The institution was given a land plot with the right of permanent (indefinite) use. How to account for this area: behind the balance sheet or on the balance sheet? How to formalize the acceptance of land for registration in the program “1C: Accounting of a government institution 8”. You will find answers to these questions in the article by 1C experts.
Clause 333 of the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n, as amended on October 12, 2012, establishes that land plots used by institutions on the right of permanent (perpetual) use (including those located under real estate objects) are recorded on off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use” on the basis of a document (certificate) confirming the right to use the land plot, at their cadastral value (the value indicated in the document for the right to use the land plot located outside the territory of the Russian Federation) Federation).
Article 5 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” establishes that the objects of accounting of an economic entity are:
- facts of economic life;
- assets;
- obligations;
- sources of financing its activities;
- income;
- expenses;
- other objects if this is established by federal standards.
If an institution has the right to use a land plot, then the land plot is an asset and must be accounted for on the institution’s balance sheet.
By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 29, 2014 No. 89n, corresponding changes were made to paragraph 71 of the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n, hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 157n, now land plots used by institutions on a permanent basis (perpetual) use (including those located under real estate) must be taken into account in the corresponding analytical accounting account of account 103 00 “Non-produced assets” on the basis of a document (certificate) confirming the right to use the land plot, at their cadastral value (the value specified in document for the right to use a land plot located outside the territory of the Russian Federation).
Clause 2 of Order No. 89n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 29, 2014 establishes that the changes approved by this order are applied when forming indicators of accounting objects on the last day of the reporting period of 2014, unless otherwise provided by the accounting policy of the institution. The transition to the application of accounting policies, taking into account the provisions of this order in terms of the working chart of accounts of accounting (budget) accounting of state (municipal) institutions, is carried out according to the organizational and technical readiness of the accounting entities.
Thus, before December 31, 2014, institutions should write off off-balance sheet land plots used by institutions on the right of permanent (perpetual) use (including those located under real estate) and put them on the balance sheet - to account 103 11 “Land - immovable property of the institution." According to the explanations of the methodologists of the Ministry of Finance of Russia, these transactions should be documented with an accounting certificate f.0504833.
Article 11 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” establishes that assets and liabilities are subject to inventory. During the inventory, the actual presence of the relevant objects is revealed, which is compared with the data of the accounting registers.
Thus, in order to identify the actual availability of property, compare the actual availability of property with accounting data and check the completeness of reflection in accounting in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 11 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, it is necessary to conduct an inventory of land plots, including those located under real estate objects. If the institution has documents (certificates) confirming the right to use the land plot, based on the inventory results, the object should be written off off-balance sheet and placed on the balance sheet at its cadastral value.
In accordance with paragraph 20 of the Instructions for the application of the chart of accounts for accounting of budgetary institutions (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n), acceptance for accounting in accordance with the Act on the results of the inventory of objects of non-produced assets identified during the inventory is reflected in the debit of the corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 010300000 “Non-produced assets” (010311330, 010312330, 010313330) and the credit of account 040110180 “Other income”.
It should be noted that if an institution has a land plot taken into account off its balance sheet, it may be taken into account as treasury property on the balance sheet of the relevant property management body. The same object should not be simultaneously accounted for on the balance sheets of the institution and the treasury. Write-offs from the treasury balance sheet and acceptance onto the institution’s balance sheet must be carried out in concert.
Accounts in 2021 in a government institution
In the new edition, Order No. 209n must be applied mainly when maintaining budget (accounting) records from January 1, 2021, as well as preparing budget (accounting) and other financial statements for 2021
However, there are a number of exceptions that apply when maintaining records already in 2021 and drawing up the specified reports for 2021.
In January 2021, land tax payers will no longer prepare returns for the past year. As of the 2020 tax period, land tax declarations have been cancelled. Article 398 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has lost force.
This change was introduced by Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2021.
Despite the abolition of reporting, payment amounts, as before, must be determined independently.
The inspectorates will send out tax payment notices, which will include the amount due. But you should not expect to receive such a notification. The inspectorate may send it much later after the due date for payment of the tax.
