The procedure for writing off receivables and payables always raises many questions even among accountants with excellent track record, since in the activities of almost every organization situations always arise when the counterparty refuses to pay or simply liquidated without paying off the obligations.
In the article we will consider the main issues of reflecting and recording accounts payable and receivable, that is, how, where, when and on the basis of what documents to write off this debt in accounting.
Inventory of payments is a reconciliation of the amounts of receivables and payables according to the data of your organization and the data of its counterparties.
According to Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, namely Part 1 of Art. 11 – organizations are required to conduct an inventory of their assets and liabilities.
In accordance with Part 3 of Art. 11 of Law N 402-FZ, economic entities themselves establish the cases, timing and procedure for conducting an inventory, as well as the list of objects subject to inventory. But there is one exception: some assets and liabilities are subject to mandatory inventory, which is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, federal and industry standards.
The inventory process establishes the correctness and validity of reflecting the amounts of receivables and payables through documentary verification.
The basic principles of conducting an inventory are established by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 N 49 “Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations.”
The number of inventories in the reporting year, as well as the date of their conduct, the list of property and financial liabilities being verified, are established by the head of the organization (clause 2.1 of the Methodological Instructions), except for the cases provided for in clauses 1.5 and 1.6 of the Methodological Instructions for Inventory.
In accordance with clause 4 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting Policy of the Organization” (PBU 1/2008), when forming an accounting policy, the organization approves the procedure for conducting an inventory of its assets and liabilities.
Thus, the timing and frequency of inventories are established by the economic entity independently and are fixed in the accounting policies, in accordance with the specifics of the organization’s activities.
According to clauses 27, 77, 78 of the Accounting Regulations N 34n, an inventory of calculations is required (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 14, 2015 N 07-01-06/188):
- when writing off receivables and payables;
- before preparing annual financial statements;
- when creating a reserve for doubtful debts.
The inventory procedure is as follows:
The accountant needs to draw up a certificate of debt (receivable or payable). The certificate indicates the information reflected in the accounting records of the debt. The certificate must also contain information about the names of the organization’s debtors and creditors, the grounds for the debt, the period of the debt and details of the documents confirming it. For convenience, debt amounts in the certificate are grouped by accounting accounts.
Based on a certificate of debt (receivable or payable) as well as acts of reconciliation with counterparties or other documents in which debtors and creditors confirm the existence and amount of debt, an act is drawn up (clauses 73, 74 of the Accounting Regulations No. 34n, Instructions, approved. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 88).
The act is drawn up on the basis of the unified form N INV-17. The organization has the right to develop its own document to record inventory results. But it must be remembered that such a document must contain all the details established in Art. 9 of Law N 402-FZ, and its form must be approved by the head.
This can be done in the annex to the accounting policies.
If the organization decides not to create a reconciliation report, then the agreement on the amount of debt can be confirmed by a letter from the counterparty acknowledging its debt.
Amounts of debt recognized and not recognized by debtors and creditors, as well as amounts of unrecoverable debts with an expired statute of limitations or for liquidated counterparties are reflected in the act separately.
Based on bad receivables or payables identified during the inventory, it is necessary to prepare an order from the manager to write off bad debts.
So, based on the results of the inventory, the organization can identify bad receivables and payables that must be written off.
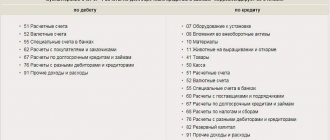
Accounts receivable
In order to see and understand what accounts receivable is, you should create a balance sheet. The debit balance on settlement accounts (such as 60, 62, 66-70, 73, 75 and 76) will be the receivable, that is, the amount owed to the company by other firms, individuals and funds.
Let's look at what accounts receivable includes:
| Accounts receivable | On what account is it reflected? |
| Debts of buyers, customers | 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” |
| Debts of suppliers and contractors for advances transferred to them (prepayments), as well as recognized claims | 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” |
| Debts of insurance companies for insurance claims, issuers of securities owned by the company, for dividends, etc. | 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” |
| Debts of budgetary bodies and extra-budgetary funds for excessively transferred taxes and contributions | 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” 69 “Calculations for social insurance” |
| Debts of employees on accountable amounts, loans, compensation for damage, etc. | 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” |
| Debts of founders and participants on contributions to the authorized capital | 75 “Settlements with founders” |
The composition of accounts receivable will depend on how exactly it was formed. It can form when:
- sale of goods (work or services) on an advance payment basis (that is, the goods have already been shipped to the counterparty, but payment for it has not yet been received);
- purchasing products (raw materials) on an advance payment basis;
- overpayment of taxes and fees;
- issuance of accountable money.
