What is accounts receivable
The work of any organization is associated with the occurrence of debt. It comes in two types:
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
– accounts receivable
– accounts payable
Usually there are no difficulties in understanding what accounts payable is. If we explain it in terms familiar to the average person, then accounts payable are all the amounts that a company owes to its counterparties, the budget (in the form of taxes) or other creditors.
The opposite situation occurs when accounts receivable are formed. All amounts that the company expects to receive will be the amount of accounts receivable.
For example, a company overpaid VAT to the budget. The amount of tax that is transferred in excess of the accrued amount will be a receivable. The same situation arises if an organization transfers money to a counterparty on account of a future delivery. With regard to funds paid to employees: the “accounts receivable” includes wage debts to employees, as well as funds issued on account.
The amount of such debt is formed throughout the year and is reflected in the balance sheet in line 1230, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n dated July 2, 2010.
| IMPORTANT! In the vast majority of cases, the debt of counterparties to the organization is reflected in the balance sheet asset in the section reflecting the value of current assets |
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |
Line 1230 of the simplified balance sheet explanation
Thus, all debt to the company is included in reporting Form No. 1.
Liquidity of debts as an asset
Accounts receivable is a financial current asset with which a company can quickly pay off its obligations to others.
The speed with which an asset can be used to pay bills indicates liquidity. The faster an asset can be converted into cash, the higher its liquidity.
But in practice, the presence of a large share of debtors, especially with reserves on account 63, indicates the company’s problems. Debts are unpaid bills issued to customers and clients. They used the products or services, but did not pay any money.
Or, on the contrary, the advance was paid to the contractor, but the work was not completed. The company must constantly monitor the level of such arrears, as there is a high risk of fraud and financial losses.
Arrears arise for the following reasons:
- Imprudence in choosing clients when concluding a transaction.
- Insolvency of buyers.
- Difficulties in selling products.
- Lack of daily work with debtors.
- Rapid growth in sales volume.
The optimal indicator of the level of receivables is when the balance of the accounts included in line 1230 of the balance sheet and the company’s funds coincide with obligations to creditors. To track fluctuations in existing debts, you can conduct financial analysis using a special ratio.
Measuring Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable on the balance sheet tend to increase or decrease, which can be either positive or negative. To measure the proper level of the indicator, the turnover ratio is used in finance.
It is advisable, for convenience in accounting, to open analytical accounting on account 76 on subaccounts.
All these account balances are added up, then the balance on the passive account is subtracted from them. 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”.
Just remember that the balance on all accounts must be expanded.
Types of receivables in a company
All receivables are divided into two large groups:
- Long-term
- Short term
Both varieties fall into balance after a year.
All debts that are repaid within 12 months constitute short-term “receivables”. As a rule, such debt includes overpayment of taxes, shipments to counterparties “on credit,” or prepayment for goods or services.
Long-term debt appears when the debt is not paid off within a year. As for settlements with counterparties, the possibility of this type of debt arising should be specified in the agreement with the partner. However, if the counterparty simply does not pay its obligations for a long time, then such debt also belongs to the category of long-term.
Of course, it is in the interests of each organization to have a significant share of short-term debt out of the total amount of “receivables”.
It must be taken into account that no matter what type of debt, after missing the repayment deadline, it becomes overdue. It is not in the best interests of the company to have overdue accounts receivable .
There is often great doubt that the debt will ever be repaid. Often such overdue debts are never closed, that is, they become hopeless. A debt can be doubtful for three years, and then becomes uncollectible. Ultimately, such debt must be written off as a loss.
What affects the composition
In the process of indicating all the necessary information in this line, data on the balance of “receivables” for accounts 46, 62, 68,69, 71, 73, 75, 76 is used, with the exception of the loan balance on account 69 (the formed reserve for debt obligations).
According to the available clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in a situation where the transfer of funds takes place as payment in full or in part towards future deliveries of goods or is subject to display in the balance sheet, taking into account the minus amount of VAT .
