Many people buy vehicles because this purchase simplifies life in general. After complete re-registration through the relevant authorities, you become the full owner of the car.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call. It's fast and free!
This is where the question about transport tax arises. It must be paid for the right to own and operate a vehicle.
What is the tax base of the vehicle?
The tax base is a physical or other characteristic of an object that is subject to taxation. This base is a mandatory component of all tax elements. The purpose of the tax base is to express the object of taxation and its quantitative characteristics. Essentially, measuring its parameters.
Object and tax rate
Items subject to taxation are:
- Motor transport;
- Motorbike;
- Moped;
- Bus;
- Airplane;
- Helicopter;
- Motor ship;
- Yacht;
- Sailing ships;
- Snowmobile.
And many more vehicles have been legally registered in the Russian Federation.
Motor vehicles subject to taxation are also considered to be vehicles that have been in use for up to five years and have an engine capacity exceeding 300 cubic centimeters.
The tax rate depends entirely on the engine size, traction force or gross vehicle weight, and the type of vehicle. The very size of the tax rate on a vehicle is specified in paragraph 1 of Art. 361 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the law, it can be valued up or down.
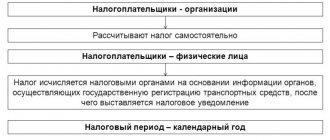
If an individual pays
For individuals, tax obligations arise at the time the vehicle is registered in the name of the owner. At the same time, the duties of the tax authorities include calculating the amount of tax, as well as sending information about the amount and procedure for calculating the tax to the owner of the car. It is important to note that according to paragraph 3 of Art. 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the owner of a vehicle who has not received a notification from the tax office about the need to pay transport tax does not bear the corresponding obligations. According to clause 4 of Art. 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if a tax notice is sent by registered mail, the tax notice is considered received after six days from the date of sending the registered letter.
In the latest clarifications regarding paragraph 5 of Art. 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Tax Service specialists emphasize that when determining the location of a vehicle, it is necessary to take into account not only the region of its registration, but also the place of registration of the owner of this vehicle. Thus, the tax is paid at the place of registration of the owner of the vehicle, which is also considered the location of the car.
Information about the change of address of the owner of the car must be provided to the tax office where he previously lived. In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 85 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the responsibilities for transmitting such information are assigned to the authorities carrying out registration (migration registration) of individuals at the place of residence (stay). This is necessary so that the traffic police and the Federal Tax Service carry out the necessary procedures for re-registering the vehicle at a new address.
An individual can make the tax payment process in any of the many available ways:
- in a bank (by depositing funds into your current bank account and, accordingly, making a payment from your account, or making a payment without opening an account);
- through a payment terminal;
- through the Federal Tax Service website;
- by bank card;
- from an electronic wallet.
You can pay tax without leaving your home, using a bank card (if you have connected to online banking), through the Federal Tax Service website and the government services portal.
Determination of the tax base for transport tax
It is defined as follows:
- In relation to vehicles having an engine and traction power measured in horsepower;
- In relation to non-self-propelled water transport, whose capacity is in registered tonnage;
- In relation to other swimming or aeronautical vehicles, in the unit of transport itself.
Vehicle with engine
Vehicles with an engine include a vehicle driven by an engine. The definition covers tractors and self-propelled machines.
Motor vehicles are cars:
- Passenger cars;
- Freight;
- Buses;
- Specialized vehicles.
Tractors:
- Wheeled and tracked;
Self-propelled transport:
- Snowmobile;
- All-terrain vehicle;
- Grader;
- Loader;
- Excavators.
As well as military vehicles, wheeled or tracked, and motorcycles and mopeds.
Aeronautical vehicles
A typical aeronautical transport includes an airplane, but there is also a helicopter. An airplane is an air vehicle that is heavier than air mass; it is helped to rise into the air by the lifting force of jet engines.
Helicopter is a rotary-wing aircraft. It rises into the air with the help of the lifting driving force of several rotors, from which the drive goes to the engines.
Water towed vehicles
A non-self-propelled floating vessel used for shipping purposes. Mixed navigation vessels:
- Ferry;
- Drilling station;
- Floating crane;
- Barge.
Also used for industrial shipping.
Not subject to taxation
Objects not subject to tax:
- Boats with oars and boats with a motor have a tractive force that does not exceed five horsepower;
- Motor vehicles adapted and equipped for a disabled driver, and also cars with an engine power that does not reach one hundred horsepower.
- Cars donated by social protection authorities in accordance with the procedures established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- Industrial water vehicles;
- Water and air vehicles intended for the transport of passengers, which are considered the property of companies or individuals of entrepreneurial activity. Their work should be focused on passenger transportation or the transportation of large-tonnage cargo.
Special vehicles:
- Tractor;
- Self-propelled combines;
- Milk tankers;
- Special vehicles for transporting birds and livestock;
- Special transport for emergency veterinary care;
- Special transport for transporting fertilizers;
- In general, almost all transport that is used in agricultural work.
- Official transport owned by federal services or the executive branch.
- Transport that is on the federal wanted list, but only if the fact of theft or theft is confirmed by the owner of the transport and the corresponding document is issued by the traffic police;
- Air transport of sanitary and medical services;
- Water transport included in the unified Russian International Register of Ships;
- Water station floating platforms, floating drilling rigs.
