Balance sheet changes 2013:
First of all, it should be noted that when filling out the balance sheet for 2013, you need to rely on the Law “On Accounting” No. 402 of December 6, 2011.
The main change is that since 2013 the balance sheet must be submitted only once a year: the annual balance sheet for 2013 - until the end of March 2014 (no later than 3 months after the end of the reporting year). There is no longer a need to submit interim reports during the year.
Another important change is that from January 1, 2013, all organizations had to maintain accounting records using any taxation system. Accordingly, all organizations must fill out and submit a balance sheet for 2013. This change did not affect individual entrepreneurs; individual entrepreneurs still do not need to do accounting and submit financial statements.
For 2013, you need to fill out 2 copies of the balance sheet: one for the tax office, the other for the State Statistics Committee.
For small enterprises, some simplifications have been made; special abbreviated financial statements for small enterprises have been developed for them, including a balance sheet and a statement of financial results. In these forms, information is indicated in an abbreviated, collapsed form.
When filling out the balance sheet for 2013, you must use the form approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n (as amended on December 4, 2012).
The developed form of the balance sheet is not mandatory for use; an organization can change the standard form depending on its needs, while maintaining the necessary set of mandatory details. The forms of the amended forms must be approved by management and reflected in the accounting policies of the organization.
Balance sheet - Form 1. From 2011 to 2014
A balance sheet is a document characterizing the general state of the assets and liabilities of an enterprise at a certain point (date) in monetary terms. The balance sheet contains summarized data about the financial position of the organization. OKUD form code 0710001.
Balance sheet data informs the owner of the enterprise about the material assets, the amount of inventories, investments and capital that he owns. The balance sheet is a necessary document for management and employees of the analytical department. Using a balance sheet, you can plan for the short and sometimes long term.
This Form 1 of the balance sheet is used starting from the annual financial statements for 2011. A new form has been approved for use since 2015.
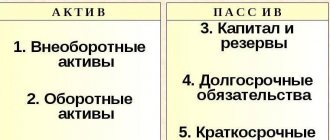
The balance sheet of an enterprise consists of two sections.
1. A balance sheet asset, which contains information about the organization’s resources. This section, in turn, consists of two parts:
- fixed assets;
- current assets.
2. The balance sheet liability reveals the essence of the sources of formation of the organization’s resources. The passive, in turn, contains the following components:
- capital and reserves;
- long term duties;
- Short-term liabilities.
The balance sheet liability and asset totals should always be the same.
The balance sheet has a standard form, which is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n (as amended by Order No. 124n dated October 5, 2011). However, any enterprise can independently develop an easy-to-use form of balance sheet, while retaining all the necessary columns and sections approved in the standard form. This also applies to the codes of summary lines, section lines and groups of articles. They must necessarily coincide with the codes specified in the standard form.
When preparing a balance sheet, you need to pay attention to the following rules:
- offsetting between items of assets and liabilities, as well as losses and profits is not allowed;
- balance sheet data at the beginning of the calendar year must match the data at the end of last year;
- Balance sheet items must be confirmed by data compiled during the property inventory process, as well as data from certain calculations and obligations.
The indicators of items given in the balance sheet are usually given in thousands of rubles (excluding decimal places). If the enterprise has operations whose amount significantly exceeds thousands of rubles, then the data, in this case, can be presented in millions of rubles (excluding decimal places).
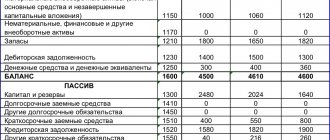
Balance sheet form 1 sample for 2013
The procedure for filling out the balance sheet for 2013 has not changed; you still need to indicate data for 3 consecutive years: the reporting year and the two previous ones. As an example of filling out Form 1, you can use the sample balance sheet presented on our website, which can be found in this article.
Balance form 1 download the current form for 2013: [wpdm_file id=219]
Along with the balance sheet for 2013, you must also provide a statement of financial results, a statement of changes in capital, form 3, and a statement of cash flows, form 4.
Balance sheet 2013 sample filling
The balance sheet (formerly Form 1) is one of the two main documents of the annual reporting, which must reflect the financial position as of December 31 of the reporting year, expressed in the form of money. The balance sheet form consists of two sections: Assets and Liabilities. The assets of the balance sheet reflect all resources, the liabilities of the balance sheet reflect the sources of their financing. The results of these two sections must match.
The balance sheet assets group group current and non-current assets - buildings, equipment, investments for a period of more than one year.
Line by line filling of balance sheet assets:
Fixed assets:
Intangible assets (1110) – residual value of intangible assets (data 1120 is not taken into account).
Results of research and development (1120) – information on R&D.
