Home > About the Center > Publications
Svetlysheva Olga Yurievna , teacher of the Center in the direction of Personnel Management and Personnel Management
There are many myths and speculations around personal data. In practice, extremes are often encountered: employers either unreasonably classify all information about an employee as secret, or do not pay attention to the protection of their personal data at all.
Let's look at the rules for working with personal data (PD).
- Rule 1. Work with personal data within the law
- Rule 2. Understand what information relates to personal data
- Rule 3. Distinguish between categories of PD
- Rule 4. Be able to process PD
- Rule 5. Competently draw up documents for working with PD
- Rule 6. Know the rights of the employee and the obligations of the employer when working with personal data
- Rule 7. Take into account the employer’s liability for violation of personal data protection
Rule 1. Work with personal data within the law
First, you need to understand the terminology and understand who is the “subject of personal data” and the “operator of personal data.”
Let's translate these concepts into the language of labor legislation:
PD subject is a candidate / trainee / employee / former employee, the one whose PD is processed.
PD operator is the employer, the one who processes the PD.
Today in Russia several regulations regulate work with PD (Table 1).
Consent to processing
The legislator stipulates that information is obtained with the consent of the person. It is expressed in writing. The document must be completed by the employees themselves. When another person provides information, consent must be obtained from the employee.
The law reflects that consent must be conscious and informed. It is given by the person about whom the information is provided or his representative. Exceptions may be reflected in laws. The law does not say that consent is expressed in writing. Such rules are established in Article 13.11 of the Code of Administrative Offences.
Based on this norm, it is indicated that in situations reflected in the law, consent is obtained in writing. It is necessary in order to prove in a possible controversial situation that information was obtained legally. A written document will help prove your case.
Rule 2. Understand what information relates to personal data
We live in an information world, and all information can be divided into two types:
- Public - information and other information to which access is not limited.
- Restricted information, which includes state secrets and confidential information, including more than 40 types of secrets: official, commercial, etc., including personal data.
Are your full names? personal data? In some cases yes, in others no.
What information constitutes “personal data”?
Any information that directly or indirectly relates to an individual.
Thus, just full name. are not PD until it is possible to determine who they belong to. In order for full name “Ivanov Ivan Ivanovich” is classified as personal data; it requires the presence of a specific person who can be identified from this data.
For example, Ivan Ivanovich Ivanov is the general director of Kompaniya LLC. Here we understand what specific person we are talking about, and in this case, full name. belong to PD.
Who approves the Personal Data Protection Regulation
The regulation on the protection of employee personal data is approved by the head of the company or a person authorized by him. And this document is put into effect by order of the head. The Personal Data Protection Regulation looks like this:
Each employee who, due to his job duties, has access to the personal data of other employees must sign a non-disclosure obligation.
The list of persons who have access to the employee’s personal data is usually drawn up as an appendix to the Regulations.
First of all, these are personnel department employees, since they collect and generate data about the employee, and heads of structural divisions (for example, chief accountant, heads of departments). However, the latter have the right to request only the data that is necessary to perform specific labor functions (for example, to calculate tax benefits, the accounting department will not receive all information about the employee, but only data on the number of his dependents). The application is designed like this:
The employer is obliged to familiarize the employee with the Regulation on the Protection of Personal Data, and the employee is obliged to sign for this. The fact of familiarization is usually documented with a receipt, which remains with the employer. Here's a sample:
Rule 3. Distinguish between categories of PD
The legislation distinguishes four categories of personal data:
- General or public - known to other people and can be published in publicly available sources. This is basic personal data: full name, place of residence/registration, information about education/qualifications, information about place of work, phone number, e-mail, etc.
- Special is information about a person’s personality. They differ from other categories in that, as a rule, they are in closed access. They can only be obtained from the person himself or upon an official request to the clinic, law enforcement agencies, court, etc. For example, race and nationality, political, religious and philosophical views, health status, details of personal life, information on criminal records, etc.
- Biometrics are the physiological or biological characteristics of a person that are used to establish his identity. This category includes photographs, fingerprint data, iris, blood type, genetic information, etc.
