Basic information about the document
An invoice is the documentary basis for accounting, calculation and deduction of VAT. An invoice is issued by the supplier - the VAT payer - to its customers: companies or entrepreneurs. In other words, any transaction for the sale of goods and services subject to VAT must be accompanied by the preparation of an invoice. For the buyer, this document serves as the basis for reducing his own VAT payable, that is, for a tax deduction.
If the buyer does not pay VAT, the supplier may not issue him invoices. However, to do this, an agreement must be signed between the parties that no invoices will be issued. Suppliers who do not pay VAT are also exempt from the need to prepare this document.
Repayment of debt to the assignee
Situation: is it necessary to draw up an invoice when returning a debt, the right to claim which was acquired under an assignment agreement? The amount returned is greater than the amount paid to the assignor. The debt is associated with payment for goods (work, services) subject to VAT.
Yes need.
If a monetary claim acquired under an assignment agreement is associated with payment for goods (work, services), the sale of which is subject to VAT, then repayment of the debt is also recognized as an object of taxation. The tax base in this case is the difference between the amount received from the debtor and the purchase price of the debt. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 2 of Article 155 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Determine the amount of VAT at the estimated rate of 18/118 (clause 4 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax must be calculated on the day the payment is received from the debtor (Clause 8, Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since the debtor has no reason to claim VAT for deduction, the invoice can be drawn up in one copy and registered in the sales book.
In line 2 “Seller” of the invoice, indicate the name of the assignee organization, in line 6 “Buyer” - the name of the organization that repaid the debt.
An example of drawing up an invoice for the return of a debt, the right to claim which was acquired under an assignment agreement
In February, LLC "Torgovaya" (assignee) acquired from JSC "Proizvodstvennaya" (assignor) the right to claim the debt for payment of goods subject to VAT and sold under a sales contract. The debtor (buyer under the purchase and sale agreement) is Alfa JSC. The amount of debt is 1,180,000 rubles. (including VAT – 180,000 rubles).
The right to claim the debt was acquired for 1,000,000 rubles. (including VAT - 152,542 rubles) based on the assignment agreement, which was signed on February 19.
On April 10, Alpha repaid the debt, the right to claim which was transferred to Hermes, in the amount of RUB 1,180,000.
Hermes assessed VAT payable to the budget on the amount of the excess of the repaid obligation over the purchase price of the debt: - RUB 27,458. ((RUB 1,180,000 – RUB 1,000,000) × 18/118).
On April 10, Hermes drew up an invoice in one copy and registered it in the sales book.
Regulatory regulation
The legal basis for the application of the document in question is the Tax Code. Paragraph 3 of Article 169 defines the cases in which an invoice is issued. This includes transactions that are subject to VAT, as well as the export of non-taxable goods from Russia to the territory of the Customs Union.
The document has a specific form, set out in Resolution No. 1137. The same act contains the rules in accordance with which invoices should be filled out. The form of the document and the procedure for filling it out are constantly being improved, and therefore changes are being made to the resolution.
Paper and electronic formats
Today, invoices are generated in the classic form, that is, on paper or in electronic format. Such an invoice, like its paper counterpart, must be drawn up in a strictly prescribed form and contain all the necessary details.
When is an electronic invoice issued? This is possible if the following conditions are met:
- an agreement has been concluded between organizations on the preparation of electronic invoices;
- counterparties have the technical ability to exchange documents in the established format via the Internet.
Otherwise there are no restrictions. An electronic document completely replaces a paper one, provided that it is drawn up in the form and certified with a digital signature.
Why is it exposed to the buyer?
An invoice is a document that confirms the provision of services, goods or rights to property, and also records their value at the time of agreement.
It is generated and issued by the seller’s accounting department not before or after payment for the goods or services, but after the buyer has completed final acceptance of the goods or services.
The main purpose of creating such an account is to account for VAT. Therefore, this document can only be completed strictly in accordance with the requirements.
This document has two functions:
- confirm receipt of the service or product by the buyer;
- record the amount of tax paid for the purpose of its subsequent deduction.
