At one time, I sketched out for myself a small diagram of the accounting sections. I noticed that visualization helps to grasp the theory faster. So why not use this in our accounting teaching? Today we will “identify” some areas of accounting with you and draw a diagram. In this practical article we will solve two problems at once:
First task . We will start your thinking process. You yourself will begin to “get” the knowledge that you already have. We'll just tie them together.
Second task . You will see that the so-called specifics of an enterprise are far from what novice accountants “wind up” in their heads.
As always, let's start with the fact that we already know the names of some areas of accounting:
- site by suppliers
- plot by buyer
- loan area
- cash area - cash desk
- non-cash area - bank
Let's take, for example, any enterprise. Just look out the window or in the classifieds section of the newspaper, or just watch the advertisements on TV. You will see a lot of different business names. Whatever these companies do, there are several main points that unite them. Let's try to highlight these moments together. I will ask leading questions, you answer silently, and then I will write my answer and you can compare. Do you agree?
Which companies require a sales accountant?
For the most part, the need for a sales accountant is typical for trade organizations. The larger the company and, as a result, the greater its turnover, the more significant the number of sales transactions are carried out daily. Thus, an employee of an organization who is responsible for sales operations is the main characteristic of a sales accountant.
At their core, the functional responsibilities of a sales accountant are extremely close to the responsibilities of a primary documentation accountant. As a rule, in a company, a sales accountant prepares and records transactions for the sale of goods, works or services, as well as prepares the appropriate package of documents required for these transactions.
Accountant operator responsibilities
Registration of employee responsibilities with internal company documentation
To ensure that employees do not have questions during their work activities, organizations draw up a job description for each staff position. This document refers to internal administrative documentation issued and approved by order of the head of the company and is intended to disclose information about the direct responsibilities of an employee holding a particular position, as well as the requirements for personnel qualifications, the employee’s rights and the boundaries of his responsibility. The introduction of this document into everyday use will minimize misunderstandings between the employee and the employer.
Thus, the introduction of a job description allows the organization to:
- Determine the boundaries of employee responsibility in the event of violations;
- Record the company's requirements for personnel qualifications;
- Determine a specific list of functional responsibilities for each position. In relation to accounting employees, we are talking about assigning a site, establishing the scope of work and the actual list of operations performed.
Why do companies work?
What more can we say about any enterprise, no matter what it does? Let's remember what the general purpose of any commercial enterprise is. Would you say to do something for the sake of the process itself? J no, of course. The goal is to make money. Any enterprise must take into account information about how much it earns while carrying out its activities.
I will note only one point: “how much one earns” is not money in the cash register or in the bank. We all know that selling doesn’t always mean getting money right away, don’t you agree?
And finally, I’ll say a couple more similarities. Agree that enterprises keep their premises and buildings clean, or at least strive to do so. In any case, for this, companies buy household supplies: mops, buckets, powders, etc.
The company also uses office supplies in its work: paper, pens, folders, etc. It doesn’t matter what the company does, it uses all this: issue a salary certificate to the employee, issue an order for the enterprise, print out a payroll for the payment of wages and many, many other things that are required for the operation of the company. All this is called stationery. Such values, material assets, are taken into account in the accounting section - Materials.
Sales accountant: responsibilities
A specific list of functional responsibilities of an accountant for sales is not established at the legislative level. In this regard, companies are given the opportunity to independently determine the actual list of responsibilities depending on the specifics of the organization’s activities.
When developing a job description for a sales accountant, it is necessary to be guided by the provisions of the current labor legislation. In the process of carrying out work, the sales accountant reports to his immediate supervisor, namely the chief accountant or deputy chief accountant, if there is one.
What should a sales accountant know?
First of all, the provisions of Russian legislation that determine the accounting methodology in commercial organizations.
Due to the fact that the formation of transactions for the sale of goods, works, and services constitutes the tax base when calculating budget payments, the sales accountant must be savvy in matters of tax legislation.
Since the entire accounting and tax accounting system is based on the use of a chart of accounts for business accounting, the sales accountant is required to understand the meaning of the accounts and their possible correspondence.
Currently, business accounting is automated. Accordingly, the importance of accounting programs such as 1C, Kontur and others will be a priority.
