The mandatory use of cash register equipment for business representatives is regulated by law 54-FZ. Violation of this requirement is fraught with penalties and suspension of the outlet's activities. Therefore, every cashier should know how to use a cash register. This employee is also required to comply with the requirements for filling out fiscal documents and know the basics of communication with buyers or consumers of the organization’s services. Is it possible to quickly learn how to work at a cash register? We’ll find out in this article.
- How to operate a cash register: step-by-step steps
- How to turn on the cash register
- Setting up a cash register
- Cash register protection
- Checkout instructions
- How to set the date on a cash register
- How to unlock a cash register
What does a cash register look like?
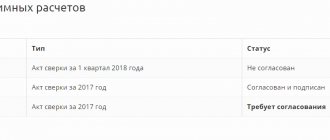
Analysis of concepts
In order to understand the concept of “cash discipline”, you first need to understand the differences between the terms “Cash Register” and “Cash Office”:
Cash register (CCT)
– this is a device necessary for
receiving
funds from your customers, and in some cases, issuing them (for example, returning goods). There can be any number of such devices and each of them must have its own reporting documents.
Enterprise cash desk (operating cash desk)
– this is the totality
of all cash transactions
(reception, storage, issue). The cash register receives revenue received, including from the cash register. All cash expenses related to the activities of the enterprise are made from the cash desk, and money is handed over to collectors for further transfer to the bank. The cash register can be a separate room, a safe in the room, or even a drawer in the desk.
So, all cash transactions must be accompanied by the execution of cash documents, which is usually meant by compliance with cash discipline.
Cash discipline
is a set of rules that must be followed when carrying out operations related to the receipt, issuance and storage of cash (cash transactions).
The basic rules of cash discipline are:
- registration of cash documents (reflecting the movement of cash in the cash register);
- compliance with the cash register limit (the maximum amount of money that can be kept in the cash register at the end of the working day);
- compliance with the rules for issuing cash to accountable persons (employees);
- compliance with the limitation of cash payments between business entities within the framework of one agreement in an amount of no more than 100 thousand rubles.
Damage to the CCP as a result of liquid or fire
What are the risks for the store?
In addition to damage to the cash register itself and other material damage, there is an important point that can lead to a violation of the law - failure to deregister the cash register.
Reference: Responsibility for failure to deregister the old cash register is established in Art. 14.5 part 5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the tax office can choose to issue a warning or impose an administrative fine:
- for officials - a warning or a fine from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - a warning or a fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles.
What to do and how to prevent it?
An accident or emergency often cannot be prevented, even if all safety instructions are followed. Much depends on the condition of the utility networks in the area rented for the store premises - they must be checked when registering a lease. If you are installing them yourself, not through utility services, then try to attract the most competent contractors and not skimp on materials. Be sure to provide 2 exits from the premises and conduct regular training for all employees.
If the situation occurs, it is important:
- React correctly . If moisture gets inside the CCP case, disconnect the equipment from the power supply as quickly as possible. In the event of a fire, first of all, follow the fire safety instructions; the main thing here is to save people, not equipment.
- Confirm the incident. After eliminating the causes of the emergency, it is necessary to obtain documents confirming it from the relevant utility or emergency services.
- Contact the service center that services the cash register. The service center engineer will conduct diagnostics. If repairs are not possible, the service center will draw up a technical examination report indicating the complete loss of the cash register and the impossibility of carrying out its restoration repairs.
- Remove the cash register from the register . Based on this act and the document certifying the natural incident, the cash register must be deregistered with the tax authorities. This can be done through the personal account of the cash register user on the Federal Tax Service website, where in the reasons for deregistration, indicate: “An application for deregistration is submitted due to the loss of cash register equipment.” There is no need to provide data from the report on the closure of the financial fund in the current situation. The documents themselves must be taken to the tax office to which the cash register is attached - and further actions must be clarified with the receiving tax inspector.
Cash documents
Cash desk operations must be carried out by an authorized employee (cashier); in his absence, these functions can be performed by a manager (IP). If there are several cashiers, a senior cashier is appointed.
