The property rights of the enterprise are extremely extensive. The company's capital can include both tangible and intangible objects, financial assets, and cash equivalents. To implement a company's activities, values that do not belong to it are often used. Such objects can be transferred under a leasing agreement. They must be reflected in accounting.
Is property recorded in off-balance sheet accounts subject ?
What are off-balance sheet accounts?
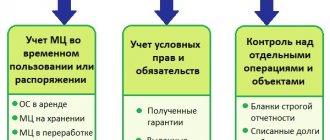
Off-balance sheet accounts (AB) are intended to store information about the objects used by the company. Their key feature is that the company does not have ownership rights to these objects. They are temporarily part of the company. Provided on the basis of various agreements. These objects may include:
- rented premises, warehouses;
- valuables transferred for safekeeping;
- raw materials accepted for processing;
- equipment adopted for the purpose of installation work.
How can a tenant account for leased objects (premises, equipment, other property) on off-balance sheet account 001?
The principle of property separation and off-balance sheet accounts
The organization of off-balance sheet accounts is based on the principle of property separation. It states that the accounting of an organization's assets should not coincide with the accounting of the assets of its owners, as well as the assets of other organizations under the care of this organization. The same principle applies not only to assets, but also to liabilities.
Objects temporarily included in the assets, provided under certain agreements, do not belong to the enterprise. However, during a certain period of time, it is the enterprise that is responsible for them, which means it must take them into account in a certain way. But such values cannot be mixed together with those owned by right of ownership within the same accounting accounts.
When and how to take into account inventories on off-balance sheet accounts ?
Off-balance sheet accounts are auxiliary accounts within the framework of accounting. They become relevant if you need to obtain information not contained in balance sheet accounts. This feature explains their name. Balances from off-balance sheet accounts will not be included in the balance sheet. They are displayed behind the total of this indicator. That is, they are recorded on the balance sheet.
IMPORTANT! Information from the accounts in question does not affect financial performance. For this reason, they will not appear in the company's financial statements.
What are off-balance sheet accounts for?
Off-balance sheet accounts perform the following functions:
- Accounting for the availability of property and tracking transactions with it. Accounting may also concern objects that belong to the enterprise, but their value is written off as expenses.
- Collection of data necessary for the formation of explanations for the main balance sheet and financial statements.
- Control over the operation of property to which the enterprise does not have ownership rights.
- Control over the safety of the objects in question.
- Supporting role to monitor the execution of property papers without delays. In particular, documents are drawn up on the receipt of objects and their disposal.
- Full organization of accounting in this area.
Properly executed off-balance sheet accounts allow you to obtain all the data on objects that are located on the territory of the enterprise, but do not belong to it. Information is necessary to analyze the company's creditworthiness and determine its financial stability.
Types of off-balance sheet accounts and their accounting
The required type of off-balance sheet account is determined depending on what kind of object is subject to accounting. There are the following types of ES:
- 001 “Fixed assets leased.” Their cost must be confirmed by an agreement concluded with the lessor.
- 002 “Valuables taken under safekeeping.” Typically, an agreement is concluded in relation to these objects, after the fulfillment of the terms of which the values become the property of the enterprise. Until this moment, the company's objects will not belong to the company. The condition is certain deductions. The postings must indicate their size.
- 003 “Raw materials taken for processing.” Materials for processing can be indicated on off-balance sheet accounts only if they were transferred by the customer and the manufacturer does not pay their cost.
- 004 “Materials for commission.” The products that were taken by the commission agent for sale are indicated.
- 005 “Equipment intended for the performance of installation services.” The equipment used to perform installation services is indicated.
Off-balance sheet accounts reflect assets owned by the enterprise that have been written off as expenses:
- 006 “Reporting forms”. May include various receipts and subscriptions.
- 007 “Bad debts written off at a loss.” Displayed on accounts for five years. It is assumed that during this time the financial position of the debtor may change.
Off-balance sheet accounts are relevant for collecting information necessary as additional information to the explanations of the statements:
- 008 “Collateral received.” Needed to store data on transferred guarantees to ensure compliance with conditions;
- 009 “Issued collateral.” Relevant for collecting information on issued guarantees to ensure payments.