As for the job responsibilities of a sales accountant, they include:
- Reflection on business accounts of transactions for the sale of goods, works and services;
- Preparation of relevant documents when carrying out the operations described above;
- Calculating the cost of goods, works and services, identifying sources of losses and costs;
- Working with account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
- Periodic (at least once a quarter) reconciliation of mutual settlements with the company’s counterparties, generation of reconciliation reports;
- Control over the status of receivables and payables. Timely elimination of emerging debts, carrying out analytical measures on the reasons for their occurrence;
- Formation of a sales book;
- Formation of a log of issued invoices;
- Monitoring the correctness of registration of primary accounting documents;
- Preparation of data on the sales area and provision of relevant information to the chief accountant / deputy chief accountant for reporting.
The specific list is established by the company independently, depending on the specifics of its activity. Often, the sales accountant’s responsibilities include working with the client bank. When determining functionality, management should build on the current regulatory framework and professional standards intended for accountants.
Any commercial organization sells something. This means that these transactions must be reflected in accounting. Let's consider how to properly regulate this process by drawing up a job description for an accountant for implementation.
Which companies require a sales accountant?
Although all businessmen are engaged in sales, not everyone needs a separate specialist to account for them. If the number of sales documents does not exceed several dozen per month, then this load is often borne by the accountant responsible for other sections. And in small businesses, all areas are often closed by one chief accountant.
Why an accountant cannot and should not conduct personnel records
But if we are talking about a medium-sized company, then, as a rule, there is already a separate specialist who is responsible for settlements with customers. And in a large business, shipment accounting is usually handled by a special unit within the accounting department. Then each employee is assigned a group of buyers, for example, on a regional basis.
Calculate the cost of accounting services
Taxation system OSNO simplified tax system 15% simplified tax system 6% Number of documents per month Number of employees TOTAL 1,600 rub. / month*rub. The price is per quarter! For a more detailed calculation, contact the manager! The cost of services is approximate. Each organization has its own specifics, therefore, to accurately determine the cost of services, a preliminary analysis of your documents is necessary. The cost of services is approximate. Each organization has its own specifics, therefore, to accurately determine the cost of services, a preliminary analysis of your documents is necessary.
What is the job of a sales accountant?
As is clear from the title of the position, this specialist is responsible for documenting the process of selling products, goods or services.
But the sales accountant’s responsibilities are not limited to issuing invoices and invoices. He must also reflect these transactions in accounting, charge related taxes (primarily VAT), monitor the status of settlements with counterparties, etc.
Audit of settlements with buyers and customers
In addition, if the amount of work is relatively small, then this specialist may be entrusted with other areas, most often adjacent ones. For example, in manufacturing companies this may be accounting for the release of finished products, and in trading companies this may be accounting for the purchase of goods.
Who do we meet at companies?
Who do we encounter when we come to any company? Who do we see when, for example, we go to the checkout in a store? What if we go buy a ticket to a travel agency or call a real estate agency to find out about apartments for sale? Who are we meeting? Isn’t it with people who are representatives of the companies we contact? Do you agree?
It turns out that every enterprise, large or small, has people. No operating enterprise can carry out its activities without human participation. Such people in relation to. So, all companies have employees. Let's discuss further.
What do employees mean to a company? What does the company do in relation to its employees? Doesn't he use their time and knowledge to carry out his activities? If you agree with this, then I’m sure you’ll agree that work should be paid, right? By paying the labor of its Employees, the company incurs costs (expenses).
Of course, the amount for the work of Employees, the so-called Payroll Fund (WF) is not everything that is related to employees. With payroll, the enterprise itself also pays taxes to various funds: Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund, Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. These amounts are directly related to conversations about pensions, benefits, social benefits, etc. Thus, any enterprise is made up of employees. Employees mean payment for labor and payment of taxes to the state from this payment (with payroll). Payroll and payroll taxes for an enterprise are considered costs (expenses).
You noticed that I write costs (expenses). This is a new term that I am gradually introducing into our accounting lexicon. We will leave the meaning and understanding of this term for future articles. Now it is important to note that there is such a term in accounting. Intuitively, I'm sure you understand what it means. More details to come.
Requirements for a sales accountant
The employee who “manages” the implementation is an ordinary accounting specialist. The legislation does not contain mandatory requirements for accountants of commercial organizations, with the exception of the main ones.
Note!
The current professional standard “Accountant” is advisory in nature for businessmen. It establishes that for “line” accounting employees, secondary specialized education may be sufficient. However, experience is not required for ordinary positions.
