I propose to consider in this article a detailed example of accepting fixed assets for accounting in 1C 8.3 in the form of step-by-step instructions. The accounting procedure for such assets is determined by PBU 6/01 “Accounting for Fixed Assets”.
When purchasing a fixed asset, accounting entries 08.04 – 60.01 (details - How to register the receipt of OS in 1C 8.3). It follows from this that the equipment is simply listed “in warehouse” under account 08.04 “Purchase of fixed assets” and is not operated, and depreciation is not charged on it.
In order for the purchased equipment (machine, car, computer, etc.) to begin to be listed as a fixed asset in the organization and to begin to be depreciated, it is necessary to correctly take it into account.
How to capitalize fixed assets in 1C 8.3: step-by-step instructions
The capitalization of fixed assets is most often associated with their acquisition. But there are other cases: contribution to the authorized capital, gratuitous receipt, receipt under an exchange agreement.
In this article we will tell you in detail how to capitalize fixed assets in 1C 8.3, and our step-by-step instructions will help you understand this.
Arrival of the OS in 1C 8.3: design options
In 1C there are two options for registering the acquisition and accounting of fixed assets:
Standard , which uses two documents:
- capitalization of fixed assets - document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment ;
- commissioning of OS - document Acceptance for accounting of OS .
Simplified , which uses a single document:
- capitalization and commissioning of fixed assets - document Receipt (act, invoice) type of transaction Fixed assets .
When the commissioning of the OS is carried out simultaneously with the capitalization of the OS, then, of course, it is more convenient to reflect all operations in one document: use the Simplified version . But it has some limitations.
The simplified option cannot be used if additional costs must be included in the initial cost of the OS when purchasing it.
Learn more Options for receiving fixed assets
Purchasing an OS in 1s 8.3 - step-by-step instructions
Let's look at the purchase of a fixed asset using the example of a standard design option.
The organization entered into an agreement with Krung LLC for the supply of industrial equipment in the amount of 159,890 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
On February 12, the box tenoning machine DOS-ShR-120 arrived at the warehouse and was accepted for accounting.
Download step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
Purchasing an OS
Generate the document Receipt (act, invoice) operation type Equipment .
You can apply for it via:
- Purchases – Purchases – Receipts (acts, invoices) – Receipts – Equipment;
- OS and intangible assets – Receipt of fixed assets – Receipt of equipment.
On the Hardware , specify:
- Nomenclature is an acquired non-current asset from the Nomenclature directory .
In the document Receipt (act, invoice) type of operation Equipment , it is impossible to indicate account 08.04.2 “Purchase of fixed assets”, since it is intended to be accepted for accounting of fixed assets only in a simplified version.
Registration of SF supplier
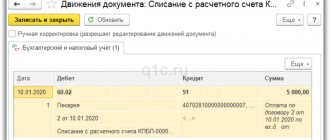
Register the incoming supplier invoice by indicating its number and date at the bottom of the Receipt document form (act, invoice) and click the Register .
Regardless of whether the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt , when this is done, no entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction.
Deduction of VAT on purchased operating systems in 1C is possible only through the document Formation of purchase ledger entries .
Acceptance of VAT for deduction on fixed assets
Acceptance of VAT for deduction on purchased fixed assets is formalized with the document Formation of purchase ledger entries in the section Operations - Closing the period - Regular VAT operations.
Free delivery of OS in 1C 8.3 - step-by-step instructions
Let us analyze the gratuitous receipt of fixed assets using the example of a simplified design option.
On September 10, Kamelia LLC donated KOUUCI KCM-8012 Press equipment to the organization with a market value of RUB 188,800. (including VAT 18%).
Download step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
Drawing up a contract for free transfer
To prevent the program from complaining about the absence of an invoice, when registering an agreement, uncheck the Supplier under the agreement submits VAT in the VAT .
If the supplier issues an invoice, then the Supplier submits VAT under the contract does not need to be cleared, but the presented VAT cannot be deducted either.
Arrival of OS
Generate the document Receipt (act, invoice) transaction type Fixed assets .
