Legislation on ASF
The main legislative document is the Tax Code of Russia (namely its 169th article), which contains all the instructions and rules on the timing and procedure for drawing up, processing and submitting such an invoice.
In addition, many specific points relating specifically to the ASF are contained in the law “On Accounting” . Also, in case of any contradictions (for example, when filling out certain columns or indicating any information), you can refer to the messages of the Ministry of Finance related to to the real topic.
Definition of the concept
An advance invoice is a document that confirms that the buyer has transferred part of the money to the seller of goods (or service provider) in the form of an advance payment. It contains all the basic information about the parties to the transaction, as well as financial information (in particular, the amount transferred, the time when the payment was made, the product or service for which these funds were transferred).
In addition, such an advance invoice also reflects tax information, due to which it also serves to obtain the necessary deductions (for this it must be submitted to the tax service during the reporting period).
What does it mean for the buyer?
For the buyer, receiving an advance invoice means confirmation that the money he transferred in the form of an advance payment has been received by the seller (or supplier). It also means that the buyer can start using services or receive the necessary goods , since the advance payment has been successfully transferred.
In addition, it also gives the right to receive deductions (which, in fact, is its main purpose). To do this, upon receipt of this document, it must be immediately registered in the purchase book (untimely or incorrect registration of an advance invoice may subsequently lead to deprivation of rights to tax deductions).
Registration in the purchase book and sales book
When transferring an advance payment, entries in the sales book from the supplier and in the purchase book from the buyer are made in the period when the “advance” invoice is issued.
When shipping goods on account of prepayment, an entry in the supplier's purchase book is made during the shipment period. An entry in the buyer's sales book is also made in the period of shipment, and not in the period of transfer of the advance payment.
A prepayment invoice is recorded in the purchase ledger and in the sales ledger in the same way as a “regular” invoice. But there are features that need to be taken into account when filling out individual fields (see Table 2 and Table 3; for examples of filling, see the article “How to correctly fill out a purchase book and a sales book in case of prepayment, as well as when issuing an adjustment invoice” ).
table 2
Rules for filling out individual fields of the purchase book when registering an “advance” invoice
| Number | Name | Content |
| What entries does the buyer make when transferring the advance payment? | ||
| column 2 | Operation type code | 02 |
| What entries does the seller make when shipping goods and deducting previously accrued VAT? | ||
| column 2 | Operation type code | 22 |
| column 9 | Seller's name | data from line 2 of the “advance” invoice |
Table 3
Rules for filling out individual fields of the sales book when registering an “advance” invoice
| Number | Name | Content |
| What notes does the seller make when receiving an advance? | ||
| column 2 | Operation type code | 02 |
| What entries does the buyer make when shipping the goods and restoring the previously accepted deduction? | ||
| column 2 | Operation type code | 21 |
| column 7 | Buyer's name | data from line 6 of the “advance” invoice |
| column 8 | Buyer's INN/KPP | data from line 6b of the “advance” invoice |
Maintain purchase books and sales books for free in an accounting web service
For the seller
For the seller, this document also indicates the completion of the advance transaction and gives the right to make the necessary tax deductions. To do this, the seller, after he receives the established amount of the advance payment (advance payment) from the buyer, must prepare such an advance invoice (how to fill out the ASF?).
This should happen no later than 5 days from the moment the funds are credited. The document must be drawn up in two copies , after which it must be registered in the appropriate book.
If the invoice is drawn up incorrectly or is not registered, the company is deprived of its rights to deduction and may receive a fine from the tax authority.
Examples of using
ASF is issued when transferring advance payment for services or goods . For example: Alpha LLC transferred funds to Gamma LLC in the amount of 305,000 rubles for the upcoming renovation of premises.
After the required amount has been received into the account of Gamma LLC, the latter is obliged to draw up an ASF within five days (days in this case are taken as calendar days, that is, both Saturday and Sunday are included in them, so if the transfer arrived on Friday, the account must be completed before the end Tuesday).
After the document is drawn up, one copy remains with Alpha LLC, one copy with Gamma LLC, after which they are required to register them in their purchase/sale books.
This invoice will need to be submitted to the tax service no later than the end date of the current tax period. Thus, the advance invoice is intended mainly to record the transaction and its tax registration, and subsequently to exercise the taxpayer’s right to receive the necessary tax deductions.
The procedure for drawing up and processing this document is strictly established (the main points regarding the design and completion of the ASF, as well as its registration, can be found in Article 169 of the Tax Code of Russia).
In addition, the advance invoice must be drawn up no later than five days from the date of the transaction. If this is not done, then the rights to deduction may be lost, and the inspectorate, in turn, may issue a fine for lack of an invoice.
