Everyone earns their bread as best they can. This has long been a well-known practice, which often has an illegal basis. It lies in the fact that a person independently looks for a job that he would like and generate income. Most often, this is difficult to implement, since many do not know what to do and how to live when there is no paid work. But there are still citizens who have found their business and earn a penny.
Someone, of course, has a big profit, but in most cases this is not the case. That is, the amounts are relatively small and are only enough for food. A lot of people work this way, but they don’t pay taxes. This is a loss for the state; the treasury is not replenished, which means there will be no money. What to do then? That's right, we need to create a law that will provide for such moments and will not allow the self-employed to be in the shadows. This is exactly what the government did, amending certain articles and creating a new bill.
Some will say that this is very good and it will be better this way, but this is not entirely true. To begin with, it is worth considering a self-employed citizen who lives in the Russian Federation.
Statistics say that there are from 12 to 25 million self-employed people in the Russian Federation:
He is an ordinary person whose income is below average. You either have a car or you don’t, but it’s almost always broken. He doesn't live richly, but he doesn't live poorly either. He tries to buy everything on sale and save money. It is worth noting that saving is not a sign that a person is financially poor. If he knows how to distribute and count money, then this is financial literacy. Such a citizen is engaged in tutoring, and maybe programming. In principle, anything, but only self-employment. That is, he has no management, no registration either, but he has income, although this is not very common. And now, such people will owe the state. Maybe a little, but still.
He already has every penny in his account, and then they decided to do taxes. It is worth saying right away that by law such a person must pay a certain amount to the country, but in practice this will not happen. Such conclusions can be drawn by looking at older reports about laws and rumors about the self-employed. The fact is that even some high-ranking officials say that this tax has not worked in past years. Apparently, such a system has already been launched, but was not successful. And now everything is repeating itself. At that time, over the course of several months, no more than 40 people applied who wanted to register. The indicator, to put it mildly, is not impressive, and besides, it shows the disinterest of citizens in such tax deductions.
Nevertheless, the law will be adopted and approved, so it is worth finding out who is included in the group called “self-employed”. It was said earlier that this is an ordinary person who works for himself. That is, he calculates all income and expenses independently, as well as his salary. But it’s worth considering how such people are described from the legal perspective:
- He bears all risks independently, just as he works. That is, he has personal involvement.
- Provides services or work for individuals (sometimes legal entities).
- Profit is made in a special way. Specifically, there must be a certain system that works in an individual way. Everything is complicated, but this is only in appearance. It is envisaged here that a person is constantly engaged in some kind of work that brings him an almost stable profit. That is, this process is established, like calculating profits and losses.
- A citizen should not be an entrepreneur.
- He must work alone and not have a single employee (hired worker) on his “staff.”
That’s all the criteria that are very easy to try and find out whether a person fits this group or not.
This law will make it possible to identify those who previously worked illegally and did not pay taxes. Apparently those who came up with this project think so. In fact, everyone has worked and will continue to work. Of course, this turn of events was foreseen at the state level, and if illegal work is discovered, fines will be imposed. Whether they will save the situation as a whole is a big question.
If we consider what the bill was created for, then we can confidently say that it has its advantages. To begin with, we must not forget that there are citizens who are ready to share their income with the state and save for their retirement. Therefore, for them this project will be an ideal option for realizing such ideas. In addition, this niche of self-employed citizens was not protected in any way. And this law provides that there are no unlawful actions on both sides. If everything really turns out to be as presented, it will help many of those who want to save for their retirement and work completely legally. In any case, a certain part of the self-employed were waiting for such a law in order to feel safe not only for the present time, but also in the longer term. Therefore, it will still be useful for someone.
Reasons for legalizing self-employed people in Russia
Finance Minister Anton Siluanov, during the session “Russian Tax System: Image of the Future” at the Gaidar Forum in Moscow, said that business bears a large burden in the form of labor taxes, and this is one of the problems of the tax system in Russia.
