New criteria for fixed assets
The Federal Standard does not replace Instruction No. 157n (as amended on September 27, 2017), but establishes fundamental accounting rules for fixed assets (fixed assets).
The two documents exist in parallel, and in the near future we can expect that this instruction and the acts detailing it (No. 162n, 174n, 182n) will be adjusted in accordance with the provisions of the Federal Accounting Service. One of the most important differences lies in the very interpretation of the term “fixed assets”. From January 1, 2021, this concept includes not just material objects, but material values that are assets. This means that in addition to the standard requirements for an object, a new one appears - to have useful potential. This means that the object can be used to perform state (municipal) functions or provide services, pay off obligations, or exchange for other assets. An object can be accepted for accounting as a fixed asset only if its initial cost is reliably estimated.
If these criteria of the federal standard are not met, then the object is accounted for in an off-balance sheet account. Please note: in contrast to instruction No. 157n, there are no conditions for mandatory state registration of rights to real estate in the FSB.
Another innovation is the ability to classify leased objects or those received for use free of charge as fixed assets. The requirements for such OS are dictated by the FSBU "Rent". In addition, some treasury property should now be taken into account as fixed assets. At the same time, two groups of objects are removed from the category of fixed assets: biological assets, if they are used for the production of bioproducts, and real estate intended for sale. Perennial plantings themselves (not producing bioproducts) remain part of the OS. A separate accounting account may be allocated for them.
A cultural heritage asset is recognized by the OS only in two cases: if there is an opportunity to obtain future economic benefits or useful potential associated with the specified asset, or if its useful potential is not limited to cultural value. In other cases, such an object is reflected in off-balance sheet accounts at a conditional valuation of 1 ruble.
There are few significant differences in the definition of the accounting unit and the procedure for accepting fixed assets for accounting. It is worth mentioning that the FSB introduces the concept of “OS complex”, that is, it allows objects with an equal useful life and insignificant cost to be considered as an inventory unit.
New in budget accounting in 2021
In 2021, accounting, reporting and taxation of a government institution is carried out with the mandatory application of the new Federal Accounting Standards:
- “Personnel payments”;
- "Intangible assets";
- "Non-produced assets";
- "Borrowing costs";
- "Cooperative activity";
- “Information about related parties”;
- "Financial instruments".
Apply the standards in accounting from 01/01/2021, and in reporting - starting from reporting in 2021.
In 2021, the following FSBUs were introduced:
- "Stocks";
- "Concession agreements";
- “Long-term contracts”;
- “Reserves. Disclosure of information about contingent liabilities and contingent assets";
- “Budget information in accounting (financial) statements.”
Starting from the 2021 reporting period, the provisions of the Federal Accounting Standards Service “Statement of Cash Flows” are applied, which relate to the reflection of information on derivative financial instruments. In addition, take into account the changes when preparing annual reports for government institutions for 2021: The Ministry of Finance has adjusted instructions No. 33n and 191n (Orders No. 292n dated November 30, 2020, No. 311n dated December 16, 2020). Here's what's changed:
- new accounts have been added to the certificate of availability of property and liabilities on off-balance sheet accounts (form 0503130);
- for Information on accounts receivable and payable (form 0503169) established new requirements for filling out KOSGU 560, 660, 730, 830;
- in Information on changes in balance sheets (form 0503173) included a new section.
Requirements for assessing objects
The federal standard did not ignore the assessment of fixed assets. He introduces new terms that distinguish between two types of possible operations on objects:
- Exchange transactions - assets are exchanged for money or other material assets; the cost of work performed, services provided or rights to use the asset can be taken into account towards the cost of the object. This exchange is based on the market value of the property. In exchange transactions, the object is valued based on the amount of actual costs.
- Non-exchange transactions - assets are transferred free of charge or for little money. In this case, the initial cost is determined based on the fair value of the object.
The founder must decide how to value different categories of objects, and the choice must be reflected in the accounting policies of the institution.
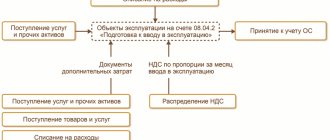
Authorization of expenses in budget accounting
A distinctive feature of accounting in government organizations is the mandatory authorization of expenses incurred. Transactions are reflected in special accounts PAS - 0 500 00 000. An account is used to reflect obligations of the current period and plan years. 0 502 00 000 “Liabilities”. Please note that it is necessary to register transactions only on the basis of documents confirming the fact of accepting a specific obligation. The list of such documentation that the organization uses in its activities should be fixed in the accounting policy.