- Other is additional information that may change frequently and may not be categorized as public, custom, or biometric data. For example, corporate data, information that is located in the organization: wages, different types of length of service, vacation periods, etc.
What does personal data consist of?
The processed personal data of the employee is regulated by the Basic Law of the Russian Federation, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other parts of federal legislation. In general, documentation on this issue can be divided into two large categories:
- provided by the employee himself;
- collected by the employer.
The first category is presented at the time of concluding an employment contract. Such employee personal data include:
- Full name, telephone number, residential address, registration;
- insurance identification documents;
- employment history;
- pensioner's ID;
- documents confirming the grounds for providing benefits;
- diplomas and other documents confirming education and profession;
- photo cards;
- documents regarding military registration;
- documents confirming marital status, etc.
Each item in this category falls under the basic principle of protecting employee personal data - ensuring maximum confidentiality. Only state law enforcement agencies can operate with such information, only when necessary and in most cases with the direct permission of the employee.
The second category of personal data is dealt with by the employer. This includes all papers related to the career and financial situation of full-time and freelance employees. The second category reflects any changes in the employee’s workplace, fixation of vacation time, sick leave, base rate (if any), wage scale for piecework (if any), overtime, non-material incentives for regular staff, both individual and group . All this information, with the obvious exception of financial information, is usually subject to a lesser degree of confidentiality.
Rule 4. Be able to process PD
PD processing includes any action or set of actions performed using automation tools or without using such tools with PD, for example collection, systematization, storage, use, transfer, destruction, etc.
Processing of any categories of PD is permitted with the written consent of the employee.
Processing of general PD is carried out if:
- processing is necessary to achieve the goals provided for by law (for example, Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), to implement and fulfill the functions, powers and responsibilities assigned by the legislation of the Russian Federation to the employer. For example, transfer of personal data when transferring taxes to the budget system of the Russian Federation, since the employer is a tax agent;
- processing is necessary for the performance of an employment contract to which the employee is a party. For example, transfer of information to the tax office;
- the employee has provided access to personal data (or at his request) to an unlimited number of persons. For example, an employee asked for a newsletter to post information about his anniversary.
Processing of special categories of PD occurs in the following cases:
- The PD was made publicly available by the employee himself;
- processing is carried out in accordance with the legislation on state social assistance, labor legislation, the legislation of the Russian Federation on pensions under state pension provision, on labor pensions;
- processing takes place in accordance with the legislation on compulsory types of insurance and insurance legislation.
Processing of biometric PD is carried out without the consent of the employee:
- if photos and recordings were taken at mass and public events;
- in connection with the implementation of international treaties of the Russian Federation on readmission - the state’s consent to accept back into its territory citizens who are subject to deportation from another state;
- in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on defense, security, counter-terrorism, transport security, anti-corruption, operational intelligence activities, public service, criminal executive legislation of the Russian Federation;
- in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on the procedure for leaving the Russian Federation and entering the Russian Federation, on citizenship of the Russian Federation. For example, an employee is sent on a business trip outside the Russian Federation.
At the same time, it should be remembered that when placing video cameras, it is necessary to take into account the requirements of the law, since covert surveillance of an employee is illegal.
The explanations of Roskomnadzor “On the issues of classifying photo and video images, fingerprint data and other information as biometric personal data and features of their processing” indicate that the development and adoption of a local act is required, in which it is necessary to determine the purposes of installing video cameras. Also, the organization must install signs “Attention! Video surveillance is underway." Each employee should be notified of the installation of security cameras personally against a signature, and written consent must be obtained from employees for video recording in the workplace.
How personal data is processed
PD can be processed in different ways:
- without the use of automation tools / non-automated processing, if such actions are carried out with the direct participation of a person;
- using automation tools when processing PD in information systems.
The employer must provide a certain degree of personal data protection depending on the category of data (Table 2):
To use PD in automated systems, the employer must have a secure IT infrastructure and monitor that PD is always available, to prevent their loss and transfer of PD to third parties.