Types of Invoices
The concept and cases of using invoices are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in Article 169. It follows from it that 3 types of payment and settlement documents are currently used:
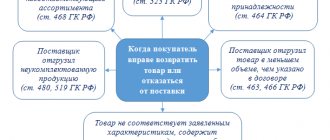
- The main or shipping is provided by the supplier to the customer upon delivery of goods, performance of work or provision of services, as well as during the legal transfer of rights from one economic entity to another. The description, format and content of such documents are regulated by clause 5 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- The prepayment is sent by the contractor to the customer if the latter has paid an advance for the goods, works or services supplied. The procedure for filling out is approved by clause 5.1 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- An adjustment is formed when the price or quantitative characteristics of the supply change. Information on settlement and payment documents is updated in the event of a decrease in the price of goods, work, services or the volume of supplied products. This type of document has been used since 2011 (245-FZ dated July 19, 2011).
Shipping and advance payments differ in the moment of preparation. A shipping invoice is issued upon completion of delivery of products, performance of work or provision of services, while advance payment is subject to prepayment. There are significant differences in the content of such settlement documents, because prepayment invoices are drawn up even before the actual delivery. Some of the information to be included in the form is simply missing.
NTVP "Kedr - Consultant"
LLC "NTVP "Kedr - Consultant" » Pravo-info » Articles from magazines » ADVANCE PAYMENT AND SHIPMENT IN ONE QUARTER: WHAT TO DO WITH VAT?
Zatsepin A.V.
Often, organizations receive advance payment against future deliveries and fully ship the goods in the same quarter. Many people believe that in such a situation there is no need to charge VAT on the prepayment amount. Let's see if this is really the case and what risks arise in this situation.
Federal Tax Service: advance tax must always be calculated
Having received an advance payment, you are obliged to calculate VAT on the received amount at the calculated rate <1>, and no later than 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment, issue an advance invoice <2>.
That is, strictly speaking, according to Chap. 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon receipt of an advance payment, tax must be calculated regardless of when the shipment takes place.
However, on the date of shipment, which, as we have agreed, falls in the same quarter as the advance payment, you must:
— calculate VAT on the cost of shipped goods <3>;
— draw up a shipping invoice <4>;
— deduct VAT from the advance payment and register the advance invoice in the purchase book <5>.
If the advance amount and the cost of the goods coincide, then in the end the advance VAT payable to the budget is 0 rubles. Hence the temptation not to charge it at all. But the Federal Tax Service is against this. In their explanations, tax officials, literally interpreting Ch. 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, indicate the obligation to charge VAT and issue an invoice both upon receipt of an advance payment and upon shipment <6>.
Ministry of Finance: calculate VAT if there are more than 5 days between advance payment and shipment
In general, the Ministry of Finance agrees with the position of the Federal Tax Service, but with some reservations. So, according to officials:
<if> the goods will be shipped within 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment, then advance invoices should not be issued <7>. Moscow tax officials expressed a similar opinion <8>;
<if> the period between prepayment and shipment is more than 5 days, then it is necessary to charge tax and issue invoices for the advance payment. Even when payment and shipment occurred in one quarter.
Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation: advance payment received in the quarter of shipment is not considered
The Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in 2006 indicated that for VAT purposes an advance payment received in the same tax period when the goods were shipped is not recognized as an advance payment. True, at that time the matter concerned the calculation of VAT on export prepayments <9>.
The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation voiced a similar position in 2009 on the issue of the possibility of deducting VAT on an invoice that does not indicate the payment document number, despite the fact that the advance payment and shipment occurred in the same quarter <10>. And although since then Ch. 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has changed significantly; some courts consider the approach of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation to be universal and support sellers who do not calculate VAT on advances in this case <11>.
Which option should you prefer?
The approach of the Federal Tax Service is most consistent with the letter of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and does not bear any financial risks.
Proponents of a different approach who decide to simplify document flow should be prepared for claims from tax authorities. Yes, maybe they will be able to convince the court that advance VAT could not have been charged, but how much time and effort will they spend on these convictions? It turns out to be an argument for the sake of an argument.
Meanwhile, based on the results of the audit, tax authorities may charge non-payment of VAT on the advance payment. And this means collecting tax, penalties, and maybe a fine in the amount of 20% of the tax amount <12>. After all, having calculated the tax on the prepayment for you, the tax authorities will not take into account the due deductions of the advance VAT. And, according to the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, this is legal, since the taxpayer, having the right to apply deductions, did not take advantage of this right. In other words, if you need a deduction, declare it in your declaration <13>. Tax authorities have already adopted this position of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation <14>.
And in order to claim a deduction from the advance payment, you will still have to first charge VAT <15>.