Accounting entries for authorizing expenses of government organizations should be reflected in the context of creditors, contracts and agreements and other analytical indicators that are established for the accounting entity in its accounting policies. Consolidation and generalization of information, bypassing the organization of reliable analytical accounting, is unacceptable. Balances of accepted obligations at the end of the reporting year are subject to mandatory re-registration in the next period.
Current authorization transactions in a government institution with examples for 2021:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| The amount of obligations assumed under a contract concluded as a result of competitive methods of identifying suppliers, performers, and contractors | 0 502 07 000 | 0 502 01 000 |
| Operation in other cases of acceptance of obligations | 0 506 00 000 | 0 502 01 000 |
| Amounts accepted by the institution at the expense of previously formed deferred liabilities | 0 502 09 000 | 0 502 01 000 |
How to correctly prepare any accounting entries, read the article “Accounting entries: what they are and how they are used.”
How to group objects
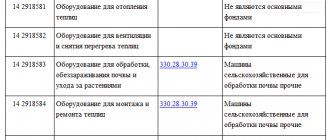
The federal standard introduces new principles for combining fixed assets. Instead of two groups (“Non-residential premises” and “Structures”), the new classification has one - “Non-residential premises (buildings and structures)”. In the new classification, there were also no separate groups for the library collection, soft furnishings, jewelry and jewelry; all these accounts are transferred to the “Other fixed assets” group.
Keep records according to the new rules in the program “Kontur-Accounting Budget”
But investment real estate is allocated - real estate, parts thereof or movable property intended for rental. The accountant should study which of the objects that are listed on account 01 will need to be transferred to the OS category.
| Instruction No. 157n (as amended on September 27, 2017) | Federal standard "Fixed assets" |
| 0 10101 000 “Residential premises” | 0 10101 000 “Residential premises” |
| 0 10102 000 “Non-residential premises” | 0 10102 000 “Non-residential premises (buildings and structures)” |
| 0 10103 000 “Structures” | 0 10103 000 “Investment property” |
| 0 10104 000 “Machinery and equipment” | 0 10104 000 “Machinery and equipment” |
| 0 10105 000 "Vehicles" | 0 10105 000 "Vehicles" |
| 0 10106 000 “Industrial and household equipment” | 0 10106 000 “Industrial and household inventory” |
| 0 10107 000 “Library fund” | 0 10107 000 “Biological resources” |
| 0 10108 000 “Soft inventory” 0 10109 000 “Jewelry and jewelry” 0 10110 000 “Other fixed assets” | 0 10108 000 “Other fixed assets” |
To correctly take into account OS according to the updated groups, objects must be moved: exclude objects from one group and include them in another. Their cost does not change.
Fixed assets between accounts are transferred one-time, based on the situation at the beginning of January 2021, through account 0 401 30 000 “Financial result of past reporting periods”. The basis for the transfer is an accounting certificate (form 0504833).
Which depreciation method to choose
With the introduction of the federal standard, the list of methods for calculating depreciation expanded, while Instruction No. 157n offered only the linear method. The federal standard offered more options. In total, the accountant has three methods for calculating depreciation.
- Linear method. It involves the accrual of equal amounts of depreciation monthly over the entire useful life (USI). To calculate the payment, you need to divide the initial cost of the object by the investment cost.
- Reducing balance method. Convenient for those objects that quickly become obsolete or are operated in difficult conditions, in an aggressive environment. The method allows for accelerated depreciation by applying an increasing factor from 1 to 3 to the annual amount. The residual value of the object is taken as a basis (costs of purchase and commissioning minus accruals already paid off at the beginning of the reporting year), the depreciation rate is also taken into account based on the SPI and wear indicator.
- Method of calculating the amount of depreciation proportional to the volume of production. The method is good for objects for which the production potential inherent in them is indicated (that is, it is clear how many products the object can produce over its entire service life). The calculation is based on the actual volume of products produced for the reporting period, multiplied by the depreciation rate (initial cost / estimated volume of products over the useful life).