But updated declarations for periods up to 2021 will continue to be accepted by the Federal Tax Service - at the location of the land plots.
After the abolition of land tax declarations, a new obligation was introduced for land owners. If the Federal Tax Service did not take into account data about the site when calculating the tax and did not indicate it in the notification, you need to inform it about this site and provide documents confirming ownership. This will need to be done before December 31 of the year following the expired tax period. For failure to comply with this requirement, the company faces a fine of 20% of the unpaid tax amount.
Setting the deadline for paying land tax is no longer the prerogative of local authorities (Part 2 of Article 356 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Starting with the payment of tax for 2021, a single deadline for payment of land tax is introduced (paragraph 2, paragraph 1, article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- no later than March 1 - annual payment;
- before the end of the month following the reporting quarter - advance payment.
These changes were introduced by Federal Law No. 325-FZ of September 29, 2021.
Starting from the new year, it is necessary to apply updated budget classification codes in accounting and take into account the changes associated with them:
- in the order of formation of BSC No. 85n - new KVRs (246, 247, 614, 624, 635 and 816);
- the current order No. 207n for all participants in the budget process (both regional and local) will be replaced by new lists of the KBK No. 99n;
- Amendments have been made to the procedure for applying KOSGU No. 209n. For example, subarticle 139 of KOSGU was added, which reflects income from reimbursement of costs for measures to reduce injuries, occupational diseases, etc.
The amendments should be taken into account when updating accounting policies for the next year.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2020 N 98n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2020 N 99n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 29, 2020 N 222n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 12, 2020 N 236n
In 2021, a number of reports to the Federal Tax Service and the Pension Fund must be submitted using updated forms:
- 6-NDFL for the first quarter - no later than April 30;
- DAM for 2021 no later than February 1;
- VAT return for the fourth quarter of 2021 – no later than January 25;
- income tax return for 2021 – until March 29 inclusive.
The remaining government institutions, maintaining accounting and tax accounting of fixed assets in 2021-2021, in addition to the unified chart of accounts, use charts of accounts approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2021 No. 174n or dated December 23, 2021 No. 183n (depending on the type of organization) and others regulations.
To account for fixed assets, a synthetic account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” is provided. The budget accounting account number consists of 26 digits, and only 18–26 digits are used in the accounting of the institution. Depending on the group and type of fixed assets, as well as the essence of their movement, the code in the 22–26 digits changes in the account number.
The new OKOF applies only to buildings, structures and premises that were put into operation and registered after January 1, 2021. There is no need to revise the groups of previously received property; the previous classification remains for them.
When real estate objects are received, the manager or an employee authorized by him signs form 0306030 “Act of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure)”, to which documents on state registration of rights are attached. If we are talking about moving an object from one materially responsible person to another within the same institution - form 0306032 “Invoice for internal movement of fixed assets”.
Documentary evidence of state registration of the emergence and transfer of rights is a certificate of state registration of rights. Its form is given in Appendix 14 to the Rules for maintaining the Unified State Register of Rights to Real Estate and Transactions with It. The date of state registration of rights is the day the corresponding entries are made in the Unified State Register of Rights.
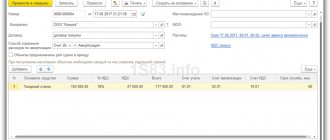
Acceptance of land plots for accounting into account 103.11 based on inventory results is formalized by the document “Free receipt of legal acts” (menu “OS, intangible assets, legal acts – Accounting for non-produced assets” of the main menu of the program, interface “Full”) with the business transaction “Capitalization of surplus legal acts based on inventory results "
Article 11 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ dated December 6, 2021 “On Accounting” establishes that assets and liabilities are subject to inventory. During the inventory, the actual presence of the relevant objects is revealed, which is compared with the data of the accounting registers.
According to paragraph 334 of Instruction No. 157n, “analytical accounting for account 01 is carried out in the Card of quantitative and total accounting of material assets in the context of lessors and (or) owners (balance holders) of property for each object of non-financial assets and under the inventory (account) number assigned to the object by the balance holder ( owner) indicated in the transfer and acceptance certificate (other document).”