You can apply for it via:
- Purchases – Purchases – Receipts (acts, invoices) – Receipts – Fixed assets;
- OS and intangible assets – Receipt of fixed assets – Receipt of fixed assets.
Calculations link, please indicate:
- Account for settlements with the counterparty - 98.02 “Gratuitous receipts”;
- Account for accounting of settlements for advances - 98.02 “Gratuitous receipts”.
In the table section, indicate:
- Fixed asset - donated equipment from the Fixed Assets directory .
- The amount is the market value of the fixed asset, but not lower than the residual value of the fixed asset from the supplier.
Regardless of the Accounting Account in the tabular part of the document, the costs of acquiring fixed assets will be automatically taken into account in account 08.04.2 “Purchase of fixed assets”, and then written off to the Accounting Account established in the document.
Recognition of income in the form of property received free of charge in NU
Income in the form of property received free of charge for income tax purposes is recognized as part of non-operating income at a time on the date of signing the act of its transfer (clause 8 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To recognize income under NU in 1C Accounting 8.3, fill out the document Transaction entered manually, transaction type Transaction in the Transactions - Accounting - Transactions entered manually section.
In the document please indicate:
- Debit - 98.02 “Free receipt”;
- Credit - 91.01 “Other income”;
- Subconto 1 - Free receipt of property, work, services, property rights , Type of article Free receipt of property, work, services, property rights ;
- Subconto 2 - fixed asset received free of charge;
- Amount - do not fill in, in accounting, income is recognized in the amount of accrued depreciation;
- Amount NU Dt , Amount NU Kt - the cost of the gratuitously transferred fixed asset.
Depreciation calculation
Monthly depreciation is calculated when you run the Month Closing procedure, the Depreciation and Depreciation of Fixed Assets operation in the Operations – Period Closing – Month Closing section.
In our example, the equipment Press KOUUCI KCM-8012 was accepted for accounting as a fixed asset and put into operation on September 10, therefore, depreciation in accounting and accounting records is accrued from October.
Recognition of income in the form of property received free of charge in accounting
Income in the form of property received free of charge is recognized monthly in the accounting system in the amount of accrued depreciation as part of other income (clause 8 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To recognize income under Accounting in 1C Accounting 8.3, fill out the document Transaction entered manually, transaction type Transaction in the Transactions - Accounting - Transactions entered manually section.
In the document please indicate:
- Debit - 98.02 “Free receipt”;
- Credit - 91.01 “Other income”;
- Subconto 1 - Free receipt of property, work, services, property rights , Type of article Free receipt of property, work, services, property rights ;
- Subconto 2 - fixed asset received free of charge;
- Amount —the amount of accrued depreciation;
- Amount NU Kt - do not fill out.
Test yourself! Take the test:
See also:
If you are a subscriber to the BukhExpert8: Rubricator 1C Accounting system, then read additional material on the topic:
If you haven't subscribed yet:
Activate demo access for free →
or
Subscribe to Rubricator →
After subscribing, you will have access to all materials on 1C Accounting, recordings of supporting broadcasts, and you will be able to ask any questions about 1C.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
What costs are not included in the initial cost of a fixed asset?
The initial cost of fixed assets does not include (clause 17 of the Standard “Fixed Assets”):
- costs of opening new production facilities;
- costs of introducing new products or services;
- costs of operating in a new location or with a new group of service consumers (including costs of personnel training);
- operating losses incurred until the level of income from fees for the use of investment property (rent) reaches the level of income planned when recognizing the investment property as part of a group of fixed assets;
- administrative, general and other general overhead costs;
- costs of performing operations accompanying the construction or creation of a fixed asset object, but which are not necessary to deliver the object to its destination and bring it into a condition suitable for use.
Costs that are not included in the initial cost of a fixed asset are written off to the financial result (cost of finished products, work, services).