This means that if the tax authorities make a claim, then they will have to declare both the accrual of VAT on the prepayment and the deductions of the same amount upon shipment in an updated declaration <16>. Therefore, a fair question arises: why not do this right away and why bring it to conflict?
You may also be charged with failing to provide advance invoices. This is a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income, expenses and objects of taxation, the fine for it is <17>:
<or> 10,000 rubles, if advance invoices were not drawn up within one quarter;
<or> 30,000 rubles, if invoices were not drawn up in two or more quarters.
How legal this is, the courts do not have a unanimous opinion. Some consider the fine to be legitimate <18>. Others, on the contrary, point out that the mere absence of invoices, provided that prepayment amounts are included in the tax base, is not a gross violation of accounting rules <19>. The absence of one invoice cannot be considered such a violation, because the Tax Code refers to the lack of invoices in the plural, that is, two or more <20>.
Also note that if you preferred the approach of the Ministry of Finance and did not issue advance invoices because the shipment took place within 5 days after receiving the advance, then during a tax audit, letters from the financial department will protect you from a fine <21>.
Although, in general, the paucity of arbitration practice may indicate that fines are extremely rare just for the lack of invoices.
* * *
In general, it is better to charge advance VAT and issue advance invoices - peace of mind is more valuable.
——————————-
<1> clause 1 art. 154, sub. 2 clause 1, clause 14 art. 167 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<2> clause 3 art. 168, clause 5.1 art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<3> sub. 1 clause 1 art. 167 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<4> clause 3 art. 168, paragraph 3 of Art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<5> clause 8 art. 171, paragraph 6 of Art. 172 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<6> Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 20, 2011 N ED-4-3/11684, dated March 10, 2011 N KE-4-3/3790
<7> clause 1 Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 03/06/2009 N 03-07-15/39
<8> Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated May 26, 2009 N 16-15/052780
<9> Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 27, 2006 N 10927/05
<10> Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 10, 2009 N 10022/08
<11> Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service dated September 12, 2011 N A57-8868/2010, dated September 7, 2011 N A57-14658/2010
<12> clause 1 art. 122 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<13> clause 1 art. 80 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated April 26, 2011 N 23/11
<14> Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2011 N SA-4-7/ [email protected]
<15> clause 8 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service dated January 26, 2010 N A55-6564/2009
<16> Art. 81 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of September 12, 2011 N A57-8868/2010; FAS DVO dated November 28, 2008 N F03-4597/2008
<17> pp. 1, 2 tbsp. 120 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
<18> Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central Election Commission dated June 22, 2006 N A14-28631/2005/1202/24
<19> Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service ZSO dated February 20, 2007 N F04-504/2007(31371-A67-31)
<20> clause 3 art. 120 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northern Territory of February 25, 2003 N A56-25760/02
<21> Art. 106, paragraph 2 of Art. 109, sub. 3 p. 1 art. 111 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 35 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 28, 2001 N 5
First published in the magazine "Glavnaya Ledger" 2012, N 2
What is it needed for
In one of the articles, we talked in detail about what a regular invoice is needed for and how to fill it out. In this article we will figure out what is an advance invoice? The unified invoice form approved by RF PP No. 1137 is the same for both cases of prepayment and for payments for the sale of delivered products, the actual performance of work or the provision of services. To answer the frequently asked question, what kind of document is this - why is an advance invoice for buyers needed and how to draw it up correctly, it is necessary to define an advance invoice.
The advance invoice is a direct legal basis for the fact of exemption from the tax burden and the customer’s acceptance of the amounts of value added tax claimed for deduction. An advance invoice is a component of payment documentation that is presented by the seller for funds paid by the customer as an advance payment.
According to the rules approved by the current tax legislation. When an invoice is issued for an advance payment by the supplier, it is regulated by clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, it must be issued within 5 days after the customer transfers the advance amounts. Based on the documents received from the supplier, the buyer has the right to deduct VAT from the amount specified in the prepayment document when making mutual settlements with the budget and transferring tax payments (Clause 12 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If, when making an advance payment, the customer has not received the proper documentation from the seller, VAT in the advance report without an invoice is deducted, provided that the seller is also a value added tax payer. To do this, you must attach to the report a cash receipt or a receipt order, in which the VAT for this operation will be indicated as a separate line.
An advance invoice has the legal force equal to the shipping invoice. The form in which documents are drawn up is also uniform. It was approved by Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011 (Appendix No. 1 to RF PP No. 1137). The only difference is the content and amount of information that is entered into the document issued on an advance payment basis.
Advances for utilities without an invoice
If the supplier, after receiving the advance payment, does not issue an invoice to the buyer, this is a violation of the procedure established in paragraphs 1 and 3 of Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But to hold the supplier liable under Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax inspectorate can do so only if he did not issue an invoice at all when receiving the advance payment. If the supplier followed the procedure that was in force before January 1, 2009 (when receiving an advance payment, he wrote out an invoice in one copy and took it into account in the Sales Book), it will not be possible to attract him under this article. After all, he will have an invoice for the advance payment in his hands. And for the fact that he did not send another copy to the buyer, the current legislation does not provide for liability.
