Who are the committent and the commission agent? Let's consider this example. The counterparty transfers the goods to our organization for sale. We find a buyer and sell the goods. Then we transfer the money to the counterparty. We charge a fee for our services.
Another example is when we purchase materials and goods for another counterparty. We also receive a reward for this.
In both cases, we are the commission agent , and the counterparty is the principal .
At the same time, we must report to the committent, indicate what and in what quantity we bought or sold.
Let's consider how to take into account such operations in the 1C: Enterprise Accounting program.
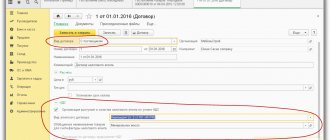
The contract is the basis of the transaction
Any business with a counterparty officially begins with the conclusion of an agreement. In the future, it is expected that the contract will be executed, taking into account the specifics of its conclusion. In the 1C:Accounting configuration, you can register two types of contracts with principals - for sale and for purchase.
Fig.1 Creating a contract
Fig. 2 Types of agreement
For each type of contract, the following details are required:
- organization;
- counterparty;
- contract number;
- agreement date;
- contract currency;
- the procedure for calculating commissions (for different types of contracts the choice of calculation methods is limited).
When concluding a sales contract, there is a certain procedure for the commission agent, which corresponds to the sequence of reflection of specialized documents in the program:
- Receives goods from the consignor;
- Sells the goods of the principal;
- Calculates own remuneration for commission sales services and reports for goods sold;
- Pays the principal for what is sold.
Let's take a closer look at each stage.
Basic concepts of commission relationships
A commission agreement is concluded between the principal, who is the owner of the goods, and the commission agent, who assumes the obligation on his own behalf, but at the expense of the principal, to carry out transactions with this product. The commission agent receives a certain remuneration for his services. This type of relationship can also be used for the sale of work or services, but most often a commission agreement is concluded specifically for the sale of goods.
Before entering into an agreement, the parties must agree on its essential terms. In accordance with Chapter 51 of the Civil Code, in an agreement of this type, such a condition is its subject matter. In other words, the contract must provide that the commission agent undertakes the obligation to carry out transactions with the principal’s goods at his expense, but on his own behalf. All other conditions are not essential, and in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 990 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation may be absent from the commission agreement.
Until the moment when ownership of the goods passes to the buyer, the principal is considered its owner. The commission agent undertakes to transfer to him everything received under the commission agreement, as well as to draw up a report.
Receipt of goods from the consignor
“Receipt (goods, services, commission)” is issued. It is available from the full interface, in “Purchases”.
Fig.3 Receipt (goods, services, commission)
Here, a sales commission agreement is applied; the tabular section contains a list of goods taken on commission. This fact is noted by indicating the off-balance sheet accounting account 004.01 “Goods accepted for commission/Goods in warehouse.” The posting Dt 004.01 will be generated.
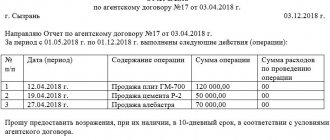
How to write a report
Today, there is no unified form for reporting to the committent, so representatives of enterprises and organizations have the right to write it in any form or according to a template developed within the company. The only condition: you need to ensure that the document complies with the norms of business documentation and office work standards, in addition, it must contain certain information.
In particular, the report must indicate:
- date and number of the document;
- names of partner enterprises (committent and commission agent);
- number and date of the commission agreement within the framework of which this document is formed.
Next, the report should contain the main part, designed in the form of a table, where information about the goods sold is entered in numbers:
- Product Name;
- volume;
- price;
- benefit received;
- information about the documents accompanying each transaction;
- information about suppliers;
- the overall result of the commission agent's activities.
The table may be supplemented with some other columns (depending on the conditions specified in the commission agreement).
