When calculating transport tax on expensive passenger cars, for some time now it is necessary to apply an increasing coefficient, but only if the car model is on the list of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia, a specified number of years have not passed since the date of its release and its average cost is 3 million rubles. and more. And this is not all the hassle regarding vehicles. Sometimes a vehicle is stolen, what to do with the transport tax in this case - and there is no vehicle, and still have to pay the transport tax?
A list of expensive cars for calculating transport tax for 2019 has been published.
Also, payment according to Plato introduces confusion into the procedure for paying transport tax: sometimes we reduce the transport tax by the amount of payment to Plato, sometimes not; then we recognize as expenses only the amount of payment to Plato that exceeds the transport tax, then we take the entire amount into account as expenses; either we do not pay advance payments for transport tax when making payments to Plato, or we pay. We will consider all this in more detail in the article.
Who pays?
Transport tax is paid by persons who, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, are registered cars, motorcycles, motor scooters, buses and other self-propelled machines and mechanisms on pneumatic and caterpillar tracks, airplanes, helicopters, motor ships, yachts, sailing ships, boats, snowmobiles, motor sleighs, motor boats, jet skis, non-self-propelled (towed vessels) and other water and air vehicles (Articles 357, 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Vehicles that are not subject to transport tax are listed in paragraph 2 of Article 358 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This:
- rowing boats, as well as motor boats with an engine power not exceeding 5 horsepower (hp);
- passenger cars specially equipped for use by disabled people, as well as passenger cars with an engine power of up to 100 hp. (up to 73.55 kW), received through social protection authorities in the manner prescribed by law;
- fishing sea and river vessels;
- passenger and cargo sea, river and aircraft owned (with the right of economic management or operational management) by organizations and individual entrepreneurs whose main activity is passenger or cargo transportation;
- tractors, self-propelled combines of all brands, special vehicles (milk tankers, livestock trucks, special vehicles for transporting poultry, for transporting and applying mineral fertilizers, veterinary care), registered to agricultural producers and used in agricultural work for the production of agricultural products;
- vehicles owned by the right of operational management to federal executive authorities and federal state bodies in which the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for military or equivalent service;
- airplanes and helicopters of air ambulance and medical services;
- ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships;
- offshore fixed and floating platforms, offshore mobile drilling rigs and drilling ships.
Subject to transport tax
- For organizations and entrepreneurs who carry out river, sea and air transportation, the following relaxation of the tax regime is provided: self-propelled vessels and aircraft belonging to them are not subject to transport tax.
- A similar benefit applies to agricultural producers. Tractors, combines and some other agricultural equipment (for example, milk tankers, livestock trucks, veterinary care vehicles) are not subject to transport tax, provided that they are used specifically for agricultural work.
- Government bodies engaged in law enforcement or military service do not pay this tax either.
- Airplanes and helicopters used in medicine are also exempt from transport tax, as are platforms (mobile and stationary) for oil drilling in the seas.
- Ships listed in the Russian International Register of Ships are also not subject to transport tax.
The tax is not paid if a car or other vehicle from an individual or organization is stolen by criminals (if the victim has documents issued by the internal affairs bodies).
IMPORTANT! The tax rate and the amount of payment depend on the power of the vehicle. Power is usually indicated in horsepower. If the data is indicated in kilowatts, then they are converted to horsepower on the basis that 1 kilowatt is equal to 1.3592 horsepower. For some property, such as aircraft, the tax is calculated on each kilogram of thrust.
Transport tax in case of theft or theft of a vehicle
We will especially focus on the theft or theft of a vehicle. In case of theft or theft of a vehicle, it is not subject to transport tax while it is wanted. But in order for such vehicles not to be taxed, it is necessary to confirm the fact of their theft or theft with a document issued by an authorized body. However, neither the Tax Code of the Russian Federation nor other regulations contain a specific list of documents confirming the fact of theft or theft of a vehicle. The Federal Tax Service of Russia believes that the fact of theft or theft can be confirmed by one of the following documents (Information of the Federal Tax Service of Russia “On the new procedure for terminating the registration of a wanted car”):
- certificate of theft (theft) of a vehicle;
- a certificate or resolution to initiate a criminal case in connection with theft or theft of a vehicle, issued by law enforcement agencies;
- by resolution, or decision, or determination of the courts that have entered into force;
- a certificate of termination of a criminal case on the fact of theft or theft of a vehicle, issued by an authorized body due to the fact that the statute of limitations for criminal prosecution has expired.