The organization makes prepayments to suppliers for communication services, gas, electricity, etc. However, prepayment invoices have not been received from all suppliers. Is failure to issue invoices for advances received a violation? How is this situation reflected in the buyer’s accounting?
08 Feb 2021 juristsib 2527
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Who is entitled to Chernobyl payments in the Belgorod region
- What benefits are provided if the husband does not work 2020
- List of Benefits for Chernobyl victims in 2021 What payments are provided
- Bill on early release under Article 228, Part 4 in 2020
When is an advance invoice issued?
The rules for issuing invoices for advance payments are regulated by Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the supplier is obliged in any case to issue an invoice to the buyer if he pays an advance, and this must be done within five days. Prepayment can come in both monetary and material form.
But tax legislation provides for a number of exceptions in which prepayment invoices are not issued:
- Delivered goods, works, services are not subject to VAT under Art. 149 and paragraph 2 of Art. 146 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- delivery is subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (clause 1, article 164);
- goods, works or services have a positive cycle of the production process (Government List No. 468 of July 26, 2006);
- goods, works and services are sold outside the Russian Federation.
At the moment, there is no liability for failure to provide an advance payment from the supplier on time. But if the supplier does not provide the required document within the allotted five days, the customer has the right to go to court and, after a court decision, receive the necessary documentation.
VAT calculation
If an enterprise applies a general taxation system, then it is obliged to issue invoices to its customers.
This document reflects the “outgoing” VAT, which is then deducted from the “incoming” VAT. Thus, taxation on this tax occurs.
As a general rule, the VAT tariff rate is 18%. These funds are included in the cost of the product/work/service.
But when an invoice is issued, you need to indicate on a separate line:
- Unit price excluding tax.
- The amount of VAT.
- Unit price including VAT.
The amount specified in the document will be applied by the opposite party to the transaction as “input” for offset, and by the seller – as “output” VAT for offset.
Based on these documents, the amount of tax payable to the budget will be calculated, so you should be very careful when filling it out.
In Moscow and the region they will not refuse a deduction without an advance invoice
We interviewed tax inspectorates in Moscow and the Moscow region to find out how local inspectors resolve the most popular issues regarding advance invoices. In the territorial tax inspectorates, we found out, firstly, whether it is possible to deduct VAT on a shipment invoice if the seller did not issue an advance invoice. And secondly, will the inspection fine a seller who has not issued an advance invoice (for example, if prepayment and shipment occurred within five days).
Lucky companies that are registered with the capital's Federal Tax Service No. 14, 17
and
21
.
Here, failure to issue an advance invoice when the difference between shipment and payment is five days is not considered a violation. But the most advanced inspectors work in the capital’s inspections No. 1, 5, 13, 21
and in the Moscow Region
Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service for the city of Dmitrov
. Here they believe that advance invoices are not needed at all if shipment and payment occurred during the same tax period and the lack of documents did not result in a reduction in the tax base.
We recommend reading: What are paid rewards?
Formation order
The procedure for issuing an invoice for prepayment is enshrined in the RF Government Regulation No. 1137 dated December 26, 2011. Each completed invoice must indicate its unique serial number, date of compilation, full and short names, address, INN and KPP, details and legal form of both parties. If funds in the account are deposited in intangible form, this is also indicated.
In the tabular part, information about the product is entered - its name and physical characteristics. When describing the goods, the word “advance” is indicated in the first column in brackets. In columns 2 to 6, dashes are entered; they are filled in only in the event of actual delivery of the goods.
If an advance payment is made by the customer before determining the exact name of the purchased goods, work performed or services provided, column 1 (product name) indicates the general name of the purchased items (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-09/22 dated July 26, 2011).
In column 7, the VAT tax rate is entered in the format 10/110 or 20/120 due to the fact that when making an advance, the tax is allocated from the amount and is not charged. Column 8 contains the calculated tax amount. Cell 9 indicates the advance amount. Columns 10-11 are not filled in with indicators; dashes are placed in them.
IMPORTANT!
Value added tax must be indicated in ruble-kopeck format, without rounding. This is stated in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-07/18585 dated April 22, 2014, as well as in the regulations for filling out settlement documents by RF PP No. 1137.
The remaining columns are not filled in, since at the prepayment stage there is not enough information to enter into the form cells (clause 5.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
We remind you that shipping calculations and advance payment forms differ significantly in their content. Payment documents for prepayment contain less information, and the requirements for registration are not so strictly regulated. The most important difference is the format for indicating VAT, since in this case it is separated from the advance payment.
