Accounting for semi-finished products of own production and their evaluation
Semi-finished products of our own production are materials that have been processed at a completed technological stage. They can be used for subsequent processing at the same enterprise or can be sold to a counterparty for further processing.
At full-cycle enterprises, where raw materials go through several stages of processing or reprocessing, account 21 “Semi-finished products of own production” can be used to account for semi-finished products produced in each processing stage.
Semi-finished products of own production can be classified as work in progress (clause 63 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting No. 34n, approved by the Ministry of Finance on July 29, 1998). There are several methods of assessment:
According to the requirements of Article 319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the cost of semi-finished products of own production is determined based on the assessment of finished products. Therefore, in tax accounting only one assessment method is used:
- Direct costs of the enterprise.
The accounting policy must include a list of direct expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-06/4/78 dated August 26, 2010). For example, the list of direct expenses includes: material costs, labor costs, social contributions, accrued depreciation.
When calculating the cost of finished products, semi-finished products of own production are included in the calculation in the form of a complex item or are included in detailed cost items.
Specifics of posting
The key problem when reflecting semi-finished products of own production is their valuation. In this case, three approaches are used:
- Cost of objects. Theoretically, this method is considered the most correct option. But it is accompanied by a rather labor-intensive calculation process. Moreover, the accuracy of the calculations will be highly questionable.
- Conditional price. It is determined in accordance with a special price tag that is introduced at the enterprise.
- Transfer price. It is used in all cases of internal cost accounting. He assumes that one workshop sells semi-finished products, and the other, accordingly, purchases them. This method is effective in situations where the selling unit has the right to independently set the price. In this case, the second workshop can purchase them internally or externally at its discretion.
Account 21 in accounting
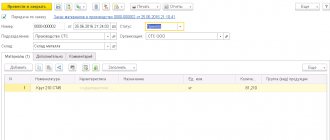
Semi-finished products of own production are accounted for on account 21 in correspondence with account 20 - when semi-finished products are used in own production, and with account 90 - when semi-finished products are sold to a counterparty:
The debit of account 21 reflects the receipt of semi-finished products and their surpluses discovered during inventory. The account credit takes into account the consumption of semi-finished products during transfer for subsequent processing, their sale or identification of shortages in the warehouse.
On account 21, analytical accounting can be maintained by storage location, by name, type, grade, and so on.
Account 21
As stated above, this article can be used to reflect information about semi-finished products of own production. This means that as soon as the products to be further processed are ready, they are moved to a special warehouse. The transactions will be reflected in 21 accounts. Wiring may be accompanied by some difficulties. In general, the entry looks like this: db sch. 20 CD count. 21. Analytics is carried out by item and storage location. The spread of the semi-finished method was due to psychological reasons. The fact is that managers and accounting employees, especially those who do not directly work in accounting, sought to see the movement of material assets as they really are. The semi-finished method ensures this fully.
Typical postings for 21 accounts “Semi-finished products of own production”
The main entries for 21 accounts used in accounting are shown in the table below:
| Account debit | Account credit | Operation description |
| 21 | 20 | Receipt of semi-finished products of own production |
| 21 | 23 | Receipt of semi-finished products manufactured by auxiliary production |
| 21 | 40 | Receipt of finished products for subsequent use as semi-finished products |
| 21 | 91.01 | Surplus semi-finished products identified during inventory were capitalized |
| 20 | 21 | Semi-finished products are sent to production for subsequent processing |
| 23 (25;26) | 21 | The cost of semi-finished products is included in the costs of auxiliary production (overall production costs; general business expenses) |
| 28 | 21 | Write-off of defective semi-finished products of own production |
| 91.02 | 21 | The cost of semi-finished products of own production, written off or sold, is reflected in other expenses |
| 94 | 21 | The identified shortage of semi-finished products is reflected |
Features of objects
The concept of semi-finished products manufactured by an enterprise independently is, in its economic essence, similar to the category of work in progress. Like WIP, they do not go through all stages of the technological process. Accordingly, semi-finished products cannot be called the final product. However, their essential feature is that at the previous stage they were brought to a certain state of readiness. Therefore, semi-finished products can subsequently:
- Sold to third party companies.
- Sent to the next workshop to create the finished product.
- Transferred to a structural unit (for example, to auxiliary production).
Examples of transactions on 21 accounts
Example 1. The cost of semi-finished products includes only the cost of raw materials and materials
Let's say VESNA LLC produces parts that are used in its own production. In January 2021, 150 parts were manufactured. The costs included:
- Raw materials and materials - 1,200,000 rubles;
- Salary and social contributions - 980,000 rubles;
- Depreciation charges - 450,000 rubles.