Sales report to the consignor
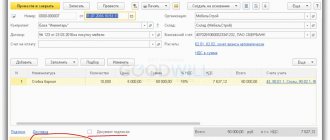
For the convenience of settlements and in order to reduce document flow at the end of the month, the commission agent draws up the document “Report to the Principal”, accessible from the full interface, section “Purchases”. The document contains several tabular parts, since it solves the problems of informing the principal about the goods sold, about calculating the amount of remuneration, and about mutual settlements with buyers and the principal.
On the “Home” page, information about the counterparty, the agreement, and the method of calculating remuneration is entered. The program can calculate the amount automatically, but only after information about the goods and services sold is entered.
Fig.5 Calculating the amount
The “Products and Services” tab can also be filled out automatically by clicking “Fill” based on sales results. In addition to the list of goods sold and prices, information about buyers must be entered.
Fig.6 Entering data
“Cash” displays data on received payments.
Fig.7 Data on received payments
“Settlements” shows the accounts of settlements with customers and the principal, as well as the method of calculation - deduction from revenue, or direct receipt from the principal.
Often for such calculations they take the account 76.09. The “Report to the Principal on Sales” records the debt owed to the principal for remuneration and reflects the commission agent’s revenue under the relevant agreement.
Fig.8 Sales report to the consignor
To analyze the status of settlements with the principal, you can use standard accounting reports, which are available from the full interface, section “Reports”.
The balance sheet for account 76.09 in the context of the counterparty and the agreement shows the status of the debt until the moment of transfer of the DS to the principal.
Fig.9 Balance sheet
Reflection of a transaction under a commission agreement in 1C
Example.
The organization Prima LLC (committent) entered into a commission agreement with the organization Orel LLC (commission agent) for the purchase of goods in the amount of 100,000 rubles. (including VAT). The agreement is valid from October 3, 2021 to October 11, 2021. Both organizations apply a common taxation system. The commission agent's remuneration under the contract is 7% of the cost of purchased goods.
Orel LLC purchased from various suppliers. From LLC "Mir" in the amount of 25,000 rubles. (including VAT). LLC "Hall" in the amount of 35,000 rubles. (including VAT). From Atlas LLC in the amount of 40,000 rubles. (including VAT). After purchasing the goods, the commission agent made payments to the suppliers.
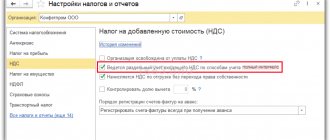
To be able to maintain in the program “1C: Accounting 8”, ed. 3.0, commission trading transactions must be placed in the “ Main – Functionality”
"On the "
Trade
" tab, the following checkboxes: "
Purchase of goods or services for principals (principals)
" and "
Purchase of goods and services through commission agents (agents)
."
Debiting from current account
A document is being prepared, accessible from the full interface, section “Bank and cash desk”. A special feature of filling out this document is the use of an input mechanism based on the “Report to the Principal”. Here the payment amount is calculated automatically.
Fig.10 Calculating the payment amount
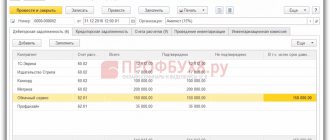
Postings will be generated that take into account detailed records of sales documents and settlements with customers.
Fig. 11 Postings will be generated
After completing the calculations, the principal's balance should be zero.
When concluding a commission purchase agreement, the sequence of actions of the commission agent changes slightly:
- Purchases goods for the consignor;
- Reports on purchased goods to the consignor.
Committent, commission agent and sub-commission agent. Part 2: implementation in 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0
This article continues the story begun in the previous article about how commission trade accounting is organized in the 1C: Accounting 8 edition 3.0 program. In the example we are considering, three actors (organizations) are involved: the principal, the commission agent and the sub-commission agent. Now we are interested in implementation.
Let me remind you of the content of the example. The Committent organization uses the services of an intermediary to sell its goods - the Commission Agent organization. The commission agent participates in settlements and acts on his own behalf. In accordance with the agreement, his commission is 10% of the sale amount.
In turn, the “Commission Agent” organization also uses the services of an intermediary to sell goods - the “Subcommission Agent” organization. The subcommissioner also participates in settlements and acts on his own behalf. His commission is 5% of the sale amount.