Protection requirements
Chapter 14 of the Labor Code provides requirements regarding data protection. The responsibility of the manager is established to take into account the requirements when processing information. The purpose of processing is to ensure legal provisions and assist a person in finding a job. To determine the scope of information, you must be guided by the basic law of the country, the Labor Code.
Receiving information is allowed only from the employee himself. When it is possible to obtain it from a third party, the person must inform the company management about this in advance. You will be required to sign a consent form. The employer does not process data classified as special. This is information about intimate life, race, etc.
Measures to protect information are taken by the company's management. Paid with company funds. The order of protection is reflected in the laws. Employees are familiarized with the documentation reflecting the data collection procedure against signature.
It has been established that a person should not be deprived of his powers in order to maintain a secret. The development of protective measures is carried out by employers together with employees. Exceptional situations are reflected in laws.
Rule 5. Competently draw up documents for working with PD
In some cases, for example, when posting an employee’s PD on an organization’s website, the processing of different categories of PD requires the written consent of the employee, which must include:
- FULL NAME. employee, address, information about his identity document;
- name (full name) and address of the employer receiving the employee’s consent to process personal data;
- purpose of PD processing;
- list of personal data for the processing of which the employee’s consent is given;
- a list of actions with personal data for which consent is given, a general description of the methods of processing personal data used by the employer;
- the period during which the consent is valid, as well as the procedure for its withdrawal;
- employee signature.
The organization must approve the Regulations on the protection of personal data of employees.
It regulates the procedure for receiving, storing, using and protecting personal data, establishing the rights and obligations of the employer and employees, and also determining the responsibilities of the parties to the employment contract.
What information is indicated in the Personal Data Protection Regulations
The procedure for storing and using personal data of company employees is determined by the Regulations on the Protection of Personal Data. This is a mandatory internal (local) document of the company; it is developed by the HR department.
The law has not established a strict form for this document, but it must meet the requirements for the protection of personal data of an employee of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The Regulations must indicate:
- the purpose and objectives of the company in the field of personal data protection;
- concept and composition of personal data;
- in which structural units and on what media (paper, electronic) this data is accumulated and stored;
- how personal data is collected;
- how they are processed and used;
- who (by position) in the company has access to them;
- how personal data is protected from unauthorized access;
- employee rights to ensure the protection of their personal data;
- responsibility for the disclosure of confidential information related to the personal data of employees.
Rule 6. Know the rights of the employee and the obligations of the employer when working with personal data
Employers, employees and their representatives must jointly develop measures to protect employees’ personal data; employees must not waive their rights to maintain and protect secrets.
In order to ensure the protection of personal data stored by the employer, employees have the right:
- to full information about their personal data and the processing of this data;
- free free access to your personal data, including the right to receive copies of any record containing the employee’s personal data, except in cases provided for by federal law;
- identifying your representatives to protect personal data;
- access to medical records reflecting their health status through a health professional of their choice;
- requirement to exclude or correct incorrect or incomplete PD, as well as data processed in violation of legal requirements (if the employer refuses to exclude or correct PD, the employee has the right to declare in writing to the employer his disagreement with the appropriate justification for such disagreement);
- addition with a statement expressing the employee’s own point of view on the PD of an evaluative nature;
- the requirement that the employer notify all persons who were previously informed of incorrect or incomplete employee PD of all exceptions, corrections or additions made to them;
- familiarization, against signature, with the employer’s documents establishing the procedure for processing personal data, as well as their rights and obligations in this area.
Employer Responsibilities
- All employee PD should be obtained from the employee himself. If an employee’s PD can only be obtained from a third party, then written consent must be obtained from the employee. In this case, the employer must inform the employee about the purposes, intended sources and methods of obtaining PD, as well as the nature of the PD to be received and the consequences of the employee’s refusal to give written consent to receive it.
- The employer does not have the right to receive and process information about the employee related to special categories of personal data, except in cases provided for by law, for example, when assigning temporary disability benefits.
- The employer does not have the right to receive and process the employee’s PD about his membership in public associations or his trade union activities, except in cases provided for by law. For example, if an employee performs state or public duties, the employer must release the employee from work for a while while maintaining his place of work in accordance with Art. 170 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- When making decisions affecting the interests of an employee, the employer does not have the right to rely on the employee’s PD obtained solely as a result of their automated processing or electronic receipt.