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the amount of the advance payment and other advance payment for work or services provided is displayed in the first section “Non-current assets” of the balance sheet, and, for example, the amount of the advance payment due to the purchase of inventories for production needs is displayed exclusively in the second section “Current assets” .
The analysis showed that the main source of growth in receivables is Company 3. If receivables were not insured under an agreement with this buyer, then the risk of financial damage increases. At the next stage, settlements with the problematic counterparty and other companies are detailed, taking into account the deferments granted to them:
Company 3 remains problematic. Only this company did not meet the debt repayment deadlines, even taking into account their extension. Further work consists of establishing a dialogue with this counterparty; if there is no response, you can go to court.
What are accounts receivable on the balance sheet?
Clause 27 of PBU 4/99 states that accounts receivable on the balance sheet is an important indicator that must be explained in the explanations to the report.
If settlement is delayed, the amount goes into the category of doubtful debts.
What is accounts receivable in simple words?
This type of debt may include accountable amounts, overpayments in settlements with employees, loans provided and obligations of third parties to repay damage and material damage. Accounts receivable are funds payable by counterparties in favor of our company, but on deferred payment terms with the consent of both parties.
Accounts receivable management
In relation to accounts receivable, it is necessary to systematically monitor outstanding balances, correlate them with the expected timing of receipt of payments, identify illiquid debts and find out the reasons for this phenomenon. Working with accounts receivable involves collecting the most detailed information about the current state of payments and finding ways to reduce doubtful debts.
Debts of counterparties can be divided into groups:
- According to the criterion of repayment periods - short-term (period up to 1 year, line 1230 in the balance sheet) and long-term (more than a year).
- When assessing the effectiveness of collection methods - current (for which the deadlines for payment have not been met), doubtful (with missed deadlines, but with no doubt about the receipt of money in the near future), hopeless.
Overdue accounts receivable are cases when money did not arrive in the bank account on the appointed deadline for goods already shipped or goods were not received within the agreed period subject to full prepayment. The second option for moving into the category of overdue debts is that the statute of limitations has expired.
Overdue accounts receivable – how many months or years? A debt is classified as overdue on the day after the payment deadline.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation makes it possible to resolve the issue of returning money within 3 years (Article 196).
What we reflect in line 1230 of the balance sheet: accounts receivable
- Purpose of the article: reflection of information on accounts receivable
- Line number in the balance sheet: 1230
- Account number according to the chart of accounts: Debit balance 60, 62, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 – credit balance 63
Accounts receivable in the balance sheet are the amounts generated in the accounting accounts at the end of the reporting period. They show what debts suppliers, customers, employees and tax authorities have to the company.
Accounts receivable may include:
- advances paid to suppliers for work, supplies, services;
- debts of buyers, contractors for services received but not paid for (goods, work);
- debt of accountable persons, that is, employees of the enterprise;
- overpayment of taxes, fees, insurance contributions to funds;
- wage debts of employees;
- debt of participants (founders) on contributions to the authorized capital;
- other types of arrears.
How are account balances reflected?
All of the listed types of receivables correspond to their numbers, which are approved by a special Chart of Accounts, on the basis of which business transactions are recorded.
At the end of the year, each organization must draw up a financial report, which is called a balance sheet or Form No. 1. Debts of other persons to the company are included in the balance sheet as the sum of the expanded debit balance of a number of accounts minus the credit balance of 63 accounts.
This means that you cannot take the difference between the debit and credit balances for calculation. The balance sheet must include account balances that are simultaneously formed as debits and credits. Such accounts are called actively passive.
Moreover, there are no guarantees of return.
It is worth recalling that the formation of a reserve is considered solely as an adjustment to estimated indicators in accordance with PBU 21/2008.
What you should pay attention to
The reserve for doubtful debts can be formed for any type of receivables; it is enough just to recognize them.
In addition, not only a debt obligation with a closing period has come into question, but also one whose term has not yet arrived, but which has a high probability of non-payment in full or in part.
