In recommendation:
– how to account for finished products at production costs; – how to account for finished products at accounting prices; – how to account for jointly produced products; – how to account for by-products; – how to account for semi-finished products of own production.
Finished products are products that have gone through all stages of technological processing and meet established requirements (customer, state standards, technical conditions). It is taken into account by type, grade and storage location in natural and cost terms.
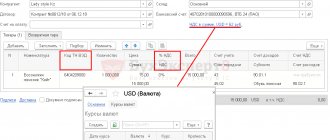
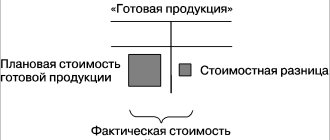
Depending on the adopted accounting policy, finished products can be accounted for at actual production costs or at accounting prices.
Documents for the sale of finished products
In the production cycle, the sale of released goods is the final and important indicator for the manufacturing company. As a result of sold products, the company receives working capital for further development of production. Let's consider the entire cycle of preparing documents for accounting and selling finished products.
Documentary accounting of finished products
The release of finished products is a complex production process, in the end of which the goods arrive at the finished goods warehouse. Each production stage is accompanied by primary documents:
- Receipt of materials to the warehouse for production purposes. Grounds for posting materials – consignment note TORG-No. 12;
- Issuance of material assets from warehouse premises to production upon request-invoice M-11;
- Finished products are sent for storage to the warehouse using the delivery note form MX-18. This form is used only in manufacturing companies.
Each “primary” is fixed with accounting lines:
The entire process of manufacturing goods is recorded by the materially responsible person in the card for recording the released products. An accounting card is created for each type of product, where a serial number of the item is assigned.
Information on the card is entered on the basis of the MX-18 invoice for the released goods. Documents must be filled out in clear handwriting without blots or corrections, with the indication and signature of the responsible persons.
For the overall result, a general register is compiled for the movement of released goods. If there are several warehouses in production, then the register is formed for each warehouse separately. All indicators are transferred to the summary statement after the end of each month and submitted to the accounting department for reconciliation with analytical accounting.
In production, it is important to document all operations with primary documents that reflect the movement of finished products. If necessary, it is possible to develop additional forms of documents.
Documentation of sales of finished products
Preparation of documents for accounting for the sale of finished products has two directions: retail and wholesale trade. When implementing, their documentation is different. Let's take a closer look.
- Documents for retail trade consist of:
- Cash receipt, indicating complete information about the products sold;
- Or a strict reporting form (SSR) and a cash receipt order.
In accounting for retail sales, the following entries are generated:
- Dt50.01 Kt90.01 - revenue received from retail sales;
- Dt90.02 Kt41 – the amount of the cost of goods sold is written off.
Important for entrepreneurs involved in retail trade: in 2021-2021. For retail, online cash registers are being introduced, the receipts of which contain not only information about the product, but also information from the entrepreneur himself. This information will be transmitted to the tax office.
Failure to issue a cash receipt or BSO to the buyer faces a fine in the amount of:
- Entrepreneur – 2 thousand rubles;
- Officials – 2 thousand rubles;
- Legal entities – 10 thousand rubles.
- Documents for selling finished products wholesale:
- Invoice for payment for goods;
- Consignment note TORG-12;
- Invoice (if the seller is a VAT payer), which is registered in the book of purchases and sales;
- Contract of sale;
- UPD is a universal transfer document that combines an invoice, a delivery note, and a certificate of work performed.
The peculiarity of filling out the UPD form is the status number:
- If we put it in status No. 1, this means that the document is intended for calculating VAT and income tax. Used instead of invoices and transfer deeds;
- Status No. 2 means that this document confirms the expenses of the enterprise, and it replaces only transfer documents.
From July 1, 2021, the UPD was supplemented with one more detail: government procurement identifier - column No. 8.
A package of documents is prepared in 2 copies (except for the invoice), one for the buyer, the other for the seller, with the appropriate signatures of the manager or financially responsible person and a seal.
Important: when selling goods wholesale, the seller may not issue documents such as an invoice, invoice, or certificate of completion, but combine them into one UPD document.
When self-pickup from the manufacturer's warehouse, the buyer is issued a pass-permission to remove the goods from the warehouse with a delivery note with a list of shipped products.
The pass is signed by the director of the organization and the chief accountant. The recipient of the goods is required to present a power of attorney for the purchase of manufactured products.
An accountant prepares wholesale trade transactions:
- Dt62.01 Kt90.01 revenue from the sale of goods. Base – consignment note TORG-12;
- Dt90.03 Kt68.02 VAT charged;
- Dt90.02 Kt41.01 cost of goods sold was written off on the basis of the TORG-12 invoice;
- Dt51 Kt62.01 the invoice was paid by the buyer. Basis payment order.
The buyer-wholesaler can only be an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity.