Cash documents must be prepared by the chief accountant or other appointed official (manager, individual entrepreneur, cashier, etc.), with whom an agreement has been concluded for accounting services.
In 2021, cash transactions are documented with the following documents:
- Receipt cash order (PKO) – filled in every time receipt of money at the cash register
. If cash is issued by check or BSO, then it is allowed to draw up a PKO for the total amount of cash received for a working day (shift).Note. From July 2021, SSR (strict reporting forms) are generated at cash registers. It is prohibited to use printed BSOs instead of checks.
- Expenditure cash order (RKO) - filled in when issuing money from the cash register
. When receiving an order (for example, from an employee who went to buy office supplies), the cashier must make sure that the cash register order is signed by the chief accountant (manager) and check the employee’s identification documents. - Cash book (form KO-4) – data on each incoming and outgoing cash order is entered into the book. At the end of the working day, the cashier must check the cash book data with the data in cash documents and display the amount of cash remaining in the cash register. If there were no cash transactions during the day, the cash book will not be filled out.
- Accounting book (form KO-5) - filled out only if the enterprise employs several cashiers. Entries in the book are made during the working day at the time of transfer of cash between the senior cashier and cashiers and are confirmed by their signatures.
- Payroll and payroll – are prepared when issuing wages, stipends and other payments to employees.
Note: with regard to the obligation to maintain documentation established by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 N 132 (forms KM-1-KM-9, TORG-1-TORG-31, etc.), the Ministry of Finance indicated that with the introduction of online cash registers this optional (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 16, 2021 N 03-01-15/54413).
Cash documents can be maintained in paper form or electronically:
- Documents on paper
are drawn up by hand or using a computer (other equipment) and signed with handwritten signatures. - Documents in electronic form
are drawn up using a computer (other equipment) ensuring their protection from unauthorized access and signed with electronic signatures.
We remind you
, that such reporting documents as: KUDIR, BSO Accounting Book and documents related to the use of the cash register (report and journal of the cashier-operator)
do not apply
.
Let's summarize
If the CCT has stopped working normally, calmly and clearly carry out all the stages of self-diagnosis. It is better to always have the cash register operating instructions and documents for the cash register (technical passport of the cash register, technical passport of the FN unit) nearby.
Conclude a contract for servicing the cash register with a service organization. This will help reduce the downtime of the CCP due to breakdown, and regular maintenance of the CCP by service center technicians will reduce such risks to a minimum. Service center specialists will help you with telephone consultation and will be able to connect to the cash register via remote connection mechanisms.
What should you pay attention to when concluding a contract for servicing a cash register with a service center?
- The SC must be authorized by the CCP manufacturer. The masters of such centers undergo regular advanced training from CCP manufacturers; the necessary spare parts for CCP repair are always available.
- The time the technician arrives to respond to your request and the time it takes for the equipment to be fully operational. The smaller it is, the better for you - the forced downtime of the cash register in the event of a serious breakdown will be minimal.
- Possibility of providing replacement equipment. In case of complex repair of your equipment in the service center. For example, if a barcode scanner or display (cash register monitor) breaks down.
Look at the sales statistics and, based on them, calculate the possible financial risks of the organization if the cash register is down due to a serious breakdown. It may be beneficial for you to increase your cash register fleet : there will be no queues at the point of sale, and if one cash register fails, the sales process will not stop.
How to operate a cash register: step-by-step steps
Every cashier at their workplace should have a step-by-step instruction or guide on how to operate an online cash register, because a cashier must perform the following actions daily:
- at the beginning of the working day, check the serviceability of the cash register;
- turn on the cash register;
- check the presence of a receipt printing tape (if it is missing, install a new one);
- register a cashier (possibility of some cash register models);
- display test reports (current and for the previous shift);
- meet the buyer;
- punch the receipt of the purchased product or service;
- carry out the plan for the break (check the actual amount in the safe and in the machine’s memory, add new product items or other actions as necessary);
- at the end of the shift, recalculate the revenue received and compare it with the value in the memory of the cash register equipment.