On January 18, 2021, the sub-commission agent shipped the goods to the buyer and issued an invoice for sale on his behalf. To process this operation, the program uses the Sales document with the transaction type Goods. The “header” of the document indicates the buyer’s counterparty and the agreement with him. Type of contract – With the buyer.
In the tabular part, on the Products tab, select the appropriate item - the product on commission, its quantity and price. Since the remuneration of the commission agent and sub-commission agent in our example is calculated as a percentage of the sale amount, the goods are shipped to the buyer at the consignor’s price. Accounting account 004.01 “Goods accepted for commission. Goods in warehouse."
According to clause 7 of the Rules for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices used in calculations of value added tax, a commission agent selling on his own behalf goods (work, services), property rights to the buyer is obliged to issue an invoice to the buyer and register it in the journal of received and issued invoices. The invoice issued to the buyer is registered (created) in the “footer” of the Sales document.
When posting a document in accounting, it will write off the commission goods shipped to the buyer from the credit of account 004.01, generate the posting Dt 62.01 - Kt 76.09 (the buyer must pay the sub-commission agent, and the sub-commission agent must transfer these funds to the commission agent) and offset the advance (Dt 62.02 - Kt 62.01), since in our example the buyer made an advance payment against future deliveries.
According to clause 20 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, used in calculations of value added tax, commission agents (agents) do not register in the sales book invoices issued by them to the buyer when selling goods (works, services), property rights on their own behalf. Therefore, please note that the document did not make an entry in the Sales VAT accumulation register (sales book).
But the document made an entry in the auxiliary register of sold goods and services of the principal (principal). In this register, the program remembers everything that was sold under a specific principal and agreement. The register is used to automatically fill out the Report to the Principal document.
Submit your application
An example of filling out the document Implementation and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 1.
Picture 1.
The subcommissioner is obliged to report to the commission agent. He writes a report to the commission agent. He reports on the goods sold, transfers to the commission agent the details of the buyers and information about the invoices issued to them. The subcommissioner claims a commission.
In the program, you need to generate a document Report to the principal with the transaction type Sales Report.
On the Main tab, the commission agent, the agreement with him, the method of calculating the commission fee are indicated (in accordance with our example - 5% of the sale amount), the item-service for remuneration, the income account and the VAT account are indicated (accounting accounts are set from the Accounts information register inventory accounting). If the commission fee relates to the main type of activity (income account 90.01), then the subaccount is indicated - Nomenclature group (filled in from the Nomenclature directory).
The tabular part on the Goods and services tab is filled in automatically using the “Fill” button -> Fill in sold under the contract. Using this command, the program will “look” into the accumulation register of Sold goods and services of principals (principals) and fill out the tabular part with a list of goods sold to each buyer, indicating the date of sale, and calculate the amount of the commission. In our example, there was only one implementation.
On the Cash tab, the subcommissioner reports that when goods were shipped to the buyer, the advance payment was offset.
The Settlements tab is used to indicate settlement accounts (we use default accounts, which are set in the information register of Settlements with counterparties), and there is also a checkbox there that allows you to withhold the amount of the commission from the principal's revenue.
After filling out the document (Products and Services tab), on the Main tab, using the appropriate button, an invoice is issued for the amount of the remuneration.
The document's entries are very simple. The commission for the subcommissioner is revenue. Therefore, when carried out, the document in accounting and tax accounting will accrue revenue (Dt 62.01 - Kt 90.01.1), VAT will be charged on the amount of revenue (Dt 90.03 - Kt 68.02) and will deduct the amount of commission from the principal's revenue (Dt 76.09 - Kt 62.01) .
The document will also make an entry in the Sales VAT accumulation register (sales book) and write off entries for goods sold in the Sold goods and services register of principals (principals). An example of filling out the document Report to the committent and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2.
