Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states:
- When selling goods (work, services), the place of sale of which is the territory of the Russian Federation, by taxpayers - foreign persons who are not registered with the tax authorities as taxpayers, the tax base is determined as the amount of income from the sale of these goods (work, services), taking into account tax The tax base is determined separately for each transaction involving the sale of goods (work, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation, taking into account this chapter.
- The tax base specified in paragraph 1 of this article is determined by tax agents. In this case, tax agents are recognized as organizations and individual entrepreneurs registered with the tax authorities, purchasing goods (work, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation from foreign entities specified in paragraph 1 of this article. Tax agents are obliged to calculate, withhold from the taxpayer and pay the appropriate amount of tax to the budget, regardless of whether they fulfill the taxpayer’s obligations related to the calculation and payment of tax, and other obligations established by this chapter.
Let's consider the situation using the example of a foreign organization from which we will purchase services.
In the “Counterparties” directory, enter the “Non-resident (services)” counterparty and set the “Supplier” flag.
Menu: Full interface - Directories - Contractors
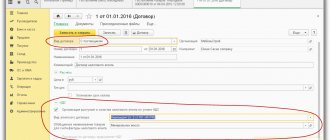
After recording the counterparty on the “Accounts and Agreements” tab, open the default agreement with the supplier and go to the “Advanced” tab.
Let's set the flag "The organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT", Type of agency agreement - select "Non-resident":
Let's look at our example in the first quarter of 2013.
Who is recognized as a tax agent for VAT?
According to the Tax Code (161 Tax Code of the Russian Federation), there is a certain list of situations in which even persons who are not obliged to pay VAT and report on it must pay tax for their partners. These include the following situations:
- in case of receiving supplies from foreign persons who have not received tax resident status in the Russian Federation;
- in case of receiving federal and municipal facilities for rent;
- when selling ownerless property, confiscated property, property that must be sold by court;
- in case of sale of a vessel that is not registered in the Russian International Register;
- in the case of the sale of raw scrap metal, hides and waste paper (except for entities on a special regime).
Important! A tax agent is understood as any business entity paying remuneration to a non-resident who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service. The exception is taxpayers who use special regimes such as UTII, simplified tax system, PSN and unified agricultural tax.
The main responsibility of the tax agent is the timely withholding of the tax liability from the remuneration due to a non-resident or a VAT defaulter. It is necessary to withhold the tax in full, and then submit written information to the Federal Tax Service in accordance with 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Payment of VAT (agency)
We will not pay VAT in full.
On January 31, 2013, we will create a document “Outgoing payment order” with the type of operation “Tax transfer”.
Menu: Full Interface - Documents - Cash Management
In this case, be sure to set the “Paid” flag. We indicate account 68.32 and be sure to indicate the outgoing payment order, according to which the payment to the foreign supplier was reflected, as the third analytics:
The postings of the document “Outgoing payment order” will be as follows:
Tax agent obligations for VAT from January 1, 2021
The main change of the new year was the increase in the VAT rate to 20%. In addition, the settlement rate has also increased, which is now 20/120. Innovations also include the fact that from 2021, foreign organizations that provide services in electronic form in the Russian Federation are required to independently organize VAT payment and submit appropriate reports (rate 16.67%) in accordance with Law 303-FZ. This can be done in one of the following ways:
- when sales are carried out by an agent under a contract, the VAT report and payment are made by the representative;
- when a foreign company is directly involved in sales, it is necessary to register with the Federal Tax Service, obtain a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) in the Russian Federation, and then pay VAT independently.
In the second case, refusal to register as a Russian taxpayer does not oblige the buyer to become his tax agent and pay fines. That is, an organization or entrepreneur will not receive a VAT deduction, even if one of them decides to pay VAT on their own.
In this case, electronic services mean the following types of services provided in the customs territory of the Russian Federation:
- providing access to programs and computer facilities via the Internet;
- hosting and data storage abroad;
- advertising and promotion of goods on the Internet;
- design, support, and website administration remotely;
- access to repositories of electronic books and publications;
- search, delivery of information.