Arriving at the workplace, the cashier must make sure that there is no damage to the body of the cash register equipment and information input/output wires, as well as the presence of the necessary seals on the device (if any). You also need to clean the product from dust and dirt. At the end of the preparation, the cashier checks the reliability of the cash register’s connection to a 220 Volt household network (if the equipment is stationary) and the connection to the Internet.
You need to pay attention to the correct installation of the receipt tape. Quite often, the roll is installed upside down, and then they are surprised at the incorrect printing and blame the supposedly faulty printer. The correct position of the roll in the printing device is clearly indicated in the equipment instructions. It is due to the presence of only one layer for printing on thermal tape. Check the ribbon installation when printing the report.
Next, the cashier prints a report for the previous shift. If the amounts are visible in the previously printed report, the employee of the previous shift forgot to reset. If this was not corrected in time and noticed by the inspection authorities, the institution is subject to penalties.
For this reason, how to operate a cash register is a must-have skill even for a junior cashier just starting out in their career. The way out of this situation is to urgently print the report before 24 hours have passed from the date of the first printing of the previous shift's check. If necessary, you need to correct the date and time of the transaction, count the money in the appropriate compartment and reconcile it with the report of the previous shift.
When recalculating the amount, you need to keep in mind non-cash payments to customers. It is reflected on the check as a separate line. Such money is stored in the company’s personal account, and not in a cash safe. It is also recommended to be prepared for the fact that the accountant or owner of the enterprise may ask the cashier to provide an official issue during the working day. This is completely normal. The proceeds must be transferred to collectors, to the specified account or personally to the owner of the institution.
At the end of the work shift, a final report is performed. To do this, you need to have a sufficient balance of the cash register tape. About the successful completion of zeroing, the printed paper will contain the phrases “Registers cleared,” “Report is valid,” and so on. The report is assigned an individual number and stamped with a date and time. These parameters are also subject to mandatory verification by the cashier.
The control tape (if any) should be carefully rolled up and stored at the place of calculation for 3 days and 3 years within the enterprise. If you want the amount of non-cash payments to be transferred to the specified bank account, the shift must be closed at the bank payment terminal. The cashier must wait for a report on the correct sending of transaction information to the tax service in the case of an online cash register or take such documents directly to the federal tax service building. The end of the shift is marked by turning off the cash register.
Checkout instructions
Information is entered into the cash register using the built-in or external keyboard. Some devices include a scanner. It is needed to read barcodes to instantly provide information about the product. Due to this element, the time allocated for the transaction is saved. The rules for operating cash registers are clearly regulated. The basic principles are contained in the current state legislation.
Such documents are:
- Law 54-FZ “On the use of cash registers when using cash payments (or) payments using a payment card”;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the registration and application of cash registers used by LLCs or individual entrepreneurs.”
A significant number of cash registers are equipped with a function to match the purchased product to a certain category (alcohol, groceries, clothing, and so on). To do this, after entering the amount, the cashier presses a special button. This is convenient for cash collection, when reporting is required for each category of products sold. At the same time, category keys are subject to mandatory configuration, regardless of whether they are taxable or not. You also need to clearly know the rules for linking taxes to categories.
After this, you need to carefully study the information on the receipt. You need to start doing this by clicking the Submit button. It is indicated by an up arrow. This will cause the command to output the receipt to the top of the device. Thanks to this, you can see the full amount indicated on the check. It includes every added product. The amount value can be shown on the cash register screen. Often the cashier takes into account a discount on an item that is on sale.
In this case, perform the following steps:
- enter the cost of the goods;
- click on the button indicating the product section;
- enter the discount amount as a percentage;
- Press the % button on the device keyboard.
If the cashier processes several pieces of the same product, first you need to enter the exact number of products on the keyboard. Next, click on the Quantity (QTY) button and enter the price of one product item. At the final stage, the cashier clicks on a specific product category. For example, a consumer buys 2 packets of sugar, costing 6.99 rubles. In this case, the cashier presses 2 on the keyboard, then the Qty button, then dials 699 and the product section button.