Example. A budgetary institution, under a supply agreement, purchased an air conditioner in the amount of 20,000 rubles. A separate contract was concluded for the installation of the air conditioner. Installation cost – 8,000 rubles. The cost of installing the air conditioner is included in its initial cost. Expenses were made at the expense of the institution's own funds. When installing the air conditioner, electricity from a budgetary institution was used. Electricity costs are general business expenses and are not included in the initial cost of the fixed asset. The accounting records the following entries:
Debit 2,106 31,310 Credit 2,302 31,734 – investments in the purchase of an air conditioner in the amount of 20,000 rubles are reflected;
Debit 2,106 31,310 Credit 2,302 28,734 – expenses for installing an air conditioner are reflected in the amount of 8,000 rubles;
Debit 2,101 34,310 Credit 2,106 31,310 – the air conditioner was accepted for accounting in the amount of formed investments in the amount of 28,000 rubles;
Debit 2,109 81,223 Credit 2,302 23,734 – energy costs are reflected.
Free receipt of OS in 1s 8 2 step-by-step instructions budget
Download Go to the “Purchase” section (1) and select the “Receipt of goods and services” link (2). A window will open to create an invoice for receipt.
To create an invoice, click the “Add” button (3) and select the “Equipment” link (4). An invoice form will open for you to fill out. Guest, you have free access to a chat with an expert accountant. Order a call back to connect or call: (free within the Russian Federation).
In the form that opens, enter the following information:
- supplier of fixed assets (7);
- details of the contract with the supplier (8);
- date of receipt of the fixed asset (5);
- to which warehouse the property was received (9).
- your organization (6);
In the “Equipment” tab (10), click button 11, then button 12. The nomenclature directory will open - a list of your organization’s property. In the item reference book, click the “Add” button (13).
advant24.ru
A business transaction is reflected using a manual transaction since objects received from founders - individuals - are not accepted for tax accounting.
Entries in tax accounting accounts are made in such a way that the condition is met: NU + PR + VR = BU To reflect in tax accounting the capitalization of a fixed asset (Electric furnace), received on January 16.
2006, the founder must go to the “Tax Accounting” tab and fill in the columns in accordance with the figure.
Tax transactions in the 1C:Accounting 8.0 program are stored in a separate journal “Journal of transactions (tax accounting for income tax)”.
Free receipt of OS in 1s 8 3 step-by-step instructions budget
In the “Invoice No.” field, indicate the number of the invoice under which the property was received.
The lower section consists of five tabs (5):
- Services;
- Additionally.
- Returnable packaging;
- Equipment;
- Goods;
In the “Equipment” tab, click the “Add” button (6) and enter data on the received fixed asset. In the “Nomenclature” field, indicate the name of the OS; in the “Quantity” and “Price” fields, indicate the quantity and price of the received equipment.
“Accounting account” 1C 8.3 will be determined automatically, depending on the type of equipment received (fixed assets, equipment to be installed).
When all the data has been entered, you can save the document; to do this, click the “Post and close” button (7).
Now the purchase of fixed assets is reflected in accounting as the debit of account 08 (if you bought fixed assets) or 07 (if you bought equipment that requires installation). The second stage is the acceptance of the OS for accounting in 1C 8.3 - commissioning.
Purchase and acceptance for accounting of fixed assets in the 1C program: Accounting of a government institution 8th edition 1.0
We fill in the fields “Name” and “Full name”, be sure to select “Capital investments” in the “Type of NFA” field.
After selecting an item from the directory, fill in everything line by line. We save and post this document.
In order to accept this fixed asset for accounting, you need to enter the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets and intangible assets.” It is convenient to create it immediately from the document “Purchase of fixed assets, intangible assets.”
When you click on the “Accept for accounting” button, processing of document generation opens.
Click “Generate”. A document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets and intangible assets” is created, in which part of the data on the “General” tab is automatically filled in from the purchase document.
Budgetary accounting of fixed assets in 2021 (nuances)
Read about the regulatory documents governing accounting in budgetary structures. In this article we will refer to orders No. 157n and 162n as the basis for budget accounting.
In addition, the facility must be used to carry out the activities of the institution permanently or repeatedly. Another feature is that the operating systems are not owned by the institution, but are quickly managed.
