Step-by-step instruction
On April 01, the Organization on the simplified tax system (income-expenses) received from the supplier an act for the provision of services for monthly subscription services for the computer program for the period from 04/01/2021 to 03/31/2022 in the amount of 12,000 rubles. (including VAT 20%).
The services are fully paid to the supplier.
According to the Organization's accounting policy, expenses for continuing services are recognized as these services are consumed based on the cost, total period of provision and the number of days in the current month.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C |
| KUDiR | ||||||
| Reflection in accounting of subscriber services | ||||||
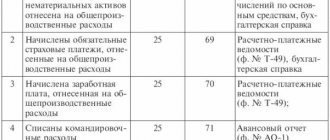
| April 01 | 60.01 | 60.02 | 12 000 | Advance offset | Receipt (act, invoice, UPD) - Services (act, UPD) | |
| 97.21 | 60.01 | 12 000 | Accounting for deferred expenses | |||
| Write-off of deferred expenses for April | ||||||
| April 30 | 26 | 97.21 | 986,30 | Write-off of deferred expenses | Closing the month - Write-off of deferred expenses | |
Reflection in accounting of subscriber services
Regulatory regulation
BU: Expenses for the maintenance of computer programs are taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities (clause 5, clause 7 of PBU 10/99). Until the service is provided, payment must be reflected in accounts receivable (clause 3, clause 16 of PBU 10/99).
Simplified tax system: Subscription fees for servicing computer programs are taken into account in expenses under the simplified tax system (clause 19, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Expenses for work and services of third-party organizations can be recognized at the moment when one of the events last occurred (clause 1, clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- services and work are performed and accepted by the organization;
- payment to the contractor has been made.
When making a one-time payment for services that are ongoing in nature, expenses can include the cost of only the services actually provided (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 12, 2008 N 03-11-04/2/195).
We agree with the position of the Ministry of Finance and believe that a one-time write-off of expenses for the entire amount at once is unlawful, since in this case:
- the requirement of economic justification for expenses is not met (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): we write off what has not yet actually been provided;
- there are no grounds for recognizing expenses established by paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for services of third parties, since payment of an advance by the buyer (invoice 60.02) several months in advance does not mean that the supplier provided services for all these months (even if the supplier submitted documents for the entire amount of the advance). pp. 1 item 2 art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation recognizes such expenses only at the time of repayment of the debt . But the buyer’s debt (account 60.01) will arise only when the services are provided to him actually, and not exclusively “on paper” (i.e., monthly, and not at a time).
In addition, a one-time write-off of ongoing expenses is unlawful (and hardly advisable), given the potential for termination of the contract and the need to make accounting adjustments in this regard.
The amount of input VAT is included in the price and taken into account in expenses (clause 8, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In KUDiR on the simplified tax system (income-expenses), the amount of incoming VAT must be shown as a separate line (clause 8, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This is an independent and separate type of expense for the purposes of the simplified tax system.
Read more Expenses for the purchase of works and services under the simplified tax system
Accounting in 1C
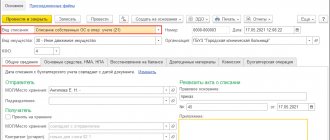
The receipt of an act from the service provider is reflected in the document Receipt (act, invoice, UPD) transaction type Services (act, invoice, UPD) in the section Purchases – Receipt (acts, invoices, UPD).
In the Accounts , indicate:
- Cost account - deferred expense account 97.21 “Other deferred expenses”;
- Future expenses — element of the RBP directory, formatted as follows:
Type for NU - Other ; - Type of asset in the balance sheet - Accounts receivable ;
- Amount — the cost of subscription services for the entire period (indicated for reference);
- Recognition of expenses - By calendar days ;
- The write-off period from... to... is the period of provision of services (in our example from 04/01/2021 to 03/31/2022);
- Cost account - an expense account to the debit of which the RBP will be evenly included (in our example - “General business expenses”);
In accounting, expenses for ongoing services will be written off evenly over the period of their provision as deferred expenses.