How to issue a check to a buyer
To understand how to use an online cash register, an employee needs to understand the algorithm for issuing a receipt to a buyer:
- The cashier scans the item, thereby opening a receipt
- The buyer hands over the payment to the cashier
- After receiving the funds, the cashier completes the sales process by generating a cash receipt
If necessary, an electronic version of the cash receipt is sent to the buyer’s e-mail or phone number.
In order to simplify the process of entering personal data, the developers have created a Federal Tax Service application with which the buyer can transfer his personal data to the cashier via a QR code.
When paying for a purchase, you may need to deposit funds in different ways. For example, if the buyer does not have enough money on the card, he can pay the remaining amount in cash. In this case, the cashier generates one check. In which both payment methods are recorded, indicating the amount of each of them.
Operations for which a receipt must be generated include:
- Sale. The check is issued after the cashier receives the funds or after the funds are written off from the client’s payment card.
- Return. A refund receipt is issued if a refund was issued to the buyer based on the return of the goods to the store. The return receipt must be accompanied by a return application, which indicates the buyer’s passport details, date and reason for returning the goods.
- Making adjustments. An adjustment is necessary if the sale was made at an incorrect price or without using an online cash register (for example, when there was a power outage). In this case, a correction check is issued.
- Making an advance payment. A check is issued when the buyer makes an advance payment.
- Making an advance payment. The difference from an advance payment is that an advance payment is made for a specific specific product, while an advance payment is a payment for an unspecified product (for example, the purchase of a gift certificate).
- Issue of goods on credit/installments. The algorithm for generating and issuing a check in this case will be the same as for a regular sale, the differences lie in the absence of the fact of transfer of funds to the cashier and the indication of the payment method indicated in the check.
Calculation sign
A payment attribute is a cash receipt detail indicating the reason for the receipt/disbursement of funds to/from the organization's cash desk.
The calculation attribute can be specified in four options:
- “Receipt” - will contain a sales receipt. For example, when a buyer purchases household appliances in a store.
- “Return of receipt” will be indicated on the return receipt. For example, if household appliances turned out to be of inadequate quality, and the buyer decided to return the goods.
- “Expense” - will be indicated in the receipt upon receipt of the goods on a paid basis. For example, a point for accepting scrap metal - issuing money when accepting metal;
- “Refund of expenses” - will be present on the receipt if the operation involves returning the goods to the client. For example, a customer returns money to pick up an item.
From January 1, 2019 , the requirements to update the FDF to version 1.05 come into force. In the new version, such details will appear as “Attribute of the subject of payment, indicating a specific subject of payment, for example, “lottery winning”, “excise goods”, “service”, prepayment, advance payment, etc.
Payment method indicator
The payment method attribute indicates how the payment was made.
The sign of the payment method can be indicated both in the form of a code word and in the form of a digital designation:
- Code ADVANCE PAYMENT 100% (or 1 in the digital version) - indicates that the seller has received an advance payment for the goods in the amount of 100%;
- Code ADVANCE PAYMENT (or 2) - the buyer made a partial advance payment for the goods;
- ADVANCE code (or 3) - receiving an advance for an item that has not been defined. For example, if a buyer purchases a gift certificate, the seller cannot find out in advance which product will be purchased, in this case the payment method is indicated as “advance”;
- Code FULL PAYMENT (or 4) - indicated when the buyer pays in full and immediately receives all of his goods;
- Code PARTIAL SETTLEMENT AND CREDIT (or 5) - this can include the situation when the buyer purchases goods on credit, while paying a down payment, i.e. the goods will be partially paid for, and the remaining amount will be issued as a loan;
- TRANSFER ON CREDIT (or 6) - here the payment method will be to purchase the goods on credit in full without a down payment, and the goods in this case are transferred to the buyer immediately;
- LOAN PAYMENT (or 7) - is indicated when the buyer makes a payment to repay the loan, and it does not matter whether the next payment is made or the payment is made in full.
No Internet access
Access may be unavailable due to an emergency situation with the provider, for non-payment of communication services, or for other reasons.
What are the risks for the store?