NOTE! Fixed assets do not include objects classified as inventories in accordance with clause 99 of Order No. 157n.
For example, fishing gear, gas-powered saws, etc. The service life can be determined
Accounting for fixed assets in the budget
18th category - code of the type of activity: if there is no possibility of assignment to a specific type of activity - 0; budgetary activities - 1; entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities - 2; activities at the expense of targeted funds and gratuitous receipts - 3.
19-20 digit - code of the synthetic account of the Chart of Accounts of Budget Accounting.
Table 1. Structure of the account number of the chart of accounts of budget accounting 1-17 digits 18 digits 19-20 digits 22-23 digits 24-26 digits Code of functional classification of budget expenditures Code of type of activity Code of synthetic account Code of analytical account Code of classification of operations of the public administration sector Administrator
· Received from - sending organization.
· Code according to OKOF, Depreciation group, Useful life, etc.
— necessary information for accounting for the OS object. Rice. 3 1.4.
On the Committee Members tab, the list of institution commission members can be filled out in two ways: · by selecting from the Employees directory; · via the hyperlink Fill out the composition of the commission, which refers to the directory of Permanent commissions. 1.5. On the Act Details tab, the details of the Certificate of Acceptance and Transfer of Objects of Non-Financial Assets received from the sending institution (form.
0504101). 1.6. After
"1C: Accounting 8" (ed.
3.0): Accounting for fixed assets received as a gift from an individual (+ video)
10 PBU 6/01, approved.
by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n, p.
How to take into account in the value of an asset works (services) received free of charge
In accordance with clause 43 of the “Revenue” Standard, approved. By order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 27, 2018 No. 32n, when receiving work and services provided by individuals or legal entities free of charge, accounting entries are not reflected in the accounting accounts. Information about these works and services is disclosed in the Explanatory Note.
However, if we are talking about the formation of the initial cost of an object in respect of which gratuitously provided work (services) form its initial cost, reflection in the accounting accounts is necessary.
The fact is that when maintaining budgetary (accounting) records, an institution must ensure the formation of reliable information about the availability of state (municipal) property, its use, the obligations it has assumed, the financial results obtained and other information (clause 18 of the Conceptual Framework Standard, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 31, 2016 No. 256n).
Since specific works and services form investments in a fixed asset, transactions to assign the fair value of these works and services to increase the initial cost of a fixed asset must be reflected in accounting, even if they are provided free of charge.
Investments in fixed assets with gratuitous receipt of capital investment amounts, incl. for the purpose of forming the cost of objects, they are reflected in the debit of the corresponding analytical accounting accounts, account X 106 ХХ ХХХ and the credit of the corresponding analytical accounting accounts, account X 401 10 190.
At the same time, investments in fixed assets are of a capital nature, since they increase the cost of fixed assets (clause 7 of the order, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 29, 2017 No. 209n). Accordingly, in categories 24 -26 of account number 401 10, subarticles 195-198 of KOSGU are indicated, depending on the type of counterparty.
Example. A budgetary institution, under a supply agreement, purchased an air conditioner in the amount of 20,000 rubles. Installation of the air conditioner is carried out by an individual (not an employee of the institution) free of charge. The market cost of installation is 8,000 rubles. The cost of installing the air conditioner is included in its initial cost. The accounting records the following entries:
Debit 2,106 31,310 Credit 2,302 31,734 – investments in the purchase of an air conditioner in the amount of 20,000 rubles are reflected;
Debit 2,106 31,310 Credit 2,401 10,197 – reflected free installation of an air conditioner in the amount of 8,000 rubles;
Debit 2,101 34,310 Credit 2,106 31,310 – the air conditioner was accepted for accounting in the amount of investments generated - 28,000 rubles.
Accounting for objects received for free use
The federal accounting standard for public sector organizations “Rent”, applied since 2021, has changed the procedure for reflecting lease accounting items by both the lender and the borrower.