Important! It should be remembered that electronic services do not include services for ordering goods online, consultations by e-mail, software implementation, or organizing access to the Internet.
VAT tax agent: postings
Let's look at the tax agent's VAT transactions using a specific example. Let’s assume that a non-resident supplier provided services worth RUB 200,000 to a Russian entrepreneur in 2010. At the same time, the agreement concluded between them does not say anything about the inclusion of VAT in the cost of products. According to current legislation, an entrepreneur must withhold and pay to the budget an amount of 40 thousand rubles.
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| The tax agent charged VAT (on the advance amount paid) | 76 (NA) | 68.32 |
| The tax agent transferred the obligation to the budget | 68.32 | 51 |
| A previously paid service was provided | 26 | 60 |
| The buyer has allocated input VAT | 19.04 | 76 (NA) |
| VAT offset for deduction | 68.02 | 19.04 |
The main problems that have arisen as a result of the transition period and the increase in the VAT rate in 2021 relate to transactions carried out between VAT payer organizations. Tax agents are required to pay the liability in full on the day the remuneration for goods and services is paid. That is, there are two options for calculating and paying VAT:
- An advance transferred before the beginning of 2021 is subject to VAT at a rate of 18%, VAT on goods in 2021 is charged at a rate of 20%.
- If products delivered before 2021 are paid for only in the new year, then the tax rate will be 20%.
This scheme does not apply to the following entities:
- carrying out transactions with confiscated property sold in court or ownerless valuables;
- works through a representative (agent) in the Russian Federation with a foreign entity;
- carries out railway transportation within the Russian Federation in the interests of a non-resident;
- buys and then sells animal skins, nonferrous and ferrous metal scrap, and waste paper.
These entities will pay VAT (20%) on sales from the beginning of 2021. Compensation of the 2% rate is carried out at the expense of the buyer.
Receipt of service
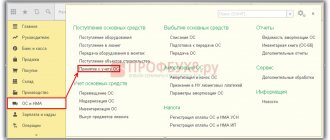
On January 23, 2013, we will introduce the document “Receipt of goods and services” with the transaction type “Purchase, commission”.
Menu: Full Interface – Documents – Procurement Management
The document is entered with the VAT calculation option “18% on top” (the “Prices and Currency” button, the “Amount incl. VAT” flag is unchecked).
Note! Primary documents will be without VAT, we reflect VAT in the program!
At the bottom it displays “No invoice required”:
To reflect incoming services, for example, on account 44, the cost item must have the nature of costs “Distribution costs”:
To offset the advance payment according to 60.02, you must fill out the “Advance payment” tab using the “Fill in” button:
The postings of the document “Receipt of goods and services” will be as follows:
Note ! The appearance of invoice 19.04 in correspondence with account 76.NA will not entail an automatic deduction of VAT in the purchase ledger, as in the usual situation.
By clicking the “Go” button we can look at “Document movements by registers”:
We will see the tax amount reflected in the “VAT presented” register with the value type “Tax Agent (Foreigners)”. This register is necessary for further reflection of the deduction in the purchase book (after payment of agency VAT).
Payment of VAT by a tax agent
If the subject of the Russian Federation acts as a tax agent, then the “first event” rule does not apply here. That is, VAT is paid upon payment of funds to the supplier. Therefore, the application of rates is carried out as follows:
| Event | VAT rate until 2021 | VAT rate from 2021 |
| According to the contract, VAT is not included in the price of the goods | 18% | 20% |
| VAT is included in the price of the goods | 18/118% | 20/120% |
| VAT is paid by the foreign supplier (his agent) for electronic services | 15,25% | 16.67% |
VAT is calculated and paid by the tax agent in the following ways:
- by withholding VAT from the supplier’s remuneration (in this case, the payment amount is reduced by agency VAT);
- reimbursement of the obligation by the buyer (in this case, the contractor will receive the amount according to the contract, and VAT will be paid at the expense of the buyer).
