Reference
To register the acquisition of future fixed assets in the 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 configurations, two methods are available:
- quantitative nomenclature accounting
- individual accounting of objects
Quantitative nomenclature accounting
Quantitative accounting is supported using elements of the Nomenclature directory on account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” (not to be confused with equipment for installation, which is accounted for on account 07 “Equipment for installation”). In this case, the use of all demand fulfillment procedures (for example, orders to suppliers) is available. All movements are performed according to the rules of quantitative movement of items.
This method is advisable to use in the case when receipt transactions are processed by supply service employees. Accounting account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” is set for the financial accounting group of the item to which the incoming items belong, on the Own item tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace.
Direct commissioning of fixed assets from account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” is not provided.
To form the initial cost of fixed assets, account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is used. The transfer of components to a future fixed asset item is carried out using the documents Internal consumption of goods with the transaction type Write-off to expenses/assets. Corresponding account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is specified by the totality of the expense item and the recipient department (in which the object will be accepted for accounting) on the Expenses tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace. In operations, an expense item is used with the distribution option For non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed assets, but if an asset item is used when writing off an item, then account 08.04.2 is indicated directly in the document.
Individual accounting of objects
It is possible to register a future fixed asset as a unique (without quantitative accounting) inventory item from the Fixed Assets directory. The initial cost is immediately formed on account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning”.
This option is convenient for use in cases where the receipt is registered by an accountant for fixed assets. It allows you to eliminate the entry of unnecessary data into the Nomenclature list. Receipts are documented in the documents Receipt of services and other assets. The targeted allocation of the cost of an incoming object to the initial cost of a fixed asset is determined by using an expense item with the distribution option For non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed assets, which is indicated in the rows of the tabular part of the documents for the Purchase of services and other assets.
Corresponding account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is set for the totality of the expense item and the recipient department (in which the object will be accepted for accounting) on the Expenses tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace. Account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is also used in the case of creating a fixed asset object using the enterprise’s own resources.
General scheme of options for accepting a fixed asset for accounting after the formation of the initial cost:
As it was in 1C: KA 1.1 and 1C: UPP 1.3
In configurations 1C: KA 1.1 and 1C: UPP 1.3, in order to reflect the purchase of both low-value and expensive operating systems, it was necessary to credit everything to account 08.04 and take into account all fixed assets regardless of cost. And fixed assets that require configuration should first be accounted for in account 10, and then written off with the document Request-invoice to account 08.04 to form the initial cost and then taken into account
Let's look at the example of individual accounting of objects in the 1C:KA 2 configuration - the receipt of fixed assets, with subsequent acceptance for accounting and depreciation.
Master data setup and administration
Before completing the purchase of a fixed asset, you first need to set up our program so that it is possible to maintain non-current assets. To do this, go to the master data and administration section - Setting up master data and sections - Non-current assets
Default Accounting for non-current assets
disabled. Therefore, in order to correctly reflect the purchase of the OS, this option must be enabled.
In the example under consideration, the accounting parameters for non-current assets use version 2.2
Purchase of fixed assets
As was the case in 1C:KA 1.1 and 1C:UPP 1.3
In the configurations 1C:UPP 1.3, 1C:KA 1.1, to reflect the purchase of the OS, it was initially necessary to fill out the document Receipt of goods and services; in these configurations, this document does not need to be filled out.
There is an analogue here - Purchasing services and other assets
. The document is located in the section panel Regulated accounting - Fixed assets - Documents on fixed assets - Purchase of services and other assets.
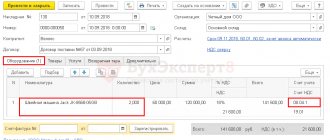
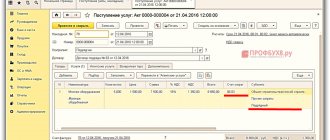
The document looks like this
the Expenses and other assets tab
Important:
in order to include the cost of an incoming object as part of the initial cost of a fixed asset, it is necessary to indicate in the rows of the tabular part of the documents for the Purchase of Services and Other Assets the use of an expense item with the distribution option To non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed Assets.
Also, in order for the program to understand that this is an OS object, it is necessary to indicate the Accounting account in the reg. on the Regulated Accounting and MFP tab. accounting, set the account 08.04.2
As it was in 1C:KA 1.1 and 1C:UPP 1.3
One of the obvious differences between 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 from previous configurations: when filling out the OS receipt document, you do not need to select the type of operation - Equipment.
Go to the Additional tab. This is a required field to fill in - Division, please indicate it.
Next, when we have filled out everything necessary, we submit the document. Now let's see what transactions the document made, click
We see that the program does not automatically make entries according to regulated accounting, to view preliminary entries
you must click More - Reflect in accounting when opening
Click Reflect in Reg. accounting
Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
We move on to accepting the OS for accounting in the 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 programs. For this, as with the configurations of the previous generation, the document Acceptance for accounting of OS is used. It is located in the section Regulated accounting - OS documents - Acceptance for accounting of assets - Create.
