt (act, invoice)
)
.
In the % duty
You must indicate the rate of import customs duty, after which the amount of customs duty will be calculated automatically.
If the customs duty is established as a fixed amount, you must indicate a specific amount in the Duty
.
The VAT amount will be calculated automatically as the product of the customs value of goods, calculated at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of registration of the customs declaration, taking into account the amount of customs duty and the corresponding tax rate.
The following will be automatically filled in at the bottom of the table:
- name and quantity of imported goods;
- invoice value of goods (if the actual customs value of goods differs from that indicated in the table, then the adjusted customs value must be entered into the document manually);
- in the VAT
- the amounts of VAT calculated at the top of the table, distributed between product items in proportion to the invoice value of the goods; - in the Accounting account
- customs duty accounting accounts for accounting and accounting purposes, which, depending on the accounting policy adopted by the payer, can be adjusted; - customs VAT account;
- VAT accounting method (for those who use separate VAT accounting), which depends on the further use of the purchased goods.
An organization has the right to deduct the amount of VAT actually paid when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, after accepting the goods for registration and in the presence of documents confirming the payment of VAT.
Presentation for deduction of the amount of VAT paid as part of the customs payment is made by the document Formation of purchase ledger entries
(section
Operations - Regular VAT operations
).
Data for the purchase book on the amounts of tax to be deducted in the current tax period are reflected on the Purchased assets
.
To fill out a document using accounting system data, it is advisable to use the Fill
.
The amount of VAT paid when importing imported goods into the territory of the Russian Federation is reflected in line 150 of section 3 of the VAT return.
For more details, see the video (the video was made in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, release 3.0.39.60).