In practice, the issue is resolved taking into account the peculiarities of accounting organization in the company. If there is only one shipping specialist, and the chief accountant has no time to train him, then it is logical to hire an employee with experience for this position.
If several employees are involved in sales, then it is quite possible to hire a newcomer to the staff by assigning him a mentor from among experienced specialists.
The shipping specialist must have a good understanding of the regulations governing accounting. This is, first of all, the law “On Accounting”, the PBU system and the Chart of Accounts with the attached instructions. Such an employee should have the most thorough knowledge of PBU 9/99 “Organizational Income”. Because Since shipment is closely related to the calculation of taxes, the sales accountant must also know the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
But basic documents do not regulate all the subtle aspects of accounting and taxation. Therefore, the shipping specialist must also be familiar with the explanations of government bodies (Ministry of Finance, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation) on issues within the scope of his duties.
Any employee should have such personal qualities as honesty, integrity and a responsible attitude to their duties, and an accountant is no exception.
But the specifics of the profession (working with numbers and documentation) also impose additional requirements. An accountant must have a mathematical mind and be attentive to detail. Or more precisely, to understand that there are no small details in his work, and you must always check every number.
At the sales site, qualities such as communication and stress resistance become especially important. After all, a shipping specialist must constantly communicate both with employees of his sales department and with counterparties, for example, to reconcile payments.
Accounting areas - preparing a list
May 06, 2015 Comments (0)
At one time, I sketched out for myself a small diagram of the accounting sections. I noticed that visualization helps to grasp the theory faster. So why not use this in our accounting teaching? Today we will “identify” some areas of accounting with you and draw a diagram. In this practical article we will solve two problems at once:
First task. We will start your thinking process. You yourself will begin to “get” the knowledge that you already have. We'll just tie them together.
Second task. You will see that the so-called specifics of an enterprise are far from what novice accountants “wind up” in their heads.
As always, let's start with the fact that we already know the names of some areas of accounting:
- site by suppliers
- plot by buyer
- loan area
- cash area - cash desk
- non-cash area - bank
Let's take, for example, any enterprise. Just look out the window or in the classifieds section of the newspaper, or just watch the advertisements on TV. You will see a lot of different business names. Whatever these companies do, there are several main points that unite them. Let's try to highlight these moments together. I will ask leading questions, you answer silently, and then I will write my answer and you can compare. Do you agree?
Rights and duties of an accountant for sales
This specialist usually performs the following functions:
- Preparation of shipping documents and sending them to counterparties.
- Reflection of sales information in accounting.
- Calculation of taxes related to sales, including maintaining a sales book.
- Control of receivables and payables.
- Reconciliation of payments with customers, participation in the inventory of payments.
- Preparation of summary information on your site for reporting.
An accountant, like any employee, has “basic” rights set out in Art. 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: conditions established by law and timely payment of labor, rest of a certain duration, etc. But these rights are usually reflected in an employment or collective agreement.
The job description, as a rule, includes those rights, the implementation of which directly helps the employee perform his duties:
- Receive information necessary for work from colleagues.
- Participate in discussions and make proposals for organizing work within your competence.
- With the permission of the manager, involve other employees to help solve assigned tasks.
- Sign certain types of primary documents.
Accounting for land plots in accounting and tax accounting
Land is a special type of non-depreciable asset. It can be purchased, sold, resold, sold partially or completely; at the same time appear in accounting as a fixed asset or a product for resale. Land, as an asset, is not subject to depreciation (Article 256-2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), since it does not lose its value during operation.
The plot is accepted for accounting in the amount of all actual costs for it, including state duties for registration of ownership rights (PBU 5/01 r. 2, 6/01 r. 2). Land tax is calculated based on the cadastral value of the plot.
Documenting
The purchase and sale of land plots are formalized by an agreement in 3 copies. Two of them - to the participants of the transaction, one - to Rosreestr for registration. A land lease agreement for a period of more than a year is also registered in Rosreestr (Article 609-2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The legislation does not provide for special unified forms that take into account the diversity of land plots and their types. When registering a landowner, it is recommended to use the following documents:
- Act OS-1 “On the acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings and structures).” The document contains a number of indicators that should be ignored (crossed out) when filling out: manufacturer, depreciation rates, useful use, residual value, etc. At the same time, there are no special columns containing the characteristics of the land plot. They can be reflected in the field (section) “Other characteristics”.