Despite the less stringent design rules, remember that the prepayment invoice is a legal document that is important for the tax authorities when carrying out the procedure for deducting value added tax.
The prepayment document is prepared in two copies - one for each party, signed by the manager and chief accountant (if any) and handed over to the buyer.
Basic data
In column 1 of the main table, you should indicate the name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights (subparagraph “a”, paragraph 2 of the Rules for filling out invoices), for which an advance was received. Since this is a requirement of the legislator, you cannot write single phrases on the advance invoice, for example, “advance payment” or “advance for goods.”
You need to understand that accounting software developers can automatically insert common phrases into column 1 when preparing an advance invoice when printing. You should not trust this and succumb to the temptation to leave “everything as it is”; it is better to correct the information with the correct data manually.
The name of goods (works, services), property rights can be taken from the paragraph where the subject of the contract is described, as recommended by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in letters dated March 6, 2009 No. 03-07-15/39 and dated February 25, 2009 No. 03- 07-14/26. If the contract contains a reference to a specification with a large number of names, then it is not prohibited to write the general name of the group of goods. Additionally, in this column you can indicate the details of the contract. For example, prepayment (advance payment) for office supplies under agreement No. 15 dated January 25, 2021. The main thing is that you can clearly identify the purpose of the advance. Otherwise, there may be a risk that the buyer will not be able to claim VAT deduction on such a document.
When simultaneously issuing an advance invoice for the supply of goods and performance of work (provision of services, property rights), it is necessary to reflect both the name of the goods and a description of the work (services, property rights).
For example, prepayment (advance payment) for the supply of office furniture, delivery and assembly of furniture under agreement No. 20 dated January 18, 2019.
If the sale of goods (work, services, property rights) for which an advance was received is taxed at different VAT rates, then in the document they must be shown in separate lines, with each line indicating its own tax rate and amount. Please note that previously the Russian Ministry of Finance expressed an opinion according to which it allowed the advance payment to be indicated in one line, highlighting the maximum VAT rate of 20/120 and the tax amount (letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated March 6, 2009 No. 03-07-15/39).
It should also be noted that the words “advance” or “prepayment” themselves may not be indicated in column 1, since the invoice for an advance payment is easy to distinguish by the rate; it is always indicated by the calculation method.
In the advance invoice, columns 1a, 2, 2a, 3, 4, 5, 6 are not filled in, since the need for this is not mentioned in paragraph 5.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You can safely put dashes in these points.
In column 7 you need to enter the estimated rate - 10/110 or 20/120 (clause 4 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In column 8, indicate the amount of VAT on the advance payment. If several advance payments have been received, you can enter the total amount.
In column 9 you need to enter the full amount of the advance.
Advance invoices are signed by the same persons as during the shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights).
Accurate document flow
The advance invoice must be drawn up in two copies: one copy for yourself, and the second for the buyer. Be sure to register your copy in the sales book (clause 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book), the buyer must do the same (clause 21 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book).
It must be remembered that the supplier is obliged to transfer the VAT allocated in the advance invoice to the budget, and the buyer has the right to submit it for deduction (clause 9 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that if you are a buyer and you have doubts about the correctness of the document, and the supplier does not meet you halfway and refuses to redo the papers, then you have the right to protect yourself and not claim VAT on it for deduction.
At the time of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights), the parties to the transaction once again register an advance invoice. This time, the supplier makes an entry in the purchase ledger and the buyer makes an entry in the sales ledger. It is not allowed to make reversing entries in the books, since amounts with a minus are not provided for by the filling rules. The VAT allocated in the advance invoice can be deducted by the supplier (clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The buyer, in turn, is obliged to restore the previously accepted deduction (subclause 3, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and pay tax to the budget.
A special case
An invoice for an advance payment may not always be issued. For example, if the shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) was made within five days after the advance payment, then according to the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 18, 2017 No. 03-07-09/1695, an advance payment document is not required. This is confirmed by other letters from the department - dated October 12, 2011 No. 03-07-14/99 and dated March 6, 2009 No. 03-07-15/39. But there is another opinion. It was expressed by the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
According to the point of view of tax authorities, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the exemption of the seller from issuing an advance invoice (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 10, 2011 No. KE-4-3/3790).
Also, subparagraph 1 of paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that when performing transactions for the sale of goods (work, services), property rights to persons who are not VAT taxpayers, and to payers exempt from fulfilling taxpayer obligations related to the calculation and payment of tax , with the written consent of the parties to the transaction, invoices are not drawn up. This norm applies to buyers using the simplified tax system (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-07-09/1380), as well as to all those who fall under the definition given in Article 145 of the Tax Code “Exemption from duties taxpayer."