When transferring personal data of an employee, the employer must comply with the following requirements:
- Do not disclose the employee’s personal data to a third party without the employee’s written consent, except in cases where this is necessary in order to prevent a threat to the life and health of the employee, as well as in other cases provided for by law. For example, when calling an ambulance or transmitting information to the labor inspectorate, tax office, etc. during an audit.
- Do not disclose the employee’s personal information for commercial purposes without his written consent.
- Allow access to employee PD only to specially authorized persons, while these persons should have the right to receive only those employee PD that are necessary to perform specific functions.
- Warn persons receiving the employee’s PD that this data can only be used for the purposes for which it was communicated, and require these persons to confirm that this rule has been complied with, for example, to issue a written obligation to not disclose PD.
- Transfer the employee's PD within one organization in accordance with local regulations, with which the employee must be familiarized with signature.
- Do not request information about the employee’s health status, with the exception of information that relates to the issue of the employee’s ability to perform a job function.
- Transfer the employee's PD to employee representatives, for example trade unions, in the manner prescribed by law, and limit this information only to those employee PD that are necessary for the said representatives to perform their functions.
Protection of the employee’s personal data from unlawful use or loss must be ensured by the employer at his expense.
The employee has the right to appeal in court any unlawful actions or inaction of the employer in the processing and protection of his personal data.
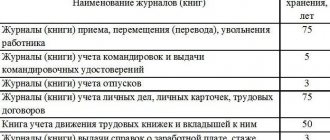
Personal data logs
The employer is obliged to maintain confidentiality when working with personal data of employees. To do this, you should keep special logs.
Logbook of internal access to personal data of employees
The journal for recording internal access to personal data of employees indicates: the date of issue and return of documents (personal files) to employees of the organization; purpose of issuance, name of documents issued, period of use. If there were a lot of documents and they were issued according to the inventory, when returning you need to check their availability according to the inventory. The employee returning the documents must be present. When issuing documents, warn that you cannot make notes or corrections in them, make new entries, remove documents (for example, from a personal file) or add new ones.
Logbook for issuing personal data of employees to organizations and government bodies
In the journal for recording the issuance of personal data of employees to organizations and government bodies, the following are recorded: incoming requests (date of receipt, number and date of the incoming document, from which body the request was received); date of transfer of personal data; content of the transmitted information; date of notification of refusal to provide information (if any).
In addition, the personnel officer must regularly check the availability of documents and other media containing personal data of employees. You should also keep a special journal for this.
Rule 7. Take into account the employer’s liability for violation of personal data protection
In accordance with the Administrative Regulations, the subject of state control (supervision) over compliance of PD processing with legal requirements are:
- documents the nature of the information in which suggests or allows the inclusion of PD in them;
- PD information systems;
- PD processing activities.
Persons guilty of violating the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of personal data are brought to disciplinary and financial liability in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws, and are also brought to civil, administrative and criminal liability in the manner established by federal laws (Table 3) .
Since penalties for violations of personal data have been increased, employers should be more attentive to the processing of their employees’ data and take into account these basic rules.
09.04.2021
Notice about the processing of personal data
According to Art. 22 of the Law of July 27, 2006 No. 152-FZ “On Personal Data”, from July 1, 2011, all legal entities and individuals whose activities are related to the collection and processing of personal data (PD) in electronic form (PD operator) must notify Roskomnadzor about this. These are government agencies that deal with personal data, almost all employers with a personnel service, carriers, insurers, and banks. By order No. 706 of August 19, 2011, Roskomnadzor approved recommendations for filling out the notification form, and the form was approved by the Russian Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications by order No. 346 of December 21, 2011.
The notification is generated in the form of a table on the operator’s letterhead. In a separate field indicate the full and abbreviated name, legal form, TIN and address of the operator. Separately, there are “data processing purposes” corresponding to the statutory objectives and activities carried out.
The “PD categories” field indicates what data (personal, biometric, special) are being processed. In the field “categories of subjects whose PD is processed,” this category should be indicated, for example, “employees who are in an employment relationship with the operator.”