In addition, in this letter, the Federal Tax Service of Russia indicated the need to annually confirm the fact that a vehicle was being searched in connection with its theft or theft.
Indeed, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 360 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax period for transport tax is a calendar year. In addition, the new rules for registering motor vehicles with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, approved by Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated June 26, 2018 N 399, have simplified the procedure for terminating the registration of vehicles that are on the wanted list. According to the new rules, the registration of the wanted car with the traffic police can be terminated. To do this, the owner of the car must submit an application to the traffic police to terminate the registration of a wanted vehicle. In this case, the traffic police authorities transmit information about the deregistration of the vehicle to the tax authorities. Based on such information, the tax authorities stop calculating transport tax to the owner of the vehicle, regardless of the period of search for the car.
How much tax should I pay?
The amount of transport tax is calculated as the product of the tax base and the tax rate (clause 2 of Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the tax base is determined separately for each vehicle (Article 359 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- in relation to vehicles with engines, with the exception of air vehicles for which the thrust of a jet engine is determined, as the vehicle engine power in horsepower;
- in relation to air vehicles for which the thrust of a jet engine is determined - as the nameplate static thrust of the jet engine (the total nameplate static thrust of all jet engines) of the aircraft at take-off mode in terrestrial conditions in kilograms of force;
- in relation to non-self-propelled (towed) water vehicles, for which gross tonnage is determined - as gross tonnage in registered tons.
- In relation to water and air vehicles not mentioned above, the tax base for transport tax is determined as a unit of vehicle separately from other vehicles.
The basic rates of transport tax are established in paragraph 1 of Article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
But constituent entities of the Russian Federation can set their own transport tax rates. In any case, deviations in the transport tax rate established by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation should not differ from the base rates by 10 times. This restriction was introduced by paragraph 2 of Article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, this restriction does not apply to passenger cars with an engine power (per horsepower) of up to 150 hp. (up to 110.33 kW) inclusive. For such vehicles, tax rates can be reduced by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation by more than 10 times. This relaxation was made to encourage the purchase of low-power vehicles. Since such vehicles are less harmful to the environment.
Also, the tax rate may be different for each category of vehicle. In addition, the transport tax rate may depend on the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture of the vehicles and (or) their environmental class.
The calculation of the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture of the vehicle is made from the year following the year of manufacture of the vehicle. The number of years is determined as of January 1 of the current year in calendar years.
Basic rates of transport tax are applied if tax rates are not determined by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Transport tax table 2021 by region
The current transport tax rate by region for 2018 can be found on the Federal Tax Service website.
Let’s look at what tariffs are in effect in the regions this year for cars of category “B”:
| Region | With car power up to 100 hp. | Car power from 100 to 150 hp. | Car power from 150 to 200 hp. |
| Republic of Adygea | 10 | 20 | 40 |
| Amur region | 15 | 21 | 30 |
| Belgorod region | 15 | 25 | 50 |
| Vladimir region | 20 | 39 | 40 |
| Ivanovo region | 10 | 20 | 35 |
| Kaliningrad region | 2,5 | 15 | 35 |
| Nizhny Novgorod Region | 22,5 | 31,5 | 45 |
| Moscow region | 10 | 34 | 49 |
| Leningrad region | 18 | 35 | 50 |
For trucks, transport tax is calculated at a different rate:
For 2021, the truck tax rate has been significantly reduced. The changes affected primarily heavy vehicles weighing more than 12 tons.
This is due to the fact that owners of “heavy cargo” are required to pay tax through the “Platon” system and the reduction in the rate is an avoidance of double taxation.
In 2021, the transport tax has several features:
- Transport tax is paid once, in the whole amount by individuals and quarterly by legal organizations.
- Taxpayers no longer need to calculate their taxes themselves. This was the case before, but now, if there is no receipt, you need to contact the territorial branch of the Federal Tax Service to obtain a duplicate. Previously, it was possible to independently calculate and pay the tax.
- Payment must be made according to a receipt, which arrives at the place of registration of the car owner. The payment document indicates the number that is entered during online payment to simplify the procedure.
