About income tax in 2021
Income tax in Russia is represented by the personal income tax (NDFL), the normative regulation of which is enshrined in Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Table: income tax 2021: what percentage are deductions depending on the tax base.
| Personal income tax rate | The tax base |
| 13 % | Salaries, dividends, other income of residents (except for those indicated in the last line), citizens from the EAEU, refugees, etc. (Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated January 24, 2018 No. 03-04-05/3543, dated May 14, 2018 No. 03-04-06/ 32214) |
| 30 % | Income of non-residents (those who live in the country for less than six months) |
| 35 % | Winnings, prizes, interest-free loans from residents, dividends from non-residents |
On average, the share of budget revenues in 2011–2017 from personal income tax revenues was 3.5% in relation to GDP (for comparison, in 2021, revenues from personal income taxes amounted to 3.53%, from corporate income taxes - 3.57%) (data from the document “Main directions of budget, tax and customs tariff policy for 2021 and for the planning period 2021 and 2021”).
However, is this a lot or a little in comparison with similar indicators in other countries? Let us turn to data from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), which includes 36 developed countries. Published data show the amount of state budget revenue from personal income tax (Tax on Personal Income) as a percentage of GDP.
It is important to emphasize that many European countries included in the above OECD analysis (in particular, Austria, Germany, Italy) have a progressive taxation system: the tax rate is determined depending on the size of the tax base. In some countries, income up to a certain threshold is exempt from taxation, then the rate gradually increases (for example, in France the rate for individuals varies from 0 to 75%).
The issue of reforming the personal income tax collection system in Russia is raised quite regularly: for example, in 2021, Deputy Prime Minister Olga Golodets spoke about the Government of the Russian Federation considering the idea of transitioning to a progressive scale of personal income tax (which means that for part of the population it is possible to increase income tax in Russia), and in March In 2021, a draft law on the introduction of a progressive scale of taxation of personal income was submitted to the State Duma of the Russian Federation for consideration.
It seems that in the near future there is no reason to expect that in Russia there will be an increase in income tax in 2019 (or, more precisely, an increase in the personal income tax rate) for the bulk of the population. There are a number of reasons for this.
- At the time of active consideration of the issue of reforming the collection of personal income tax (including at the beginning of 2019), it was a question of choosing a source of increasing budget revenues - personal income tax or VAT, and, as you know, VAT was chosen.
- The second aspect, which seems very relevant when deciding on a tax increase, is the size of the tax burden: in accordance with the principle of inadmissibility of excessive taxation. The latter should not paralyze the exercise by citizens of constitutional rights and freedoms.
Obviously, the Ministry of Finance is of the same opinion: responding to massive requests from citizens, the department published Letters dated 05/07/2018 No. 03-04-05/30463, dated 04/12/2018 No. 03-04-05/24386, in which it explained that the rate increase Personal income tax is not planned. The fact that there is no need to wait for the introduction of a progressive rate is stated in Letter No. 03-04-05/62106 dated September 26, 2017.
PFDL is a direct type of tax, which is calculated as a percentage of the entire total income of an individual, excluding some documented expenses. Current legislation prescribes that absolutely all income that a taxpayer receives, be it sales or wages, is subject to personal income tax.
In general, the following representatives of the Russian Federation are taxpayers:
- individuals who are tax residents of Russia and stay on its territory for more than half of the calendar year;
- individuals who are not tax residents of Russia, but still receive taxable income on its territory.
In general, there are only five tax rates: 9%, 13%, 15%, 30%, 35%, which are set depending on the type of income that a particular taxpayer receives and the type of taxpayer himself. But as was said earlier, in many places there are now rumors about increasing tax rates for the next few years.
If you believe the numerous forecasts of various analysts and the media, then the personal income tax may well rise to as much as the fifteen percent mark. And the state itself says in this regard that the increase is completely justified and possible, just in some regions, where today there are significant shortcomings in the budget and financing of the subject.
Although for now the issue of personal income tax is, to put it mildly, up in the air, the same analysts and simply interested citizens are really building real budget plans and options for further development of the situation instead of simple assumptions. By 2019, tax reform may indeed quite logically occur in Russia, leading to an increase in the personal income tax rate.
Maybe these are all just assumptions without clear grounds and rumors on the spot out of nothing, but still citizens are clearly confident that the country will definitely undergo some changes in the near future. Recent events and statements by the State Duma fully confirm all these fears, so we can already talk about changes, at least using the example of personal income tax.
Personal Income Tax (or Personal Income Tax) is a mandatory monetary contribution to the tax office for each type of personal income.