According to clause 11 of the Rules for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices, a commission agent selling goods on his own behalf must receive from the principal an invoice issued by him in the name of the buyer and register it in the invoice log. Therefore, when the commission agent issues the corresponding invoices, the sub-commission agent will need to return to the document Report to the principal, on its basis create the document (documents) Invoice received and in the list that appears select the type of invoice - Invoice for receipt (see Fig. .3).
Figure 3.
In the opened form of the document Invoice received, the number and date of the invoice received from the commission agent are indicated, and also, using the Select link, the invoice issued by the sub-commission agent to the buyer is selected. Transaction type code – 04 Goods, works, services of the principal. When carried out, such a document is recorded only in the invoice journal. The document Invoice received is presented in Fig. 4.
Figure 4.
The “Commission Agent” organization, having received a report from the sub-commission agent, creates a document in its program, Commission Agent (Agent) Sales Report.
On the Main tab, a subcommission agent is selected, an agreement with him is selected, and the method for calculating the commission is indicated. As a cost account for commission fees, the default document uses account 44.01 “Distribution costs in organizations engaged in trading activities” with the analytics Services of commission agents (cost item with expense type Other expenses), which completely suits us. VAT account - 19.04 “VAT on purchased services.” You must select the Commission deducted from revenue checkbox.
The Sales tab using the “Fill” button → Fill by sale or Add from sale is filled in with all goods transferred for sale to the sub-commissioner, and then manually adjusted based on the report received from the sub-commissioner. The bookmark contains two tabular parts.
Buyers are indicated at the top of the table. The lower tabular part is filled out separately for each buyer. It indicates the goods sold, their quantity, sale price and transfer price. The commission amount is calculated automatically for each line. Accounting account 004.02 “Goods transferred on commission.” The remaining invoices, in the case of transfer of goods to a subcommission, have no significance. In the upper tabular part, for each buyer, the total amount and the VAT amount are calculated automatically based on the cost of goods sold. In accordance with paragraphs. a, i, j, l clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, when the committent (principal) draws up an invoice issued to the commission agent (agent), the date of issue of the invoice by the commission agent (agent), the name and details of the buyer are indicated. Therefore, it is necessary to check the SF checkbox and indicate the date of the invoice issued by the subcommissioner to the buyer. Documents An invoice issued in the name of each buyer will be created automatically when posting the document. Invoices are recorded only in the invoice journal.
On the Cash tab: indicate the type of payment report - Advance offset, buyer, date of advance offset, amount including VAT, VAT rate and VAT amount.
Then, on the Main tab, an invoice issued by the subcommission agent for the commission is registered. The document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales is shown in Fig. 5.
Figure 5.
When posting, the document will write off from the credit of account 004.02 the goods sold transferred to the subcommission (entry 1), accrue on the debit of account 62.01 the debt for the goods sold by the sub-commission agent and on the credit of account 76.09 the debt to the principal (entry 3), take into account the debit of account 44.01 expenses for commission fees ( entry 4), will allocate in the debit of account 19.04 the amount of VAT presented by the sub-commissioner (entry 5), and will deduct the commission from the proceeds (entry 2).
The document will make entries in the accumulation registers of VAT presented, VAT advances under commission agreements and Sold goods and services of principals (principals). The result of the document The report of the commission agent (agent) on sales is shown in Fig. 6.
Figure 6.
In turn, the commission agent must report to the committent. Therefore, having received a report from the sub-commissioner, he writes his report to the committent and also reports on the goods sold, buyers and invoices issued directly to them.
He, like the sub-commission agent, creates in the program the document Report to the Principal with the transaction type Sales Report.
The document on the Main tab specifies the principal, the agreement with him, the method of calculating the commission (in accordance with our example - 10% of the sale amount), the item-service for remuneration, and accounting accounts.
The Goods and Services tab and the Cash tab are filled out in exactly the same way as for the subcommission agent. After filling out the document, on the Main tab, using the appropriate button, an invoice for the amount of the remuneration is issued.