Failure to comply with the law . During a network outage, the cash register's fiscal drive stops transmitting OFD data . On the daily report (closing a shift), you can check information on the number of unsent documents. This data is also displayed in the “settlement status report,” which can be generated on the cash register at any time. You can also check in your personal account on the website of the Fiscal Data Operator with whom the agreement has been signed.
The fiscal drive can work without Internet access for up to 30 calendar days (it accumulates sales data in its internal memory), then it is blocked. When access to the Internet is restored, it will transfer all data to the OFD and will automatically be unlocked for further sales. Important! 30 days before the FN blocking has nothing to do with fines - violation of the law occurs already from the first check not transferred to the OFD.
Reference: According to Article 1.2 of 54-FZ, it is necessary to transfer all data on transactions (cash receipts, reports) in real time, at the time of payment of buyers to the Federal Tax Service through Fiscal Data Operators (FDO). Data transmission is carried out via the Internet. An exception is made for cash registers that operate in areas without access to the network - remote and hard-to-reach settlements, closed military installations - then the cash register is allowed to be used offline.
If fiscal documents were not transferred to the tax authority, administrative liability is provided for such a violation under Part 4 of Art. 14.5 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- for officials - a warning or a fine from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - a warning or a fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles.
The tax authority may consider how valid the reason for the violation was , but if the data was not transmitted for a long enough time, and measures were not taken to eliminate the failure (evidence of the measures taken is required), then most likely such a reason will be considered unjustified.
What to do and how to prevent it?
Restore access as quickly as possible. For the period while you clarify and eliminate the reason for the disconnection (bill not paid, breakdown at the provider, etc.), you can organize a mobile access point in advance, and purchase a cash register with support for working via Wi-Fi.
What if the network is available, but the cash register still does not transmit data to the OFD?
Check:
- physical connection of the network cable to the cash register,
- the correctness of the network settings for transmitting OFD data through the configuration utility for cash registers. Network settings are available on the official OFD websites. Contact the organization that provides technical support for the cash register, they will be able to check the settings remotely.
If the data is still not transmitted, the issue may be on the side of the fiscal data operator.
Make sure, together with OFD technical support, that:
- a new fiscal drive has been activated,
- paid for OFD services,
- there are no technical problems on the OFD side,
- a new registration card was received with the Federal Tax Service after replacing the fiscal storage unit.
Applying a correction check
A correction check is created by the cashier if payments were made without using an online cash register:
- Inability to use online cash register due to breakdown
- Inability to use the cash register due to a power outage
- The occurrence of surpluses or shortages in the cash register due to the inattention of the cashier
In any of these situations, the cashier will have to generate a correction check. The differences from a regular check with a correction check are quite significant:
- Firstly, it is impossible to indicate the list of goods that were purchased on the correction receipt. This is due to the fact that in almost every situation in which the formation of this fiscal document is necessary, there is no possibility of establishing which specific goods were purchased. As an example, we can take the formation of such a check when a shortage is detected at the end of a work shift.
- Secondly, it is worth paying attention to such details as a sign of calculation. When generating a fiscal document for correction, this detail can be of only two types:
- “arrival” when surplus is detected
- "expense" when a shortage is detected
The correction check must always be accompanied by an explanatory note detailing the reason for the correction. The explanatory note will be useful in the event of a tax audit, because Federal Tax Service employees pay special attention to correction checks.
Most often, correction checks are confused with refund checks. A refund receipt is generated when the cashier needs to correct an operation that has already been completed. For example, when a cashier mistakenly punches out an extra item. In this case, it is necessary to cancel the operation by generating a new fiscal document with a settlement attribute, which will indicate “return of income”. The check must also contain the amount of the erroneously issued check. Additionally, a new receipt is generated indicating the correct purchase amount.
Theft of cash register
What are the risks for the store?
As in the case of an emergency, in addition to material damage, theft threatens to violate the law - if the cash register is not deregistered. Responsibility under the same article.
Help: The tax office can choose to issue a warning or impose an administrative fine:
- for officials - a warning or a fine from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - a warning or a fine from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles.