- Act 401-APK “On the registration of land”. It is intended for organizations and enterprises in the agricultural sector and contains information about the land plot, its book value, type, quality of land, etc.
- Inventory card OS-6 “Accounting for fixed assets”.
Responsibilities of the sales accountant
Like any employee, a sales accountant can be held accountable for violations in their work. Disciplinary liability under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, depending on the severity of the offense, varies from reprimand to dismissal. Financial liability for an ordinary employee is generally limited to his average monthly earnings.
Full compensation for damage is possible only in special situations provided for in Art. 243 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The Code makes exceptions, for example, in cases where the damage was caused intentionally or was the result of a criminal act.
Because registration of shipment is associated with the calculation of taxes, then in case of violations, administrative, and in case of significant arrears, criminal liability may be applied to the guilty person.
Important!
In practice, the head of the company is most often punished for any tax violations, sometimes together with the chief accountant. Ordinary specialists are usually brought in as witnesses.
How to resolve conflict situations with employees
If an error is discovered in settlements with counterparties, which led to the application of tax sanctions, the question arises: who is to blame? It is clear that in such a situation the positions of the employer and employee will be directly opposite. Sometimes these conflicts end up in court.
In all such cases, a detailed job description will help solve the problem, and, if necessary, will become evidence in court. To prevent problematic situations from arising in principle, settlements with customers should be handled by a high-level professional. But finding such a specialist on the labor market and getting him interested is not so easy, especially for small companies.
Highly qualified accountants often work for large consulting firms because these employers can offer them attractive working conditions and the opportunity to solve interesting and varied problems.
Buildings as an image of enterprises
Remember one of the very first articles where I tried to represent the abstract term “enterprise” in the form of... remember? Of course the building! I said that any enterprise means either renting offices and premises, or having its own building. What does this idea tell us? What does it mean for businesses to have premises for rent or their own building? Let's try to come to an answer to these questions together.
What is rented space or own building for companies? Isn’t it the same when we live in our apartments and pay for utilities and electricity? And who rents an apartment pays rent? If you agree, then answer the following question: what do these utilities, electricity, and rent mean for your personal budget? Is it not costs? Here! The same goes for enterprises.
Enterprises either rent premises or have their own buildings. For “being” in the building, the enterprise pays rent, electricity, etc. The enterprise that owns the building pays utility bills, electricity and other payments for the maintenance of the building. Thus, it turns out that every enterprise has costs (expenses) for its “place in the sun.”
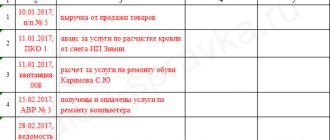
Sales of goods, works, services
Work on selling products in an organization begins with concluding an agreement with the buyer; the agreement can sometimes be an invoice for payment. Once the intent to purchase has been secured by contract, the buyer is usually issued an invoice. The invoice indicates the seller’s details, including bank details, the amount of payment, taxes (VAT, excise taxes) included in the cost of goods (work, services).
The invoice is issued by an authorized person, usually a manager or accountant, in 2 copies: one for the buyer, the second for the accounting department. Signed by the manager and chief accountant. Own copies are filed in chronological order, copies of the buyer are sent to him.
Settlements with buyers and customers are carried out on account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”. Revenue is reflected in subaccount 90.1 “Revenue”.
Goods, finished products
To ship goods and products, a consignment note TORG-12 is issued in two copies and transferred to the warehouse to the warehouseman. The storekeeper releases goods based on a power of attorney.
If the organization has shipped products or goods and ownership has passed to the buyer, then the fact of sale is reflected in the accounting records with the following entry:
Debit 62 Credit 90.1 - revenue from the sale of products (goods) is reflected. Revenue is reflected together with VAT.
At the same time, it is necessary to reflect the write-off of the cost of goods (products) in the debit of subaccount 90-2 “Cost of sales”, income from the sale of which is recorded in subaccount 90.1.
Debit 90.2 Credit 41 (43,45,20...) - the cost of goods sold is written off.
The organization must charge VAT simultaneously with the sale. She must issue an invoice within five calendar days from the date of shipment of the goods.
Debit 90.3 Credit 68 “Calculations for VAT” - VAT has been charged.