Semi-finished products are valued at the cost of raw materials and materials. Generated postings:
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 20 | 10 | 1 200 000 | The cost of raw materials and materials written off for the manufacture of parts is taken into account | Requirement invoice |
| 20 | 70 (69); 02 | 1 430 000 | Costs (wages, social contributions, depreciation) for the production of finished products are reflected | Payroll. Depreciation calculation |
| 21 | 20 | 1 200 000 | Semi-finished products are received into the warehouse | Shift production report |
| 20 | 21 | 1 200 000 | Semi-finished products transferred to production | Requirement invoice |
Example 2: Semi-finished products are valued at direct costs
Let's look at the previous example: VESNA LLC produces parts that are used in its own production. In January 2021, 150 parts were manufactured. Costs include:
- Raw materials and materials - 1,200,000 rubles;
- Salary and social contributions - 980,000 rubles;
- Depreciation charges - 450,000 rubles.
Semi-finished products of own production are valued at direct costs: raw materials and materials; salary; social contributions; accrued depreciation and so on, according to accounting policies. Generated postings:
| Dt | CT | Amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 20 | 10 | 1 200 000 | The cost of raw materials and materials written off for the manufacture of parts is taken into account | Requirement invoice |
| 20 | 70 (69) | 980 000 | The amount of salary and social contributions is reflected | Payroll. |
| 20 | 02 | 450 000 | Accrued depreciation reflected | Depreciation calculation. |
| 21 | 20 | 2 630 000 | Receipt of semi-finished products of own production to the warehouse (1,200,000 + 980,000 + 450,000) | Shift production report |
Selling on the side
A new addition to the Instructions for using the Plan is that the sale of semi-finished products can be carried out not only to enterprises, but also to individuals. If these operations are carried out systematically, then account 21 does not apply. When reflecting processes, an account is used. 43, summarizing information about finished products. However, if this fact is episodic in nature, then writing off 21 accounts is carried out as follows:
- db sch. 90.2 CD count. 21 or
- db sch. 91.2 Kd 21.
The choice of account 90 or 91 will depend on whether the sale of semi-finished products is part of the company’s normal activities or not. Meanwhile, the key entries will be:
1. db count 21 CD count. 20 – semi-finished products are transferred to the warehouse.
2. db sch. 20 CD count. 21 – the unit received previously produced products for further processing.
Solution
The practical use of management accounting (previously it was known as operational-technical accounting) eliminates the difficulties that arise. With its help, semi-finished products can be taken into account in physical terms. Meanwhile, experts note that the unfinished method is preferable. It does not involve maintaining an account 21. The transfer of products to the warehouse is reflected exclusively in management documentation. In this case, it is advisable inside the account. 20 show the movement of semi-finished products in physical equivalent.
Off-balance sheet 21 account: 1s
Reflection of funds whose value is up to 3 thousand rubles, excluded from reporting upon commissioning, is carried out in a special article. Subaccounts are opened for account 21. They correspond to the analytical articles of the account. 101, on which fixed assets were reflected before write-off. Sub-accounts can be opened for account 21:
- 21.04 – on machinery and equipment.
- 21.05 – on vehicles.
- 21.06 – for production and household equipment.
- 21.09 – for other OS.
For this article, analytics is carried out in accordance with the nomenclature, financially responsible persons and divisions, types of activities in total and quantitative terms.
Advantages and disadvantages
Using account 21, a specialist can reflect the production cycle. This, in turn, ensures tighter control over the work of financially responsible employees. However, count 21 has a number of disadvantages. In particular, on the account. 20 “fictitious” turnovers are formed (in economic terms). They will expand as the number of processing steps increases. At the same time, account 21 will be used to calculate each intermediate stage of production. This, in turn, will increase the labor intensity of the specialist’s work. Accordingly, the semi-finished method is complex, cumbersome and economically unprofitable.
Financial statements
Regardless of which method - semi-finished or unfinished - a company uses, it needs to pay taxes. The buyer company can recover the tax. To do this, you need to specify the operation code correctly. It is important not to make a mistake here. If the restoration is carried out according to an adjustment invoice, code 18 is entered. If this operation is carried out in relation to the deduction claimed for deduction from the listed advances, then the numbers will be different. In particular, the code is 21. Often, enterprises confuse these numbers. Companies often indicate one invoice code - 21.