In parallel with this, if in relation to the overdue receivables at the date of the reporting period there is confidence in the closure of debt obligations, then there is no need to create a reserve.
Which accounts make up the amount of accounts receivable?
When determining the amount of accounts receivable, it should be remembered that its amount is not formed on any one account, but consists of a set of values that are reflected in the debit balances of many accounts. This is enshrined in the order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
The calculation uses balances on the following accounts:
- If the company has a work in progress, then the turnover on account 46 will show the volume of work already completed
- Account 60. Shows the status of settlements with various suppliers
- Account 62 reflects the status of settlements for transactions with customers
- Accounts 68, 69. Show balances for settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds
- Accounts 70, 71, 73. They show the status of settlements with employees of the organization
- Account 75. This is the debt incurred in relation to the founders
- Account 76. Reflects settlements with other counterparties
Line 1230 of the simplified balance sheet explanation
Typical transactions taking into account movements on account 63:
- debit 91.2 - Credit 63 - doubtful debts are reflected in expenses as a percentage depending on the time of delay;
- debit 63 – Credit 62 (60, 76) – bad debt written off against the reserve;
- debit 63 – Credit 91.1 – the reserve for doubtful debts was restored when the debtor fulfilled its obligations.
Since the amounts for account 62 in Form No. 1 do not coincide with the balance sheets of the accounting department, the breakdown of receivables, taking into account the formed reserves, is given in Table 5.1 of the Explanations to the balance sheet, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n.
The table should reflect the movement and structure of arrears at the beginning and end of the reporting and previous years. At the same time, the table format allows you to see the whole picture of debt formation and repayment.
Example of display in line 1230 of the balance
Requirements for drawing up a balance sheet can be found in PBU 4/99.
For example, Solovushka LLC has account balances that are reflected in the balance sheet.
According to the requirements of Order No. 66 n, amounts in the balance sheet must be in thousands or millions of rubles according to OKEI codes, which means line 1230 will look like:
Line 1230 of the balance = 60 account + 62 account – 63 account + 76 account = 20+30-10+5 = 45 thousand.
After this period has expired, the debt is written off.
Accounts receivable control goes through several stages:
- The terms for the transfer of funds are established in the agreement.
- Control of overdue payments with a delay period of up to 7 days, accompanied by clarification of the motives for what happened, development of debt repayment schedules and freezing of cooperation.
- If the period of delay in payment is from 7 to 30 working days, then it is necessary to charge a fine to the counterparty, remind him of his obligations, and meet with management.
- If there is a delay of 1 to 2 months, a written claim must be submitted.
- Longer delays are a reason to go to court.
Accounts receivable accounting
In accounting, receivables are accumulated not on one, but on several active-passive accounts. The occurrence of debt is indicated by the appearance of a debit balance for a group of settlement accounts. In which account are accounts receivable reflected in accordance with the coding of the Chart of Accounts (Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000):
- 60 or 62 for settlements with suppliers or customers;
- 68 and 69 – for cases of overpayment of taxes, fees and insurance premiums;
- 70, 71, 73 – for transactions with employees;
- 75 for debts of the founders;
- 76 for settlements with different types of debtors.
If accounts receivable are repaid, account 62 will participate in the following correspondence:
The debt is written off to 91 accounts - for example, when a loan is forgiven for an employee, an entry D91 - K73 is made.
The write-off of doubtful debts, which was included in the reserve, occurs by posting D63 - K62 (60).
Analysis and valuation of receivables
Valuation of receivables means establishing its market value as of the current date.
Doubtful debts and receivables
Currently, it is established at the legislative level that each organization, subject to certain conditions, must create a reserve for doubtful debts.
Such a reserve is created when there is debt from counterparties. In this case, one of the following conditions must be met:
- The debt must be overdue
- The company has information about serious problems in the financial sector of the counterparty
However, even if there are accounts receivable, a reserve may not be created if the company knows for certain that the debt will be repaid by the counterparty.