“30% of insurance premiums alone! I'm not even talking about VAT or income tax. In other countries there is no such burden. And here we are losing the competition, the competitiveness of our tax system compared to other countries. I believe that here we have a need to work, look and optimize the tax system, make it competitive in this part, redistributing the tax structure, reducing the burden on labor.”
According to estimates, due to informal employment, the budget annually loses 3 trillion rubles in revenue, which is almost 3% of gross domestic product. At the same time, about 25% of Russians’ labor income is invisible to the state, and 13 million people do not pay taxes. The numbers are impressive. And even despite the fact that some of the so-called informal employment is hired workers receiving wages “in an envelope,” the number of self-employed people is also large and the state’s shortfall in taxes is also significant. In this situation, the emergence of a new tax - a tax on professional income - is completely expected, and the actions of the state, which is attempting to bring a significant and rapidly increasing segment of the population “out of the shadows”, are quite natural.
Without assessing the statements and actions of the government, we conclude that from the official point of view, regulation of self-employment is a reconfiguration of taxation and a kind of adaptation to current changes in the labor market.
At the same time, we agree that the structure of the tax system should ideally lead to a whitewashing of the economy. So it is clear that the purpose of introducing the category “self-employed” is to legalize a significant number of persons providing services (producing and selling goods) privately, but not registering their activities anywhere, and most importantly, not paying taxes.
Laws and regulations on self-employed people in Russia
So what laws have been passed? What definitions are given? And how is the legal activity of self-employed citizens defined by law?
Federal Law No. 422-FZ dated November 27, 2018 “On conducting an experiment to establish a special tax regime “Professional Income Tax” in the federal city of Moscow, in the Moscow and Kaluga regions, as well as in the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan)” was adopted. A from 1 As of January 2021, changes are already being made to it (Federal Law dated December 15, 2019 N 428-FZ).
The experiment must be carried out for ten years, until December 31, 2028. During this period, tax rates will not increase, and the income limit that gives the right to switch to this special regime will not decrease (parts 2, 3 of Article 1 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
In which regions is a tax regime for self-employed people introduced?
In test mode, taxation of self-employed people began in 2019 in Moscow, Moscow region, Kaluga region and Tatarstan. From 2020, professional income tax will be introduced in 19 more regions:
- St. Petersburg,
- Leningrad region,
- Voronezh region,
- Volgograd region,
- Nizhny Novgorod region,
- Novosibirsk region,
- Omsk region,
- Republic of Bashkortostan,
- Rostov region,
- Samara region,
- Sakhalin region,
- Sverdlovsk region,
- Tyumen region,
- Chelyabinsk region,
- Krasnoyarsk region,
- Perm region,
- Nenets Autonomous Okrug,
- Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra,
- Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug.
The application of tax on professional income by foreign citizens who are not citizens of member states of the Eurasian Economic Union is not provided for by law. EAEU states: Russian Federation, Republic of Belarus, Republic of Kazakhstan, Republic of Armenia and Kyrgyz Republic.
The Cabinet of Ministers expects that by the end of 2024, 2.4 million citizens will receive official self-employed status.
Definition of self-employment
Please note that the term “self-employed” is not legally defined. However, we will assume that the self-employed are individuals who receive income from work activities in which they do not have an employer and do not attract employees under employment contracts. Self-employment is employment in which remuneration is directly dependent on the income (or potential income) received from the goods and services produced.
Text of the law on self-employed citizens of the Russian Federation
You can view the text on the official resources of the Russian government. Why there? Firstly, this is reliable and unfalsified information, which is checked before it goes to the site. Secondly, the law stipulates many points. For example, conditions, rules and much more. You need to read all this independently and completely, otherwise you may miss something important. There is no point in placing text inside this article, since all aspects cannot be considered properly.