- 011 “Funds received for rent.” This account is placed in the reporting of both the lessor and the tenant.
All account data is indicated in a special accounting plan. An enterprise can open other accounts that are not in the plan if this is required to support its activities.
An organization has the right to open a sub-account to an existing off-balance sheet account or introduce a new account if it is not provided for in the plan. The main thing is that this change is properly spelled out in the accounting policies.
IMPORTANT! Organizing off-balance sheet accounts is extremely important. If, as part of a tax audit, objects are discovered that do not appear in the reporting, they will be written off as non-operating income. That is, they will be subject to income tax.
Features of accounting on the AP
Off-balance sheet accounts are presented in the form of a table with two columns. One of them displays debit, the other – credit. Accounting for APs is carried out using a simplified system. No double entry required. That is, you don’t have to write the same amount in debit and credit. The following transactions must be indicated in the debit column:
- getting objects;
- acquisition or issuance of security.
The loan column displays:
- disposal of the object;
- termination of security.
The debit will show the income, and the credit will show the expense.
Working Chart of Accounts 2021 - Table for download
My working PS is below at the GoogeDocs link
Savicheva Olga
Practicing economist and corporate accountant
Ask a Question
If you need to copy or download an accounting chart of accounts, there is a special button below. Just click on it and you will be redirected to the official GoogleDocs resource. This is exactly the option we use in the accounting department for analytics and reconciliation. PS We have no intention of harming you in any way or stealing anything. The link is posted on the official resource of the Google search engine, as you can see for yourself.
Our Accounting Plan in GoogleDocs
Transactions with off-balance sheet accounts
On off-balance sheet accounts, just like on regular ones, procedures for registering and writing off values are carried out. You can also make sales from off-balance sheet accounts. There are some nuances to take into account.
How to put an asset into an off-balance sheet account
The legislation does not regulate the accounting of individual off-balance sheet values, leaving the accounting department to independently choose a strategy, specifying it in the accounting policy. An organization can open an additional account for, for example, low-value property, assigning it a number next to the planned ones and reflecting this in the policy. It is convenient to account for low-value assets in off-balance sheet accounts because:
- such assets will not get lost among the “voluminous” balance sheet assets;
- property is assigned to a specific employee responsible for it.
Sales from an off-balance sheet account
If management decides to sell an asset held in an off-balance sheet account that they previously used and continue to do so, they must write off the asset as a credit to the corresponding off-balance sheet account. The funds received from the sale must be reflected as income from sales and VAT must be added. At the same time, in tax accounting, this operation will entail the reflection of income included in the income tax base.
ATTENTION! Since the initial cost of the asset was already taken into account at the time of commissioning, it is not reflected in accounting or tax accounting, otherwise distortions in financial results are possible.
Write off an asset from an off-balance sheet account
Objects can not only be accounted for in off-balance sheet accounts, but, if necessary, can be written off from them. This happens if the asset has become completely unusable, or it is about to be sold, for these reasons it is no longer used in the activities of the enterprise. Information about the transaction is entered into a special journal of material assets, which is maintained specifically for objects of off-balance sheet accounts. The following information is required:
- name of the asset;
- date of its commissioning;
- price;
- inventory number;
- person responsible for it (full name, position);
- write-off date (added after this operation).
After the date of write-off is entered in the journal, the enterprise can no longer use the specified asset, which is confirmed by a special act.
Fundamentally important concepts
Modern accounting accounts come in three classes:
- active;
- passive;
- active-passive.
Active and passive accounting accounts allow for so-called double entry. This is a fundamental principle of global accounting: one transaction (for example, salary payment) in the same amount is reflected twice in different accounting accounts.
Initial
or
ending balance
is nothing more than the cash balance in a specific account. It is exactly the same on the last day of the ending month and the first day of the beginning. If this is so, there is no error in accounting. In other words, the ending balance (the balance of the calendar month on the account) and the opening balance (the balance of the next month on the first day) for one account will definitely converge.
Accounting entries are recorded in a characteristic tabular manner, which in professional language is called an “airplane”. The left side of the plate is debit (D or Dt), the right side is credit (K or Kt).