Reference. A consignment note is an accounting document designed to confirm the transfer of rights to goods or property from the seller to their buyer.
It must include data on the quantity of goods, its partial and total cost, as well as details of the selling party.
It can be drawn up either in the form of a standard unified document, a sample of which is available on the Internet, or on a form independently developed by the selling company. It is provided both in paper and electronic form.
Most often, this document is used for retail sales of goods.
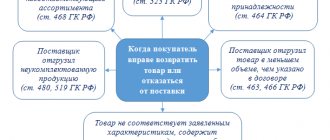
When is an invoice issued?
Most often, the primary document in question is issued by the seller when carrying out transactions that, in accordance with tax legislation, are subject to VAT. The sale of most goods and services, including gratuitous transfers, is subject to taxation. But there are exceptions - they are listed in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Also, companies and individual entrepreneurs working with VAT are required to generate invoices upon receipt of payment for future shipments. Such documents are usually called advance invoices.
In addition, VAT payers are required to issue invoices when exporting to the EAEU countries.
There are cases when the paper is issued by an entity that does not pay VAT. Such an obligation arises for companies and individual entrepreneurs if they, on their own behalf, sell goods that belong to another organization - a VAT payer. We are talking about mediation activities under commission agreements and the like.
Filling by lines
Rules for filling out an invoice line by line:
- the first line is the serial number of the document in accordance with the established document flow rules;
- the date of preparation should not be earlier than the date of the original document;
- date and correction number are filled in if necessary;
- in the line “Seller” the full or abbreviated name is indicated in accordance with the constituent documents;
- the postal address is indicated in the “Address” line;
- in line 3, “same person” is entered if the seller and the shipper are the same person. Otherwise, you must provide the shipper's mailing address. When filling out an invoice for services and property rights, a dash is placed in this line;
- in term 4, according to the same rules, the data of the consignee is written;
- in line 5 “to the payment and settlement document” a dash is placed if the form is drawn up upon receipt of payment, partial payment or for upcoming deliveries using a non-cash form of payment;
- for line 7, the currency codes are given above.
The columns are filled in as follows:
- Column 1 indicates the name of the product or service provided;
- in column 2 - unit of measurement, if possible. A dash is placed upon receipt of payment or partial payment for upcoming deliveries. Columns 2 and 2a are filled out taking into account the All-Russian Classifier of Units of Measurement, introduced by Decree of the State Standard of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 1994 No. 366;
- Column 3 indicates the quantity or volume of the goods. If this indicator is not defined or is missing, you must put a dash. A dash is also added when payment or partial payment is received for upcoming deliveries;
- Column 4 (product price) is filled out according to similar rules;
- in column 6, if there is no excise tax amount, a corresponding note is made;
- in column 7 (tax rate) for transactions specified in paragraph 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an entry “without VAT” is made;
- Column 8 is filled out according to similar rules;
- columns 10-12 are filled in if the country of origin of the goods is not Russia, in accordance with the OK of the world (MK (ISO 3166) 004-97) - 025–2001.
This is what the completed document looks like.
If the form is an advance or correction form, this must be indicated. As well as what changes are made to the form and on what basis. The signature of authorized persons is required: manager (trustee), chief accountant. A seal is not a mandatory requirement, but can be supplied (for example, at the buyer’s request).
All forms are stored in chronological order for at least 4 years, recorded in the journal of received and issued invoices, in the book of purchases and sales in order to be able to verify the calculation and payment of VAT.
The procedure for issuing a document during implementation
Let's consider a basic example - the seller releases the goods, and the buyer makes payment upon delivery. The invoice is issued within 5 days, starting from when the goods were shipped, services were provided or work was performed.
One copy of the invoice is issued for the supplier himself, the second for the buyer. The document must be registered in the Invoice Journal (hereinafter referred to as the Journal). In addition, the seller makes an entry in the Sales Book and indicates the details of the corresponding invoice. And the buyer, accordingly, makes a similar entry in his Purchase Book.
How can a seller reflect advances?