Fill out the form
On the Main tab
- division in which the object is registered
- OS group
- depreciation group
On the Depreciation tab
- depreciation method
- useful life
On the Expense Reflection tab
— indicate the expense item for depreciation
In the expense item on the Regulated accounting and MFI tab, you must indicate the account for reflecting depreciation expenses
On the Fixed assets tab - select our fixed asset
The OS card in 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 is called Operation Objects.
We carry out the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets. Let's look at the wiring
Significant error
A significant error can be identified before and after the statements are approved. The procedure for correcting such an error is given in paragraph 9 of PBU 22/2010.
An error discovered after approval of the financial statements is corrected:
- In the current reporting period, entries in the relevant accounting accounts. The corresponding account in the records is the account for retained earnings (uncovered loss).
- Recalculation of comparative reporting indicators for the reporting periods reflected in the organization’s financial statements for the current reporting year.
Recalculation of comparative indicators of financial statements is carried out by correcting indicators of financial statements. It's as if there was no mistake.
For example, this error needs to be corrected in 2021. We make entries to reflect transactions of the past 2021 in correspondence with account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).” Next, when reporting for 2021 is compiled, the figures for 2021 need to be recalculated, as if the error had never happened.
Depreciation calculation
Next month it is necessary to calculate depreciation on fixed assets. The document Depreciation of fixed assets can be created automatically when performing routine operations when closing the month. Menu item Financial result and controlling - Month closing
Or if you need to first look at the amounts for depreciation, then you can only post the document Depreciation of fixed assets. The document can be found in the same section Regulated accounting - Fixed assets - Depreciation of fixed assets
We create a document Depreciation, indicate the date of the document and post it.
In this way, accounting for fixed assets can be organized in 1C:KA and 1C:ERP 2, of course, there are many more nuances in accounting for non-current assets, when a fixed asset is assembled from several components, modernization and depreciation charges after modernization, changing the parameters and state of the operating system, accounting leasing operating systems and much more. Therefore, this area of accounting requires special attention and detailed study. If you encounter a problem in accounting for fixed assets, then leave a request on our website and we will definitely help you!
In accounting
Correcting errors of the previous period in accounting depends on what kind of error it is, namely, significant or insignificant.
The right to determine the severity of the error in accordance with PBU 22/10 is given to the organization itself, but with recommendations.
The company's management has the right to determine the significance of the error and how exactly the error affected the final annual financial statements.
An error should be considered significant if it affects the economic decisions made by interested parties on the basis of the financial statements prepared for this reporting period.
Physical deterioration
Physical wear and tear is a decrease in the original value of property for the consumer. It is calculated in two ways, see table 2.
| Name | Description | Formula | Decoding |
| Based on scope of work | It is suitable for items with established performance | I = (Tf x Pf) / (Tn x Pn) | Tf – time that the object actually served Pf – average quantity of products produced per year Tn - SPI according to the norm Mon – normal productivity |
| By period of use | It is established by comparing the actual and normative SPI. Valid for determining the wear and tear of any OS. |
Calculation formulas on video:
How to correct the tax base for profits
To correct data on the tax base, you must be guided by Articles 54 and 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The tax was overpaid
If mistakes made resulted in excessive payment of income tax, you can submit an amendment. Although, tax authorities do not require submission of an updated declaration in this case, provided that the year with the error and subsequent years were profitable (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/17177).
It is enough to reflect in the income tax return for the current period the losses of previous tax periods identified in the current reporting (tax) period, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
On this topic:
When can a tax error be corrected without “clarification” - RF Armed Forces
Minor error
A minor error is corrected in the month in which it was discovered.
Profit or loss arising as a result of correcting an error must be reflected as part of other income or expenses of the current reporting period in account 91. This is the procedure prescribed in paragraph 14 of PBU 22/10.
The error was identified before the annual financial statements were approved
If an error is identified before the annual financial statements are approved, corrections can be made in 2021.
According to paragraph 8 of PBU 22/10, a significant error of the previous reporting period, identified after the submission of financial statements to shareholders, members of the LLC, to the tax office, but before the date of its approval, is corrected in the manner established by paragraph 6 of PBU.
It is necessary to make entries on the relevant accounting accounts for December of the reporting year.
The corrected statements must be re-sent to all interested parties. These are the same recipients. Those who received the first version of reporting.
It is important to know:
Correcting accounting errors
How to put an OS on the balance sheet of an enterprise
To be placed on the balance sheet, a fixed asset must cost more than 40,000 rubles and have a useful life of more than 12 months. All costs are collected according to Dt 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. When the property is completely ready, it is transferred to the account. 01 "Fixed assets".
Key Points for Small Businesses:
- Depreciation can be calculated throughout the year in any reporting period, but at least once a year.
- Companies are allowed to balance the cost of the seller with installation costs, and if the OS was built, then with the cost of the contractor’s work. Other costs (delivery, promotions, information services, customs duties) and other costs for fixed assets that were purchased can be written off immediately.
- The accounting feature affected inventory worth over 40,000 rubles. Deciphering the concept of inventory, you need to look at the OS OK 013-2014 classifier. Such inventory, when registered, can be fully depreciated.