When exporting goods taxed at a zero rate, an advance invoice is also not issued, since, according to paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code, the tax base does not include payment received by the company for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), which are taxed at a tax rate of 0% in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and if there is no tax base, then, accordingly, there is no VAT on it.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that, according to paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, errors in invoices that do not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the seller, buyer, property rights, names of goods (works, services), property rights, their value, as well as The VAT rate and the amount of tax presented to the buyer are not grounds for refusing to accept tax amounts for deduction.
Prepayment and shipment in one quarter. Do I need an advance invoice?
(Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 16, 2012 No. VAS-17397/11 “On refusal to transfer the case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation”)
According to paragraph 3 of Art.
168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , upon receipt of payment amounts (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of
goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) sold on the territory of the Russian Federation, the corresponding
invoices are issued
no later than five calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the specified amounts payment (partial payment).
According to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods, taxpayers are required to issue invoices
for the specified funds
, regardless of what tax period the prepaid goods are shipped
.
At the same time, if the shipment
goods are carried out
within five calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of advance payment
(partial payment),
invoices
for advance payment (partial payment)
are not required
to be issued
to customers (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2011 No. 03-07-14/ 99).
However, tax officials do not agree with the Ministry of Finance.
In a letter dated March 10, 2011 No. KE-4-3/3790, the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation indicated that, regardless
from the fact that within five calendar days after the VAT taxpayer receives an advance payment for the upcoming supply of goods (work, services) falling within the same tax period or for different tax periods, the goods (work, services) are shipped, invoices
are issued in two copies both for the amount of the prepayment received, and for the shipment of goods
(work, services) against the specified prepayment.
If
If the VAT payer - the seller,
within five days from the date of receipt of the advance payment
for the upcoming supply of goods (work, services) in one tax period,
these goods (work, services)
are shipped then the corresponding invoices are registered in the sales book
.
Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation
in resolution No. 10022/08 dated March 10, 2009, he indicated that for the purposes of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation,
an advance payment received by the taxpayer in the same tax period in which the actual sale of goods took place cannot be recognized as an advance payment
, since, according to
paragraph 1 of Art.
54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers-organizations calculate the tax base at the end of each tax period on the basis of data from accounting registers and (or) on the basis of other documented information about objects subject to taxation or related to taxation.
Payments made in the same tax period with the shipment of goods
, for the purposes of applying Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
are not considered advance payments
.
To which the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, in a letter dated July 20, 2011 No. ED-4-3/11684, reported that with regard to the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated March 10, 2009 No. 10022/08, this dispute was considered regarding the application of the provisions of Art. 169, 171-173 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
when using VAT deduction in September 2004 on invoices in which payment order numbers were not indicated.
Based on the results of consideration of the case materials, the court concluded that since payment for services was made for the current month in accordance with the settlement procedure established by the contract, there is no reason to consider payments on disputed invoices to be advance payments; accordingly, the supplier had no obligation to indicate the number of the payment and settlement document when processing invoices.
In this regard, extend this resolution to the application of the norm of paragraph 12 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
, effective from 01/01/2009, there are no grounds.
In the commented Determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, he again returned to this controversial topic
.
The court indicated that for the purposes of Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an advance payment received by the taxpayer in the same tax period in which the actual sale took place cannot be recognized as an advance payment.
goods, since according to
paragraph 1 of Art.
54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers-organizations calculate the tax base at the end of each tax period on the basis of data from accounting registers and (or) on the basis of other documented information about objects subject to taxation or related to taxation.
Therefore , if the shipment of goods occurred in the same period with receipt of payment
on account of the upcoming delivery, then, since such payments cannot be considered advance or other payments on account of the upcoming supplies,
the supplier does not have the obligation to calculate VAT twice on the above amounts for the disputed period
.
However, despite extensive arbitration practice, regulatory authorities do not change their position.
Therefore, issuing an invoice for prepayment is safer.
An invoice for advance payment must be issued in 2021
21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (paragraph 1, clause 1, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). We will tell you when you need to issue an invoice for an advance payment in our consultation. 2 tbsp. 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, as a general rule, the earliest of the following dates is recognized as the moment of determining the tax base (clause
As a general rule, an invoice for an advance payment for 2021 must be drawn up in two copies on paper and (or) electronically no later than five calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment (p. Individual entrepreneurs, regardless of the taxation system applied, are required to pay contributions for themselves to the OPS and compulsory medical insurance.
