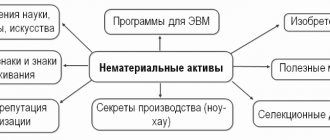
Refund of advance payment to buyer in seller's accounting
According to tax legislation, the seller, having received an advance payment amount on the basis of a concluded agreement, is obliged to issue an advance invoice to the buyer, which must indicate the estimated amount of VAT, calculated at the applicable rate of 20/120 or 10/110. This must be done before the expiration of 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance payment (Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the seller was unable to fulfill the supply agreements, but negotiated with the buyer the possibility of returning the advance and returned it, transferring the full amount of the advance payment to the account of the counterparty, then in accordance with clause 5 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, he has the right to accept the previously paid amount of tax as a deduction. To do this, the following conditions must be met:
- the contract under which the advance was transferred to the supplier has been terminated or its terms have changed accordingly;
- the advance payment is returned to the buyer, and the fact of its return is reflected in the accounting;
- no more than a year should pass from the date of refusal of delivery (clause 4 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For the return of the advance payment and VAT refund, the supplier issues and registers an adjustment invoice (SF) in the purchase book. When returning the advance payment to the buyer, the purchase book is filled out as follows:
- in gr. 2 – transaction type code “22”;
- in gr. 3 – number and date of the advance SF;
- in gr. 7 – details of the payment order confirming the return of the prepayment;
- in gr. 9 and 10 – name of the selling company, its INN/KPP;
- in gr. 15 – amount of advance received;
- in gr. 16 – VAT claimed for deduction on advance payment (from group 8 of advance SF). In case of incomplete return of the advance in gr. 16 indicate the part of the tax corresponding to the amount of the refund.
Payment "for the wrong thing"
Let's look at the most insidious mistakes. For example, the purpose of the payment is incorrect, that is, the name of the goods or services is incorrect. Buyers clearly indicate the wrong name of goods or services on the payment order. For example, instead of “payment for installation” - “rent”. Sometimes instead of “ and vice versa. For example, they transfer money for the transportation of goods, but in the payment slip they indicate “payment for tools.” The larger your company, the higher the risk. And it’s really bad if the name of the goods for which the bank tracks cash withdrawals is mistakenly indicated. For example, a company receives payment for building materials. And he writes off money from the account mainly with the purpose of payment “for food products”, “rent of commercial equipment”. The bank will ask for clarification and may block the client-bank connection. In this case, it will refer to the Methodological Recommendations approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on July 21, 2021 No. 18-MR.
And after comparing payment receipts with the company’s OKVED codes, bankers may be interested in a situation where the main receipts into the account are not related to the company’s activities. Sometimes questions arise from one-time payments, especially for large amounts. For example, if a wholesale company received payment for advertising services. And if deposits with an incorrect payment purpose become regular, suspicions will turn into confidence.
To reduce the likelihood of errors, it is better to include the text in the invoice that must be indicated in the purpose of payment. If your counterparty nevertheless manages to transfer money to you “for the wrong reason,” immediately inform him about it and try to get a written response in which the buyer confirms the correct purpose of the payment. You will forward this correspondence to the bankers if they have any questions.
Errors in the names of goods and services will also interest tax authorities. In this sense, such mistakes are especially risky for “simplifiers” and “imputers”, as well as entrepreneurs on the PSN. If the tax authorities see in the statement receipts for goods or services that do not fall under the special regime, they will demand that taxes be paid according to the general system. You will have to prove that the company or individual entrepreneur conducts only activities that fall under the special regime (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga District of October 25, 2021 No. F06-26038/2017). Therefore, for large payments, it is safer to agree with the supplier on the correct name of the goods.
But it is best to indicate the specific name of goods, works or services on the payment slip (Appendix No. 1 to the Central Bank Regulations dated June 19, 2012 No. 383-P). Take it from the contract, invoice or specification. If there are a lot of products, you can indicate a generic name, for example, “office supplies.” Or indicate the goods that make up the largest share of the purchase price.
Refund of advance payment to the buyer: postings from the seller
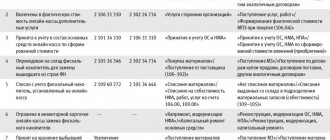
In the accounting records of the supplier, advances received are reflected in account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” subaccount “Advances received”, the credit of which records the receipt of the advance, and the debit records its return. Let's consider what accounting records accompany the operations to reflect the received advance and its return using an example.
Example
Based on the contract for the supply of a batch of polymers, an advance payment in the amount of 600,000 rubles was received on September 10, 2020. and on the same day, an invoice with the amount of VAT - 100,000 rubles was issued to the buyer LLC "Liya". (600,000 x 20 / 120).