In order for VAT on services to be reflected simultaneously with the expenses themselves:
- in the section Taxes and reports - simplified tax system - procedure for recognizing expenses - incoming VAT, check the Accepted expenses for purchased goods (work, services) ;
- VAT should be highlighted in the receipt document.
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02 - offset of advance payment to the supplier;
- Dt 97.21 Kt 60.01 - accounting for software subscription services 2021-2022 in accounts receivable.
How to write off input VAT under the simplified tax system?
Simplified people cannot be classified as VAT payers.
In other words, they do not have to charge this tax during the sale of work, goods and services. However, this does not apply to the purchase of valuables, since in this situation an input tax appears, which is included in the purchase price. How to correctly account for input VAT will be discussed in detail in this article. By the way, the specifics of accounting directly depend on what exactly was purchased 09.09.2016
Situation one: purchase of materials
Maintaining tax records. Input VAT on materials should be recognized as an independent expense at the time the purchase price is written off. This needs to be done because the input VAT on purchased materials in the list of expenses that are taken into account during the “simplification” is included in a separate paragraph (according to Article No. 346.16, paragraph 1, subparagraph 8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, it is recorded separately in the Accounting Book.
Experts remind that writing off the price of materials is permissible only after the valuables have been capitalized and paid to the supplier. In the book of income and expenses, after fulfilling the prescribed conditions, two entries are necessary:
- For the total purchase amount, namely the cost of materials excluding VAT (Article No. 346.16, paragraph 1, subparagraph 5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- The amount of “input” VAT (according to letter No. 03-11-11/03 of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 18, 2010, article No. 346.16, paragraph 1, subparagraph 8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If payment was made not for the entire batch of materials, but only for a part, then the tax, accordingly, must be recognized as an expense as a part. In other words, the costs should include that part of the VAT that fell on the paid amount of acquired assets (Article No. 164, paragraph 4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The formula presented below will help to isolate the tax from the total amount of payment (the calculation must be confirmed by an accounting certificate):
The amount of “input” VAT attributable to the paid cost of purchased materials = payment amount X 18/118 (10/110).
Accounting. VAT should be reflected in the price of materials (based on Article No. 170, paragraph 2, subparagraph 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 6 of PBU No. 5/01 entitled “Accounting for inventories”). This is explained by the fact that “simplified” do not apply to VAT payers. For this reason, this tax will not be considered refundable for a particular company/organization (based on Article No. 346.11, paragraph 2, Article No. 170, paragraph 2, subparagraph 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In other words, the following entry must be made for the entire purchase price, including VAT:
D 10 K 60 – reflection of the cost of materials, taking into account “input” VAT.
It is worth noting that most accountants, in order to bring accounting and tax accounting closer together, take into account “input” VAT separately from the purchase price, namely on account 19 called “VAT on purchased values.” Here you should know that such actions do not constitute any violations, but they will not be able to help in achieving unity of accounting, since during tax accounting, VAT is written off as expenses immediately after the procedure for paying for purchased materials. As for accounting, VAT is written off after the release directly to production, no matter when exactly the payment for materials was made. This means that VAT will be written off within different time frames. Accordingly, this tax can be identified separately only in tax accounting under the simplified tax system. There is a possibility of getting very confused in accounting, since here you will have to separately write off the cost of materials, as well as the tax related to it, as expenses. Also, when accounting for VAT separately in accounting, it is necessary to consolidate this procedure using accounting policies.
It is necessary to consider another rather important point - this is the maintenance of analytical accounting for suppliers on account No. 60. It is recommended to do this regardless of whether VAT is allocated on account No. 19 or taken into account in the purchase price. So, based on accounting data, you can easily find out whether a particular debt to suppliers of materials has been repaid. This will also prevent you from getting confused about the payments made.
Situation two: purchasing an OS
Maintaining tax records. VAT paid at the time of purchase of the OS should be included in the original price of the lenses. In other words, it is taken into account in the price of the property and in no case separately. Accordingly, the tax is written off in combination with the costs of purchasing fixed assets (fixed assets) according to the degree of their payment, submission of a package of documents for state registration (if necessary), and commissioning. Experts also advise recognizing costs every quarter in equal parts throughout the first year of use of a particular facility.