What to do and how to prevent it?
- Call the police and open a criminal case. If the cash register has been stolen, you must immediately call the police, fill out a statement, and obtain an act of initiating a criminal case.
- Remove the cash register from registration. On the basis of the act of initiating a criminal case, deregister with the tax authorities. This is also done through the personal account of the cash register user on the Federal Tax Service website, only in the reasons for deregistration it is necessary to indicate: “An application for deregistration is submitted in connection with the theft of cash register equipment.” Copies of documents on the initiation of a criminal case should be taken to the tax office to which the cash register is attached. Check with the receiving tax inspector for further steps.
What to do if, as a result of the investigation, the cash register is found?
If a cash register is deregistered with the sign of “Theft”, and then found, for further use you need to provide the following to the tax authorities:
- act of returning stolen property from law enforcement agencies,
- application for exclusion of cash register equipment from the “Theft” status.
If during the investigation the service life of the fiscal drive unit expires, it is also necessary to provide the tax authorities with data on closing the fiscal drive archive.
If you have problems, how to use the cash register
It is possible that when operating modern generation equipment, certain malfunctions may occur.
In case of minor troubles and force majeure circumstances, the following recommendations will help the user.
- Internet connection lost. In this case, sales may not be suspended. However, the main thing is not to forget to transfer the receipts that he did not receive to the fiscal data operator after the connection is restored. In addition, failure to exchange information with the operator for 30 days will lead to the failure of the fiscal drive.
- The paper is jammed or torn: the machine must be stopped and the ribbon must be rethreaded. The equipment is then activated according to the manual. Most models automatically resume printing. To check whether the information has been sent to the merchandise accounting program and the fiscal data operator, you need to generate an X-report and check the data with accounting, analyze the number of pending checks.
- The power supply has been cut off: trade must be suspended. You can't sell anything without a cash register. In addition, the law stipulates that within 5 minutes after payment for the purchase, a receipt must be given to the buyer. If models with a backup power supply are not used, then the above requirement cannot be met. However, you can use the following option: after the operations have been completed, draw up a correction check for the final cost of the delivered products. The employee’s written explanation is attached to the document; energy sales act indicating a power outage. Meanwhile, even these measures may not save you from tax penalties.
The device is suddenly blocked if the fiscal drive breaks down, its memory is full, or the date and current time are incorrectly set on the equipment. This problem can easily be resolved on your own: to do this, you just need to replace the drive, re-register the device with the tax service, and correct the date and time.
Power failure
Often happens due to planned or emergency work, less often due to emergencies and natural disasters.
What are the risks for the store?
- Software failure - for example, violation of the integrity of product or sales databases due to interrupted data transfer.
- Breakdown of the cash register at the hardware or software level due to surges in the power supply voltage.
- Failure to comply with the law. If, in the absence of electricity, they do not close the outlet and do not stop sales, but record them only in the cash book or do not record them at all, this is a violation.
Reference. According to Article 14.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, working without a cash register is strictly prohibited . A representative of the tax authority may bring to administrative liability an official and a legal entity that has not issued a check to the buyer: for officials - a fine in the amount of 25% to 50% of the amount of the calculation made without using a cash register, but not less than 10,000 rubles; for legal entities - from 75% to 100% of the settlement amount made without the use of cash register, but not less than 30,000 rubles. Repeated commission of an administrative offense, if the amount of settlements without the use of cash registers totaled 1 million rubles or more, entails, in addition to fines, disqualification for a period of 1 to 2 years; and in relation to individual entrepreneurs and legal entities - administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days. An exception is the use of a correction check or a statement of violation. Administrative liability for a violation can be avoided if, immediately after its commission, complete and reliable information is sent to the tax office in the form of a correction check or a statement of violation, and no one has yet informed the Federal Tax Service about the violation committed and the amount for which it was committed. If the incident coincided with a tax audit, and the check was not issued to the tax inspector, he may immediately recognize this incident as an offense, so it is better to avoid such situations.
What to do and how to prevent it?