Who can be self-employed
A special tax regime can be applied by individuals engaged in activities where the law does not require mandatory registration as an individual entrepreneur, while even those registered as an individual entrepreneur do not lose the right to apply the special regime. (Parts 1 and 6 of Article 2 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ dated November 27, 2018). Individuals should not have employees with whom employment contracts have been concluded, and the income taken into account when determining the tax base under the special tax regime should not exceed 2.4 million rubles in the current year (clauses 4 and 8 of part 2 of article 4 of the Federal Law of November 27 .2018 No. 422-FZ).
What taxes do self-employed people pay?
The majority of self-employed citizens are clearly dissatisfied with the new law. Some of them even declare that they are not going to write a statement anyway, thereby obliging themselves to pay tax on their activities. Among such citizens, two main groups can be distinguished:
- Representatives of the first group fundamentally do not want to pay tax on their earnings. They believe that the state spends tax revenues in the budget inefficiently due to the high level of corruption.
- Representatives of the second group believe that they already pay taxes. After all, the purchase of any product or payment for any service includes the amount of value added tax. Also, these citizens regularly pay for utilities and all kinds of services that the state provides them. They believe that this is quite enough to fulfill their tax obligation to the country.
However, unfortunately, for representatives of both groups, as well as all citizens who, for any reason, refuse to withdraw their earnings “from the shadows” and pay taxes on it, from January 1, 2021, such activities will be considered illegal and will be subject to action articles of administrative, tax and even criminal legislation. The consequences can be dire, from the closure of activities and seizure of property, to fines of various sizes, and in especially severe cases, even criminal liability.
The new law even establishes specific penalties for citizens who refuse independent voluntary registration:
- In the first case detected, a fine of 20% of the detected amount of profit is imposed (however, the fine cannot be less than 1,000 rubles).
- In case of a repeated case, detected within 6 months after the previous one, all profits received (but not less than 5,000 rubles) are already confiscated in favor of the state.
Those who still do not joke with the state and follow the legal path will face the following taxes on their income:
- 4% of income in the case of providing services to other citizens, or for activities related to the sale of goods.
- 6% of income, in the same case if services or goods are sold to legal entities.
- 1.25% of income goes to the Pension Fund.
- 0.5% of income – Mandatory Health Insurance Fund.
It is worth noting that these interest rates are relevant for those self-employed citizens whose annual income from activities does not exceed 2.4 million rubles, or 200 thousand rubles per month. If exceeded, the rate is calculated in accordance with the excess amount. But it is worth recalling that the amount cannot exceed 10 million rubles, otherwise the status of a self-employed citizen will be automatically canceled.
But in order for people to begin to bring their activities “out of the shadows,” it is clearly not enough to introduce penalties. Citizens need to be interested by showing them the positive sides of such a decision. To achieve this, the state has introduced the following incentive measures:
- Self-employed citizens have the right to count on a tax deduction of 30 thousand rubles as compensation for insurance premiums and part of tax fees.
- For clients of these citizens - a refund of 1.5% of the amount of tax paid (but not more than 10 thousand rubles during one calendar year).
- Additional insurance guarantees.
As for deductions to the pension fund, self-employed citizens can only count on a minimum social pension from the state, but such citizens must worry about more themselves. To increase the final amount of your pension, you need to consistently pay contributions to the Pension Fund over a long period of time, or, after creating an individual pension capital system, join such a system.
According to the law, funds received from taxes from self-employed citizens, as well as fines for refusal to register, will go to the regional and municipal budgets. The regional budget will receive money from taxes on activities at the place where they are carried out, but the municipal budget will receive tax fees at the place of registration of the taxpayer.
Registration of self-employed
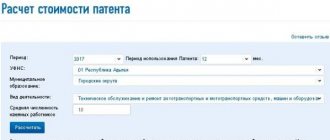
The official application of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for taxpayers of tax on professional income is the “My Tax” application, which helps to register and work, ensuring interaction between the self-employed and tax authorities, and also replaces the cash register and reporting.