Accounting for transactions with land plots: postings
Actual expenses for the purchase of land are collected on account 08 in correspondence with accounts 60, 76. Payment of the state duty and its inclusion in the cost of the land plot is carried out by entries:
- Dt 68 Kt 51 - the fee for registering land ownership has been paid;
- Dt 08 Kt 68 - the duty is included in the initial cost of the land.
Further accounting of land depends on the purposes of its use. If a company builds buildings on the territory, but at the expense of investors, then such an object cannot be recognized as OS - it will remain on account 08. Upon completion of construction, the accountant will make an entry:
- Dt 76 Kt 08 - land was transferred to the investor in connection with the completion of construction work.
If the owner uses the land for his own purposes and for his own money, then the site should be included in the OS by posting:
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - the land plot was accepted as part of the OS.
When purchasing land from the state for the construction of OS (under contracts of 2007-2011), a tax difference arises: in the NU, spending on land is recognized as an expense, but in the BU it is not. The accountant should reflect a permanent tax asset in accounting on a monthly basis until expenses are completely written off in tax accounting:
- Dt 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Kt 99 subaccount “PNA” for the amount of Z / n / 12 months. × 20%,
Where:
Z is the initial cost of the site;
n is the number of years to write off expenses for the purchase of land.
The sale of land is recorded by the following records:
- Dt 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate” Kt 01 - the cost of land is written off;
- Dt 62 Kt 91 - revenue from the sale is reflected;
- Dt 91 Kt 45 subaccount “Transferred real estate” - the initial cost of the sold plot is reflected as part of other expenses.
We remind you that the sale of land is not subject to VAT.
When land is added to the company’s authorized capital, the accountant will make the following entries:
- Dt 75 Kt 80 - reflects the debt of the founder for the contribution to the management company;
- Dt 08 Kt 75 - a land plot was received on account of the founder’s contribution to the management company;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - land is accepted for accounting as an asset.
The transfer of land as a contribution to the management company of another legal entity is reflected in the following entries:
- Dt 58 Kt 76 subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the Criminal Code” - reflects the debt on deposits in the Criminal Code;
- Dt 76 subaccount “Settlements for deposits in the management company” Kt 01 - the plot was entered as a contribution to the management company.
If the initial cost of the transferred land differs from the estimate agreed upon by the founders, the difference should be attributed to the appropriate subaccount of account 91 in correspondence with account 76 (subaccount “Settlements for deposits in the management company”).
The accountant reflects the receipt of a land plot free of charge with the following entries:
- Dt 08 Kt 83 - land was received from the founder, whose share in the management company is more than 50%, while the company has no income;
- Dt 08 Kt 98 - land was received free of charge from other persons;
- Dt 08 Kt 01 - land plot put into operation;
- Dt 98 Kt 91 - income from the gratuitous receipt of a land plot is recognized.
If your company transfers a land plot free of charge, then the accounting entry is as follows:
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - reflects the cost of land donated to another company.
Income and expenses do not arise in tax accounting when transferring land free of charge (Articles 249, 250, paragraph 16 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But then a permanent tax liability is formed in accounting, which is taken into account simultaneously with the write-off of the cost of land and the costs of its transfer (clause 7 of PBU 18/02):
- Dt 99 subaccount “PNO” Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - reflected PNO due to the difference in accounting when transferring property free of charge.
When concluding an agreement for the exchange of wiring from a company transferring land and accepting other property in return, the following:
- Dt 08, 10, 41 Kt 60 - valuables were received under an exchange agreement;
- Dt 62 Kt 91—reflects income from the transfer of land under an exchange agreement;
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - the cost of the transferred land plot has been written off;
- Dt 60 Kt 62 - the obligations of the parties are fully repaid upon fulfillment of the terms of the exchange agreement.
The financial result from barter transactions in the accounting of transaction participants is zero.
In exceptional cases, a land plot may be withdrawn (Article 49 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). Government agencies are obliged to notify the owner of the land plot about this. The owner or user of land has the right to claim compensation in the amount of the market value of the land plot, the real estate located on it, as well as losses and lost profits from the seizure (Articles 56.8, 56.9 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation). On the date of termination of ownership of land, the following entries are made:
- Dt 91 Kt 01 - disposal of land;
- Dt 76 Kt 91 - other income includes the amount of compensation for seizure.
Is this compensation included in the taxpayer’s income and is it necessary to pay taxes on it? Find out the answer to this question in ConsultantPlus by getting trial access to the system for free.