The seller is obliged to register an invoice in the period in which he received the advance payment (clause 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Resolution No. 1137 of December 26, 2011).
| Prepaid expense | Shipment of goods/services | Settlement of advance payment | |
| Book (registration SF) | Sales book | Sales book | Book of purchases |
| Mandatory registration of the Federation Council | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| Moment of registration of the Federation Council | On the day of receiving the advance | On the day of shipment | On the day of shipment or any day within three years |
| KVO for Northern Fleet (most used) | 02 | 01 | 22 |
| Indication of the counterparty in the Federation Council | Buyer | Buyer | Themselves |
| Section and line of VAT amounts in the declaration | Section 3, page 070 | Section 3, pp. 010-050 | Section 3, page 170 |
We have prepared an overview of common mistakes when preparing advance invoices
When is an advance invoice issued?
If the buyer makes an advance payment for a future delivery, the supplier must also issue an invoice. In this case, it does not matter whether the buyer made the payment in full or in part - the document is issued for the transferred amount. The seller charges VAT on the prepayment received, and the buyer, subject to certain conditions, can claim his input tax as a deduction.
When is an advance invoice issued? The issuance period is 5 days, calculated from the date on which the advance payment was received. The document is taken into account by the supplier in the following order:
- the advance invoice is reflected in the Sales Book;
- when the goods are sold, a shipping invoice, that is, a “real” invoice, is drawn up;
- the shipping document is noted in the Sales Book for the entire amount of delivery;
- at the same time, an entry regarding the advance invoice is made in the Purchase Ledger.
The buyer has a similar document accounting procedure, but with the opposite sign: instead of entries in the Purchase Book, there is a Sales Book, and vice versa. Both the buyer and the seller's documents are also subject to registration in the Journal.
What's the situation
Under an agreement for the sale of printed materials, organization A transfers books to organization B for a fee, in addition, company B pays company A for postage for the delivery of these books.
Organization A issues a delivery note (TORG-12) dated 09/06/2017, since the books were sent within this period, then upon delivery on 09/13/2017 issues a certificate of services rendered and an invoice for the total amount of the contract (books and delivery). In particular, to close the contract, company A must provide the books and arrange delivery, that is, the transfer of books is documented by a bill of lading, and the delivery is documented by an act upon delivery, that is, more than 5 days after the bill of lading. The invoice is issued for the total amount with the date of the act. Is this legal? Or, due to the fact that 5 days are given for issuing an invoice, the delivery note should be dated no earlier than 09/09/2017? Is it possible to accept a delivery note, document and invoice with current data or is it possible to accept some of the documents and the dates must be changed?
When an intermediary issues an invoice
Let us separately mention the peculiarities of working with invoices of commission agents and other intermediaries (agents, forwarders, attorneys). When selling the goods of the principal with VAT on his own behalf, the commission agent must draw up an invoice and highlight the amount of tax in it. This will allow the buyer to claim their input tax as a deduction. Moreover, an invoice should also be issued if the commission agent himself does not pay VAT, for example, being on a simplified taxation system. The fact is that in this case, the commission agent, being an intermediary between the buyer and the owner of the goods, actually takes on the latter’s function in calculating VAT and drawing up documents.
The commission agent registers the exposed document only in the Journal. The second copy is intended for the buyer. The commission agent transfers the document details to the principal, and he issues an invoice to the intermediary himself. In this case, the document must have the same number that the commission agent assigned to it. He notes the received invoice in the Journal.
If a commission agent buys goods from a third party for a VAT payer, he re-issues an invoice issued by the seller to his address. In this case, the received and issued invoices should also be recorded in the Journal without being reflected in the Books.
Common Mistakes
Errors that are most often encountered when filling out an invoice and their consequences:
- if the name, TIN, and address of the organization are incorrectly indicated or missing, it is difficult to establish the authorship and addressee of the document, so it may be declared invalid;
- if it is impossible to determine from the document what goods were transferred or service was provided, VAT will not be refunded;
- incorrect indication of currency, incorrect indication of the quantity of goods, errors in prices, incorrect calculation of cost lead to the fact that the exact cost of the goods cannot be determined. Thus, the document becomes uninformative;
- incorrect calculation of VAT. The absence of a VAT amount may also raise questions from regulatory authorities.