The registration process is very simple. So, if you have a taxpayer’s personal account and after installing the “My Tax” application on your phone or tablet, select the registration mode “Through the personal account (personal account) of an individual,” confirm your mobile phone number and select the region of activity. If you do not have a personal account as an individual, during the registration process the “My Tax” application adds the need to scan the citizen’s general passport and add a photo.
Example of NPD calculation
The state compensates all self-employed people with a tax deduction of up to 10,000 rubles. Let's look at how this happens, using the example of a specialist who periodically receives payments for his services from individuals and companies:
| Month | Income | Percentage: 4 from individuals, 6 from legal entities, in rubles | Deduction amount: 1% from individuals, 2% from legal entities, in rubles | Tax amount, in rubles |
| January | 150 thousand rubles. from individuals | 6000 | 1500 | 4500 |
| February | 80 thousand rubles. from individuals and 50 thousand rubles. from legal entities | 3200+3000=6400 | 800+1000=1800 | 4600 |
| June | 40 thousand rubles. from individuals and 40 thousand rubles. from legal entities | 1600+2400=4000 | 400+800=1200 | 2800 |
| September | 150 thousand rubles. from individuals and 50 thousand rubles. from legal entities | 6000+3000=9000 | 1500+1000=2500 | 6500 |
| October | 150 thousand rubles. from individuals | 6000 | 1500 | 3500 |
| November | 50 thousand rubles. from individuals and 50 thousand rubles. from legal entities | 2000+3000=5000 | 500+1000=1500 | 3500 |
| December | 190 thousand rubles. from legal entities | 11400 | Deduction exhausted | 11400 |
| In a year | 1 000 000 | 47 800 | 10 000 | 36 800 |
The tax service independently calculates the amount of deductions and limits. In the “My Tax” web application or the taxpayer’s Personal Account, the amount is automatically reduced by the difference in deduction. This will happen until the self-employed person exhausts the limit of 10 thousand rubles. The deduction is provided one-time and is not renewed in the next reporting period. That is, if a self-employed person received full compensation from the state in 2021, then there will be no refund in 2021, and the tax will be withheld in full at 4% and 6%. There are no time restrictions. For self-employed people with low incomes, the deduction compensation period will last for several years.
Income not included in the income of the self-employed
Now let’s look at some of the nuances of the tax regime, the differences between the activities of the self-employed and individual entrepreneurs and other types of income-generating activities. For example, income that cannot be recognized as income of the self-employed (Part 2 of Article 6 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018):
- Wages, that is, income received within the framework of an employment relationship with an employer;
- Income received from the sale of real estate and movable property, as well as income received from the transfer of property rights to real estate, excluding income from rental (hire) of residential premises,
- Income (salaries) of state and municipal employees,
- Income from the sale of personal property of citizens used for personal, household or other similar needs,
- Income from the sale of shares and shares in the authorized (share) capital of organizations, and mutual funds of cooperatives, and mutual investment funds, securities, as well as derivative financial instruments,
- Income from conducting activities under a simple partnership agreement (joint activity agreement) or a property trust management agreement,
- Income from the provision (performance) of services (work) by individuals under civil contracts, provided that the customers of the services (work) are the employers of these individuals or persons who were their employers less than two years ago,
- from the activities specified in paragraph 70 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, received by persons registered with the tax authority in accordance with paragraph 7.3 of Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (we are talking about individuals (not individual entrepreneurs) who received income from other individuals, for example, for childcare, tutoring or cleaning of residential premises),
- Income from the assignment (assignment) of rights of claim,
- Income received in kind
- Income from arbitration management, from the activities of a mediator, appraisal activities, activities of a notary engaged in private practice, and advocacy.
Income is recognized on the date of receipt of funds or their receipt in bank accounts (Part 1, Article 7 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018).