- Regional authorities may exempt or provide a tax discount for certain categories of beneficiaries. These could be pensioners, parents of disabled children, a mother or father from a large family, etc.
- You must declare your right to the benefit yourself and regularly confirm your social status to maintain the benefit.
In general, the procedure for calculating and paying transport tax is well established and is carried out according to a certain scheme. But many car owners still have questions.
How transport tax is paid: at the place of registration or registration, is discussed in the article: transport tax is paid locally. Read here what the amount of fines for non-payment of transport tax is.
Transport tax on expensive cars
For passenger cars, the cost of which is 3 million rubles.
and more, increasing coefficients may be applied. Depending on the cost of a passenger car, the following increasing factors are applied: 1.1 - for passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million to 5 million rubles. inclusive, if no more than 3 years have passed since the year of manufacture of such cars;
2 - for passenger cars with an average cost of 5 million to 10 million rubles. inclusive, if no more than 5 years have passed since the year of manufacture of such cars;
3 - for passenger cars with an average cost of 10 million to 15 million rubles. inclusive, if no more than 10 years have passed since the year of manufacture of such cars;
3 - for passenger cars with an average cost of 15 million rubles, if no more than 20 years have passed since the year of manufacture of such cars.
If you have such cars, you need to check the list of cars with an average cost of 3 million rubles, subject to application in the next tax period, approved by the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia. The list is approved for each tax period and posted no later than March 1 of the next tax period on the official website of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia on the Internet information and telecommunications network. For 2021, such a list is certified by the Information of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia “List of passenger cars with an average cost of 3 million rubles, subject to application in the next tax period.”
If your car model is not on the list approved for the corresponding tax period, then the increasing factor is not applied to it, for example, for a Tesla car. If you find your car model in the list, then you need to calculate the average cost of the car. The average cost of a car is determined in the manner approved by Order of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of Russia dated February 28, 2014 No. 316 “On approval of the Procedure for calculating the average cost of passenger cars for the purposes of Chapter 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.”
The Procedure provides formulas for calculating the average cost of a car for a certain basic version of the car. The calculation of the average cost of a car differs depending on whether the manufacturer or an authorized representative of the manufacturer is represented in the Russian Federation, and whether data on the recommended retail price are provided by the manufacturer or an authorized representative of the manufacturer.
If data on the recommended retail price of the manufacturer or an authorized representative of the manufacturer is provided, then the calculation of the average cost of cars is based on determining the average cost of cars based on the recommended retail prices for cars of this make, model and year of manufacture of the corresponding basic versions of cars as of July 1 and December 1 the corresponding tax period.
If data on the recommended retail price by the manufacturer or an authorized representative of the manufacturer is not provided, or if the manufacturer or an authorized representative of the manufacturer is not represented in the Russian Federation, then the calculation of the average cost of cars is based on determining the average cost of cars based on the retail prices for new cars of this make, model and year of manufacture the corresponding basic versions of cars as of December 31 of the corresponding tax period, indicated in Russian catalogs.
As you can see, the price of a taxpayer’s purchase of an expensive car does not matter for the application of the increasing coefficient. If the average cost of a car is equal to or higher than 3 million rubles, then you need to calculate the age of the car.
The age of such cars is calculated from the year of manufacture of the corresponding passenger car. For example, if a taxpayer has an Audi A6 Limousine quattro with a diesel engine type and an engine capacity of 2967, a car with a year of manufacture in 2017, then for such a car an increasing factor is applied when calculating the transport tax for 2021, 2021 and 2021, and for 2020 The year no longer applies, since the list sets the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture of such a car to 3 years.
For expensive passenger cars, advance payments for transport tax are also paid taking into account an increasing coefficient.