Exploration assets (1130-1140) - information related to mineral deposits (their search, exploration), as well as about the special equipment used for this.
Fixed assets (1150) – residual value of fixed assets.
Income-generating investments in tangible assets (1160) – the residual value of fixed assets accounted for in account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets”.
Financial investments (1170) – financial investments of an enterprise for a period of more than twelve months (debit 58, debit 55 subaccount “deposits”).
Deferred tax assets (1180) – account balance. 09 “Deferred tax assets”.
Other (1190) – other non-current assets not reflected above.
Total (1100) – the total amount of all non-current assets reflected in lines 1110-1190.
Current assets:
Inventories (1210) – the cost of the enterprise’s inventories is reflected; to fill out this line of the balance sheet, information is taken from the following accounting accounts: 10, 15, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45 , 97.
VAT on purchased assets (1220) – the amount of VAT presented by the supplier, but not accepted for deduction for any reason, that is, the balance of account 19 is indicated here.
Accounts receivable (1230) – receivables from counterparties to the organization, data to be filled in is taken from accounts: 60, 62, 70, 71, 73, 68, 69, 75, 76.
Financial investments (1240) – financial investments for a period of less than twelve months.
Cash and equivalents (1250) – funds of the enterprise in cash in rubles (accounts 50 and 51), foreign currency (account 52), checks and letters of credit (account 55).
Other (1260) – other current assets not reflected in the lines above.
Total (1200) – the total amount of all current assets indicated in the balance sheet form.
Balance – the sum of all total values (1100 + 1200).
For an example of filling out this section, see the completed sample form below.
The liabilities of the balance sheet reflect the sources of formation of assets:
§ fixed capital (contributions of founders) and additional capital, all reserves, the result of revaluation of fixed assets and the amount of retained earnings;
§ long-term loans, credits;
§ short-term loans, obligations to suppliers and employees, which must be repaid within a year.
Line by line filling of balance sheet liabilities:
Capital and reserves:
Authorized capital (1310) – the authorized capital of the enterprise, reflected under loan 80 (credit balance account 80).
Own shares (1320) – own shares purchased from shareholders, the value of which is reflected in debit 81 (debit balance of account 81).
Revaluation of non-current assets (1340) - the amount by which the value of non-current assets (fixed assets and intangible assets) has changed as a result of the revaluation (if carried out) (account 83).
Additional capital without revaluation (1350) - the amount of additional capital minus the amount indicated in the previous line (account 83).
Reserve capital (1360) – the line is filled in if the organization creates reserve capital, the data for filling out the balance line is taken from the account. 82.
Retained earnings (uncovered loss) (1370) – retained earnings in the balance sheet are filled in based on the results of the financial result obtained on the account. 84.
Total (1300) – the sum of lines 1310 – 1370.
Long term duties:
Borrowed funds (1410) – long-term loans, loans for a period of over 12 months. (account 67).
Deferred tax liabilities (1420) - taken from credit 77.
Estimated liabilities (1430) – estimated liabilities in the balance sheet are taken from loan 96 for a period of more than 12 months.
Other (1450) – other liabilities for a period exceeding 12 months.
Total (1400) – the total value for the section, the sum of lines 1410 – 1450.
Short-term liabilities:
Borrowed funds (1510): short-term loans and borrowings (account 66), as well as long-term loans transferred to the category of short-term (account 67).
Accounts payable (1520) – the enterprise’s debt to counterparties and personnel; the data for filling out this line of the balance sheet is taken from accounts: 60, 62, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76, 68, 69.
Deferred income (1530) – credit balance of account. 98.
Estimated liabilities (1540) – credit account. 96 for a period of less than 12 months.
Other (1550) – other liabilities for a period of less than 12 months, not specified above.
Total (1500) – the total value for the section, the sum of lines 1510 – 1550.
Balance – the sum of the total values for each section of liabilities (1300 + 1400 + 1500).
For a completed example of this section, see the sample form below.
Based on the results of the completed balance sheet, the sum of lines 1100 and 1200 should be equal to the sum of lines 1300, 1400 and 1500, that is, the sum of all assets should be equal to the sum of liabilities. If the equality of assets and liabilities of the balance sheet is satisfied, it means that no errors were made in accounting, the completed form can be safely submitted to the relevant authorities.
Data in Form 1 must be entered for the last three years: the reporting year and the two previous ones. Data for December 31, 2011 and 2012 is filled in based on the reports of these years, that is, they simply need to be imported.
If an enterprise uses a simplified taxation system, and until 2013 the organization did not report on this form, then it will be necessary to restore data for the two previous years, that is, fill out the columns for two specific dates - December 31, 2011, December 31, 2012. To restore data, you can use information from existing registries and a complete inventory.