Reflection of the “Invoice” of the tax agent in the sales book
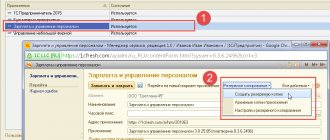
To reflect the tax agent’s “Invoice” in the sales book, it is necessary to create and fill out the regulatory document “Creating Sales Book Entries.”
Menu: Full interface – Documents – Maintaining a sales book
In the document, indicate the date 03/31/2013, click the “Fill” button - “Fill out the document”:
The “Accrued for payment” tab will be filled in; after posting the document, no postings will be generated, only movement will occur in the “VAT accrued” register:
VAT return from 2021
In addition to the fact that the tax agent is obliged to transfer VAT to the budget, he must also submit a tax return containing the necessary breakdown of charges. This applies not only to VAT payers, but also to those who are exempt from paying this tax, that is, economic entities under special regimes.
The declaration form is given in the Order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] The tax agent will be required to fill out:
- title page;
- 1 section (general information about the obligation);
- Section 2 (contact details of the counterparty, his details, and for each of them it is necessary to fill out a separate sheet);
- Section 3 (to be completed if the tax agent plans to receive a deduction);
- Section 12 (to be completed if reporting is submitted by a VAT evader).
Important! The report must be submitted within the same deadline as provided for all VAT payers, that is, before the 25th day of the month following the end date of the next quarter.
Registration of deduction
VAT paid in accordance with the duties of a tax agent can be deducted. Moreover, filling out section 3 of the VAT return is possible only in the next period after the transfer of remuneration to the supplier. However, in this regard, the position of the tax authorities diverges from judicial practice and the position of the Ministry of Finance. The possibility of receiving a deduction depends both on the date of payment and on the fact of receipt of the goods:
- the deduction can be declared in the payment period if the goods were received in the same reporting quarter;
- You can request a deduction only in the case of the next filing of a declaration (if the fact of making an advance payment and the delivery date do not coincide and fall in different quarters).
Transfer of advance payment to the lessor
When leasing municipal property from local governments, the tenant acts as a tax agent for VAT (clause 3 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A tax agent for VAT in 1C 8.3 in the Contracts , in the VAT should: PDF
- check the box The organization acts as a tax agent for the payment of VAT ;
- select the appropriate Type of agency agreement - Rent (paragraph 1, clause 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- indicate the Generalized name of goods for the tax agent invoice .
Find out in more detail about the legislative part and settings in 1C when performing the duties of a tax agent during a lease.
The transfer of rent to the landlord is reflected in the document Write-off from the current account, transaction type Payment to supplier in the Bank and cash desk section – Bank – Bank statements – Write-off button.
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Write-off from a current account using this example:
- VAT rate - set to Without VAT .
- Amount – the amount of the rental payment minus VAT.
Renting municipal property in 1C 8.3 - transfer of advance payment under a rental agreement.
Postings
Responsibility for failure to fulfill obligations
If a tax agent untimely or intentionally fails to withhold VAT from remuneration to a supplier who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service and does not have resident status, then he is subject to the following penalties:
- 20% of the amount of unwithheld and unpaid tax (123 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- penalties for each day of delay (75 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 200 rubles for failure to submit a VAT return on time upon fulfillment of the duties of a tax agent (126 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 5% of the amount of the unpaid obligation for each month of delay in case of failure to submit or late submission of the declaration, but not less than 1000 rubles and not more than 30% (119 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From the point of view of tax legislation, it is considered incorrect if the unrecovered VAT is paid at the expense of the buyer. In this case, a fine of 20% will be charged, as well as penalties for the entire time of non-payment of the obligation. In this case, the agent must withhold VAT from the remuneration amount for the subsequent delivery and transfer the non-payment to the budget. If the transaction was a one-time transaction, then the law does not explain further actions in such a situation. That is, repaying the debt with the buyer’s funds will still be preferable. Bring the tax agent to criminal liability under Art. 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation should not, since this measure provides for fairly large amounts of fines, forced labor, as well as imprisonment for repeated intentional violations on a large and especially large scale.