How to report to the self-employed
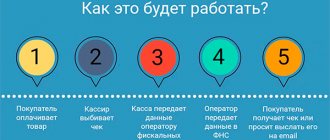
A self-employed person independently decides what income to report in the taxpayer’s Personal Account. They will not control all receipts from cards or other accounts of individuals. The application is not synchronized with bank accounts, where money may be received as a gift or compensation for the unused portion of the loan insurance. Therefore, you will not need to pay taxes on any income. But if a check was created for the customer, then tax will have to be paid. It will automatically be reflected in the Personal Account of the self-employed.
The self-employed person sends a check from the “My Tax” application to all customers – legal entities. This may be an electronic or paper version of the document. Legal entities use this primary document for their own reporting. The check must indicate:
- TIN of the self-employed;
- description or summary of the service, product or work provided;
- sum.
Electronic and paper checks are useful when making NAP payments. The tax amount for all deposited checks will be calculated by the tax authority. A letter will be sent to your office by the 12th of the next month. The amount must be paid by the 25th, after the notice is issued. If the tax amount has not reached 100 rubles, then the notification will not be sent. The amount will automatically roll over to another month and be added to the next payment.
When a self-employed person fails to pay taxes on time, the Federal Tax Service will impose a fine of 20% of the settlement amount. If the violation is repeated within six months, the amount of the fine will be equal to the amount of payment received.
about the author
Klavdiya Treskova - higher education with qualification “Economist”, with specializations “Economics and Management” and “Computer Technologies” at PSU. She worked in a bank in positions from operator to acting. Head of the Department for servicing private and corporate clients. Every year she successfully passed certifications, education and training in banking services. Total work experience in the bank is more than 15 years. [email protected]
Is this article useful? Not really
Help us find out how much this article helped you. If something is missing or the information is not accurate, please report it below in the comments or write to us by email
Permitted activities of self-employed people
So what can self-employed people do? Let us turn to paragraph 70 of Article 217 of the Tax Code (Tax Code).
Self-employment includes persons engaged in the following activities or having the following professions:
- Care (supervision) for young children, seriously ill people, the elderly (over 80 years old), as well as persons who require outside help,
- Tutoring, homeschooling,
- House cleaning, washing, ironing, drying, cooking, caring for the garden, garden, homestead,
- Services of a personal trainer, security guard,
- Organization (management, maintenance and repair of the house) of the household sphere,
- Repair and construction work (electrical, plumbing, roofing, finishing and the like) in residential and other small real estate properties,
- The work of photographers, the creativity of artists, web designers,
- Manufacturing and repair of shoes and other leather products,
- Tailoring and repair of clothes,
- Installation of computer programs,
- Installation and maintenance of computer equipment, refilling copiers, printers,
- Tuning musical instruments,
- Diagnostics and repair of electronic household appliances, household (garden) items,
- Yard work (landscaping, plowing, cutting firewood),
- Working with animals (feeding, grazing, training),
- Handmade pottery, jewelry, wood and metal products,
- Key cutting,
- Processing of livestock and hunting products (wool, hides, horns and hooves),
- Translation of text from foreign languages,
- Medical services (massage, preventive therapy) that are not highly qualified,
- Work of stylists, hairdressers, cosmetologists (manicure, pedicure, skin care),
- Renting out your own real estate (apartments, rooms, garages, cottages),
- Preparation of diplomas, abstracts, coursework, articles and materials for Internet resources,
- Organization of holidays and ritual events.
Unauthorized activities for self-employed people
At the same time, there are restrictions on types of activities (Part 2 of Article 4 of Federal Law No. 422-FZ of November 27, 2018). For example, you cannot do:
- Carrying out the sale of excisable goods and goods subject to mandatory marking by means of identification in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation,
- Resale of goods, property rights, with the exception of the sale of property used by them for personal, household and (or) other similar needs,
- Extraction and (or) sale of minerals,
- Carrying out business activities in the interests of another person on the basis of agency agreements, commission agreements or agency agreements, with the exception of services for the delivery of goods and acceptance (transfer) of payments for specified goods (works, services) in the interests of other persons,
- Persons applying other taxation regimes provided for by part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, or carrying out entrepreneurial activities, income from which is subject to personal income tax, with the exception of cases of applying other taxation regimes and calculating personal income tax on income from entrepreneurial activities up to transition to the specified special tax regime.