But on September 25, 2020, the contract was terminated, the advance was returned, and the accounting records of Tsvet LLC reflected the following transactions:
| Contents of operation | D/t | K/t | Amount in rub. |
| 10.09.2020: | |||
| Receipt of advance payment | 51 | 62/AP | 600 000 |
| VAT charged (600,000 x 20 / 120) | 76 | 68/2 | 100 000 |
| VAT paid | 68/2 | 51 | 100 000 |
| 09/25/2020 upon return: | |||
| Debt to the buyer is taken into account | 62/AP | 76 | 600 000 |
| Refund of prepayment made | 76 | 51 | 600 000 |
| VAT paid when returning the advance payment to the buyer is claimed for deduction | 68/2 | 76 | 100 000 |
Accounting for advances issued and received (prepayments)
In cases where the amount of the prepayment exceeds the cost of delivery, the difference is either returned by the supplier to the bank account or taken into account as an advance payment for subsequent deliveries. Accounting records for the issuance of an advance against the future supply of material assets are presented in table. 9.6.
| Table 9.6 | |||
| Journal of business transactions | |||
| Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | Valuation, rub. | |
| debit | credit | ||
| 1. Prepayment has been made to suppliers | 60.2 | Advance amount | |
| 2. Inventories received as prepayment have been capitalized | 10, 41 | 60.1 | Inventory cost – VAT |
| 3. VAT included | 60.1 | VAT amount | |
| 4. The advance payment has been offset | 60.1 | 60.2 | Credit amount |
| 5. The difference was returned to the supplier’s bank account | 60.2 | Difference |
In cases where the prepayment amount is less than the contractual delivery cost, a credit is applied to the prepayment amounts, and the remaining accounts payable are paid in the usual way.
Example 9.1. An advance payment was made to the materials supplier in the amount of RUB 10,000.
In cases where the amount of the prepayment exceeds the cost of delivery, the difference is either returned by the supplier to the bank account or taken into account as an advance payment for subsequent deliveries.
Accounting records for the issuance of an advance against the future supply of material assets are presented in table. 9.6.
| Table 9.6 | ||
| Journal of business transactions | ||
| Contents of a business transaction | Account correspondence | Valuation, rub. |
| debit | credit | |
| 1. |
How to reflect the buyer's advance refund
The buyer accounts for the amounts of advances issued to partners in a special subaccount to account 60 “Settlements for advances issued”, the debit of which reflects the occurrence of receivables, i.e. transfer of an advance, and for a loan - repayment of such debt.
If the seller is obliged to calculate and pay VAT on the amount of the advance received, then for the buyer the opposite is true. He may deduct the VAT included in the advance tax return received from the supplier, or he may not do so - this is his right. Depending on whether the buyer exercises this right or not, the algorithm of his actions when returning the advance payment depends.
The buyer can recover VAT if the contract provides for advance payments, and the basis for the deduction is the SF he has for the advance and the payment order for the transfer of the advance payment to the supplier. If a tax deduction was claimed, then when the advance payment is returned from the seller, the buyer will have to restore the tax. If VAT on the advance tax return was not claimed, then the tax will not have to be restored. Returning to the example discussed above, let us recall how the buyer will record in the accounting transactions the transfer of an advance payment and its return from the supplier in both of these situations:
Option 1
Let us assume that Lia LLC, upon receipt of an advance SF from Tsvet LLC on September 11, 2020, declared VAT deductible, and on September 26, 2020, the company’s account received a refund of the prepayment in the full amount - 600,000 rubles, which became the basis for the restoration of the previously refunded " advance tax. Postings:
| Contents of operation | D/t | K/t | Amount in rub. |
| 10.09.2020: | |||
| Prepayment under the supply agreement has been transferred | 60/AB | 51 | 600 000 |
| 11.09.2020 | |||
| VAT on advance payment taken into account | 19 | 60/AB | 100 000 |
| VAT deduction claimed | 68/2 | 19 | 100 000 |
| 26.09.2020: | |||
| Refund of advance taken into account | 51 | 60/AB | 600 000 |
| VAT restored | 60/AB | 68/2 | 100 000 |
The insidiousness of numerology
The next point in our program is the inaccurate contract or account number. It will cause particular suspicion when purchasing goods from suppliers that inspectors consider to be at high risk. However, it is possible to make excuses. If the mere fact of an inaccurate contract or invoice number does not mean that the inspectors will consider the expenses unpaid. Provided that it is possible to determine which expenses the payment actually relates to. Confusion is possible if a company has several agreements with a counterparty. So it’s safer to indicate a specific contract or account number on the payment slip.
For example, a company has two contracts with a buyer. He must transfer payment for goods shipped under one contract. But he indicated the details of another agreement in the payment slip. It is not necessary to specify the purpose of the payment if it can be identified. That is, the receiving company can determine which contract and invoice the payment actually relates to. For example, if the buyer missed a digit in the invoice number.