Transport tax payers
| The subject of the Russian Federation | Tax rates in rubles per unit of power | |||||||
| power up to 20 l. With. | power from 20 to 35 hp. With. | power over 35 hp. With. | power over 40 hp. With. | power over 45 hp. With. | power over 50 hp. With. | power over 100 l. With. | power over 150 hp. With. | |
| Republic of Adygea | 5 | 7 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Republic of Bashkortostan | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| The Republic of Buryatia | 5.6 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 11.1 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.1 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.8 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.8 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.8 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.8 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago | 27.8 rub. - if the motorcycle was produced less than 5 years ago |
| 5 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 10.1 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 24.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 25.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 25.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 25.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 25.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | 25.2 rub. – if the motorcycle’s age is in the range from 5 to 10 years | |
| 4.6 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 9.2 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.5 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.9 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.9 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.9 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.9 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | 22.9 rub. - if the motorcycle is more than 10 years old | |
| Altai Republic | 4 | 6,5 | 19,5 | 19,5 | 19,5 | 19,5 | 19,5 | 19,5 |
| The Republic of Dagestan | 4,2 | 7,5 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| The Republic of Ingushetia | 2 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | 3 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| Republic of Kalmykia | 9 | 11 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Karachay-Cherkess Republic | 4 | 8 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Republic of Karelia | 7 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Komi Republic | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Mari El Republic | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| The Republic of Mordovia | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | 4 | 8 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | 4 | 8 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Republic of Tatarstan | 8 | 12 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Tyva Republic | 5,5 | 6,6 | 23,1 | 23,1 | 23,1 | 23,1 | 23,1 | 23,1 |
| Udmurt republic | 4 | 5 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| The Republic of Khakassia | 8 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Chechen Republic | 3 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Chuvash Republic | 6 | 14 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| Altai region | 6 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Krasnodar region | 8 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 35 | 50 | 50 |
| Krasnoyarsk region | 2 | 5 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 12,5 | 12,5 |
| Primorsky Krai | 6 | 13 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Stavropol region | 5 | 9 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 |
| Khabarovsk region | 4 | 7 (up to 30 hp) | 10 (power 30-40 hp) | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 31 |
| Amur region | 6 | 12 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Arhangelsk region | 6 | 12 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Astrakhan region | 5 | 10 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Belgorod region | 5 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Bryansk region | 4 | 6 | 8 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Vladimir region | 2 | 5 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Volgograd region | 6 | 10 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 24 |
| Vologda Region | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 50 | 50 |
| Voronezh region | 4 | 8 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Ivanovo region | 4,5 | 11 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Irkutsk region | 4 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 7 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 10 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 13 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 13 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 13 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 13 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) | 13 (if the motorcycle was produced less than 7 years ago) |
| 2.5 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 5 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 6 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 8 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 8 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 8 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 8 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | 8 (if the motorcycle was produced more than 7 years ago) | |
| Kaliningrad region | 4 | 8 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 | 21 |
| Kaluga region | 5 | 6 | 8 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Kamchatka Krai | 9 | 18 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Kemerovo region | 5 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 50 |
| Kirov region | 6 | 12 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 50 | 50 |
| Kostroma region | 10 | 13 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 50 | 50 |
| Kurgan region | 3 | 7 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Kursk region | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Leningrad region | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Lipetsk region | 8 | 16 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Magadan Region | 3 | 6 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Moscow region | 9 | 16 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Murmansk region | 4 | 8 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Nizhny Novgorod Region | 9 | 18 | 27 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Novgorod region | 10 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 (up to 90 hp) | 50 (over 90 hp) | 50 |
| Novosibirsk region | 2 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Omsk region | 5 | 8 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Orenburg region | 1 | 2 | 2,5 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Oryol Region | 6 | 12 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Penza region | 8 | 11 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 37 | 50 | 50 |
| Perm region | 10 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 | 19 |
| Pskov region | 6 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Rostov region | 4 | 7 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Ryazan Oblast | 4 | 6 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 50 | 50 |
| Samara Region | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Saratov region | 4 | 15 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Sakhalin region | 5 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Sverdlovsk region | 4,5 | 9,4 | 32,9 | 32,9 | 32,9 | 32,9 | 32,9 | 32,9 |
| Smolensk region | 5 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Tambov Region | 10 | 20 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Tver region | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Tomsk region | 5 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Tula region | 6 | 15 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| Tyumen region | 5 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Ulyanovsk region | 6 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Chelyabinsk region | 4,6 | 7,7 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Transbaikal region | 3 | 6 | 13 | 13 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Yaroslavl region | 7,5 | 12,7 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
| Moscow | 7 | 15 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Saint Petersburg | 10 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 (up to 90 hp) | 50 (over 90 hp) | 50 |
| Jewish Autonomous Region | 4,8 | 7,1 | 11,9 | 11,9 | 11,9 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra | 8 | 16 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | 4 | 8 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 6 | 16 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Republic of Crimea | 4 | 6 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Sevastopol | 2 | 4 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
Federal Law No. 436-FZ dated December 28, 2017, which came into force at the end of December 2021, excited all vehicle owners. The media reported that he was giving new benefits on transport tax for pensioners (2018), and in some cases even canceling the tax. In fact, Federal Law No. 436-FZ does not cancel the transport tax for pensioners in 2019, but only writes off the debt incurred as of 01.01.