What will change in KOSGU from November 21, 2021 and in 2021
Federal Law No. 122-FZ dated July 21, 1997 “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it” establishes that the registered right of a state (municipal) institution to a land plot is confirmed by a certificate of state registration of rights.
The concept of “land” includes objects of non-produced assets in the form of land plots, as well as capital expenses inseparable from land plots, which include non-inventory expenses (not related to the construction of structures) for cultural and technical measures for surface improvement of land for agricultural use, made at the expense of capital investments (land planning, uprooting areas for arable land, clearing fields of stones and boulders, cutting off hummocks, clearing thickets, cleaning reservoirs, reclamation, drainage, irrigation and other works that are inseparable from the land), with the exception of buildings and structures built on this land (for example, roads, tunnels, administrative buildings, etc.), plantings, underground water or biological resources ( clause 79 of Instruction No. 157n ).
Commercial and “disinterested” structures provide reporting to regulatory authorities in different ways. The differences lie not only in the composition of the documentation, but also in the timing of submission: for state employees, their own schedule and frequency have been developed.
- one of the goals of the activities of a municipal institution - a state task - is carried out using funds from a certain level of the state budget;
- the property is not owned by a budgetary institution, but by right of operational management, and the owner is the Russian Federation or its subject;
- if a budgetary organization owns a land plot, it is provided for use indefinitely;
- the obligations of property owners are not identical to the obligations of a budgetary institution;
- Even if the owner has assigned to a budget organization the right to manage valuable property and real estate, the organization cannot dispose of it without permission.
For example, if an organization submits an application to the commission in February 2021 to establish the cadastral value of a land plot in the amount of its market price and the commission satisfies the request, then the organization must apply the new cadastral value for taxation from January 1, 2021.
These changes do not affect the obligations of institutions to the Federal Tax Service. As before, annual accounting reports are submitted on paper or in electronic format. The deadline remains the same - no later than 3 months from the end of the reporting period, that is, until March 31. But 03/31/2021 is Sunday, therefore, we report to the Federal Tax Service until 04/01/2021.
Updates to the financial statements of public sector institutions have corrected not only the forms, but also the format for providing information. Absolutely new in budget accounting in 2021 for budgetary institutions is the rule of electronic reports. Now public sector employees generate reports only in electronic form. These adjustments were signed by the President of the Russian Federation and published on November 28, 2021 (amendments to Law No. 402-FZ).
- Cash flow statement - Order No. 278n. The standards of this PBU should be applied to reporting for 2021, but there is an exception. Derivative financial instruments should only be reported for 2021.
- Accounting policies, estimates and errors - Order No. 274n. The provisions of this regulation should be applied from the beginning of the new year. The institution’s accounting policy for 2021 will have to be drawn up according to new rules.
- Revenues - Order No. 32n. Establishes general provisions and requirements for the assessment and recognition of such an accounting object as income.
- Events after the reporting date - Order No. 275n. The standard defines key instructions for reflecting events that occurred after the reporting date. Again, the instructions should be applied when preparing your 2021 financial statements.
- The impact of changes in foreign exchange rates - Order No. 122n. The innovations regulate the procedure for determining the value of currency accounting items.
What will the new federal budget be like for three years?
Adopted by the State Duma on November 26, 2020
Approved by the Federation Council on December 2, 2020
Article 1. Main characteristics of the federal budget for 2021 and for the planning period of 2022 and 2023
1. Approve the main characteristics of the federal budget for 2021, determined based on the projected volume of gross domestic product in the amount of 115,533 billion rubles and an inflation rate not exceeding 3.7 percent (December 2021 to December 2020):
1) the projected total volume of federal budget revenues in the amount of 18,765,101,678.2 thousand rubles;
2) the total volume of federal budget expenditures in the amount of 21,520,068,140.5 thousand rubles;
3) the upper limit of the state internal debt of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2022 in the amount of 18,315,272,293.1 thousand rubles;
4) the upper limit of the public external debt of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2022 in the amount of 72.0 billion US dollars, or 61.0 billion euros;
5) federal budget deficit in the amount of 2,754,966,462.3 thousand rubles.
