In GOST ISO 15489-1-2007, the concept of a document is defined as information with details recorded on a tangible medium. The presence of details makes it possible to identify information that was created and stored by a legal entity or individual on a medium in order to confirm business activities or legal obligations. In turn, the information carrier is a certain material object used to store linguistic, visual or audio information. The media can be paper, flash drives, disks and other modern technical means. The document is a mandatory element in the internal organization of work of any enterprise, regardless of its legal form and type of activity. As an information carrier, a document can serve as a basis for making management decisions, material for conducting reference work, evidence of execution of decisions, and more.
Let us note that in management activities, a document is both the subject and the result of work, since the decision made is recorded and secured in one document.
The author of the document can be either an individual or a legal entity that created the information. Each document can have legal force, that is, the ability provided by current legislation, the procedure for execution and the competence of the body that issued it. The legal force of a document is ensured by certain details, a list of which is established for each individual type of document, and by a conclusion. The composition of the details, as well as the sequence, zones and layout of their placement on the document are established by the state standard.
Basic functions of documents
All official documents can perform several functions at once, satisfying the specific needs of citizens. At the same time, the functions of documents are divided into:
- General – informational (created with the aim of storing information), social (created with the aim of satisfying social needs), communicative (used as a means of communication between individual structures related to the same object, including a company, enterprise, public institution, etc. d.) and cultural (created for the purpose of preserving and transmitting the cultural traditions of society).
- Specific - managerial (the document is created as a management tool and includes planning, reporting, organizational and other types of documents), legal (when the document is a means of changing and consolidating legal relations within society, and, in addition, acts as an evidence base in the courts) , historical (created for the purpose of preserving in the archive historical information relating to the development of society).
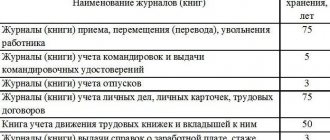
On the periods of temporary storage of documents on personnel
The terms of temporary storage of documents of the Archive Fund of the Russian Federation before their transfer for permanent storage are established in Art.
22 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ. Before changes are made to paragraphs. “b” of paragraph 4 of this article, for documents on personnel, a temporary storage period was provided until they entered the state and municipal archives - 75 years. However, according to the amendments introduced by Federal Law No. 43-FZ, this norm from the text of paragraphs. "b" clause 4 of Art. 22 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ was excluded. Now a separate article is devoted to the periods of temporary storage of documents on personnel - Art. 22.1. Please note that Federal Law No. 43-FZ provides for a reduction in the storage period for personnel documents from 75 to 50 years.
True, this innovation does not apply to personnel documents:
- created before 2003;
- formed in connection with the passage by citizens of public service that is not the state civil service.
So, depending on the creation date, documents are stored:
| Personnel documents created | Until 2003 (clause 1 – 3, part 1, article 22.1 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ) | Since 2003 (clause 1 – 3, part 2, article 22.1 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ) |
| In state bodies, local governments and organizations that act as sources of acquisition of state and municipal archives with archival documents | For 75 years from the date of creation with an examination of the value of documents after the expiration of the specified storage period | For 50 years from the date of creation, with an examination of the value of documents after the expiration of the specified storage period |
| In state and municipal archives, which receive documents on the personnel of liquidated state bodies, | From the date of receipt until the expiration of 75 years from the date of creation with an examination of the value of documents | From the date of receipt until the expiration of 50 years from the date of creation with an examination of the value of documents after |
| local governments, state, municipal and non-governmental organizations | after the expiration of the specified storage period | expiration of the specified storage period |
| In other organizations | At least 75 years from the date of creation | At least 50 years from the date of creation |
Based on Part 3 of Art. 22.1 of Federal Law No. 125-FZ, documents on personnel generated in connection with the passage by citizens of public service that is not the state civil service are stored:
- in government bodies in which citizens served in public service that is not the state civil service - for 75 years after termination of public service with an examination of the value of documents after the expiration of the specified storage period;
- in state archives that receive documents on the personnel of liquidated state bodies, named in clause 1, part 3, - from the date of receipt until the expiration of 75 years from the date of termination of public service with an examination of the value of the documents after the expiration of the designated storage period.