Let us add that self-employed citizens can combine their commercial activities with regular employment. This is not prohibited by law when the labor sphere does not intersect with one’s own business.
General conditions of the special regime
It is impossible to apply a special regime for paying taxes on income that:
- come from the employer in the form of wages;
- appeared from the sale of an apartment, other real estate or car;
- civil servants receive, in addition to the amounts they receive for renting out living space;
- paid for services under the GPA, if they came from a customer who was the employer of this individual in the previous two years;
- arrived in kind;
- arose during the sale of part of the authorized capital, a share in a mutual fund, other securities and other assets.
To pay NTD, download the “My Tax” smartphone application and log in to the system. There is no need to install an online cash register and submit a tax return. If an individual entrepreneur wants to pay taxes under a special regime, he can write an application and switch to it at any time. If he exhausts the amount limit, or the NPA is unprofitable, the individual entrepreneur can return to the previous one or switch to a new regime. There are no legal restrictions on this matter.
Self-employed people who pay personal income tax are not deducted insurance premiums. The state will not accrue insurance experience or points to them. But if you want to receive an official pension from the state, then you can buy experience. To do this, you will need to annually transfer to the Pension Fund the amount that is prescribed in Article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If a self-employed person does not do this, then he will not be able to claim an insurance pension payment, but only a social pension payment, which is issued 5 years later. In addition to the fact that the social pension is lower, it is also not indexed by the state. Everyone decides for themselves whether to pay insurance premiums or not. Perhaps, wisely investing the amount of 30 thousand rubles per year will bring greater benefits than transferring it to the Pension Fund.
Everything about professional activity tax
The professional income tax is not an additional tax - it is a new special tax regime. The transition to it is voluntary.
Persons who have not switched to this tax regime are required to pay taxes taking into account other tax systems that they apply in the usual manner. Individuals and individual entrepreneurs who have switched to a new special tax regime (self-employed) will be able to pay tax on income from self-employment at a preferential rate of 4 or 6%, which will allow them to legally conduct business and receive income without the risk of penalties for illegal business activities.
A special tax regime significantly simplifies business support for a business:
- The declaration is not submitted to the tax authority;
- Income accounting is carried out automatically in the mobile application;
- No need to buy cash register equipment. The receipt is generated in the “My Tax” mobile application;
- There is no obligation to pay fixed contributions for pension and health insurance;
- There is no need to register as an individual entrepreneur;
- Income is confirmed by a certificate from the application;
- 4% - from income from individuals;
- 6% - from income from legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. No other mandatory payments;
- The amount of tax deduction is 10,000 rubles, the rate of 4% is reduced to 3%, the rate of 6% is reduced to 4%. The calculation is automatic. The tax is calculated automatically in the application. Payment - no later than the 25th of the next month;
- Registration without a visit to the inspectorate: in a mobile application, on the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia, through a bank or government services portal;
- Salary is not taken into account when calculating tax. The length of service at the place of work is not interrupted.
Amount of contributions to the budget
In the special regime, self-employed people pay to the state:
- 4% if the settlement is with an individual;
- 6% if the customer is a legal organization.
At the initial stage, the state compensates each self-employed person with a tax deduction. As a result, payments to the budget will be even less: 3% from income from citizens and 4% from income from legal entities. There are no such low rates under any other tax regime. It’s cheaper just not to pay any taxes at all.
The total amount of income received cannot exceed 2.4 million rubles per year. It doesn’t matter whether you received 2 million rubles in January, or 15 thousand rubles for the whole summer. The limit does not affect monthly income. For most self-employed people, the annual limit is sufficient. But if it is exhausted, you will need to file a tax return separately for the remaining income and pay 13%. If this is not done, the tax authority will impose a fine.