The institution has the right to determine the depreciation method independently, taking into account the specifics of the activities, but the main criterion should be the potential economic benefit. The chosen method must be indicated in the accounting policy.
Important! The purpose of operating an asset may change, which means the organization must check whether the chosen depreciation method is appropriate. This must be done at the beginning of the reporting year. If necessary, the method can be changed, but previous accruals do not need to be recalculated.
Another innovation: the federal standard obliges to charge depreciation even on those objects that are idle, temporarily not used, or prepared for further write-off. The exception is objects whose residual value is equal to zero. Instruction No. 157n allowed to suspend the accrual of depreciation amounts during such periods.
The federal standard also shifted the initial cost boundaries for low-value operating systems. Objects worth up to 10,000 rubles are accounted for on an off-balance sheet account; depreciation is not charged on them. Previously, there was a limit of 3,000 rubles. For objects costing from 10,000 to 100,000 rubles, depreciation is equal to 100% of the original cost at the time of commissioning. A special rule for the library fund is that the amount of depreciation for objects of the library fund worth up to 100,000 rubles is calculated and accrued at 100 percent at the time of commissioning. For objects over 100,000 rubles, depreciation amounts are determined according to the method chosen by the institution. This limit was previously set at 40,000 rubles.
What has changed in reporting
The developers of the federal standard did not ignore reporting issues. As of January 1, 2021, accountants must report the book value of assets, depreciation method, accumulated depreciation, and more. It is important to reflect in the reporting changes in the valuation of objects in the reporting period, which will affect the SPI, and the depreciation method. In addition, it is necessary to provide a comparison of the residual value of the object at the beginning and end of the reporting period.
Maintain budget accounting and generate reports in the Kontur-Accounting Budget program
Information must be prepared for all groups of fixed assets, this applies to investment real estate, assets with zero residual value, idle facilities, etc. Before the FAS “Fixed Assets” came into force, the institution included reporting information only for some types of fixed assets. Now information about the amounts is reflected in the reporting, but not for all groups that are listed in the standard. Therefore, in the near future we expect changes to Instruction No. 157n, related, in particular, to accounts 0 10100 000, as well as the appearance of new lines in forms 0503168, 0503768, as well as balance sheet 0503130, 0503730. These changes will be reflected in the reporting for 2018.
Changes in accounting from 2021
One of the main innovations is an increase in the minimum wage. Since January, its value has been 9,489 rubles. The value of this indicator is linked to the size of the subsistence minimum determined for the category of the country’s working population. The rule of correlating the minimum wage and the cost of living will only be relevant if the cost of living increases. If the cost of living is adjusted downward, the minimum wage will remain at the same level.
An increase in the minimum wage will entail changes in accounting in terms of calculations for wages, certificates of incapacity for work and child benefits. From 2018, the temporary order of indexation of child benefits becomes permanent - the amount of these social payments will be adjusted by inflation annually from February of the new reporting period.
How to get started with the new standard
To properly implement FSBU, an institution must take several steps. And you should start with an inventory, which will give an idea of the state of fixed assets balances for correct accounting and application of the chosen depreciation method. It is necessary to check the property that was accounted for before January 1, 2021 on account 0 10100 000 for compliance with the standard. Having received data on objects that were previously reflected in off-balance sheet accounts or, according to some criteria, were not included in the fixed assets group, the accountant must put them on the balance sheet at their original cost.
Inventory results are standardly reflected in the Inventory List in the section on non-financial assets (form 0504087). It is important to mention that leasing objects, long-term lease with the right to buy, free (indefinite) use, and other rental payments are classified as NFA. For this purpose, by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 17, 2017 No. 194n, additional columns were introduced into the inventory form: status of the accounting object, target function of the asset. New columns in the inventory have also appeared for objects that, after the introduction of the standard, do not meet the criteria of an asset. They are also entered into the Statement of Discrepancies based on the inventory results (form 0504092).
This needs to be done in order to divide the fixed assets into groups, including highlighting the objects of the “Investment Real Estate” group (currently they are taken into account according to separate analytics on account 101 and behind the balance on accounts 25 and 26).
In conclusion, I would like to note that the reform in public sector accounting and all the accompanying changes are associated with a change in the key task. If previously it was important to build control over settlements with the budget, now the assessment of the capitalization of organizations and the quality of the assets themselves comes to the fore.