Types and classification of documents
All documentation is classified according to specific functions, purpose and content, as well as the degree of accessibility of information. The Document Management Institute has identified a number of factors that divide documents into separate types and types. Documents created for the purpose of servicing the sphere of management are classified according to the following types of grounds:
- By origin: personal origin - a document not related to official activities (personal correspondence, personal memories, etc.); created in a person’s private life;
- official – documents that are created by an individual or legal entity, in compliance with the established procedure for registration and certification; Official documents include identification documents confirming education, specialty, work experience, etc.;
- official – official management documents that are a direct part of the current activities of the enterprise.
- written documents containing information, recorded in any type of writing;
- internal guidance documents created and used to organize the internal document flow of the organization;
- simple documents, the content of which addresses one issue (letter, application, etc.);
- secret documents, work with which requires special permission; this type of document is classified as classified with a special mark;
- individual documents containing information in the form of related literary text; this type of document may be devoted to one or more issues related to a specific management task;
- original (original) of an official document – the first copy having legal force; an authentic copy has a handwritten signature of an official, a seal imprint, an approval stamp, and in addition, this document must contain information that confirms its authenticity (date and place of creation, author’s data);
- long-term storage documents (stored for over 10 years);
The storage periods for each individual type of document are determined by the requirements of the Federal Archive Service and are enshrined in lists of documents containing information on their storage periods.
- According to the method of transmission, documents are divided into : letters; telegrams and telephone messages; emails; faxes.
- According to the deadlines for execution, documents are divided into : urgent, secondary, final and periodic.
- Based on their functionality, documents are divided into : those requiring a response (requests, proposals, complaints) and those not requiring a response (covering letters, confirmations, reminders, warnings).
- According to the accessibility factor, documents are classified as : open use, limited access and confidential.
Is it necessary to issue orders for payment of monthly premium every month?
author of the answer,
Question
We are introducing monthly bonuses; this will be stated in the Regulations on Bonuses. Is it necessary to issue a monthly order for the payment of bonuses?
Answer
The payment procedure, registration of bonuses and the conditions for their accrual are established in commercial organizations by local regulations - legislation does not require issuing an order for this payment. a local act of your organization determines whether an order needs to be issued.
Rationale
The employer rewards employees who conscientiously perform their job duties. In particular, by paying bonuses. He has the right to establish various bonus systems, incentive payments and allowances ( Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
).
According to this norm, remuneration systems, including tariff rates, salaries (official salaries), additional payments and allowances of a compensatory nature, including for work in conditions deviating from normal conditions, systems of additional payments and incentive allowances and bonus systems, are established by collective agreements , agreements, local regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulations containing labor law standards.
Thus, the payment procedure, size, design of bonuses and the conditions for their accrual should be established by the local regulations of your organization. The legislation does not require issuing an order for this payment. That is, a local act of your organization determines whether an order needs to be issued.
When paying bonuses and developing documents for bonuses to employees, the following must be taken into account.
1) Local regulations, including bonuses, should not worsen the employee’s position in comparison with the current legislation ( Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
).
2) A mandatory condition for inclusion in any employment contract is the condition of remuneration ( Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
),
therefore the employer must indicate the possibility of making incentive payments in the text of the employment contract. In addition, the employer cannot unilaterally cancel bonuses if they are provided for in the employment contract.
3) Labor costs include bonuses for production results, bonuses to tariff rates and salaries for professional excellence, high achievements in work and other similar indicators ( Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
That is, the employer must establish production indicators for which bonuses are provided.
Such indicators can be established in plans and confirmed by reports on work performed. 4) Expenses must be economically justified and documented ( Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
). Therefore, if a company suffers losses, then the payment of large bonuses for production indicators by the tax authority may be considered unlawful.
| She answered the question: I.V. Tarasova, leading expert of IPC "Consultant + Askon" |
What is included in the list of technical documentation for electrical equipment?
Main types of technical documents in the field of electrical engineering:
- Order on the appointment of an employee responsible for electrical equipment.
- Order on the creation of a commission to test knowledge of electrical safety.
- Electrical technician training program.
- Order on the procedure for providing access to electrical installations.
- Journal of activity records for orders.
- General plan with electrical communications.
- Technical passport for equipment.
- Operating and job descriptions.
- Plan for reconstruction and maintenance of electrical installations.
- List of employees who can issue a projectile.
- List of employees who can inspect electrical installations.
- Security product inspection log.
Some of these documents are directly related to security. Therefore, special requirements are imposed on the storage of especially valuable securities.