Tax rate
The basic rates for transport tax are established in Article 361 of the Tax Code. Regional authorities can reduce or increase transport tax rates by no more than ten times. In addition, regional authorities can set tax rates taking into account the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture of vehicles and (or) their environmental class.
Basic tax rates are shown in the table:
| Type of vehicle | Tax rate, rub. in year | |
| Passenger cars with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 100 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 100 l s up to 150 l s | 3,5 | |
| over 150 l s up to 200 l s | 5 | |
| over 200 l s up to 250 l s | 7,5 | |
| over 250 l s | 15 | |
| Motorcycles and scooters with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 20 l inclusive | 1 |
| over 20 l s up to 35 l s | 2 | |
| over 35 l s | 5 | |
| Buses with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 200 l inclusive | 5 |
| over 200 l s | 10 | |
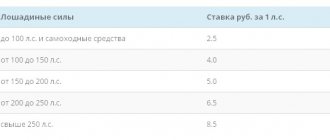
| Trucks with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 100 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 100 l s up to 150 l s | 4 | |
| over 150 l s up to 200 l s | 5 | |
| over 200 l s up to 250 l s | 6,5 | |
| over 250 l s | 8,5 | |
| Snowmobiles, motor sleighs with engine power (each horsepower) | up to 50 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 50 l s | 5 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 10 | |
| over 100 l s | 20 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 20 | |
| over 100 l s | 40 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 25 | |
| over 100 l s | 50 | |
| Other self-propelled vehicles, pneumatic and tracked machines and mechanisms (per horsepower) | 2,5 | |
| Non-self-propelled (towed) ships for which gross tonnage is determined (from each registered ton of gross tonnage) | 20 | |
| Airplanes, helicopters and other aircraft with engines (per horsepower) | 25 | |
| Airplanes with jet engines (per kilogram of thrust) | 20 | |
| Other water and air vehicles without engines (per unit of transport) | 200 | |
For which vehicles the tax base is not calculated?
Calculation of the vehicle tax base
Now we will try to describe how to calculate the transport tax base. Transport and machines equipped with a mechanism, self-propelled and towed, are subject to taxation.
The tax base is indicated by the producing enterprise in the technical document. The owner just needs to find the technical characteristics of the vehicle and enter them into the declaration form. With this form, contact the tax authority, and it will calculate your tax base based on the characteristics you provide. The transport fee is paid once a year.
The tax base indicated in technical passports or in accordance with the law:
- The technical parameters of ground transport equipped with motors are indicated in the technical passport. Measured in horsepower.
- The traction force of air transport equipped with air-breathing engines is indicated in the technical passports. Measured in kgf.
- The traction force of any water transport that is not equipped with a motor and can only be moved with the help of a tug is also indicated in the technical passport. Measured in tonnage.
- The power of other vehicles, without classification, is measured in their own weight.
Transport for which the tax base is not designed
Referring to Article 358, which states that the tax base is not calculated for the transport described below:
- Oar boats. Vessels with an engine no more powerful than five horsepower;
- Passenger vehicles equipped for people with disabilities.
- Industrial vessels;
- Special equipment used in agricultural work and production of agricultural products;
- A stolen vehicle that is officially wanted.
- Death of the payer, owner of the vehicle.
- Other officially confirmed circumstances that have factors for stopping tax payment.
A car owner whose vehicle falls under the tax base must pay tax in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. You need to pay where your vehicle is located, that is, in a specific city and region. The tax must be paid on strictly designated dates, otherwise you will be subject to a penalty.
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now: +7 (Moscow) +7 (812) 309-53-42 (St. Petersburg) It's fast and free!
Free online consultation with a car lawyer
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now: +7 (Moscow) +7 (812) 309-53-42 (St. Petersburg) It's fast and free!
Procedure for calculating tax and advance payments
Transport tax is calculated separately for each vehicle. Organizations independently determine the amount of transport tax. Individuals do not need to calculate tax: the inspectorate will send them a request to pay transport tax. To calculate the amount of transport tax that needs to be paid to the budget, multiply the tax base by the tax rate. If you own the vehicle for less than a year (for example, a few months), then the tax is paid only for those months. To calculate transport tax for several months, you need to determine the coefficient:
| Number of full months during which the car is registered to the company | : | 12 months | = | Correction factor |
The tax amount is calculated as follows: the tax base is multiplied by the tax rate and by the correction factor. In this case, the month of registration of the vehicle, as well as the month of deregistration of the vehicle, are taken as a full month. In case of registration and deregistration of a vehicle within one calendar month, this month is taken as one full month.
At the end of each reporting period (Q1, Q2 and Q3), firms pay advance payments for transport tax. They are calculated as follows: the total amount of transport tax (the product of the tax base and the tax rate, taking into account the correction factor) is divided by 4.
And at the end of the tax period (year), the difference between the annual tax amount and the amount of advance payments transferred during the year is transferred to the budget.
Regional authorities may exempt certain categories of firms from paying advance payments for transport tax. In this case, Osvobozhdeniye residents will have to remit tax only at the end of the year.