To avoid the situations listed above, we provide backup power. For this there is:
- Backup power sources (diesel generators, storage power sources based on batteries). Such systems can supply a retail outlet with electricity for up to several days.
- Compact household uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) that support the operation of connected equipment for 20 minutes or longer.
- Cash registers with a built-in rechargeable battery - similar to laptops, can operate without an external power source for several hours.
Some UPS models are equipped with sensors for monitoring the charge level and residual battery voltage, as well as software - you can find out the remaining operating time of the cash register unit.
Such a safety net will help you correctly complete the check processing (calculate the buyer), close a shift at the checkout (if necessary), and even continue the sales business process while the UPS is operating.
What to do if a backup source or CCP with battery was not purchased?
It is urgent to de-energize all cash register equipment - disconnect the power plugs from the network. After the power supply is restored, be sure to check the functionality of the cash register: conduct a test sale of an inexpensive product (for example, a package), then make a return. To comply with the law, stop the sales process during a power outage.
Who monitors compliance with cash discipline?
All employees associated with their implementation must control the correctness of actions for carrying out cash transactions. If the organization has a chief accountant, then he is responsible for monitoring the work of the accounting department and the operating cash desk that is part of it. The general responsibility for the activities of the company lies with its director, and the individual entrepreneur himself is responsible for the activities of the individual entrepreneur.
Checking cash discipline in 2020–2021, which may result in an administrative fine or subsequent on-site inspection for the person being inspected, is carried out by tax authorities (Clause 1, Article 7 of Law of the Russian Federation of March 21, 1991 No. 943-I).
The objectives of this audit are to identify the facts:
- incompleteness and untimeliness of receipt of revenue;
- exceeding the cash payment limit;
- exceeding the cash balance limit;
- use of prohibited, faulty or non-compliant cash register equipment;
- failure to issue cash receipts or BSO;
- discrepancies between actual cash balances in the cash register and the amounts indicated in the documents;
- issuing large sums on account for unreasonably long periods.
What is a calculation sign
A settlement attribute is a detail that can reflect the following information:
- If the attribute “receipt” , then it reflects the fact of receiving money for a product or service from the buyer. This operation is most often carried out when the buyer interacts with the cashier. She confirms the fact of payment.
- When the “receipt return” , funds are returned to the client for the returned goods. Returns are most often made if the product does not fit in size or is of poor quality.
- “expense” attribute should be selected by the cashier when the store buys something from individuals, for example, farm products.
- The sign “return of expenses” means that the visitor returned the previously received cash to the store. Such details can be seen on a fiscal receipt when a store returns a product purchased from an individual.
It should be noted that the attribute “settlement attribute” is mandatory for reflection in the fiscal receipt, both in paper and electronic form. Ensuring this requirement is not always within the competence of the cashier, since a programmer or other specialist with the appropriate specification is most often responsible for the algorithms for entering details.
How is cash discipline checked?
Checking cash discipline in 2020–2021 is carried out by decision of the head of the Federal Tax Service in the manner established by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 17, 2011 No. 133n. During the verification process, the following are studied:
- All documents that are related to the execution of cash transactions.
- Fiscal memory reports.
- Documents for the purchase, registration and maintenance of cash registers.
- Documents related to the acquisition, accounting and destruction of BSO.
- Accounting registers of accounting or business transactions.
- Order for cash balance limit.
- Expense reports.
At the same time, inspectors are given unlimited access to the cash register, including its passwords and cash.
During the inspection, any other documents related to the subject of the inspection, as well as explanations, may be requested.
Find out how a bank checks cash discipline in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. If you do not already have access to this legal system, a full access trial is available for free.
Content:
- How to obtain permission to operate a cash register?
- Started working with a cash register
- The procedure for the cashier when accepting funds from the buyer
- What is a calculation sign
- What is a sign of a payment method?
- When can a correction check be used?
- How can a cashier close a shift?
- Is it necessary to keep records in the cashier-operator's journal?
- Is the use of a cash book and orders relevant?