Similar accounting can be explained by the content of paragraph 3 of Article No. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which states that the initial cost of fixed assets under the simplified tax system should be determined according to the procedure established in the accounting legislation. If we consider paragraph 8 of PBU 6/01 entitled “Accounting for fixed assets”, you can pay attention to the fact that non-refundable taxes are also included in the initial cost of fixed assets. And due to the fact that “simplified” cannot deduct “input” VAT, this tax will be non-refundable for them. It is for this reason that it is included in the cost of the OS.
The costs of purchasing OK in the Book of Income and Expenses should be reflected together with the “input” VAT (here there is no need to highlight this tax as a separate line in the Book). Thus, leading experts recommend reflecting the cost of an object including VAT in section No. 2 of the Book after all the conditions necessary for recognizing the costs incurred have been met. In section No. 2, an entry should be made for the entire initial cost of the OS that was paid.
Section No. 1 should include this cost in equal parts on the last days of the quarters that remain before the end of the tax period. For example, if all conditions are met in the 1st quarter of 2021, on June 30, September 30, December 31, you can write off the initial cost of the fixed asset as an expense item.
Accounting. As noted above, VAT for representatives of the simplified tax system is considered a non-refundable tax. For this reason, it must be included in the initial cost of the fixed assets (based on paragraph 8 of PBU 6/01). And if we take into account the fact that in tax accounting the costs of acquiring fixed assets are written off taking into account VAT, then there is no point in allocating “input” VAT on account 19. Otherwise, the cost of the object (initial) will be incorrectly determined and, accordingly, tax expenses will be underestimated.
For this reason, all costs that were associated with the acquisition of the operating system, including VAT, should be collected on account “08”. When the facility is put into operation, you will need to transfer all expenses to account 01, which will indicate that it has been accepted for accounting. After the manipulations have been performed, it will be possible to reflect the paid initial cost in section No. 2 of the Book of Income and Expenses.
As in the situation with materials, experts recommend maintaining analytical accounting for OS suppliers and doing this on account 60. In this case, it will not be difficult to find out information on payment for the object - just look at the accounting data.
Post:
Comments
Write-off of deferred expenses for April
To automatically account for monthly subscription service costs, run the Month Closing routine operation Write-off of deferred expenses in the Operations - Month Closing section.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt Kt 97.21 - accounting for subscription service costs in proportion to the number of days of the current month as part of general business expenses for the month.
Entries to the simplified tax system registers
The document generates movements according to the register Book of Income and Expenses (Section I) :
- registration entry for simplified taxation system expenses for the amount of subscriber services for the month.
Similarly, subscription services are included in expenses every month until the entire amount is written off.
Book of income and expenses
The amount of services for the current month is reflected in KUDiR. Input VAT is shown as a separate line.
To display VAT in KUDiR (Reports – Book of Income and Expenses of the simplified tax system) as a separate line, set the switch in the report settings:
- VAT printing mode - Output as a separate line .
See also:
- How to take into account ongoing subscription services in the 1C program?
- Purchasing software under the simplified tax system Income - Expenses
- [24 and 25.02.2021 entry] Declaration under the simplified tax system for 2021 in 1C
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- simplified tax system 15%, purchase of ongoing services with VAT in 1C When accepted as expenses for simplified tax system 15% RBP from 1C suppliers...
- Transition from the simplified tax system (Income) to the simplified tax system (income - expenses) You do not have access to view. To gain access: Complete...
- Intangible assets when switching from the simplified tax system for income to the simplified tax system for income and expenses Good afternoon! The LLC has 08 intangible assets on its account. In the current...
- Individual entrepreneurs without employees, insurance premiums for income over 300 thousand when switching from the simplified tax system, income-expenses to the simplified tax system, income of individual entrepreneurs without employees from 01/01/2021. switches from the simplified tax system (D-R) to...