Postings to off-balance sheet accounts using an example
Two enterprises entered into an agreement with each other for the supply of goods. One of the parties provides security for payment in the form of equipment pledged. The cost of the equipment is 200,000 rubles. Payment under the contract was not made, and therefore another enterprise receives the equipment at its disposal and then sells it. These transactions will be reflected using the following entries:
- DT 008 “Payment Security” 200,000 rubles;
- KT 008 “Write-off of collateral” 200,000 rubles;
- DT 002 “Accounting for valuables received under a pledge agreement.” Document – pledge agreement;
- KT 002 “Sale of valuables.” Document – act of acceptance and transfer;
- DT 51 CT 91 “Income from sales.” The document is a bank statement.
From this diagram you can extract information about the movement of values and the transaction amount. All operations are confirmed by primary documentation.
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary organizations
If the organization is classified as a budget organization, off-balance sheet values are recorded in it according to a simplified scheme - there is no need to keep corresponding records. When property is capitalized, the necessary entry is made in the debit of a certain off-balance sheet account. At the time of write-off, this entry is made against the loan. It is allowed to introduce additional off-balance sheet accounts for greater reliability of management accounting, naturally, indicating them when developing accounting policies.
So. Off-balance sheet accounts allow you to display information about property that is located on the territory of the enterprise, but does not belong to its property. Other data is also stored on the AP. Having off-balance sheet accounts during tax audits will allow you to avoid making unnecessary tax deductions. It is also a source of important information about the company's activities. The information allows you to track operations carried out by the enterprise.
Description of the document
Chiefs, managers and accountants of the organization need to receive timely and up-to-date information about the status of accounts, because this data directly influences management decisions. Let's say a company needs to pay suppliers a certain amount. With proper accounting, an employee only needs to look at the documents to understand whether the necessary money is available. Information is also added there about who should pay the company, how much money is on deposit, etc. This is very convenient and greatly simplifies the work, especially when it comes to large companies.
Accounts
Account
To understand what a chart of accounts is, you first need to understand the concept of “bookkeeping accounts.” This is a way of reflecting property by composition and sources of its formation. Business transactions are also subject to sorting according to monetary, natural and labor criteria. It is quite difficult for an unprepared person to understand what is hidden behind this definition. But in reality, everything is much simpler: in essence, an accounting account is a table containing the following information:
- Debit turnover is the sum of all transactions reflected in debit.
- Credit - all transactions reflected in the loan.
Note! Debit (increase) is on the left, and credit (decrease) is on the right. We can say that a debit is what a company owes, and a credit is what it owes to others.
For convenience, each operation is assigned a two-digit number from 01 to 99. This is very convenient because it eliminates the need to write the full name of the asset each time. Here's what a simplified accounting account would look like:
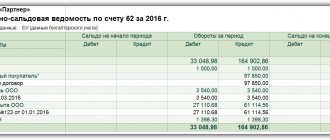
| Debit | Credit |
| Balance at the beginning: 50,000 rub. | |
| 7,000 rub. — received from Konstruktor LLC | 8,000 rub. — paid by Stroymaterialy LLC |
| 3,000 rub. - received from Yagel LLC | |
| Balance at the end: 52,000 rub. | |
Every day the company pays wages, purchases equipment or materials, pays taxes and other operations. For convenience, they are grouped according to homogeneous characteristics. Each group is assigned a specific number. For example, payment for materials to suppliers belongs to account No. 50 called “Cash of the organization.” All cash on hand in the company should be accounted for in this category.
Chart of accounts
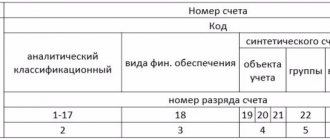
The chart of accounts is a system for recording and grouping facts of economic activity. It is used in companies of any form of ownership (except for financial organizations) that use the double entry method (correspondence of accounts) for postings. The plan indicates 99 accounting accounts and another 11 off-balance sheet accounts. Which account to use depends on the transaction category. Thus, at any time you can look into the document to clarify the current account number.
Example chart of accounts
Important information! An organization can establish a working chart of accounts that uses only the most common transactions. Small firms can get by with 15-20 positions.