Changes in the cost of shipped goods, services and works are possible both downward and upward. In this case, the seller issues an adjustment invoice to the buyer. Let's look at how to make cost adjustments in buyer and supplier accounting.
You will learn:
- how to post an adjustment invoice in 1C 8.3 in the seller’s accounting;
- how to enter a correction invoice in 1C 8.3 from a supplier in the buyer’s accounting.
For more details, see the online course: “Accounting and tax accounting in 1C: Accounting 8th ed. 3 from A to Z"
Purpose of a correction invoice
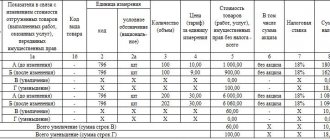
An adjustment invoice is issued by the seller when there is a change in the cost of goods shipped by him (work performed, services rendered, transferred property rights), if such clarification is associated with an increase or decrease in the price or quantity (volume) of products already sold (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). The document indicates the old and new value of goods (work, services, property rights) and the amount of change in this value. If the cost of 2 or more delivery lots has changed, then in this case you can issue either an adjustment invoice separately for each original document, or a single adjustment invoice. If such a change is repeated, a new adjustment invoice is issued, into which data from the previous adjustment document is transferred to compare the cost (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/05/2012 No. 03-07-09/127, dated 12/01/2011 No. 03-07-09/ 45, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 10, 2012 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
However, it should be remembered that before issuing an adjustment invoice, the seller must notify the buyer of a change in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered, property rights transferred) and obtain his consent to such a change.
ConsultantPlus experts spoke about the rules for filling out an adjustment invoice. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Return of goods as a new sale
When the buyer records the purchased goods, he becomes its owner. Although, as we have already found out, this is not an obstacle to a return if the parties agreed on it within the framework of a valid contract.
In a letter dated August 24, 2021 No. 03-07-14/73988, the Ministry of Finance indicated a situation where a refund on an adjustment invoice is not possible.
This procedure does not apply if there are indications that the goods are essentially being resold. That is, a new deal is concluded. And in this new transaction, the former seller is the buyer, and the former buyer is the seller.
To formalize the return of goods as a new sale, the seller and buyer must necessarily enter into a new sales contract or supply agreement. Otherwise, the former seller will not be able to deduct VAT upon receipt of the returned goods.
Also, the new seller prepares a new invoice and registers it in his sales book. The former seller can deduct VAT on returned goods based on this invoice, just as a regular buyer can deduct input VAT.
A deduction for the return of goods (work, services), registered as a new sale, can be applied within 3 years after their acceptance for registration (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As you can see, this condition for deducting VAT on actually returned goods is much softer.
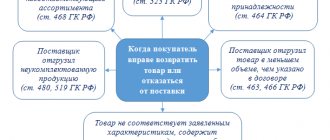
When is a correction invoice needed?
The seller of goods (works, services) must issue an adjustment invoice in the following cases:
- after shipment of goods (transfer of works, services) when clarifying the price, if the shipment of products was carried out at a preliminary price, and there was an agreement with the buyer that the final price would be determined later (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 31, 2013 No. 03-07-09/1894, dated January 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/39);
- when returning to the seller goods that were not accepted for registration by the buyer, for example, low-quality goods or when a defect is discovered (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/10/2012 No. 03-07-11/280, dated 08/07/2012 No. 03-07-09/109, dated 02.03.2012 No. 03-07-09/17, dated 02.27.2012 No. 03-07-09/11, dated 20.02.2012 No. 03-07-09/08, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05.07.2012 No. AS-4-3 / [email protected] );
- upon disposal of low-quality goods by the buyer, agreed with the seller, even if the goods have been capitalized (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 13, 2012 No. 03-07-09/66);
- when returning goods from a buyer who is not a value added tax payer, if the goods have already been accepted by him for registration (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 31, 2012 No. 03-07-09/96, dated July 24, 2012 No. 03-07-09/ 89, dated 07/03/2012 No. 03-07-09/64, dated 05/16/2012 No. 03-07-09/56);
- if the buyer discovers a discrepancy between the quantity of goods received and the quantity indicated by the seller in invoices and invoices, for example, a shortage (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/48, dated March 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/22 , Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01.02.2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] , dated 12.03.2012 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] );
- if there is a discrepancy in the volume of services (work) accepted by the customer compared to the quantity specified by the contractor in acts and invoices when the cost of these services (work) changes as a result of clarification of the quantity (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01.02.2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
About what documents are used to document the fact that the received goods do not correspond to the quantity or quality reflected in the shipping documents, read the material “How to draw up a report of non-conformity of the delivered goods?”