2. Approve the main characteristics of the federal budget for 2022 and 2023, determined on the basis of the projected volume of gross domestic product in the amount of 124,223 billion rubles and 132,822 billion rubles, respectively, and the inflation rate not exceeding 4.0 percent, respectively (December 2022 by December 2021) and 4.0 percent (December 2023 by December 2022):
1) the projected total volume of federal budget revenues for 2022 in the amount of 20,637,497,128.9 thousand rubles, including the projected volume of additional oil and gas revenues of the federal budget in the amount of 702,650,667.8 thousand rubles, and for 2023 in the amount 22,262,676,600.8 thousand rubles, including the projected volume of additional oil and gas revenues of the federal budget in the amount of 787,335,156.2 thousand rubles;
2) the total amount of federal budget expenditures for 2022 in the amount of 21,884,992,095.9 thousand rubles, including conditionally approved expenses in the amount of 547,124,802.4 thousand rubles, and for 2023 in the amount of 23,671,297,852, 6 thousand rubles, including conditionally approved expenses in the amount of 1,183,564,892.6 thousand rubles;
3) the upper limit of the state internal debt of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2023 in the amount of 20,519,245,962.7 thousand rubles and as of January 1, 2024 in the amount of 22,946,941,124.0 thousand rubles;
4) the upper limit of the state external debt of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2023 in the amount of 73.2 billion US dollars, or 61.0 billion euros, and as of January 1, 2024 in the amount of 73.6 billion US dollars, or 60.9 billion Euro;
5) federal budget deficit for 2022 in the amount of 1,247,494,967.0 thousand rubles and for 2023 in the amount of 1,408,621,251.8 thousand rubles.
Article 2. Standards for the distribution of income between the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation for 2021 and for the planning period of 2022 and 2023
1. In accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 1841 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, approve the standards for the distribution of income between the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation for 2021 and for the planning period of 2022 and 2023 in accordance with Appendix 1 to this Federal Law.
2. Income from federal taxes and fees, including taxes provided for by special tax regimes, received from payers in the territory of the Nenets Autonomous Okrug, are subject to credit to the budget of the Arkhangelsk region in accordance with the standards established by the Budget Code of the Russian Federation and this Federal Law, with the exception of income from federal taxes and fees, including taxes provided for by special tax regimes, credited to the budget of the Nenets Autonomous Okrug according to standards in accordance with Appendix 2 to this Federal Law.
3. Revenues from federal taxes and fees, including taxes provided for by special tax regimes, received from payers in the territories of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, are subject to credit, respectively, to the budgets of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug according to the standards established by the Budget Code of the Russian Federation and this Federal Law, with the exception of tax revenues from the corporate profit tax credited to the budget of the Tyumen region according to the standard in accordance with Appendix 2 to this Federal Law.
Changes 2021 on land tax
Rationale for the conclusion: When preparing an answer, we do not give. July 26, 2021 On this issue, we adhere to the following position: Depending on the terms of the agreement, real estate (part of the inventory object) and movable property leased is accounted for on an off-balance sheet account 25
“Property transferred for paid use (rent)”
.
Account 0 111 40 000 “Right of use.
July 25, 2021 Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: The fact of damage to property received by the institution for free use must be reflected
In this case, the institution does not have the right to use it for administrative work.
A legal entity accepting a donation for which a specific purpose has been established must keep separate records of all operations involving the use of donated property (Article 582 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
a person can take into account fixed assets that are transferred to him in the operational or economic management department.
It is paid by the balance holder. Let us clarify for what property categories of taxpayers are required to pay tax:
- in terms of those fixed assets that are included in the balance sheet, legal entities, both Russian and foreign, conducting their financial and economic activities within Russia with the participation of a representative office; in terms of real estate located in Russia and owned by them and other foreign legal entities. persons without permanent establishment in the Russian Federation.