Moreover, it is necessary to pay tax not only on wages, but also on absolutely any financial income: from winnings in the lottery or lotto, renting an apartment, and even interest on a foreign currency deposit in a bank! Of course, the monthly withdrawal of such interest significantly affects the budget of every Russian. But this does not prevent the government from putting forward new initiatives, either promising to abolish personal income tax altogether, or threatening to raise it to 15% or even 17%.
It is not surprising that Russians listen with alarm to anyone who promises to predict their near future.
Of course, their forecasts are not the ultimate truth, but only the probability of what the life of Russians may soon turn out to be. Well, let's find out how much (and for what reason) the tax levy may change in 2021!
Employees of most enterprises have never thought about how much personal income tax is and who pays it for them.
The fact is that the employer, acting as a tax agent, reports to the tax office for each of its employees independently, immediately calculating and deducting all the necessary interest from the salary.
Therefore, many do not even realize how much of their personal budget goes to the state every month.
Personal income tax is a fee that the state collects from each of our salaries.
| Percent | Condition |
| 9% | Certificates and mortgage payments issued before 2007; |
| 13% | Basic percentage of tax (on wages); |
| 30% | Tax on dividends (profits from joint stock companies), the main percentage of tax for non-residents; |
| 35% | Valuable prizes, income from bank deposits. |
Tax deduction
There is such a thing as a tax deduction. All tax deductions are divided into 4 main groups:
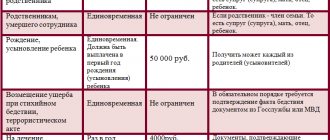
- Standard, that is, a “discount” on the payment of personal income tax to citizens with children (1 child - a discount of 1,400 rubles, 3 or more - 3,000 for each child). If the child has a disability, the tax deduction for the family increases to 12,000;
- Property - for example, if a taxpayer spent a significant amount on the construction or purchase of real estate, then he can provide a certificate of expenses to the tax office. In turn, the tax office must react and reduce the monthly tax amount, or pay it immediately in cash;
- Social, that is, a “discount” is provided to people participating in charity, students, pensioners, and so on;
- Professional - they can be obtained by individual entrepreneurs, product authors (writer, performer, inventor, artist), lawyers, notaries, and so on.
The following financial procedures are also exempt from income tax:
- alimony;
- benefits;
- payment for medical services;
- financial assistance for the birth of a child, etc.
In 2021, Russians may face an increase in personal income tax to 15 or even 17%
The planned increase in personal income tax has been one of the most discussed economic topics since 2021 - after VAT rose by 2% in 2021 and prices for goods and transport soared significantly. Of course, taxes are raised for a reason. All payments from direct taxes go to the state budget. Today, we can note several of the most objective reasons for increasing the tax rate:
- due to rising unemployment and the closure of many businesses, the number of people paying tax is decreasing every day. Recently, many professions have been modernized, and employees are literally replaced by computers - after all, some work can be handled by automated systems. Due to the lack of taxpayers, the capacity of the state budget is significantly reduced, and in order to correct this, it is necessary to increase the percentage of taxes paid by the population;
- due to rising inflation. With a significant increase in inflation, it is necessary to increase the amount of benefits and pension payments, which is an additional loss for the state;
- a decrease in oil prices, which in turn leads to a crisis and devastation of the state budget;
- Due to the crisis situation in the Russian Federation, the number of unemployed people who need to be paid benefits is increasing. In addition, a significant part of the budget is spent on financing important or problematic sectors - and important not in the opinion of the Russians themselves (medicine, education), but in the opinion of the government, which is throwing itself headlong into international conflicts. This, in turn, requires a monstrous impact on the defense industry, the re-equipment of industrial capacities for import substitution, etc.
Salary taxes in 2021 as a percentage: table
What is personal income tax
First, let’s remember what personal income tax is. It is paid, contrary to popular belief, not only from salaries, but in general from all incomes of citizens, even those received thanks to luck in some promotion or lottery. Here are some important facts related to personal income tax:
- It is paid by both tax residents of the Russian Federation and foreign citizens.
- Citizens are required to declare all income by April 30 annually.
- The tax and reporting period in both cases is 12 months.
- The amount of personal income tax can be reduced using deductions in the amount established for different situations. More precisely, the tax base decreases, and with it the amount of collection.
- Reporting can be provided on paper or electronically.
- There are as many as 5 forms related to the income contribution - from 2-NDFL to 6-NDFL. There is also a form with number 1, but it has not been used by tax authorities for a long time. The rest are declarations, summary forms for reporting, and 2-NDFL - in case you need a certificate of income.
These are the main, but not all, nuances regarding such a payment as personal income tax in 2021.