In the article, 1C experts consider in what cases the receipt of property for free use is reflected by the borrower, taking into account the application of the provisions of the “Rent” standard, and how such transactions are registered in the program “1C: Accounting of a public institution 8” edition 1 and edition 2. Cases of non-application are also considered "Rent" standard.
Legal regulation
According to Article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, under an agreement for gratuitous use (loan agreement), one party (the lender) undertakes to transfer or transfers an item for gratuitous temporary use to the other party (the borrower), and the latter undertakes to return the same item in the condition in which it received it, subject to normal wear and tear or in the condition stipulated by the contract. The rules provided for in Article 607 “Rental Objects” of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation apply to the agreement for gratuitous use.
According to paragraph 2 of the Federal Accounting Standard for Public Sector Organizations “Rent”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 31.
2016 No. 258n, this standard has been applied since 2021 when reflecting in accounting assets, liabilities, facts of economic life, and other accounting objects that arise upon receipt (provision) for temporary possession and use or temporary use of material assets not only under a lease agreement (property lease), as well as under a contract of gratuitous use.
The Lease standard has changed the procedure for recording lease accounting items by both the lender and the borrower.
Previously, objects of movable and immovable property received from the balance holder (owner) of the property for free use were accounted by the borrower on off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use” at the cost indicated (determined) by the transferring party (owner), and under the inventory (account) number, assigned to the object by the balance sheet holder (owner) (clauses 333, 334 of the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n.
According to paragraph 20 of the Lease standard, the accounting object of an operating lease (the right to use an asset) is reflected by the user (lessee) as part of non-financial assets (NFA) as an independent accounting object.
The initial recognition of an operating lease accounting object (the right to use an asset) is made on the date of classification of lease accounting objects in the amount of lease payments for the entire period of use of the property provided for in a lease agreement (property lease) or a gratuitous use agreement with simultaneous reflection of the lease obligations of the user (lessee) (creditor's rent arrears).
In accordance with paragraph 26 of the “Lease” standard, lease accounting items arising under gratuitous use agreements are reflected by the borrower in accounting at their fair value, determined as of the date of classification of lease accounting items using the market price method, as if the right to use the property had been granted for commercial (market) conditions.
Objects of accounting for operating leases on preferential terms (the right to use an asset) by the borrower are reflected taking into account the following provisions of paragraph 27.1 of the “Lease” standard.
| Extract from the document “The object of accounting for an operating lease on preferential terms - the right to use an asset, is recognized in accounting at the fair value of lease payments. The difference between the amount of lease payments and the amount of the fair value of lease payments is recognized as deferred income (deferred income) from the provision of the right to use the asset and is subject to segregation in the accounts of the Working Chart of Accounts of the accounting entity. During the period of use of the property, deferred income from the provision of the right to use the asset, as well as depreciation of the right to use the asset, are recognized evenly (monthly) as part of the financial result of the current period with segregation in the corresponding analytical accounting accounts of the Working Chart accounts of the subject of accounting." |
Purchasing and receiving an OS in 1C 8.3: step-by-step instructions
Editor of the article: Consultant The relevance of the article was checked: 05/14/2020 article Fixed assets are the assets of an enterprise that are used as means of labor in the process of the organization’s main activities.
The receipt of fixed assets in 1C 8.3, taking into account the current regulatory documents for accounting, is registered using the following accounting accounts:
- 08.04 – Acquisition of objects
- 01 – Fixed assets;
- 01.01 – OS in the organization;
- 07 – Equipment for installation;
- 08.03 – Construction of fixed assets;
- 01.01 – OS in the organization;
Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting in 1C 8.2 and 8.3 step-by-step instructions
» » Let's look at the complete step-by-step instructions for accepting fixed assets for accounting in 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0: from purchasing equipment to.
Now we need to take it into account.
To do this, go to the section “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets”: We find ourselves in the form of the list of documents “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets”. We add a new document: Please note that at the moment the fixed asset accounting account is 04/08 (as we arrived). After posting from this account, the fixed asset will be debited to the account on 01.01.
Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets in 1C: Accounting department of a state institution 8 edition 2.0
10/18/2017 23:28 8313 In one of the previous articles, we looked at the process of purchasing fixed assets on the accounts of group 106.00 “Capital Investments”. When all costs are collected in the account we need, we can accept the fixed asset for accounting. This moment comes when the fixed asset is delivered, collected and ready for registration.
It is this process that will be discussed in the article; a practical example will be considered in the 1C program: Accounting of a government institution 8 edition 2.0.
In the last article we figured out: the fixed asset remains as a capital investment until
Free receipt of OS in 1C: Accounting department of a state institution 8th edition 2.0
06/23/2017 23:08 Administrator 22182 Fixed assets can be supplied to an institution not only through acquisition for a fee, but also free of charge.
receipt of fixed assets from the founder;3.
receipt of fixed assets from other budgets (from institutions subordinate to other GRBS). Let's consider all situations sequentially. Reflection of gratuitous receipt of fixed assets in accounting is carried out using the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts.” You can find it: A list of documents opens: Click the “Create” button
As in 1C: BGU 1.0 to reflect the receipt of fixed assets from the treasury
+7 If fixed assets received by a budgetary (autonomous) institution from the treasury belong to real estate or especially valuable movable property, it is necessary to adjust settlements with the founder on account 210 06 to their book value.
1.1. To reflect the receipt of an object from the treasury, use the document Gratuitous receipt of fixed assets and intangible assets in the section OS, intangible assets, intangible assets – Receipt (Fig.
1). Rice. 1 1.2. To correctly reflect transactions and generate primary accounting documents, it is necessary to take into account the following points (Fig.
2): · Operation - Free receipt of fixed assets (other) (101 - 401.10.180) sets the parameters for selecting accounting accounts on the General tab. · Primary document (Document type, Number, from) - data of the base document.
· On the General tab: Type of NFA movement - correct filling of the details is necessary to generate the appropriate analytical indicators for the movement of NFA.
What expenses are formed from the initial cost of a fixed asset?
The procedure for forming the initial cost of fixed assets is regulated by Section IV of the Standard “Fixed Assets”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 31, 2016 No. 257n (hereinafter referred to as the “Fixed Assets” Standard).
The initial cost of a fixed asset acquired or created on its own is formed from (clause 15 of the Standard “Fixed Assets”):
- purchase prices;
- any actual costs for the acquisition, creation of a fixed asset, including its delivery to its destination and bringing it into a condition suitable for use, including:
— expenses for wages and insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance, directly related to the creation of a fixed asset;
— the cost of work (services) to create a fixed asset under a construction contract and other contracts;
— state duties and other expenses for mandatory payments to the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, made in connection with the acquisition (creation, production) of fixed assets;
— amounts of remuneration for the provision of intermediary services in the acquisition of fixed assets;
— costs for site preparation;
— costs of delivery and unloading;
— installation and installation costs;
- costs of checking the proper functioning of a fixed asset, minus income from the sale of products produced before the fixed asset is brought into a condition suitable for use (for example, samples obtained during testing of equipment);
- amounts of costs associated with the creation, production and (or) production of fixed assets - materials, services of third-party organizations (co-executors, contractors (subcontractors);
— costs of information and consulting services associated with the acquisition (creation, production) of fixed assets;
— other costs directly related to the acquisition, construction and (or) production of fixed assets;
- amounts of costs for dismantling and decommissioning a fixed asset, as well as restoration of the site on which the object is located, known at the time of acceptance of the fixed asset for accounting, recognized in accordance with the provisions of clause 15 of the Standard “Reserves. Disclosure of information about contingent liabilities and contingent assets”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 30, 2018 No. 124. Such costs are recognized if the obligation to dismantle and (or) decommission a fixed asset, as well as to restore the site on which this object is located, is provided for in a purchase and sale agreement, use agreement, or other agreement (agreement) establishing the conditions for using the object.
As you can see, the list of costs that can form the initial cost of a fixed asset is open. The decision on what expenses will be included in the initial cost of a fixed asset is made by the institution’s commission for the receipt and disposal of assets (clause 34 of the Instructions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n).