From the beginning of the tax period in 2021, movable property of organizations is not subject to taxation. The list of non-taxable property includes objects (clause
According to paragraph 4 of the “Revenue” Standard: “Income received (accrued) in the reporting period, but relating to future reporting periods, is recognized for the purposes of accounting, formation and public disclosure of accounting (financial) reporting indicators as income for future periods.
» In accordance with the “Revenue” Standard: “Revenue from interbudgetary transfers - income from the provision of grants, subsidies, subventions and other interbudgetary transfers from other budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, provided with conditions for the transfer of assets, are recognized in accounting upon the emergence of the right for their receipt by future income.
4, art. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): Having official status and classified as the cultural heritage of the peoples of Russia (works of painting, sculpture, cultural and historical monuments, and others listed in Federal Law No. 73-FZ of June 25, 2002).
25 of the Revenue Standard)
In the previous edition of the instructions, analytical accounting accounts were provided to reflect transactions with fixed assets. Now this list has been removed, presented in Appendix 1 to Instruction No. 162n and left unchanged.
It is important to remember the general rule: it is necessary to report on the results of the year no later than 15 days before the founder’s reporting deadline. Please note that annual reporting includes both quarterly and monthly reports.
They are usually delivered earlier. All forms must be sent to the founder, even if indicators are missing. When preparing and submitting annual reports for 2021, you should take into account the amendments made by:
Also remember that the chief accountant is required to sign the forms only in the part in which the financial indicators are based on accounting information. Accountants of government agencies (including government agencies) must follow two fundamental instructions when preparing reports:
- on the procedure for drawing up and submitting annual, quarterly and monthly reports on the execution of budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, approved and amended
The task is accomplished by conducting a systematic inventory. Timely calculation of material depreciation in monetary terms. Reliable reflection of transactions in accounting. Receive reliable information about the property status of an economic entity for the preparation of reliable financial and tax reporting.
Calculation and payment of fiscal payments to the state budget in terms of taxation of the organization’s property.
For some types of objects you will have to obtain special permission from the owner or founder.
Let us recall, by virtue of clause 11.
1 of Order No. 209n expenses for payment of state (municipal) contracts, contracts for construction, acquisition (manufacturing) of objects related to fixed assets, as well as for reconstruction, technical re-equipment, expansion, modernization (modernization with additional equipment) of fixed assets located in the state , municipal property received for rent or free use are included in Article 310 “Increase in the value of fixed assets” of KOSGU.
In the previous edition of the instructions, analytical accounting accounts were provided to reflect transactions with fixed assets. In addition, the following entries have been adjusted: transactions Debit Credit Changes Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
General provisions for transition
In the first paragraphs of the Methodological Recommendations [3], officials drew attention to the fact that the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 89n are applied when forming balances as of December 31, 2014. Meanwhile, they did not rule out that in 2014 it was possible to apply changes to Instruction No. 157n at an earlier date, if this was provided for by the acts of the accounting entity establishing the organization of accounting in the institution, that is, the accounting policy of the organization. The institution had the right to decide to switch to the application of both all new provisions of Instruction No. 157n, and only certain ones:
- on the organization of accounting in the institution and the implementation of internal control over the facts of economic life;
- according to the procedure for conducting an inventory of property;
- on maintaining records of individual objects of assets, liabilities, and other accounting objects;
- on the application of the institution’s working chart of accounts and other provisions of the methodology.
In this case it was necessary to proceed from:
- conditions for conducting property inventories of assets and liabilities;
- organizational and technical readiness of institutions (no later than December 31, 2014).
As noted in paragraph 1 of the Methodological Recommendations, regardless of the date of transition to the application of the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 89n, institutions must take into account that when the requirements established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting, federal and (or) industry standards by accounting entities change, the accounting policy changes . Therefore, guided by the provisions of Art. 8 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” and Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 89n, it is necessary to make appropriate changes to your accounting policy for 2014. In particular, in:
- working chart of accounts for accounting (budget) accounting;
- analytical accounting, including in the form of additional detailing of the types of receipts and disposals (according to KOSGU) [4];
- the procedure for interaction between the accounting department (structural unit,
The conditions and procedure for the seizure of land plots for state (municipal) needs are regulated by Chapter VII.1 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation, as well as Articles 279–281 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Land plots are confiscated in exceptional cases listed in Article 49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation. State (local) authorities are obliged to notify the owner of the land plot about this.