Please note that debts incurred in 2013 and previous years will be written off. If the owner has not paid for his iron horse at the end of 2014, both the debt and the penalty accrued on it will remain. It is difficult to say whether the authorities will agree in the future to recognize such arrears as “hopeless for collection.”
As the Federal Tax Service explained, the write-off procedure will be automatic - the owners do not need to apply anywhere. You can request information about whether debts have been written off through the taxpayer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website or directly from the inspectorate at the place of registration.
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax payers are the persons to whom the vehicle is registered. It does not matter whether an individual is an entrepreneur or not - the obligation to pay tax remains in any case. And legal entities pay 2 taxes on cars:
- on the property of organizations;
- directly transport.
Since 2013, companies have not paid tax on movable property, however, starting from January 1, 2015, only property belonging to the 1st and 2nd depreciation groups is exempt from taxation. Motor vehicles are not included in these groups; therefore, the company must pay both transport tax and property tax on them.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
In 2021, with regard to movable property, regions are given the right to independently decide on the introduction of benefits for this property. It will be implemented from 2021 and may have 2 scenarios:
- the region adopted a law on benefits in 2021 - the benefit will apply from 2021;
- the law has not been adopted by the region - the benefit in the region is not valid since 2021.
Since the end of 2015, another fee has been added to payments for cars for companies - for trucks with a maximum weight of more than 12 tons, to compensate for damage to the road surface. It is listed using the Plato system. Payments paid for heavy vehicles, from 07/03/2016, reduce the amount of tax accrued on these vehicles. But such a decrease is valid only for the period 2016-2018.
More information about this deduction can be found in the article “Transport tax and the Plato system (nuances).”
Who can avoid paying transport tax? The list of persons entitled to benefits under this payment is established in each region separately. However, the following can count on easing the tax burden:
- disabled people of groups I and II;
- WWII veterans;
- heroes of the USSR, holders of the Order of Glory;
- public organizations of disabled people and companies organized by disabled people;
- pensioners and large families (in some regions).
Find out who has transport tax benefits in 2021 here.
Benefits come in different forms. For example, the payer is exempt from paying tax for only one car or pays half of the tax payment amount calculated on a general basis.
Companies organizing the 2021 FIFA World Cup also do not pay the tax. Transport tax holidays may be established in free economic zones. For example, residents of the Zelenograd special economic zone are provided with a 5-year benefit on this payment.
See also “Officials told when you do not need to pay transport tax.”
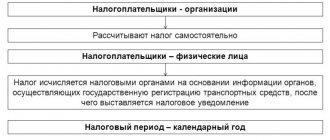
Information on the amount of tax payable to individuals is provided by tax authorities based on the information they have.
IMPORTANT! Until May 2014, the owner of a vehicle could not pay tax if he did not receive an INFS notification by mail in Russia. Since May 2014, citizens have been obliged, if they do not receive a notification from the Federal Tax Service, to independently transfer to the tax authority information about the property they have acquired, including vehicles (Law No. 52-FZ dated 02.02.2014). Read more about this here.
Legal entities calculate the amount of transport tax themselves based on data on movable property registered on the company’s balance sheet. The transport tax rate for 2017-2018 for organizations is determined by the regulations of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
What property is transport tax levied on? This issue is regulated by the provisions of Art. 358 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These are cars, motorcycles, buses, airplanes, helicopters, yachts and other self-propelled watercraft, jet skis, motor sleds and motor boats, as well as a number of other vehicles.
Find out how the tax base for transport tax is determined here.
Not all property that moves is taxed, but only vehicles of a certain capacity. So, they don’t pay tax:
- owners of low-power vehicles, for example, rowing and motor boats, if the power of the motor boat is no more than 5 horsepower;
- disabled people in special cars, if their engine power does not exceed 100 horsepower and they are received through social security authorities.