Accounting for created reserves is kept on account 63. In order to create a reserve, it is necessary to make accounting entry D91.2 K63. The same posting is used if the reserve needs to be increased (added).
The restoration of the reserve is reflected by posting D63 K91.1. But if the debt is hopeless and needs to be written off, an entry is made D63 K62 (or another accounting account for the counterparty).
Instructions for creating a reserve are contained in paragraph 7 of PBU 1/2008.
It is very important to remember that the provision for such debt is directly related to accounts receivable and its reflection in the company’s annual reports. When drawing up a balance sheet, the amount of the reserve reduces the amount of accounts receivable, the net amount is reflected in line 1230 of the balance sheet asset .
How to adjust accounts receivable?
The amount resulting from adding the debit balances of the above accounts must be adjusted before it is reflected on line 1230 of the balance sheet. How to do it?
Firstly, it is necessary to subtract from it the credit balance of account 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”, because the balance is compiled in a net assessment (clause 35 of PBU 4/99).
Secondly, the amount received must be reduced by the debit balance of subaccount 73-1 in terms of interest-bearing loans. After all, such loans should be reflected as part of financial investments on the same lines 1170 (if long-term) or 1240 (if short-term). However, interest accrued on such loans on line 1230 must be taken into account.
Thirdly, it is advisable to exclude the debit balance of account 60 in terms of advances and prepayments for work and services related to the construction of fixed assets from line 1230 and show it in line 1190 “Other non-current assets” of Section I of the balance sheet.
So, for example, when transferring an advance payment to the supplier, the following entry was made:
VAT on the transferred advance will be reflected, for example, like this:
Fifthly, line 1230 does not show VAT accrued for payment on advances received from buyers and reflected in the debit of accounts 62 or 76.
So, for example, when receiving an advance from the buyer, the following entry was made:
VAT accrued on the advance payment was reflected as follows:
Despite the fact that VAT on the advance was shown in the debit of account 62, it will not be reflected in line 1230.
The procedure for calculating the amount of receivables in the balance sheet
In order to calculate the amount of “receivables” to be reflected in the balance sheet, data from 10 accounting accounts is used.
To identify the correct debt balance for counterparties, it is necessary to generate settlement reconciliation acts and display the correct debt balance. This is necessary both for the organization itself and for the counterparty to correctly account for all obligations. After determining the amount of debt, its value can be transferred to the appropriate line of the balance sheet.
Let's give an example of filling out line 1230. At Romashka LLC, the account balances at the end of the year are as follows:
| Check | Debit balance | Credit balance |
| 60 | 10000 | 5000 |
| 62 | 25000 | 17000 |
| 63 | 8000 | |
| 76 | 3000 | 1000 |
Based on the given data, line 1230 will have the following meaning:
Page 1230 = 10000 + 25000 – 8000 + 3000 = 30000
String structure
The balance sheet is filled out as of the reporting date.
Information is entered into it based on the balances shown in the accounting cards. When calculating the balance of accounts receivable, which should be shown on the balance sheet, you need to focus on the debit balances of the set of accounts.
As a result, this is what line 1230 of the balance sheet consists of:
- in the final amount of debt, it is necessary to take into account the size of completed tasks for unfinished work reflected in account 46;
- balance of settlements with suppliers on account 60;
- the status of the debt of debtors, whose roles are buyers or customers of works/services - account 62;
- the final total for the debit of account 68, if there are overpayments of taxes and fees;
- to designate the receivable for insurance premiums, take account balance 69;
- also, line 1230 may contain information about overpaid funds to personnel (salaries overpayments are reflected in account 70, accountable funds to be returned are recorded in account 71, other transactions - account 73);
- if the debtor of the company is the founder, it is necessary to sum up the debit balance of account 75;
- The calculation must take into account the balance of account 76, which accumulates information on all groups of debtors not included in the previous categories.
Remaining debts to legal entities
As mentioned above, all these types of debt are distributed across different accounts of the balance sheet.