What should I do if there are errors in the adjustment invoice? The answer to the question is in ConsultantPlus. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
If the buyer does not pay VAT
What should the seller do when the goods are returned by a buyer who is not a VAT payer?
In this case, you need to properly arrange the paperwork.
- When returning the entire batch of shipped goods, the seller must register in the purchase book the invoice that was previously issued by him when the goods were shipped and recorded in the sales book. This must be done in the period in which adjustments related to the return of goods were made.
- If the buyer returns part of the purchased goods, the seller must issue an adjustment invoice for the cost of this goods. Based on it, the seller reduces his tax obligations in relation to the sale of the returned part of the goods.
- If a buyer, an individual, returns goods sold through retail trade using cash registers and issuing checks (without issuing invoices), then in the purchase book the seller must register the details of cash receipts issued when returning money to the buyer. Registration is carried out on the date of acceptance of returned goods for registration.
Acceptance of goods returned by a retail buyer on the basis of an application is issued with a consignment note (form No. TORG-12) in two copies. One copy is attached to the product report, and the other is given to the buyer. Based on it, he will be able to receive money for the product or exchange it.
When an adjustment invoice is not needed
An adjustment invoice is not required when the seller provides bonuses or incentives to the buyer. Such bonuses do not affect the cost of products sold (work performed, services rendered, property rights), i.e., the tax base does not change and no adjustment is required (clause 2.1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, there are situations when it is necessary to make corrections to the original invoice rather than issue an adjustment:
- If the change in cost is associated with the correction of an arithmetic or technical error that arose due to incorrect entry of the price or quantity of goods shipped (work performed, services provided) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/23/2012 No. 03-07-09/125, dated 08/15/2012 No. 03-07-09/119, dated 08.08.2012 No. 03-07-15/102, dated 07.31.2012 No. 03-07-09/95, dated 04.16.2012 No. 03-07-09/36, dated 05.12 .2011 No. 03-07-09/46, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 08.23.2012 No. AS-4-3/ [email protected] ). For example, it is necessary to correct an invoice if the error occurred due to incorrect data entry into programs designed for accounting and tax accounting (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 30, 2011 No. 03-07-09/44, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 1, 2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ). However, in practice it is very difficult to determine whether there is a technical (arithmetic) error or whether there are grounds for issuing a correction invoice.
- When the final price of a consignment of goods is determined after shipment based on quotes. In this case, corrections are also made to the “shipping” invoice, drawn up indicating the planned prices, since the calculation of the price of goods does not change (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2011 No. 03-07-09/45).
For details on the nuances of preparing corrections made to an invoice, read the article “In what cases is a corrected invoice used?”
Sometimes, when the price (tariff) or quantity (volume) of goods (work, services), property rights changes, neither an adjustment nor a corrected invoice needs to be drawn up. So, if the seller knows that the price and quantity of shipped products will be updated within 5 days from the date of sale, then he just needs to wait for these changes and issue an invoice taking into account the new prices or the updated quantity. After all, according to paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when selling goods (work, services), transferring property rights, invoices are issued no later than 5 calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), from the date of transfer of property rights.
See also “Adjustment invoice for VAT return: current or updated?”
Introductory information
The procedure for filling out adjustment invoices is established by the Tax Code.
The composition of the indicators and the rules for filling out the adjustment invoice are given in Appendix No. 2 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137 “On the forms and rules for filling out (maintaining) documents used in calculations of value added tax.” However, not all situations are spelled out clearly enough in these documents. To help you figure out whether the adjustment invoice is filled out correctly and to prevent possible conflicts with inspectors, we have compiled instructions. It combines legislative requirements, explanations of officials, and also takes into account court decisions in a convenient form.
For convenience, we will call the invoice that was drawn up when the goods were shipped (and for which an adjustment invoice was subsequently issued) the “original” invoice.
An invoice that has been corrected will be referred to as a “corrected” invoice. Accordingly, we will call an adjustment invoice with corrections a “corrected” adjustment invoice.