If the vehicle is registered or deregistered during the tax period
If a vehicle is registered to a taxpayer during a calendar year, then the tax is calculated using a coefficient.
The coefficient is calculated as the ratio of the number of full months during which the vehicle was registered to the taxpayer to the number of calendar months in the tax (reporting) period. The month of registration is taken as a full month if the registration of the vehicle occurred before the 15th day of the corresponding month, inclusive, or the deregistration of the vehicle (deregistration, exclusion from the state ship register, etc.) occurred after the 15th day of the corresponding month.
The month of registration is not taken into account if the registration of the vehicle occurred after the 15th day of the corresponding month or the deregistration of the vehicle (deregistration, exclusion from the state ship register, etc.) occurred before the 15th day of the corresponding month inclusive.
Transport tax on heavy trucks
Until January 1, 2021, in the case of payment to Plato in relation to a vehicle with a permissible maximum weight of over 12 tons, the organization did not pay advance payments for transport tax.
This was provided for in paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In addition, the organization reduced the transport tax at the end of the year by the amount paid to Plato for the corresponding tax period. If, in the event of a reduction in the transport tax for payment to Plato, the amount of tax payable to the budget took a negative value, then the transport tax was not paid. But, according to paragraph 4 of Article 2 of the Federal Law of July 3, 2016 N 249-FZ, this procedure was in effect until December 31, 2018. In this connection, from 01.01.2019, such organizations pay transport tax in the general manner, that is, pay advance payments, unless otherwise established by the laws of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, and the tax itself.
General information about transport tax
Transport tax is a direct payment to the budgets of the regions of the Russian Federation.
It is paid by the owners of cars and other vehicles. The obligation to pay tax is imposed on both legal entities and citizens - owners of vehicles. The larger and more powerful the car, the higher the tax amount. The procedure for its calculation and payment is regulated by Ch. 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and regional legislative acts. IMPORTANT! The tax rate for transport tax is set by regional authorities.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:accounts.google.comServiceLogin
Transport tax was introduced into Russian economic practice in 2003. In most countries of the world there is no such tax - instead, environmental taxes, road taxes, and taxes on movable property are levied.
The economic meaning of the transport tax is to compensate car owners for damage to the environment and road surfaces. A similar function is performed by excise taxes on gasoline and car production, so in fact the car owner is subject to several taxes at the same time. In 2010, the Government of the Russian Federation proposed to abolish the transport tax, replacing it with an increase in excise taxes on fuel. Excise taxes increased, but the transport tax remained.
With the introduction of the Platon system for trucks in 2015, the idea of abolishing the transport tax was voiced by the President of the Russian Federation. However, everything was limited only to the introduction of a tax deduction for heavy trucks, and then only for the period 2016-2018.
Another initiative of officials is to replace the transport tax with an excise tax on fuel. The meaning of the proposed payment is that a citizen or organization will pay only for the actual time of using transport.
Should you expect the abolition of transport tax in 2018 and how the government plans to ease the tax obligations of vehicle owners, read here.
When to pay transport tax?
The deadlines for payment of advance payments for transport tax and transport tax at the end of the year are established by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. But for organizations, the deadline cannot be set earlier than February 1 of the year following the expired tax period - the deadline for submitting a tax return for transport tax.
In Moscow, for example, organizations pay transport tax no later than February 5 of the year following the expired tax period (Clause 1, Article 3 of Moscow Law No. 33 dated 07/09/2008). In this case, the organization does not pay advance tax payments during the tax period.
But in the Moscow region, advance payments for transport tax are paid no later than the last day of the month following the reporting period (Clause 1, Article 2 of the Law of the Moscow Region of November 16, 2002 No. 129/2002-OZ).
Let us remind you that the reporting periods for transport tax are 2 quarters - the second and third quarters (clause 2 of Article 360 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the tax for the tax period is paid no later than March 28 of the year following the expired tax period. Individuals pay transport tax no later than December 1 of the year following the expired tax period.
Procedure for calculating transport tax
See also “How to pay transport tax if an expensive car is not on the list of the Ministry of Industry and Trade?”
Individuals pay tax until December 1 of the following year.
Tax authorities stop collecting tax from an individual either with the disappearance of the relevant property or in connection with the death of the owner. If there is a tax debt, it is paid by the heirs.
Find out about the deadlines for paying transport tax for individuals and legal entities here.