When the document is entered into accounting and tax accounting, it will accrue revenue to the commission agent (Dt 62.01 - Kt 90.01.1), charge VAT (Dt 90.03 - Kt 68.02) and deduct the amount of commission from the principal's revenue (Dt 76.09 - Kt 62.01), make an entry in the register VAT accumulation Sales (sales book).
The document Report to the committent and the result of its implementation are shown in Fig. 7.
Figure 7.
The commission agent must receive from the principal an invoice issued by the principal in the name of the buyer and register it in the invoice journal. Such an invoice, as we know, is created on the basis of the Report to the Principal document (see Fig. 8).
Figure 8.
In the form of the document Invoice received, the details of the invoice received from the principal are indicated, and using the Select link, the invoice issued by the commission agent in the name of the buyer is selected. The document Invoice received from the principal is presented in Fig. 9.
Figure 9.
And finally, we came to the organization “Committent”. The principal, having received a report from the commission agent, creates a document in his program, Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales.
On the Main tab, select the counterparty-commission agent, the agreement with him, indicate the method of calculating the commission, the account for accounting for the costs of the commission, the VAT account, and select the Commission deducted from revenue checkbox.
The Implementation tab is filled out in the same way as in the “Commission Agent” organization. In the lower tabular part, for each buyer, the goods sold, their quantity, selling price and transfer price are indicated. The commission amount is calculated automatically. Accounting account 45.01 “Purchased goods shipped”, income account 90.01.1, VAT account 90.03 and expense account 90.02.1 are established from the information register of the Item Accounting Account. In the upper tabular part, for each buyer, the SF checkbox is checked and the date of the invoice issued by the commission agent is indicated. Documents An invoice issued in the name of each buyer will be created automatically when posting the document.
On the Cash tab: indicate the type of payment report - Advance offset, buyer, date of advance offset, amount including VAT, VAT rate and VAT amount. The content of this bookmark is very important for the committent, since based on the specified data, the document restores VAT on the advance received.
Then, on the Main tab, an invoice for the commission received from the commission agent is registered. The document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales is shown in Fig. 10.
Figure 10.
When posting, the document will write off sold goods from the credit of account 45.01 to the debit of account 90.02.1 (entry 1), accrue revenue on the credit of account 90.01.1 (entry 3), accrue VAT (entry 5), and record commission expenses on the debit of account 44.01 (entry 4), will allocate in the debit of account 19.04 the amount of VAT presented by the commission agent (entry 6), withhold the commission from the proceeds (entry 2) and restore VAT from the advance received (entry 7).
The document will make entries in the VAT accumulation registers. Firstly, VAT advances under commission agreements and VAT Purchases - VAT on the advance received is restored and an entry is made in the purchase book. Secondly, VAT presented - the commission agent presented the amount of VAT on his remuneration. Thirdly, VAT Sales - in accordance with clause 20 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, principals (principals) selling goods (work, services) register property rights under a commission agreement (agency agreement), providing for sales on behalf of the commission agent (agent), register in the sales book, invoices issued to the commission agent (agent), which reflect the indicators of the invoices issued by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer. The result of the document The report of the commission agent (agent) on sales is shown in Fig. eleven.
Figure 11.
Let's see what is contained in the sales book and purchase book of the principal, in the invoice journals of the commission agent and sub-commission agent. The consignor has two entries in the sales book. An invoice for advance payment (transaction type code - 02) and a sales invoice (transaction type code - 01) were issued in the name of the buyer (column 7), information about the intermediary was filled in (columns 9 and 10). The principal's sales book, in part of our example, is shown in Fig. 12.
Figure 12.
The principal has three entries in the purchase book. An invoice from the supplier of goods (transaction type code - 01), an invoice from the commission agent for remuneration (transaction type code - 01) and VAT restored on the advance received (transaction type code - 22). The principal's purchase book, in part of our example, is shown in Fig. 13.
Figure 13.