Compensation is due for land plots that are seized for state needs. It can be obtained not only by the owner, but also by the copyright holder (user).
The amount of compensation, timing of transfer of the land plot and other conditions of withdrawal are specified in an agreement with the land owner. The amount of compensation includes:
- market value of the land plot;
- the market value of real estate on this land plot;
- the amount of losses caused by the withdrawal (including lost profits).
This procedure is established by Articles 279 and 281 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, 56.8 and 56.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
Write off the land plot from the register on the date of termination of ownership of it. When written off, reflect the book value of the land plot as part of other expenses, and the compensation received for it – as part of other income.
This conclusion follows from paragraph 12 of PBU 9/99, paragraph 16 of PBU 10/99, paragraph 31 of PBU 6/01.
As a general rule, a retiring fixed asset item is written off at its residual value. Since land plots are not subject to depreciation (paragraph 5, clause 17 of PBU 6/01), their residual value at the time of withdrawal is equal to the original value. In this regard, when disposing of a land plot, there is no need to open a separate sub-account “Disposal of fixed assets” to account 01.
Reflect transactions related to the disposal of a land plot as a result of seizure with the following entries:
Debit 91-2 Credit 01 – reflects the disposal of the land plot;
Debit 76 Credit 91-1 – reflected in other income is the amount of compensation (redemption price) for the seizure.
Non-produced assets still remain more exotic than a common occurrence in budget accounting. Nevertheless, accountants have to come into contact with this topic. Letter No. 02-14-10a/1406 of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 26, 2006 pleased many accountants who were puzzling over the accounting of land plots.
N.I. LEIMAN, O.V. GORSHENINA Legal aspect When deciding whether to reflect the cost of a land plot in accounting, it is necessary to be guided not only by the Instructions on Budget Accounting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 10, 2006 No. 25n, but also by regulations on the delimitation, use and ownership of land property , as well as transactions related to its sale and acquisition. This is in particular:
– Land Code; - Civil Code; – Law of July 21, 1997 No. 122-FZ “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 122-FZ).
Reflection of the transfer of account balances.
Taking into account the changes made to Instruction No. 157n, the working chart of accounts of the autonomous institution has been supplemented with new balance sheet accounts:
Postings in the budget. Table 4
| Account number | Name |
| 205 82 | “Calculations for unidentified receipts” |
| 209 30 | "Calculations for cost compensation" |
| 209 40 | “Calculations on forced seizure amounts” |
| 209 83 | “Calculations for other income” |
| 210 11 | “Calculations for VAT on advances received” |
| 210 12 | “Calculations for VAT on purchased material assets, works, services” |
| 401 60 | “Reserves for future expenses (by type of expense)” |
| 500 90 | “Authorization for other subsequent years (outside the planning period)” |
| 502 07 | "Obligations accepted" |
| 502 09 | "Deferred obligations" |
Thus, as new accounts are introduced, it is necessary to record the transfer of balances in these accounts.