Interested in forgot to issue an invoice consequences
At the same time, we draw your attention to the fact that, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, errors in invoices and adjustment invoices that do not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the seller, the buyer of services, the name of the services, their cost, as well as the tax rate and the amount of tax presented to the buyer during a tax audit, are not grounds for refusal in accepting tax amounts for deduction. Failure to comply with invoice requirements not provided for in paragraphs 5 and 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation cannot be a basis for refusing to accept for deduction the tax amounts presented by the seller.
Thus, if a change in the cost of services provided occurred as a result of the fulfillment of certain terms of the contract, according to which the price and (or) quantity (volume) of services provided changes, an adjustment invoice is issued. Such invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the date of drawing up the documents specified in clause 10 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Registering an advance invoice
Currently, accountants have the opportunity to register advance invoices in the book of purchases and sales (clause 2 of Appendix 5 of Government Decree No. 1137). If the customer received an invoice from the supplier based on the prepayment, then such a payment document can be reflected in the current purchase book. The contractor himself indicates the account in the sales book. When sellers have received advance payment for goods, works or services supplied, they must enter an invoice for the advance in their purchase ledger.
This news will significantly simplify the procedure for presenting documentation for deduction of value added tax. It does not matter how the payment is made - cash or non-cash. But if mutual settlements for goods supplied, work performed or services rendered are made in a non-cash form, then the advance invoice is not recorded in the purchase book.
The Ministry of Finance has revealed the secrets of processing advance invoices
By the way, let us draw your attention to the fact that the Ministry of Finance only allowed not to issue advance invoices to buyers, but did not say that sellers should not prepare them at all. And if the seller does not prepare invoices for the advances received, then he may be held liable for the lack of invoices in the form of a fine of at least 5,000 rubles. <3> Moreover, the fact that the absence of an advance invoice did not affect the amount of tax calculated for payment to the budget, for example, if the receipt of the advance and shipment occurred in the same quarter, will not matter. Moreover, there is no need to use this explanation if the advance payment and shipment occur in different quarters.
RULE 2. If the supply contract provides for an advance payment condition, but the specific amount is not specified in the contract, then the amount of VAT calculated by the seller from the prepayment and indicated by him in the advance invoice is taken for deduction. Thus, in order to easily deduct VAT from an advance payment, it is better to only establish in the contract the possibility of its transfer, but not indicate a specific amount.
Deadlines for document issuance
First, let's look at in what cases and when exactly you need to issue an invoice.
Drawing up a document is necessary to reduce the amount of tax under Article 166 based on Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
First of all, it should be clarified that the taxpayer’s right to a tax deduction is obtained when 3 conditions are met. Conditions for receiving a tax deduction :
- Services, works or goods are accepted for accounting.
- The object of the transaction is used in activities subject to VAT.
- There is an invoice for the transaction object.
These points are specified in paragraphs 5 and 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are the basis for tax refunds and deductions, while the deadlines prescribed in paragraph 3 are advisory requirements. All tax deductions for tax amounts that do not contradict Article 172 of the Tax Code are accepted for registration if the appropriate documents are available. If the basic regulations for entering purchases into the book and storing invoices are observed, the date of preparation is not significant.
The main nuances are that the date cannot be entered before the transaction is actually completed and preferably is in the same tax period as the main transaction.
The payer may be fined for failure to issue an ESCF from January 1, 2020
Igor Skrinnikov recalled that in accordance with the Tax Code of Belarus, from January 1, 2021, only electronic invoices will be used to make VAT calculations and apply tax deductions. Administrative penalties may be applied to payers who do not issue (send) ESFF.
Payers who do not issue (send) ESFF from January 1, 2021 may be subject to administrative penalties in accordance with Article 13.8 of the Administrative Code. This was announced at the press conference “Taxation 2020: the most important changes in legislation” in the BelTA press center, the head of the main department of taxation methodology for organizations of the Ministry of Taxes and Duties of Belarus, Igor Skrinnikov, answering a question from a GB.BY correspondent.
We recommend reading: Down Payment on Social Mortgage 2020 Naberezhnye Chelny
How are the date and number entered?
Various dating options are used to create invoices:
- dating the date of actual provision of services, delivery of work or shipment of goods;
- indicating a date later than the day the service was provided;
- entering the date in the date column after the required 5-day period has expired;
- invoices are issued prior to the completion of the transaction.
The most preferable dating method for the seller and buyer would be to indicate the same date in all documents, which simplifies the procedure for submitting it to the tax office and reconciling it with primary documentation.
In this case, almost simultaneously with the implementation of the trade transaction, the right to tax deduction begins. In practice, this ideal option is often not used due to the significant document flow of enterprises and delays in the transfer of tax documentation between counterparties.
Standard registration practice is to adhere to a 5-day deadline. This corresponds to the requirement of Article 168 of the Tax Code that invoices are issued no later than 5 days from the date of the transaction. In the case of a long-term rental agreement, this day is considered the last day of the paid month.