In which accounts should accounts receivable be recorded?
As we said, the choice of account depends on who owes you money. All account options are listed in Section VI “Calculations” of the Chart of Accounts. Here they are:
- account 60 - debt of suppliers and contractors for the listed advances;
- account 62 - debt of buyers and customers for goods shipped, services provided, work performed;
- accounts 68 and 69 - debt of the budget and extra-budgetary funds, when there was an overpayment of taxes, fees, contributions, as well as the amount of social insurance benefits that must be reimbursed;
- account 70 - debt of employees in the amount of overpaid wages;
- account 71 - debt of accountable persons who did not return the unused advance or did not submit an advance report;
- account 73 - debt of employees for loans received from the organization, as well as for compensation for material damage;
- account 75 - debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital;
- account 76 - debt of other debtors.
All these accounts are classified as active-passive, which means they can have a debit and credit balance. But since we consider them in relation to accounts receivable, we can say that they are active: if the receivables increase, they are debited, if they decrease, they are credited, and the balance will be debit.
Sometimes accounts receivable are reflected in account 46 “Completed stages of work in progress.”
The difference between accounts receivable and accounts payable
Accounts receivable represent what is rightfully due to the organization, but has not yet been received. And if the organization itself owes it, then this is already accounts payable.
Regardless of the repayment period of the receivable, it belongs to the current assets of the organization. Not all types of receivables are reflected in the corresponding line of the balance sheet. For example, the debt of suppliers and contractors under contracts for the purchase or creation of non-current assets is reflected in the “Non-current assets” section.
Bad debt: to recognize or not to recognize
| Enforcement proceedings | If an organization has applied to the court for debt collection, has a positive court decision in hand, and the debt is subject to collection through enforcement proceedings, then such a debt can be recognized as uncollectible only if the impossibility of its collection is confirmed by a bailiff’s resolution on the completion of enforcement proceedings, or upon liquidation of the debtor. Such debt cannot be recognized as uncollectible due to the expiration of the statute of limitations. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 28, 2014 No. 03-03-06/1/60843). |
| Liquidation, exclusion from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities | If the debtor is liquidated or excluded from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities for other reasons, then the debt is considered uncollectible as of the date of entry in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, even if the statute of limitations has not yet passed. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 8, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/73076). |
| Reorganization | If the debtor ceased operations due to reorganization, then such debt cannot be considered bad, because according to Art. 58 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, there is succession of rights and obligations of a reorganized legal entity. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/06/2016 No. 03-03-06/1/52041. Financiers believe that the debt of a debtor who has ceased operations due to a merger with another legal entity cannot be considered hopeless. |
| Bankruptcy | Writing off debt in the event of bankruptcy of a legal entity is possible only at the end of bankruptcy proceedings, even if the statute of limitations expires during the bankruptcy period, specialists from the Ministry of Finance pointed this out in letter dated 06/06/2016 No. 03-03-06/1/73076. |
To write off bad debts, you need a corresponding order from the director, an inventory of payments, an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities upon liquidation of the debtor, a copy of the bailiff's resolution on the completion of enforcement proceedings if it is impossible to write off by bailiffs.
Types of accounts receivable
Types of receivables are distinguished based on their classification criteria:
| Criterion | Types of accounts receivable |
| In order of occurrence | Normal (arising within the framework of credit policy) Unjustified (arising from violation of requirements) |
| By timing of payment | Scheduled (repayment dates have not yet arrived) Overdue (repayment period has already arrived, but the debt has not been paid) |
| By length of delay | Overdue less than 45 days Overdue from 45 to 90 days etc. |
| According to the reality of collection | Real for collection Doubtful Hopeless |
Postings for writing off debt if no reserve was created
Let's look at these postings as an example:
..2009 reflected the resulting accounts receivable in the amount of 45,000 rubles. according to the supply agreement. did not sue the debtor, no reserve was created. On 24..2012, the manager issued an order to write off the debt as unrealistic for collection.
| date | Account Dt | Kt account | Sum | Contents of operation | Document |
| ..2009 | 62 | 90-1 | 45000 | Accounts receivable reflected | Agreement |
| 24..2012 | 91-2 | 62 | 45000 | Uncollectible debt written off | Manager's order |
| 24..2012 | 007 | 45000 | Written off debt taken into account | Manager's order |
The written-off debt must be recorded in off-balance sheet account 007 for 5 years.