If the self-employed person is not an individual, but an individual entrepreneur, then he will need to change the tax regime, for example to a simplified one. At the beginning of next year, you can use the NDP again, as long as the limit allows.
Liability and fines
In case of failure to register with the tax authorities, the law provides for liability for self-employed citizens.
- a fine of 20% of illegally obtained income for the first violation;
- a fine of 100% of income for relapse.
The minimum size of the sanction is not limited.
The law does not yet provide for criminal liability. However, it should be remembered that if the activities of a self-employed citizen are detected without registration (with the help of banks, through newspaper advertisements and other methods), the tax authorities will sue. The court sides with the Federal Tax Service and brings the person to criminal liability under Article 171 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (illegal entrepreneurship), and this violation is punishable by a fine of up to 300 thousand rubles, or compulsory work for up to 480 hours, or arrest for up to six months.
Self-employed pensioner - taxes
For self-employed citizens who have reached retirement age at the time of filing the application, the entire procedure is absolutely no different. The amounts of contributions remain the same, with the exception of the contribution of 1.5% interest to the pension fund, which is excluded in this case (for obvious reasons). Self-employment can be a great option for retirees. This option is suitable, for example, when independently selling the products of your labor in the garden - fruits, vegetables.
However, again, do not forget that this should be a solitary activity. In case of help from children, grandchildren and other citizens, you will have to register an individual entrepreneurship. Older people are often seen engaging in such activities, however, there will be no relaxations in the law for them either - grandparents who sell their products in the same way as all similar citizens must obtain self-employed status by submitting a corresponding application to the local tax authorities .
Self-employment. Foreign experience
The experience of regulating the activities of self-employed citizens of foreign countries is very interesting. Let's look at the main directions of government policy regarding the self-employed population in several of the most developed countries.
Self-employment in the USA
In the United States, the share of self-employed people is constantly growing. Investopedia, a popular business and economics resource in the United States, notes that various government agencies and private research companies include various categories of professional activity in the list of self-employed people. Estimates show that about 30% of US workers fall into this category. The highest share of self-employed people is observed in agriculture, construction, and services (provided to the population and business). The professional composition of the self-employed includes artists, musicians, accountants, doctors, real estate agents, lawyers, software developers and many other professionals. In the USA, representatives of this economic category pay for themselves the so-called Self-employment tax. This tax consists of payments to the social insurance system and to the health care system, and its amount is 15.3% of profits, of which 12.4% comes from payments to social funds, and 2.9% from payments to the health insurance system . The second tax paid by self-employed people in the United States is income tax, the rates for which are progressive and depend on the amount of profit. The lower threshold for this rate is 10%, which corresponds to (pays for) profits of less than $9,225 per year. The upper level (39.6%) is set for those whose income is more than $414 thousand per year. It is important to understand, however, that in the United States, state and municipal taxes have a very large impact on the total payout of self-employed people. Thus, in some states additional payments amount to up to 5.6% of the income of the self-employed population. Another interesting fact is that the number of self-employed people in the United States is constantly increasing, and this, in turn, has a positive effect on both increasing the average income level of citizens and reducing the unemployment rate. Moreover, more than 6% of national gross income, or about $1.3 trillion, comes from the self-employed.
Self-employment in Canada
In Canada, self-employment is generally encouraged by the government. The experience of Canada is interesting primarily not because of the peculiarities of taxation of the self-employed, but because of the special immigration program for the self-employed, which allows a citizen of any country with sufficient knowledge of the English language and experience as a self-employed person in his home country for two years (proof of such activity is banking extracts and recommendations from clients) obtain a permanent residence permit in the country.