In accordance with clause 4 of the Methodological Recommendations, the transfer of account balances in terms of income calculations is carried out on the basis of a certificate (form 0504833) reflecting the following accounting entries:
Budgetary accounting entries. Table 5
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt for damage subject to compensation by court decision in the form of compensation for expenses associated with legal proceedings (payment of state fees, payment of legal costs)* | 0 209 30 000 | 0 205 30 000 |
| The transfer of balances in the amount of debt for compensation of damages is reflected in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, including in the event of insured events* | 0 209 40 000 | 0 205 40 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt on fines, penalties and penalties accrued for violation of the terms of contracts for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services* | 0 209 40 000 | 0 205 40 000 |
| The transfer of balances in the amount of debt for the sale of property is reflected due to the decision to write off non-financial assets (scrap metal, rags, waste paper, other waste and (or) objects obtained during dismantling (dismantling) of written-off, liquidated objects)* | 0 209 74 000 | 0 205 74 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt for other income not related to the implementation of contracts, agreements, including the provision of subsidies, as well as the performance by the institution of the functions assigned to it in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation* | 0 209 83 000 | 0 205 80 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt on accrued interest for the use of other people's funds due to their unlawful retention, evasion of their return, other delay in their payment or unjustified receipt or savings, as well as charges for compensation of lost benefits* | 0 209 83 000 | 0 205 80 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt for unidentified receipts* | 0 205 81 000 | 0 205 82 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of calculations for tax deductions for VAT in terms of the tax accrued upon receipt by the taxpayer of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services)* | 0 210 11 000 | 0 210 01 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in terms of tax amounts presented to the taxpayer when purchasing goods (work, services) subject to deduction* | 0 210 12 000 | 0 210 01 000 |
* If, on the date of transition to the application of the provisions of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 89n, there are credit balances for calculations in terms of the indicated income, the transfer of calculation indicators is carried out by reverse correspondence, similar to those given above.
After carrying out the inventory in the AU, account 2,210,01,000 “Calculations for VAT on purchased material assets, works, services” listed the total amount of input VAT - 25,678 rubles, which, according to tax accounting data, consisted of two amounts:
- the amount of tax accrued upon receipt by the taxpayer of payment, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods - 5,325 rubles;
- the amount of tax presented to the taxpayer upon the purchase of goods (work, services) subject to deduction - 20,353 rubles. The transfer of balances was issued with a certificate (f. 0504833).
The following entries were made in the accounting records of the AU:
Budgetary accounting entries. Table 6
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The transfer of VAT balances on prepayment is reflected | 2 210 11 000 | 2 210 01 000 | 5 325 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances regarding input VAT when purchasing goods from suppliers | 2 210 12 000 | 2 210 01 000 | 20 353 |
In accordance with clause 4 of the Methodological Recommendations, the transfer of account balances in terms of settlements of obligations is carried out on the basis of a certificate (form 0504833) reflecting the following accounting entries:
Table 7
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Regarding settlements of obligations | ||
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt to the institution for advance payments under agreements, state (municipal) contracts, not returned by the counterparty in the event of their termination, including by court decision, when conducting claims work | 0 209 30 000 | 0 206 00 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt to the institution for the listed security for applications for participation in a competition or closed auction, security for the execution of contracts, state (municipal) contracts, other collateral payments, deposits | 0 210 05 000 | 0 206 00 000 |
| The transfer of balances is reflected in the amount of debts of accountable persons not returned in a timely manner (not withheld from wages), for which claims work is being carried out as of the date of transfer, including in the case of a challenge by an individual debtor of the deductions, as well as for employees with whom employment relations have been terminated | 0 209 30 000 | 0 208 00 000 |
| Reflects the transfer of balances in the amount of debt for payments of benefits, pensions, compensations not received in a timely manner by the recipients of these payments | 0 302 00 000 | 0 304 02 000 |
| The transfer of balances in the amount of damage in the amount of debt of former employees for unworked vacation days upon their dismissal before the end of the working year for which they already received annual paid leave, identified during the inventory, is reflected* | 0 209 30 000 | 0 401 10 130 |
* With simultaneous reflection of corrective accounting entries for the corresponding settlement accounts 0 302 00 000 “Settlements for obligations”, 0 303 00 000 “Settlements for payments to budgets”.
Accounting in budgetary organizations
- You can ask questions to an expert and get comprehensive answers
- Discuss with colleagues the latest changes and their practices
- You can receive 10 hours of advanced training in IPB
- You can take training online, we will organize a broadcast and the opportunity to ask a question
- Charismatic teacher with unparalleled experience
- Cozy atmosphere for comfortable learning, coffee and delicious coffee breaks
Practitioner accountant, certified professional accountant, certified teacher of the Institute of Professional Accountants of Russia on accounting of state (municipal) institutions, teacher of the RANEPA SIU, famous lecturer in the Siberian Federal District on issues of organizational and legal features of the activities of state and municipal institutions (state, budgetary, autonomous), accounting and tax accounting, remuneration (Novosibirsk)
I. Extensive changes from 2021 for state municipal institutions according to the unified chart of accounts No. 157n and according to accounting instructions No. 174n, No. 183n, No. 162n, No. 52n
1. New requirements for analytical accounting in accounts receivable, accounts payable, and in additional off-balance sheet accounts.