Doubtful accounts receivable
Debt that has a high probability of not being repaid on time and is not secured by any guarantees is considered a doubtful debtor. If such debt is identified, it is necessary to create a reserve in accounting. It is necessary to ensure that the company’s reporting shows the actual financial result, as well as the obligations of counterparties.
As for tax accounting, reserves for doubtful debts are created at will and taxable profit can be reduced by this amount. A reserve is created only if the delay exceeds 45 days.
Write off accounts receivable
We document the inventory results and identify expired records. Documents confirming its existence and the statute of limitations are:
- Agreement and payment documents thereto;
- Documents confirming the delivery (rendering of services) – acts, invoices;
- Reconciliation report (if available);
- Mutual official correspondence confirming the fact of debt collection (claim). It is necessary to support copies of letters with a document confirming the receipt of the letter by the counterparty (for example, a receipt).
It is important to note that if there is a reconciliation report on a certain date, the period begins to be calculated from the beginning.
Documents to confirm the impossibility of collection: a bailiff’s order or an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities:
Write-off of accounts receivable - postings
In accounting, the accounting procedure is as follows:
1) If the reserve was created (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34-n):
- Dt 63 Kt 62 (60,76,71,73,70) – accounts receivable written off;
- Dt 007 – reflect the written-off debt on the balance sheet.
2) If the reserve was not formed or its size does not cover the amount of debt:
- Dt 91.2 Kt 62 (60,76,71,73,70) – accounts receivable written off;
- Dt 007 – reflect the written-off debt on the balance sheet.
The amount of the reserve is determined separately for each doubtful amount of debt. Formation of the reserve since 2011. became the responsibility of enterprises.
In tax accounting, a reserve is used to cover losses from the write-off of receivables (Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If it is not created or is insufficient, then the debt is attributed to non-operating expenses in the period when the statute of limitations has expired or the impossibility of collection is confirmed (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2011 No. 16-15 / 035618.1).
Accounting receivables posting
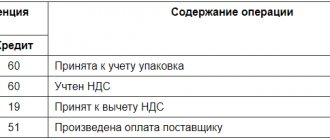
Let's consider the main transactions for settlements with debtors and creditors, in which receivables arise:
| Business transaction | Wiring | |
| D | TO | |
| The supplier has received an advance payment | 60 | 51 (51) |
| Products have been shipped to the buyer | 62 | 90 (sub-account “Revenue”) |
| Sickness benefits accrued at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund | 69 | 70 |
| Employees were paid an advance | 70 | 50 (51) |
| The employee was given a sum of money to report | 71 | 50 (51) |
| A loan was issued to an employee | 73 | 50 (51) |
| The founder's debt to pay into the authorized capital | 75 | 80 |
| Interest accrued on the loan issued | 76 | 91 (sub-account “Other income”) |
Postings for writing off receivables must be distinguished from postings for repayment. Upon repayment, the debtor fulfills his obligation to repay the debt. And when the debt is written off, it is included in the financial result of the company. Thus, repayment by the counterparty of the debt on shipped products is reflected in the following posting:
D 51 (52) K62.
And, for example, writing off a debt on a loan issued to an employee (debt forgiveness):
D91 (subaccount “Other expenses”) K73.
When a doubtful debt for which a reserve was created is written off, the posting will be as follows:
D63 K62 (60).
We write off the creditor
Every year, before preparing reports, the company is required to conduct an inventory, including accounts payable. If a claim with an expired statute of limitations is identified, it is written off on the basis of an order as part of the income of account 91 for both accounting and tax purposes. It should be remembered that, by analogy with the contractual assignment, the presence of a signed reconciliation report or receipt of an official claim from the supplier extends the statute of limitations:
Write-off of accounts receivable in accounting and tax accounting
Important! If the mortgage period is 45-90 days, then it is included in the reserve in the amount of 50%. 100% of the debt is included in the reserve only if the debt period is more than 90 days.
Accounts receivable can be written off using created reserves for doubtful debts. This transaction is reflected in accounting with the following entries:
D63 K62(76) – accounts receivable are written off against the reserve.