Agreement with a special transfer of ownership
If the contract specifies that ownership of the goods will be transferred not after shipment, as is considered by default, but, for example, after payment, such an agreement is considered an agreement with a special transfer of ownership. Shipped goods must be accounted for on account 45 “Goods shipped”.
Debit 45 Credit 41 - goods (GP) were shipped under an agreement with a special transfer of ownership.
Even though title has not passed to the buyer, VAT must be charged on the day of shipment.
Debit 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances received” Credit 68 - VAT accrued on goods shipped.
Debit 51 Credit 62 - the buyer’s payment is reflected.
Debit 62 Credit 90.1 - revenue is reflected.
Debit 60.2 Credit 45 - the cost of shipped goods is written off.
Debit 90.3 Credit 68 - VAT charged
Debit 68 Credit 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances received” - VAT accrued on shipments has been restored.
Services, works
If an organization has provided services or performed work, then this fact is documented in an act in a free form; there is no standard form, for example, an act of provision of services or an act of completed work. You also need to issue an invoice.
Postings for the provision of services and performance of work are the same as for the sale of goods and finished products:
Debit 62 Credit 90.1 - revenue accrued for services rendered.
Debit 90.2 Credit 20, 26 - the cost of services provided and work performed is written off.
Debit 90.3 Credit 68 - VAT charged.
Advance from the buyer
If the organization works on an advance payment basis and before shipment, the buyer must pay an advance payment.
Debit 50, 51.52...Credit 62 subaccount “Calculations for advances received” - the buyer transferred the advance.
VAT must be charged on the advance received at a rate of 18%/118 or 10%/110.
Debit 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances received” Credit 68 - VAT was charged on the advance.
After the goods (work, services) have been transferred to the buyer and ownership has passed to him, the following entries are made in accounting:
Debit 62 Credit 90.1 - revenue is reflected.
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements on advances received” Credit 62 - the buyer’s advance is credited.
Debit 90.2 Credit 41 (43,45,20...) - the cost of goods, works, services is written off.
Debit 90.3 Credit 68 - VAT charged.
Debit 68 Credit 76 “Calculations for VAT on advances received” - the VAT accrued on the advance received has been restored.
Job description of an accountant for the sales area
- Performs accounting work in accordance with the requirements of current legislation in terms of accounting for sales of products (goods, works, services);
- Participates in the development and implementation of activities aimed at maintaining financial discipline and rational use of resources;
- Receives and controls primary documentation for the relevant areas of accounting and prepares them for accounting processing;
- Reflects in the accounting accounts transactions related to the sale of products (goods, works, services);
- Prepares reporting calculations of the cost of products (goods, works, services), identifies sources of losses and unproductive costs, prepares proposals for their prevention;
- Provides managers, creditors, investors, auditors and other users of financial statements with comparable and reliable accounting information in the relevant areas (areas) of accounting;
- Develops a working chart of accounts, forms of primary documents used for registration of business transactions for which standard forms are not provided, as well as forms of documents for internal accounting reporting, participates in determining the content of basic techniques and methods of accounting and technology for processing accounting information;
- Participates in conducting an economic analysis of the economic and financial activities of an enterprise based on accounting and reporting data in order to identify on-farm reserves, implement savings regimes and measures to improve document flow, in the development and implementation of progressive forms and methods of accounting based on the use of modern computer technology, in conducting inventories of cash and inventory items;
- Prepares data on the relevant area of accounting for reporting, monitors the safety of accounting documents, draws them up in accordance with the established procedure for transfer to the archive;
- Performs work on the formation, maintenance and storage of a database of accounting information, makes changes to reference and regulatory information used in data processing;
- Participates in the formulation of the economic formulation of problems or their individual stages, solved with the help of computer technology, determines the possibility of using ready-made projects, algorithms, application software packages that allow the creation of economically sound systems for processing economic information.
Maintaining accounting areas
The need for services for maintaining accounting areas arises when there is a planned expansion of the organization. At this moment, new divisions and departments appear in its structure, the number of operations and concluded transactions increases. As a result, the workload on accountants increases and difficulties in servicing individual operations and processes are revealed.
offers to outsource the maintenance of certain areas of accounting.
Benefits from cooperation with a remote accounting operator:
- savings on payments to a new specialist;
- savings on the cost of connecting programs of the relevant focus;
- additional reduction in the workload falling on key specialists.