In cases where we are talking about debt balances to legal entities, we mean funds that are reflected in two accounts No. 60 and 62.
Brief instructions for analyzing receivables
Analysis of debt in a company is important. During its implementation, many indicators are assessed, but even based on the dynamics of changes in debt indicators, some conclusions can already be drawn.
| Index | 2017 | 2018 | Height, % | Deviation, thousand rubles | ||
| Sum | Percent | Sum | Percent | |||
| Total | 233810 | 100 | 324306 | 100 | 138,7 | 90496 |
| Suppliers | 227 | 0,1 | 601 | 0,2 | 264,8 | 374 |
| Buyers | 233353 | 99,7 | 316614 | 97,5 | 2721,1 | 83261 |
| Taxes | 228 | 0,1 | 6204 | 1,9 | 44350 | 5976 |
| Other counterparties | 2 | 887 | 0,3 | 885 | ||
In accordance with the data presented in the table, we can conclude that the largest weight of debt falls on buyer debts. In addition, compared to 2021, in 2018 there was a general increase in receivables for all counterparties.
As for buyers, each of them needs to be considered more carefully, in terms of contracts. It is necessary to determine the dynamics of debt and its change in accordance with the level of revenue. Only after conducting a full analysis can we say what condition the receivables are in and what risks exist for the company.
Inventory of receivable assets
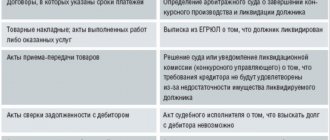
Accounts receivable are classified as financial assets of the organization, that is, they are a full-fledged part of the company’s property and must be included in the balance sheet. The procedure is carried out at certain intervals (at least once at the end of the year). In addition to the need to reflect this information in tax reporting, inventory is resorted to in the following cases: there is a change in the form of ownership; there is a risk that the documentation could be damaged as a result of a natural disaster or other force majeure; the company is preparing for closure or bankruptcy.
In the process of monitoring the receivables of the partners, the company’s employees raise all available documents: contracts, work acceptance certificates, letters of guarantee, invoices, etc. This allows you to confirm the lack of payments for goods provided / services provided, determine the amount of outstanding debts and assess the likelihood their successful collection. As a result, an act is drawn up, on the basis of which management is obliged to confirm what to do with the receivable assets - begin the procedure for reimbursement of funds or write off the debt.
Reflection of accounts receivable in the notes to the balance sheet
It is extremely rare that by the end of the year, based on the results of the analysis of the balance sheet, no debts are identified. Usually these indicators are present.
When preparing the annual report, debt amounts are reflected in the corresponding line of the balance sheet, and must also be reflected in Form No. 5, which is an appendix and is an integral part of the annual reporting. To reflect receivables and payables, there is a special table that details what type of debt is present in the company and what specific indicators it consists of. Moreover, in the explanations the amount of “receivables” is indicated regardless of whether a reserve for doubtful debts has been created or not.
When drawing up the application form, it is necessary to take into account that long-term receivables are reflected in the section with non-current assets.
Experienced accounting specialists do not recommend reflecting the presence of overdue accounts receivable in the explanations; accordingly, do not fill out the table in this part. Such advice is given so that there are no questions from regulatory authorities.
Accounting data is used to fill out information in Form No. 5. You need to know that when filling out the tabular lines, data on the balances and turnover of accounts 62, 60, 68, 69, 70, 71, 73, 75, 76 are used. Everything related to reserves for doubtful debts is reflected in account 63. Data is collected in the context analysts.
What formulas involve the accounts receivable indicator?
The DZ indicator is used in calculating various financial ratios, for example:
- financial stability;
For an algorithm for calculating financial stability, see the material “Analyzing financial stability ratios.”
- liquidity and solvency;
You will find formulas for their calculation in the material “Basic financial ratios and formulas for their calculation.”
- asset turnover, etc.
The material “Receivables turnover (formula)” will tell you how to calculate the receivables .