Minor errors in the form of missing characters, capital letters, or inaccuracies in payment details are usually not pursued by the tax authorities. It is also possible to abbreviate names if such an abbreviation allows you to identify the enterprise or product.
If the displayed document needs to be changed
In practice, it often happens that changes have to be made to documents. For example, there was a shortage of goods or its price changed. This is also required when an error is found in the invoice.
To change the information in the issued document, corrected and adjustment invoices are drawn up. The first is simply a new version of the document that contains the correct information. The corrected invoice is issued within three years from the period of issue of the original document. This is due to the right of the buyer to claim input tax deduction within a specified period. The corrected document exists independently and completely replaces the one in which the incorrect data was indicated. It is issued in cases where it is necessary to correct an error that did not lead to a change in the amount. For example, the supplier incorrectly indicated the buyer's name or tax rate. If incorrect information in the invoice does not make deduction impossible, then a corrected document does not need to be drawn up.
In what cases is a correction invoice issued? When the transaction amount is adjusted, for example, due to a change in the cost of the product. In this case, an agreement must be concluded between the parties to change the amount (annex to the agreement, act, decision). The adjustment document is drawn up for the amount of changes and is an addition to the original one.
It happens that the supplier sold several batches of goods to one buyer and issued a separate invoice for each. However, it happened that the amount in all deliveries needed to be changed. How many invoices are issued for adjustments? In this situation, there is no need to draw up several documents - the seller can draw up one for all changes addressed to this buyer.
Violation of rules and responsibility
What are the risks for a company or individual entrepreneur for violations related to the described document? The law stipulates the deadlines for issuing an invoice, but does not provide for direct liability for exceeding them. But the absence of an invoice is regarded as a serious flaw in accounting. Absence means failure to issue a document in the quarter in which the transaction took place.
For this, the taxpayer may be punished in accordance with Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If this violation is detected for the first time, the organization may receive penalties in the amount of 10 thousand rubles. If the absence of invoices is revealed in several quarters, the amount of the fine will triple. And in the case where this violation led to an understatement of tax, the fine will be 1/5 of the amount of the underpayment, but not less than 40 thousand rubles.
It must be said that it is quite difficult to “forget” about an invoice when selling a product or service. Even if this happens, the buyer will definitely remind him of the need to draw up a document, because without it he will not be able to deduct VAT. With an invoice for an advance payment, everything is different. Buyers do not always claim VAT deduction from the advance payment, so they do not ask for an invoice. In such a situation, some accountants do not consider it necessary to issue them. They reason like this: receipt of the advance and shipment occur in the same quarter (in most cases), so why issue an interim document? However, the Federal Tax Service considers this a violation if more than five days pass between the receipt of the advance payment and the shipment of the goods.
Why is it important to follow the design?
The document to which this article is devoted is necessary for the buyer to claim VAT deduction. If critical errors are made in it, the tax service will not recognize the deduction. This means that the company will have to pay additional taxes, and in the worst case, also pay a fine. Therefore, when receiving an invoice, it is important to carefully check its basic details.
To be fair, we note that not every mistake will result in a denial of the deduction. There are a number of transaction parameters that must be identified by the invoice, namely:
- buyer and seller;
- object of the contract;
- cost of goods (services) or advance payment amount;
- VAT rate and amount.
If the specified parameters are determined from the invoice, then a deduction can be claimed on it, despite other errors. Having received a refusal from the Federal Tax Service, the taxpayer can safely go to court. However, if the supplier made an error when generating the invoice, for example, in the cost of the goods or the amount of tax, then the buyer may not count on VAT preferences.
So, an invoice is very important for calculating VAT from the supplier and deducting its incoming part from the buyer. It is necessary to monitor the current form of the document, because it changes periodically. And it is extremely important to follow the procedure and deadlines for its preparation, as well as to avoid critical errors that will lead to non-recognition of the deduction from the buyer.