Transition from OSN to simplified tax system in “1C: Accounting 8”
You can print the generated document by clicking the VAT Recovery button in the document itself or by using the Print generated document command for the VAT Recovery operation from the Assistant form.
Transition Operations
Including customer advances as income
Operation “Inclusion of buyer advances into income”
Left-click on the link with the name of the operation Including customer advances as income and select the Perform operation command. The document Record of the Income and Expense Accounting Book (STS) will be automatically created. The date of the document is January 1 of the year of the beginning of the application of the simplified tax system. In the document, on the I. Income and expenses tab, the “Income” column displays the total balance of advances from buyers as of the date of transition to the simplified tax system according to data on accounts 62.02, 62.22, 62.32. This amount is taken into account in income under the simplified tax system (status “Accepted” in the second subline of the “Income” column). If the organization did not return VAT to the buyer on the advance received on the OSN, adjust the amount of income in the “Income” column. You can view (if necessary, edit) the generated document using the Open generated document command for the operation Inclusion of buyer advances in income from the Assistant form. In the column Date, No. of the primary accounting document, you can indicate the document number of the Income and Expense Book Entry (STS).
Entering initial balances for the simplified tax system
Operation “Entering initial balances according to the simplified tax system”
If the object of taxation is “Income minus expenses”, then after performing the operation Including buyer advances as part of income, perform the operation Entering initial balances for the simplified tax system. For the tax object “Income”, this operation is not required and is not displayed in the Assistant.
Left-click on the link with the name of the operation Entering initial balances according to the simplified tax system and select the Perform operation command. Documents will be automatically created: Entering initial balances for tax accounting under the simplified tax system for the relevant sections of accounting. Documents are created by the last date of the year preceding the year of transition to the simplified tax system.
You can open the list of generated documents using the command Open the list of generated documents for the operation Entering initial balances for the simplified tax system from the Assistant form.
Documents Entering initial balances are formed according to the following sections of accounting (if on the transition date there are balances on the relevant accounts that must be taken into account for the purposes of the simplified tax system):
- fixed assets;
- intangible assets;
- materials;
- goods;
- calculations of taxes and contributions;
- settlements with personnel regarding wages;
- calculations with accountable persons;
- Future expenses;
- other tax accounting expenses of the simplified tax system and individual entrepreneurs.
In the “Fixed Assets” section, information about fixed assets is recorded in the “Initial OS information (for tax accounting under the simplified tax system)” register.
Under the “Intangible Assets” section, information about intangible assets and R&D expenses is recorded in the “Initial information of intangible assets (USN tax accounting)” register.
For the sections “Calculations for taxes and contributions”, “Settlements with personnel for wages”” and “Settlements with accountable persons” the document records the balances of the calculations.
For the remaining sections, the document records information about the balances of expenses unaccounted for income tax in the “Expenses under the simplified tax system” register.
If before the transition to the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses,” the organization did not keep analytical records of inventories by batch (in the Accounting Policy form, the method of assessing inventories was established - “by average”), then after the transition to the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses” a new entry is automatically added to the Accounting Policy form with the established method of estimating inventories – “According to FIFO”. In addition, simultaneously with the documents Entering initial balances for the simplified tax system, an Operation document is automatically created to enter batch accounting of inventory balances in the Expenses register under the simplified tax system and in the accounting accounts by filling out analytics for the “Batch” subaccount.
Write-off of tax accounting balances for income tax and from registers not used under the simplified tax system
Operation “Write-off of NU balances and unused registers”
The operation is official. When it is executed, a procedure is launched that analyzes the balances of tax accounting amounts as of the date of transition to the simplified tax system, as well as balances in accumulation registers that are not used under the simplified tax system. Based on the data received, Transaction documents are generated, which are filled out in such a way as to bring the specified balances to zero. The date of the documents is January 1 of the year of the beginning of the application of the simplified tax system.
You can view (if necessary, edit) the generated documents using the command Open the list of generated documents for the operation Write off balances of NU and unused registers from the Assistant form