Let's look at the commission agent's invoice log. The commission agent issued an invoice for advance payment (transaction type code - 05) and an invoice for sales (transaction type code - 04). In column 8 the buyer is indicated, in column 10 the seller is indicated - the principal, and in column 14 - the invoices issued by the commission agent refer to the invoices in part 2 of the journal received from the principal. In column 10 of part 2 of the journal the subcommissioner is indicated (see Fig. 14).
Figure 14.
Let's look at the sub-commissioner's invoice log. The subcommissioner issued an invoice for advance payment (transaction type code - 05) and an invoice for sales (transaction type code - 04). In column 8 the buyer is indicated, in column 10 the seller is indicated - the commission agent, and in column 14 - the invoices issued by the sub-commission agent refer to the invoices in part 2 of the journal received from the commission agent (see Fig. 15).
Figure 15.
Receipt of goods for the consignor
Reflected in the document “Receipt (goods, services, commission)”. A feature of the reflection is the use of account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” to register goods purchased in favor of the principal.
Fig. 12 Receipt of goods for the consignor
The receipt document forms the debt of the principal.
Fig. 13 The receipt document forms the debt of the principal
Force majeure circumstances
6.1. The Parties are released from liability for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of obligations under the Agreement if proper fulfillment turned out to be impossible due to force majeure, that is, extraordinary and unpreventable circumstances under the given conditions, which mean: _________________________ (prohibited actions of the authorities, civil unrest, epidemics, blockade, embargo , earthquakes, floods, fires or other natural disasters).
6.2. If these circumstances occur, the Party is obliged to notify the other Party about this within _____ (__________) business days
6.3. A document issued by _________________________ (authorized government agency, etc.) is sufficient confirmation of the presence and duration of force majeure.
6.4. If force majeure circumstances continue to apply for more than _____, then each Party has the right to unilaterally withdraw from the Agreement.
Duration, modification and early termination of the contract
7.1. The Agreement comes into force from the moment it is signed by the Parties and is concluded (select the one you need)
- for a period up to "___" __________ _____.
- For undefined period.
7.2. All changes and additions to the Agreement are valid if made in writing and signed by both Parties. The corresponding additional agreements of the Parties are an integral part of the Agreement.
7.3. The commission agent has the right to refuse to fulfill the Agreement if the Principal violates the deadlines provided for by more than _____ (____________________) working days (select the one required)
- clause 2.4 of the Agreement (if the Commission Agent sells the Principal’s Goods).
- clause 2.1 of the Agreement (if the Commission Agent purchases the Goods for the Principal).
The Agreement is considered terminated from the moment the Principal receives the Commissioner's notice of unilateral refusal to perform it.
7.4. In the event of termination of the Agreement for any reason, the Parties have the right not to return to each other everything performed under it until the moment of its termination, unless otherwise provided by law (clause 4 of Article 453 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Dispute Resolution
8.1. All disputes related to the conclusion, interpretation, execution and termination of the Agreement will be resolved by the Parties through negotiations.
8.2. If an agreement is not reached during negotiations, the interested Party shall submit a claim in writing, signed by an authorized person.
8.3. The claim is sent in any of the following ways:
- by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery;
- courier delivery. In this case, the fact of receipt of the claim is confirmed by a receipt, which must contain the name of the document and the date of its receipt, as well as the surname, initials, position and signature of the person who received this document.
8.4. The claim must be accompanied by documents substantiating the demands made by the interested Party (if the other Party does not have them), and documents confirming the authority of the person who signed the claim. The specified documents are submitted in the form of duly certified copies . If a claim is sent without documents confirming the authority of the person who signed it, then it is considered unsubmitted and is not subject to consideration.
8.5. The Party to which the claim is sent is obliged to consider the received claim and notify the interested Party in writing about the results within ___ (_____) business days from the date of receipt of the claim.
8.6. In the event of failure to resolve disagreements through the claim procedure, as well as in the event of failure to receive a response to the claim within the period specified in clause 8.5 of the Agreement, the dispute is referred to the arbitration court at the location of the defendant in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.