How does an organization calculate transport tax? First, the accountant checks whether there are cars or other vehicles on account 01. Then it clarifies whether the company’s transport is subject to taxation. Then you need to find out whether the car is registered with the traffic police - tax is paid only on vehicles registered with the road inspectorate.
At the next stage, the company must find out whether it has a tax benefit. To do this, you need to check Art. 357 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and regional legislation - it is possible that additional benefits are provided in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
The amount of tax payable is determined as the product of the tax base and rate. The tax base (most often the horsepower of the car) will be determined by the accountant according to the title.
How to calculate transport tax for the year, see this material.
Transport tax rates by region in 2017–2018 can be found on the Federal Tax Service website or in our “Transport Tax Rates” section.
The amount of tax in some regions may depend on the category of the car, the increasing coefficient, the environmental class or the age of the car. In addition, the accountant needs to take into account the period of ownership of the car during the tax period.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:www.googleadservices.compageadaclk
For transport tax, the company pays advances (every quarter, if established by regional law) and an annual payment. In the region, the payment of advances can be canceled, then you need to pay the budget once - at the end of the year.
Read about tax and reporting periods for transport tax here.
The company submits tax reports once a year - based on the results of the tax period. Reports can be submitted to the TKS inspection, as well as in person (if necessary, by proxy) or sent by mail. The declaration contains information about the car, its make, number, horsepower and other information necessary to calculate the tax itself.
IMPORTANT! If the Ministry of Industry and Trade has released a new list of expensive cars, and you have already submitted a transport tax return, there is no need to redo the reporting and submit an updated declaration.
The declaration must be submitted to the tax office at the location of the head office or division to which the car is registered.
See also “The Federal Tax Service has clarified where organizations should pay tax for a car.”
Legislators differentiate tax rates by types of vehicles and their power. For tax purposes, motorcycles are placed in a separate group with scooters. There are three types of tariffs for them (Article 361 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- for equipment with an engine power not exceeding 20 horsepower, the basic standard is 1 rub. for each unit of power;
- if the motorcycle’s power is in the range from 20 to 35 horsepower, the rate increases to 2 rubles;
- For motorcycles with an engine power level of more than 35 horsepower, a basic tax rate of 5 rubles has been introduced.
Regional authorities are authorized to increase or decrease the given rates, but not more than 10 times. Our table shows the current transport tax standards in 2021 for motorcycles of various capacities in all constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
For vehicles owned by individuals, the 2021 motorcycle tax is calculated by the tax authorities and must be paid no later than December 1 of the following reporting year. The results of accruals are communicated to taxpayers via electronic notifications through personal accounts on the Federal Tax Service website or paper notifications sent by mail.
Number of Engine Power Units x Tax Rate x Motorcycle Ownership Rate
The ownership coefficient is determined by dividing the number of months in the reporting year during which the taxpayer owned the motorcycle by 12. If the vehicle belonged to one owner throughout the year, then the coefficient will be equal to 1.
Motorcycle tax in 2021 must be paid by the taxpayer to whom ownership of a specific vehicle is registered. The Federal Tax Service receives information about vehicles from the traffic police registers.
The following rules apply to legal entities:
- the tax period is equal to the calendar year, which begins on January 1;
- at the end of each year, the business entity that owns the motorcycle must calculate the tax liability, pay it off and report on transport tax by submitting a declaration form to the Federal Tax Service within the time limits established by the regional law on transport tax.
Benefits for transport tax payers can be established both at the federal and regional levels. Tax exemption is provided to motorcycle owners for the period when the vehicle was reported stolen. To receive the benefit, the owner of the vehicle must document the fact of theft and being put on the wanted list.
Income tax
The transport tax paid is taken into account in other expenses associated with production and sales.
From January 1, 2021, due to the fact that the payment to Plato does not reduce the transport tax, this payment is included in income tax expenses in full. From Article 270 “Expenses not taken into account for tax purposes”, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation invalidated clause 48.21, which did not allow reducing income tax in the amount by which, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of transport tax calculated for the tax was reduced (reporting) period for heavy goods vehicles.
Similar changes regarding the accounting of transport tax amounts from heavy trucks in expenses were made under the taxation systems of the Unified Agricultural Tax and the simplified tax system (clause 45, clause 2, article 346.5, clause 37, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).