Finally, we will designate an adjustment invoice issued when the original delivery cost is changed again as a “repeated” adjustment invoice.
Automatic reconciliation of invoices with counterparties will reduce the risk of additional VAT charges Carry out reconciliation
Results
After a shipment has already been made, it may be necessary to adjust the data on the quantity or price of goods sold in connection with reaching an agreement to change 1 of these indicators. In this case, an adjustment document is drawn up reflecting the original shipment data, their new value and the amount of change. Such a document is not used to correct errors made during registration.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How long does it take for registration and delivery?
These documents must be submitted to the tax authorities in the same period in which they were issued. It is worth noting that if an adjustment invoice is issued at the border of periods, then in some cases the tax office refuses to accept it and may even issue a fine for issuing an invoice outside the due date.
However, such situations are quite often resolved by the court in favor of the payer, thanks to which it is possible to avoid a fine and receive the necessary deduction.
Canceled and zero invoice - what is the difference
Merchants can issue a zero invoice if they do not apply VAT (for example, simplifiers), at the request of the counterparty.
However, the Tax Code does not provide for the obligation to issue zero invoices for them. Read more about VAT under the simplified tax system in the material “VAT under the simplified tax system: in what cases to pay and how to take into account the tax in 2020-2021” .
The difference between nil and canceled invoices is the tax implications. So, if you register a zero invoice in the book of purchases or sales, there will be no consequences for the merchant. In the case of a canceled invoice, things are not so simple.
Last quarter
The adjustment for the last quarter is processed in the same way as the correction account for the previous year . The basis for its creation are exactly the same errors as in the example above.
Such a document is drawn up by the taxpayer himself if he independently discovered the indicated errors (no penalties from the tax office will follow if such a corrected invoice is submitted).
This document is registered in the sales/purchase books in the same way, indicating the notes on the cancellation of the old account and entering new information with a “+” sign. Corrective invoices should be submitted to the tax service upon their completion. In this case, in addition to the invoice itself, you will also need to draw up an application for making changes .
Thus, in order to avoid possible violations and not lose the right to deductions, adjustment bills should be submitted on time, and for this you need to know the deadlines for submission and indicate accurate information in them. If errors in documents were discovered in past periods, a corrective invoice should be created and submitted to the tax office. In this case, no sanctions will follow from the service.
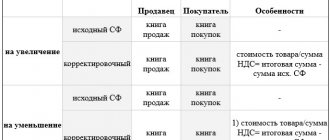
What date is indicated?
There are 2 options for specifying the date in the adjustment invoice . First: the same date is indicated as the date of drawing up the documents on the changes made.
This option is the most convenient, as it greatly simplifies the work with papers, and with such registration there will be no problems with obtaining tax deductions. Second option: indicate any date within the 5-day period allotted for issuing an invoice.
With this method, the dates of the invoice and the source documents do not coincide, which is much less convenient, although acceptable. True, in this case, as well as in the case of a completely incorrect indication of the date, which in no way corresponds to the deadlines for making changes to the initial account, problems may arise when preparing the document with the tax office.
Moreover, if such invoices are issued at the border of the tax period, the inspectorate may not count them at all, as a result of which the company may be fined for their absence and lose the right to deductions. That is why it is better to indicate the date of preparation of documents on the changes made .
Rules for storing VAT documents
The procedure for storing VAT accounting documents (including when using electronic document management) has been clarified. Thus, invoices (including adjustments, corrected ones), confirmations from the EDF operator, notifications to the buyer about receipt of the invoice must be stored in chronological order:
- by date of issue;
- by the date of preparation or correction (when the invoice is not sent to the buyer or is not received by him);
- by date of receipt for the corresponding tax period.
The list of VAT accounting documents subject to storage has expanded.
These now include copies of paper invoices issued by the seller to the developer or forwarder. These copies are certified by the developer (forwarder) and transferred to the buyer (investor, client). The buyer (investor, client) also stores seller invoices received from the developer (forwarder), issued electronically. All these documents, along with others (listed in clause 11 of the Rules for filling out invoices, approved by Resolution No. 1137) must be stored for at least four years from the date of the last entry in the accounting journal or book.
The principal (principal) is obliged to keep copies of invoices issued by the seller.
If companies use electronic document management, then they can store documents in electronic form; it is not necessary to make paper copies.