Important information: from July 1, 2021, due to changes in the UPD, old forms are considered invalid for refunding VAT from the budget.
Inventory accounting of the movement of finished products
Inventory check provides control over the accounting of finished products in production.
Based on the results of the inspection, the quantity, quality and condition of the finished product in fact are determined. All interested responsible employees participate in the inventory process.
Control can be carried out at the end of each reporting period, but there is a mandatory inventory:
- Annual accounting;
- Change of financially responsible persons;
- The presence of theft, damage, shortage of finished products;
- Emergency;
- Liquidation or reorganization of an enterprise.
If violations are detected, then all documents related to accounting and sale of finished products are raised. Particular attention is paid to the warehouse accounting card, which displays the movement of goods and the balance at the end of the period.
To improve control over the accounting of finished products and their sales, the following steps must be taken into account:
- Maintain constant control over manufactured finished products;
- Error-free execution of documents for the sale of finished products;
- Correct conduct of business transactions in accounting;
- Clearly organized payments to clients.
It is important to know that tax inspectors painstakingly check documents when selling finished products and issue counter checks to counterparties to verify documents.
Source: //buh-spravka.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet/pervichnyj-uchet-dokumentooborot-arhiv/dokumenty-pri-prodazhe-gotovoj-produkcii.html
Architecture
2.1.Roles
| Name | Description |
| !Purchasing Manager | User group: Purchasing department managers |
| !Sales Manager | User group: Sales managers |
| !Storekeeper | User group: Storekeepers |
| !Warehouse Operator | User group: Storekeepers |
| !Karshchik | User group: Storekeepers |
| !Head of warehouse | User group: Storekeepers |
| !Director of operations | User group:Production |
| !Foreman | User group:Production |
| !Contractor | — |
| !Client | — |
| !Head of Division | User group: Line managers |
| !Laboratory assistant | User group: OTC |
2.2. IT systems and entities
| IT systems | Entities |
| @1C:WMS | #ExpectedReception is a document used to reflect in the system the plan for the receipt of goods at the warehouse. Based on the plan for the arrival of goods at the warehouse, people are provided and a work plan at the warehouse is formed. #Acceptance is a document used to control the compliance of the expected and actual receipt of goods, as well as to directly reflect in the system the fact of receipt of goods at the warehouse. #Marking is a document reflecting the operation of marking goods and materials. In the same document, you select the label template to print. #TaskForMoving is a warehouse document reflecting the fact that the warehouseman has been tasked with moving goods from one cell to another. #Act of Non-Conformity is a document in which the laboratory technician reflects comments on the quality of products received from suppliers. #Placement is a warehouse document reflecting the fact that the storekeeper has been tasked with placing goods. #Shipment is a document reflecting the fact of consumption of goods and materials from the warehouse. #TransportUnits - a register of information that reflects which goods are stored in a specific box. #BuyerOrder is an expected purchase. The document formalizes a preliminary agreement on the sale of goods. #Flight - A document combining one or more buyer orders within the route of one vehicle. #Movement - A document reflecting the fact of moving goods from one cell to another. #State of Warehouse - A report showing the percentage of cells loaded, as well as their status. |
| @1C:UPP | #OrderToSupplier is an expected delivery. The document formalizes the preliminary agreement to purchase from the supplier. #Order for the Movement of Goods - The document is intended to record the needs for the movement of goods between enterprise warehouses (or between enterprise organizations). #Expense Order is a document reflecting the fact of consumption of goods and materials from the warehouse according to the inventory registers under the order accounting scheme. #Order for the Movement of Goods - The document is intended to record the needs for the movement of goods between enterprise warehouses (or between enterprise organizations). |
Documentation of the movement of finished products
The release of products from production, their receipt into the warehouse, write-off for sale, and use for needs within the enterprise are documented with appropriate documents.
Accounting for finished products in warehouses
The release of finished products from production and the receipt of goods in warehouses are formalized by specifications and acceptance acts. Quantitative is carried out in cards similar to materials accounting.
When using computer technology, it is possible to maintain records using the cardless method. At the same time, daily turnover sheets are compiled to record the release of finished products from production at warehouses and storage locations. When automating the work of a warehouse, prompt printouts of balances and movements of finished products are used for each of its names and types.
Documentation of shipment (release) of products from the warehouse
The release of finished products to the buyer is carried out according to the invoice for the release of materials (form No. M-$15$) upon presentation of a power of attorney (form No. M-$2$).
When shipping by rail, water, air, or road transport, the following shipping documents are issued:
Can not understand anything?
Try asking your teachers for help
- railway invoice;
- invoice for the carriage of goods in a universal container;
- waybill.
Such documents are signed by a representative of the transport organization, confirm the transfer of valuables, and are the basis for writing off valuables from the balance sheet.