- RKO and PKO for changeable funds
- How to work as a cashier if problems arise with the online cash register
If several tax systems are combined
The law provides for the possibility for business entities to apply several tax regimes simultaneously. In order to save money, it is allowed to generate fiscal documents on one cash register, if the following conditions are met:
- During the first launch, the owner of the cash register entered data on all applicable taxation systems (hereinafter referred to as SNO). In this case, you should read the instructions for using the cash register.
- When selling goods or services, the user creates separate receipts for each tax regime.
We must not forget that if an economic entity combines two or more SNOs, separate records should be kept for each mode.
Buying a cash register - what is important to know before purchasing
The cash register itself is not expensive - from 3,000 rubles.
But this amount is only 10 to 20% of the total cost of the turnkey cash register. When purchasing a cash register, you additionally need to purchase: required
(without this the cash register will not work):
- fiscal drive - from 6800 rub.
- agreement with OFD - from 1500 rubles.
not necessary:
- Digital signature - from 1600 rubles. Digital signature for registering a cash register. You can do without it, but then you will have to go to the tax office yourself;
- services - from 1000 rub. You can register a cash register yourself if you understand the nuances. But we strongly do not recommend that you do this, since if registration is incorrect, you will need to change the fiscal drive - this is a one-time device, and the registration service itself is not expensive on average - 1000 rubles, and some organizations even register cash registers purchased from them - free of charge .
Beware of violations
Numerous regular inspections organized by tax authorities in different regions of the country show that to this day many entrepreneurs work in violation of the rules for using cash registers, but still hope that this will go unnoticed. It should be remembered that the laws on the introduction of cash registers were adopted for a reason; thanks to them, the legal purity of the transaction is ensured. In addition, strict adherence to the rules in the event of a conflict situation will allow you to “pull the blanket over yourself,” since there will be no complaints about your activities.
To avoid violations during the work process, carefully read the rules for operating cash register equipment, because there are answers to almost all questions. Take into account the latest legal acts in force in your region. This will allow you to keep your finger on the pulse of events. Finally, remember that you should only use machines that have been included in the state register. Take into account the classifier, which regulates which units are suitable for which area. This will allow you to avoid problems with the law and conduct business for a long time and with benefit for yourself.
Sources:
- https://kontur.ru/articles/5183
- https://www.malyi-biznes.ru/kassovaya-disciplina/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/buhgalterskij_uchet/vedenie_buhgalterskogo_ucheta/kassovaya_disciplina_i_otvetstvennost_za_ee_narushenie/
- https://OnlineKas.ru/rabota-na-kasse/kak-polzovatsya-kassovym-apparatom/
- https://5cms.ru/article/work-online-kassa
- https://www.DigitalServ.ru/kak-polzovatsya-kassovym-apparatom/
- https://assistentus.ru/forma/dolzhnostnaya-instrukciya-kassira/
- https://BusinessMan.ru/rabota-s-kkm—chto-eto-uchet-i-pravila-rabotyi-na-kassovom-apparate.html
RKO and PKO for changeable funds
Incoming and outgoing cash orders should also be issued when the cashier receives and hands over cash for the exchange of funds. This procedure is regulated by Law No. 54-FZ. Every cashier whose professional responsibilities are directly related to the online cash register must know how this operation is performed.
In most organizations, cash (bills and coins) are given to employees responsible for cash registers before the start of each shift. For this purpose, cash receipts are filled out, indicating the amount issued. In the line where the basis for making calculations is indicated, the wording “For exchange” should appear. Data on the amounts exchanged must be entered by the cashier into the book of accounting of funds received.
Re-registration
Re-registration of a cash register is necessary in the following cases:
- replacement of fiscal memory,
- changing the company name or full name of the individual entrepreneur,
- changing the address of the device installation location,
- CTO changes.
To re-register a cash register, you need to contact the tax office with an application drawn up in accordance with the form specified by law, the cash register registration card, its passport, and the conclusion of the central service center (if available).
The tax inspector personally inspects the device for serviceability, integrity of the case and the presence of seals, after which he makes a note about re-registration in the passport and registration card. The presence of a representative of the central tax service center and the taxpayer itself is also required.