An organization can use the created reserve only within the limits of its size. If the written-off debt exceeds the amount, the difference is taken into account as part of other expenses. This transaction will be reflected by the following posting:
D91-2 K62 (76) - write-off of accounts receivable that the reserve did not cover.
Important! Even if a receivable is written off, this does not mean that it is cancelled. The entire amount written off should be reflected in off-balance sheet account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss.” This operation is formalized by the following posting: D007 – written off receivables are reflected.
In tax accounting, two methods are used to write off receivables:
- Write-off from the reserve for doubtful debts.
- Reflection of debt as part of non-operating income.
The amount of receivables that was not covered by the reserve is included in non-operating income. But only organizations that calculate income taxes using the accrual method can write off debt as expenses.
If you use the cash method, it will not be possible to take debts into account as expenses. If payment is not made, then the obligation is not considered fulfilled, and therefore expenses cannot be recognized. Uncollectible accounts receivable in full, including VAT, reduce taxable income.
How to avoid disputes
To write off any type of debt, you need good reasons, supported by relevant documents. These, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are:
- Expiration of the limitation period;
- Liquidation of the counterparty;
- The unreality of collection.
To “part” with the company’s debt, it is necessary to draw up a number of documents for each obligation:
- Inventory report of mutual settlements with counterparties (form INV-17);
- Resolution of the bailiff to terminate enforcement proceedings - in case of unrealistic collection;
- An extract from the state register of legal entities with a record of the completion of the liquidation procedure of the enterprise (Article 49, Article 63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) - in case of liquidation of the counterparty;
- The manager's order for write-off, signed on the basis of the listed documents.
At the same time, KZ is taken into account as non-operating income, except for debt to government agencies and extra-budgetary funds (Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 18; Article 251, clause 21), DZ is included in non-operating expenses or is included in the account. 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”.
Important: when writing off debt due to the impossibility of collection due to the debtor’s lack of property, it is necessary to take into account such debt for 5 years on the balance sheet in account 007 in order to control the likelihood of its collection when the financial condition of the debtor improves.
How to write off a bad receivable
The method of recognizing income and expenses on the date of shipment assumes that the shipment is taken into account in calculations for income tax, it turned out to be impossible to receive payment for it, so an amount has arisen to be written off.
A company can reduce its losses in two ways:
- by directly writing off bad debts as losses;
- through the reserve for doubtful debts.
When creating a reserve, you should rely on the provisions of Art. 266 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The creation of a reserve for doubtful debts is reflected in the company's accounting policies. Its provisions must not contradict the Tax Code.
Deductions are recognized as non-operating expenses and are taken into account on the last day of the reporting (tax) period. If the volume of the created reserve is insufficient to cover the bad debt, the remaining amount is written off directly through non-operating expenses. It is recognized as a loss in NU at the moment when the debt is documented and recognized as uncollectible.
As noted earlier, reserves can be created only for operations of a sales nature.
If a company has created a reserve for doubtful debts, it can also be used to write off bad advances, as well as prepayment amounts. Ministry of Finance on the basis of Art. 266-2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation recognizes such a right for the taxpayer (letter No. 03-03-06/2/1551 dated 16/01/18). It is advisable to consider the moment of writing off a hopeless “receivable” as the last day of the period in which it was recognized as such (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 272-7).
Bad receivables not reflected in accounting on time must be included in the declaration strictly according to the period when the debt arose, i.e. changes need to be made to the document. The Ministry of Finance thinks so. At the same time, court practice recognizes the right of the taxpayer on the basis of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 54-1, to reflect the uncollectible “receivable” in a later period, if the income tax was overpaid earlier (the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, definition No. 305-KG17-14988 of 01/19/18 and a number of others).
On a note! If there is a counter debt and the bad debtor is also a creditor of the organization, the position on the issue of recognition of such debt in the accounting of the judicial authorities and the Ministry of Finance differs. Courts have held that regardless of whether a firm chooses to set off or not, bad receivables must still be recognized as such. After all, according to the norms of the Civil Code, a company has the right to set off, but is not obliged to make it. The Ministry of Finance strictly adheres to the position that first it is necessary to offset, and then only recognize the uncollectible “debt” (letter No. 03-03-06/1/620 dated 04/10/11). The final decision rests with the organization.