Operational records of shipments are kept in the sales department in special journals, or in daily reports on product shipments.
Documentation of settlements with the payer
The supplier's accountant, based on the shipping documents, draws up settlement documents that must be presented for payment for goods. If payment is provided - before shipment, then settlement documents are issued on the basis of the contract. Most often, settlements with customers are made in non-cash form, the payment document is an invoice (form No. $868$).
The invoice contains the required details:
- date and account number;
- name and address of the supplier;
- supplier's bank details;
- name and address of the shipper;
- details of the consignee and payer;
- details of bank documents (if available);
- details of the contract;
- bank details of the payer;
- invoice amount, including or without VAT (this amount is equal to the buyer’s receivables);
- VAT amount;
- information about cargo shipment (bill of lading, shipping receipt);
- terms of payment;
- description of the goods, arithmetic calculation of the amount to be paid.
Note 1
The account is certified by the signature of the manager, chief accountant, and seal. This document is the basis for accruing receivables to the buyer.
Other documents when registering the sale
Settlements with the buyer are most often carried out in non-cash form. For non-cash payments, bank settlement documents are drawn up - a payment request-order. With this document the supplier:
- instructs his bank to collect payments from the buyer;
- requires the buyer to pay for the products delivered under the contract.
The payment request is accompanied by an invoice and shipping documents.
The transfer of goods is accompanied by an extract and transfer of technical documents (passports, specifications, drawings, instructions, etc.). The recipient receives a certificate of product quality, an inventory, and a picking list. To account for VAT, an invoice is issued in the supplier's accounting department and sent to the buyer.
The occurrence of claims entails the receipt by the seller of a claim act, court order and other documents. If the supplier recognizes the amount of the claim, or in the event of an award of amounts for collection, these documents become the basis for reducing the debt, returning amounts previously paid, charging fines, etc.
During commodity exchange transactions, accounting certificates are issued on the cost of goods sold.
Consolidated analytical accounting registers
A typical analytical accounting register for the journal-order form of accounting is Sheet No. $16$ for accounting for product sales. The statement has two sections:
- Movement of finished products in total terms;
- Shipment, release and sale of products.
The first section of the statement summarizes the data on product balances at the beginning of the month, receipts from production, receipts as returns, other receipts (in accounting and selling prices). Analytical data on the return of products and their consumption are provided.
The second section contains the dates and numbers of payment requests, suppliers, quantities of products, amounts submitted for invoices, and a note on payment.
Invoices
To control and account for VAT amounts included in the sales price of products, VAT payer organizations compile and maintain in established forms:
- invoices;
- log of invoices issued to customers;
- sales book;
- shopping book.
For each shipment of goods, an invoice is prepared and recorded in the sales book. The invoice is drawn up in two copies. Not compiled for transactions with securities.
The invoice contains the following details:
- serial number;
- name and details of the supplier;
- name and details of the recipient;
- Name of product;
- cost of goods;
- VAT amount;
- date of issue of the invoice.
Note 2
If the goods are not subject to VAT, the tax amount is not indicated on the invoice; the inscription “Without VAT” is written. When paying in advance, an invoice is drawn up for the amount of the advance.
The invoice is signed by the manager and chief accountant of the supplier and provided to the buyer no later than $10$ days from the date of shipment.
When sending invoices by mail, the date of submission is considered to be the date of delivery of the document to the post office.
The invoice is kept by the buyer, is included in the accounting documentation, and gives the right to a credit (refund) of the amount of VAT paid. The second copy remains with the supplier to be reflected in the journal of issued invoices. Based on the invoice, the amount of VAT owed to the budget on goods sold is calculated.
Sales book
Maintained by the supplier to register issued invoices and VAT amounts. Accounting is carried out in chronological order as sales occur in the reporting period in which the sale of goods is recognized for tax purposes, but no later than the established period.
It is allowed to maintain a sales book using a computer. In this case, after the expiration of the reporting period, the sales book is printed, the pages are numbered, laced and sealed.
Book of purchases
Buyers maintain a log of invoices received from suppliers and a purchase ledger. It is intended to register invoices provided by suppliers, to determine the amount of VAT to be offset (refunded) from the budget. Invoices are recorded in the purchase book in chronological order as goods are paid and received.
Source: //spravochnick.ru/buhgalterskiy_uchet_i_audit/dvizhenie_gotovoy_produkcii/
Terms and Definitions
Data collection terminal (hereinafter referred to as DCT) is a portable computer with a built-in bar code scanner.
Misgrading is a simultaneous shortage of one product name and a surplus of another variety, type, article, color, type, brand, etc. the same name of the product, finished product, inventory value, etc.
Quantity of goods - the quantity of goods specified in the order that must be accepted/shipped/manufactured.
A transport unit is a box or any other container that is assigned a barcode, and the system records information about the composition of the goods that are in this box.