This option is considered inconvenient for the tenant, since he receives the deduction only after a month, but according to the law, this practice is considered optimal. In long-distance trade, there may be situations where the buyer receives invoices late.
Sometimes tax authorities try to impute this circumstance to justify the refusal of a deduction, but legislative norms state that if the basic conditions are met, a deduction is made. In case of disputes, the argument will be the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-11/107 dated June 23, 2004 .
It should be remembered that such a situation is a violation, accept the requirements of Article 54 of the Tax Code for correcting tax returns and, if possible, provide evidence of innocence, for example, the stamp date of received correspondence. Sometimes situations occur when, after transferring the advance payment, the buyer asks to immediately prepare tax documents.
Such actions before the completion of the transaction are contrary to existing norms and are more undesirable than delays in drawing up. 3, paragraph 169 of the article indicates that invoices are drawn up for completed transactions, and according to 8, subparagraph 1, paragraph 6 of article 6 of the Tax Code, regulatory acts drawn up in violation of the requirements for them are invalid.
It is advisable for the seller to draw up an act after the transaction . He is not responsible for compliance with completion deadlines, unless otherwise specified in the contract, and the only applicable sanction will be a buyer’s fine under Article 120 for gross violation of accounting rules.
When is it processed - within 5 calendar or working days?
Invoices are issued within 5 calendar days after the goods are transferred according to the delivery note. Therefore, the date of the document can be indicated:
- date of preparation of the invoice;
- date of receipt of payment for work or service;
- any of the 5 working days following these dates.
It is unacceptable to issue an invoice before the actual completion of the transaction, as this will serve as a basis for denying the buyer a deduction.
You will find more information about the timing of issuing an invoice to the buyer in this material.
The date of receipt of an invoice received later than the statement may not be confirmed in accordance with FAS Resolution No. A81-4911/2012 dated October 7, 2013. You can apply for a deduction within 3 years after the transaction . According to paragraph 2 of Article 173. Since January 1, 2015, this point has also been confirmed by paragraph 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Should the dates of issue of the advance document and the certificate of completion of work coincide?
In cases of delay due to the fault of any party or postal organization, you can submit VAT during the period of receipt of the late invoice or clarify the submitted declaration. The Financial Department recommends using the first option, as it has repeatedly explained in letters.
From the point of view of the tax service, delays in filing an application for a deduction are even desirable for it, since the violator’s budget is naturally covered from inflation. There are no consequences for delays in drawing up invoices of an unsystematic nature .
In order to avoid unpleasant situations with late receipt of an invoice from the seller, it is recommended to stipulate this point in the supply agreement, since according to the law, only the buyer is responsible for the timeliness of preparation according to Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What happens if there is a mismatch?
Invoice errors in numbering and dating do not need to be corrected, since they are not critical and do not interfere with deduction, according to the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-07-09/42466 dated 10/11/2013. Violation of the rules in numbering and dating does not have consequences for either the seller or the buyer, and such documents are valid if drawn up in accordance with the basic requirements.
Discrepancies do not interfere with identification during inspection, and the inspector does not have the right to impose sanctions for them.
Invoice deadline
If you cooperate with the buyer and the contract provides for constant deliveries, then you can issue a single consolidated invoice for the entire volume of products supplied. In this case, there is no need to issue invoices for each delivery. Unified consolidated invoices are usually issued by suppliers of electricity, communication services, etc., since the supplier provides services constantly and continuously.
Porcelain Lux LLC sells tableware (sets of tea and coffee sets). In September 2021, Porcelain Lux, according to one of the concluded contracts, shipped a batch of services, and, by agreement with another buyer, received an advance payment for the upcoming delivery. For generalized information about the timing of shipment of goods and receipt of advance payment, see the table.
Responsibility for violating the rules
Since an invoice is a primary accounting document, liability for incorrect execution will be exactly the same as for incorrect execution of any other primary document.
According to the provisions of Art. 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer bears the following responsibility for its incorrect registration:
| If the offense is noticed during one tax period | then a fine of 10,000 rubles will be imposed on the payer |
| If the offense is noticed over several periods | then a fine of 30,000 rubles will be imposed |
| If the offense led to the fact that the VAT tax base was underestimated | then the fine will be equal to 20% of the unpaid amount. But it cannot be less than 40,000 rubles |
The taxpayer will be held accountable after an inspection is carried out by Federal Tax Service inspectors and an order to impose a fine is issued. If the fine is not paid on time, penalties will be assessed on this amount.
Video: useful information
Correct completion of invoices is the key to correct VAT calculation.
It is not for nothing that this tax is considered the most difficult in Russia, therefore its calculation, as well as the registration of primary documents, must be approached with all responsibility. Otherwise, large fines cannot be avoided.