At the same time, however, the list of areas of professional activity for the self-employed that they want to see in the country is limited. The list of desirable professions includes farmers, as well as those who can “make a significant contribution to the development of the culture of the state” (this is the official wording from the Canadian immigration service website), and these are primarily artists, editors, musicians, fashion designers, journalists, writers, designers, make-up artists and hairdressers, florists, jewelers, photographers, athletes, as well as numerous artisans and hand-made specialists and several hundred other professions. However, if a person who comes to Canada does not begin to pay taxes on his activities within a certain time, he is automatically excluded from being a resident of this special program and has no further basis for residing in the country.
Self-employment in the UK
In the UK there are no differences in the amount of taxes - it is the same for all working citizens. It is also interesting that the self-employed are not included in a separate category of workers. However, there is a gradation in the payment of taxes, the rate of which differs significantly depending on the profit received. The minimum income that is not subject to tax is 10,600 pounds sterling (about 850 thousand rubles). The basic tax rate is 20%, the minimum tax is 2%, the maximum is 45%. I repeat that the amount of taxation is very dependent on the amount of earnings.
Self-employment in Germany
In Germany, self-employed workers register with the Finanzamt, the German tax authority, within a month of starting their activities. Doctors, notaries and lawyers are members of trade union organizations based on the type of activity they engage in and must register with the Professional Chamber. Payment of income tax is mandatory for self-employed workers in Germany, the rate of which (15 - 42%) depends on the amount earned, expenses, and family composition of the self-employed taxpayer. Payment of insurance premiums is also required. At the same time, it is important that speech therapists, doctors, notaries and lawyers are not required to pay pension contributions.
In general, we note that the position of the self-employed in the economy, their social security and relations with the state vary greatly in different countries. The terms “self-employed” and “private entrepreneur” are often mixed, and a clear line between them is not drawn.
It is important to note that the structure of national economies and state regulation of activities in the self-employment sector have a decisive influence on the specialization of activities in the field of self-employment. If we talk about the most developed countries, for example about countries included in the OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development), then the main features of the development of self-employment can be reduced to the following:
- Growth in the number of self-employed people exceeds the growth rate of total employment in most OECD countries;
- The greatest growth in self-employment was concentrated in fast-growing sectors of the economy, such as business and social services, and the highest rates of self-employment development were among highly qualified specialists;
- In the vast majority of OECD countries, the number of men in self-employment is significantly lower than the number of women;
- In the sphere of self-employment, there is a higher intensity of work, which is associated with greater responsibility for its results, but it is worth noting that this is more than compensated by the consciousness of independence and a sense of personal satisfaction from performing one’s work;
- The greatest interest in the field of self-employment is among young people with a high level of education, as well as among highly qualified older specialists;
- Governments in almost all OECD countries have introduced programs aimed at attracting youth and women into self-employment.
Unfortunately, the picture in developing countries is completely different. There, self-employment is a necessity, not a choice. In countries with middle and low incomes, self-employment is the only income opportunity for a significant number, and often even the majority of citizens. For example, in India more than 75% of workers are self-employed, in Kenya this figure is 60%, in Bangladesh - 70%. It is also important that in most developing countries, social and medical protection covers the working population, while the self-employed are left to their own devices.
Critical view
And finally, let's return to the school curriculum again. Exactly where this article began - to the change of eras, to a reminder of the painful course of this process. After all, adjusting government programs and introducing changes to adopted laws is quite commonplace. And therefore, I consider it pointless to talk about the imperfection of the laws adopted in our country on the self-employed. After all, the law itself calls this program an experiment, which already says a lot.
But about increasing the level of income - our government officials always need to remember this. Remember that, unfortunately, in our country (here the similarities with most developing countries are clearly visible) self-employment is most often a forced necessity, and not a conscious happy choice. The income of the self-employed is also often very low. And therefore, we still need to think hard about the timeliness of taxation of this segment of the population. In any case, for self-employed people with low incomes it is worth introducing a zero rate. And the main argument for this, in addition to the president’s words about the priority of increasing income levels, can be