2. New requirements for the procedure and reflection in accounting of revaluation to fair value of non-financial assets, interbudgetary transfers.
3. New requirements for off-balance sheet recording of non-financial assets when recognized as non-assets and reinstated on the balance sheet based on the owner’s decision on their further use.
4. Application of new accounts from 2021 to correct errors of previous years. Practical examples of application for various business transactions.
5. New in the acceptance for accounting of calculations for shortages, compensation of costs and other income.
6. Changes in accounting for off-balance sheet accounts: material assets in storage received for use, strict reporting forms, prizes, cups, awards, etc.
7. Changes in the procedure for conducting cash transactions and monetary documents.
II. Explanations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on the practice of applying adopted federal accounting standards for public sector organizations
1. Explanations of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on reflecting reimbursement of costs under a concession agreement in accounting.
2. Situations of gratuitous use of property for which the GHS dated December 31, 2016 No. 258n “Rent” does not apply.
3. Is the institution obliged to always use account 10634 when posting inventories?
4. Acceptance for accounting of scrap metal remaining after repairs.
5. Documentation of materials release.
6. Accounting for medical gloves, masks, medical products.
7. At what cost should an asset be accounted for if penalties are applied to the supplier?
8. Reflection in accounting of expenses for forensic examination.
III. Necessary measures for the transition to new budgetary standards in 2021
1. We are preparing for a new reflection of intangible assets from 2021 in accordance with the federal standard approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2019 No. 181n, methodological recommendations and changes in accounting instructions:
— inventory of intangible assets, rights of use of accounting entities for software and databases;
— recognition on different balance sheet accounts depending on the terms of use under the agreement;
— termination of recognition on off-balance sheet accounts and in deferred expenses;
— new analytics for reflecting exclusive and non-exclusive rights to use the results of intellectual activity in accounting;
— creation of intangible assets on our own;
— a new procedure for calculating depreciation on intangible assets.
2. Determination of the composition of related parties and their reflection in the accounting financial statements in accordance with the methodological recommendations to the GHS “Information on related parties” dated December 30, 2017 No. 277n.
3. Non-produced assets: new analytics, assessment at initial recognition, subjects of reflection of non-produced assets in accounting, revaluation. Accounting for land plots for which ownership is not demarcated.
In 2021, the Ministry of Finance introduced a new subarticle 139 “Income from reimbursements of expenses by the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.” It must reflect income from reimbursement to the Social Insurance Fund for expenses for:
- measures to reduce industrial injuries and occupational diseases of employees;
- sanatorium-resort treatment for those who work in harmful or dangerous conditions.
Let us note that in 2021, these revenues were attributed to subarticle 134 of KOSGU “Income from compensation of costs.”
But benefits that employers pay at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund were removed from the cost structure under subarticle 213 of KOSGU “Accruals for wage payments.” This is due to the transition from 2021 of all regions of Russia to the principle of direct payments from the Social Insurance Fund (without offset).
At what cost should land plots for which ownership is not demarcated be taken into account?
In accordance with paragraph 71 of Instruction No. 157n, land plots for which property is not demarcated are recorded at: their cadastral value, in the absence of a cadastral value of the land plot - at a value calculated based on the lowest cadastral value per square meter of land plot bordering the object of registration , if it is impossible to determine such a cost, in a conditional estimate, one square meter is 1 ruble.
In accordance with paragraph 80 of Instruction No. 157n, the accounting unit for non-produced assets is an inventory item. For the purpose of organizing and maintaining analytical accounting, each inventory item of non-produced assets is assigned a unique inventory serial number, which is used exclusively in accounting registers (clause 81 of Instruction No. 157n).