If buyers often make mistakes in the purpose of payment, you can create a register. Indicate in it which payment purpose is correct. The register will come in handy if the bank requests an agreement or account specified in the payment order.
Relationship
Upon receipt of an advance payment in full or partial amount for future supplies, the business entity is obliged to charge VAT and issue an invoice. This tax amount is then deductible based on qualifying shipments. Next, we will consider in detail how VAT is offset from advances received from the client.
The invoice period is limited to five days. The exceptions are cases where the shipment was made within the specified period. But what about a buyer who transfers funds at the end of the current period if the seller does not issue an invoice? According to the interpretation of the arbitration court, an “advance on supplies” can be recognized as a payment received in the same period in which the sale of goods occurred. In addition, for failure to fulfill the obligation (invoicing), according to Art. 120 of the Tax Code, the company may be held liable:
- 5 thousand rubles. if the violation occurred during one period;
- 15 thousand rubles. – in several periods;
- 10% of the amount (minimum 15 thousand rubles), if the tax base was underestimated.
In the case of long-term supplies (oil, gas, etc.), invoices can be prepared at least once a month. The document must be issued in the same period in which the prepayment was made.
Decor
1. Prepayment is made under the contract, the buyer wants to take into account VAT on advances received.
In this case, it is necessary to monitor the status of mutual settlements and clearly determine whether a particular payment belongs to the delivery. It is also worth asking the buyer to indicate the prepayment amount in the comments to the receipt. Such control is required because:
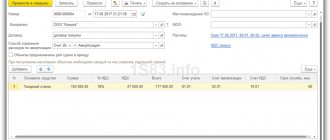
- The invoice is independently generated by the client in 1C, issued and printed in 2 copies.
- The advance amount is calculated based on the data in the “Debt Repayment” document. If the “Automatic” calculation method is selected, the difference will be calculated based on the balances of 62.01. After closing all debts, the balance will be carried forward to 62.02. This amount will appear on the invoice. Therefore, before registering a document, you need to make sure that the information provided in the database is up to date.
2. The invoice was issued in only one copy.
A document “Registration of invoices for advance payments” is created, which will automatically generate balances for all unclosed prepayments. This method has its limitations. Before registering a document, you need to make sure that:
- the sequence of calculations is relevant;
- there are no duplicate counterparties and contracts;
- debt balances are shown on account 62.01;
- balance on advances – as of 62.02;
- there are no closed balances on account 62.02;
- in case of changes in mutual settlements, you need to rewrite the document.
Description of the issue
Accounts receivable for amounts paid for the purchase of goods are reflected in the balance sheet in the amount of funds actually transferred. Before being able to deduct tax, these figures appear as a current asset. Such debt shows the right of the enterprise to receive the provided objects in the appropriate quantity, quality and required configuration.
Refunds can be made only in the event of early termination of the contract, the supplier’s inability to fulfill obligations and other similar circumstances. But in a worse situation, the company can receive not only previously paid amounts, but also compensation. Therefore, in accounting, the valuation of the asset should reflect not the amount of costs, but the cost of the purchased equipment when it is capitalized. This figure corresponds to the amount of prepayment excluding VAT from advances received.
Let's look at a few more examples of tax calculations.
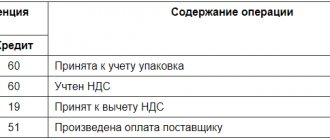
1. Supply of goods in the amount of 118,000 including VAT.
- DT 08 (19) KT 60 – materials were received (100,000) and the supplier’s invoice was taken into account (18,000);
- DT TS (technical account for mutual settlements with counterparties) KT 68 – VAT restored (18,000);
- DT 68 CT 19 – tax accepted for deduction (18,000).
2. Reflection of an advance issued without accepting the right to deduct VAT.
From the buyer's side:
- DT 60 CT 51 – advance paid (118,000);
- DT 19 KT TS – accepted for VAT accounting (18,000).
From the seller's side:
- DT 08 (19) KT 60 – equipment received (100,000) and seller’s account accepted (18,000);
- DT TS CT 19 – the tax amount was restored (18,000);
- DT 68 CT 19 – tax accepted for deduction (18,000).
Another option for processing the operation.
- DT 51 CT 62 – prepayment received – 118,000;
- DT TS KT 68 – tax charged – 18,000.
- DT 62 CT 90 – sales of products (if 62 is used as a technical account, an entry is created for the amount of one hundred thousand rubles) – 118,000.
- DT 90 CT 68 – reflects the amount of tax on products sold (the posting is not created if account 62 appears) – 18,000;
- DT 68 CT TS – the tax amount has been restored (the posting is not created if account 62 appears) – 18,000.