In the field “legal basis for processing PD”, articles of the regulatory legal act relating to the processing of PD are indicated: for example, “Art. 85–90 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation", "Art. 85.1 of the Air Code of the Russian Federation", "Art. 12 of the Federal Law “On Acts of Civil Status”, etc. A separate field indicates the actions of the operator and methods of processing PD (non-automated, exclusively automated with or without transmission of received information over the network, mixed).
In the field “start date of PD processing” the day, month, and year of the actual start of any action are indicated.
If you have a question, ask it here >>
What does the concept of “employee personal data” mean?
The concept of “personal data” has a broad meaning; it can be interpreted extensively; the Russian Federation Law “on personal data” includes any type of personal information that may be related to a specific person. Personal information includes:
- FULL NAME;
- residential address and registration address;
- Date and place of birth;
- income and education;
- Family status;
- social and property status.
This list is not closed; it may include other oral and documentary types of data relating to a specific person. Not all of the information listed is important for the employee’s effective performance of professional duties, therefore, in the context of labor relations, the concept of “personal data” has a narrower meaning.
The employee’s personal data contains information that in some way characterizes the employee from a professional perspective.
This type of data is necessary for the employer in connection with the employee’s performance of his labor functions during the period specified in the agreement. This refers to those data and documents with information received from the employee, without which it is impossible to carry out verification activities, register him for work and entrust him with the performance of duties.
The law does not contain comprehensive requirements for the composition of such information and a specific legal act - a list of information constituting the employee’s personal data. In practice, the usual list of documents, in addition to personal data, includes:
- orders for hiring an employee;
- orders on rewards and punishments;
- orders to change the employment agreement, work book.
The employee can provide the personal information about himself or herself requested by the employer orally, or in writing, as a response to the request, by filling out a special document - a questionnaire.
The employee’s personal data is received by the employer and then stored in the employee’s personal file for a certain period of time and is confidential information since it cannot be distributed or provided to a third party without the consent of the person to whom it relates.
The prohibition on illegal distribution and transfer of information, its provision to third parties applies not only to the employer.
If an employee discloses the personal data of another employee, he faces punishment; the law also allows for the possibility of dismissing such an employee.
If the employee’s personal data changes, the employer must make changes to the accounting documents. An order is issued in which the changes are prescribed; this order is duly registered in the book (journal) of orders.
Transfer of personal data to third parties
To ensure compliance with the law on obtaining the consent of an individual for the processing and transfer of personal data, you can draw up a collective agreement with employees, which lists all third parties, indicating the names, addresses, and period of data use. All employees of the organization must sign this agreement.
You need to know that the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the transfer of personal data to judicial authorities and other law enforcement agencies without the need to obtain consent for these actions.
How to transfer?
There are several types of processing. The information can be transferred within the enterprise or outside it. Article 88 of the Labor Code reflects the rules observed during the transfer. It is prohibited to disclose data to third parties or for the purpose of receiving money.
The exception is a threat to human life or health. Such cases may be reflected in labor or other laws. It is required to warn citizens who have received information about the employee about the purposes for which they will be used. The purpose is reflected when the information is communicated.
The management of the organization has the authority to ensure that this requirement is met. Persons to whom the information is transferred undertake an obligation to maintain secrecy. These rules do not apply to situations where law enforcement agencies have become the recipient of the data.
Local regulations establish rules regarding the transfer of information within the enterprise. Citizens become familiar with this act by signing it. The legislator established a new rule. Now persons registered as individual entrepreneurs are required to issue local regulations that stipulate how data transfer occurs.
Persons vested with special powers have access to information. They can receive information from the employee that is necessary for their work. Therefore, some of the documentation may be submitted by other persons. It is prohibited to send requests for information regarding a person’s health status.
This does not apply to situations where it is necessary to determine whether the employee is able to continue his activities. Similar rules apply to women who are pregnant. This is done to understand whether a transfer to another job is necessary or not. The expectant mother is transferred to a place where there is no exposure to harmful factors.
Information can be transferred to the extent required to perform functions.