Calculation
The size of the payment is calculated by simply multiplying the tax base by the rate. The latter will be discussed in the next section, but what may be subject to this fee is worth talking about here. So, you need to pay the state interest on:
- Employees' salaries.
- Winnings and prizes, including in kind.
- Money received from renting out property.
- Income from sources located outside the Russian Federation.
- Sales of property that has been owned for no more than 3 years, etc.
But income from the sale of property that was owned for more than three years, or, for example, received as an inheritance, is a non-taxable base. More details about the first and second lists are described in Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Some people are confused about what percentage of the salary is personal income tax, so this point is also worth remembering. So, the personal income tax has several rates:
- 13% - main. This is exactly how much all citizens, or rather their tax agents working in Russia, pay. Moreover, this rate is the same for both residents of the Russian Federation and for citizens who come to work from the EAEU countries, that is, Armenia, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. It is also worth noting that only those employees who officially work in the Russian Federation for more than six months pay tax on their wages.
- 9% - this is how the income of the founders of trust management of mortgage coverage is taxed.
- Non-residents of the Russian Federation will have to pay 15% of the amount of dividends from Russian companies.
- 30% - the increased tariff from wages will have to be transferred to the budget by citizens who work on the territory of the Russian Federation, but do not have citizenship of Russia and other countries included in the EAEU.
There remains another 35% - the highest rate at the moment. This is how much they pay with:
- Interest income on bank deposits.
- Winnings.
- Prizes, etc.
That is, for example, if a citizen wins 1 million rubles in the lottery, then with the deduction of only personal income tax he will have 650 thousand left. More information about rates can be found in the table on the Tax Service website.
Everyone is interested in the change in rates, since the income tax is already recognized as one of the highest among all others. Therefore, many are afraid of its increase. The next section will tell you what changes await income tax in 2021.
Personal income tax changes 2020
Six months have already passed, which means it’s time to talk about changes for the coming year, which are already ready to take effect in 2021 or are just preparing for release. But everyone is interested in whether personal income tax will be increased in 2021. Let's try to figure it out.
Now there are a lot of rumors about increasing personal income tax. For example, the Ministry of Finance proposes to increase the basic income tax rate by 2%, and reduce the deduction for insurance premiums to 21 from 30%.
This position with increased payments is also supported by the Ministry of Economic Development.
However, the project proposing to introduce such rules has not yet been submitted to the State Duma and there are no prerequisites for anything to be increased.
There is also a rumor that those citizens who earn less than 13,000 rubles per month will be exempt from income tax. However, this project is unlikely due to the following conditions:
- Too large a percentage of the population receives less than 13,000 rubles per month. That's 11 million people, almost 17%.
- The economy is going through hard times, as evidenced by many tax increases in 2021. So here we can only talk about an increase, but not a decrease.
Many note that other taxes raised in 2021 will be enough to cover shortcomings and not affect income tax. For example, the increased VAT rate from 18 to 20% copes well with the reduction in citizens’ salaries.
That is, global changes in rates are not yet expected. However, there are still changes, and it’s worth talking about the latest amendments in more detail:
- The social deduction for treatment now does not depend on the government list of drugs - this list has been abolished. Therefore, now, from June 17, 2021, under Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a deduction can be obtained for any medical services.
- Exemption from personal income tax cannot be applied to such type of payment as compensation for unused additional days of rest for military contractors.
- Now, according to Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, personal income tax is not subject to payment of additional days off for persons caring for disabled children. These days off are provided under Article 262 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- All legal payments, including those in kind, provided to beneficiaries, are classified as non-taxable income.
- The list of non-personal income tax payments has been clarified again. For example, there is no need to pay tax on travel to and from vacation spots for workers in the Far North and their families.
Despite how many tables there are on the Internet with changes in personal income tax from 2021, they are all based on assumptions, so there is no need to panic because of them.
To summarize, we can say that so far there is no talk of global changes in the personal income tax rate in 2021. Taxation rules for the sale of property and the list of those who can receive benefits may be edited. They may also make minor changes to the forms and forms, which happens quite often, but nothing can be expected regarding bets.
It is easy to justify such assumptions - over the past year in Russia enough taxes have already been raised and new fees introduced. All areas of the economy have felt the tightening of rules, and first of all the citizens of the country. But here it is important to maintain a balance, since tightening taxation inevitably leads to the growth of the gray sector of the economy.
And in Russia in 2021 it is already too large and continues to grow.
Deductions from wages include personal income tax and insurance premiums, and their percentage is established at the legislative level. In order to correctly reflect mandatory payments in Form 6-NDFL, you need to understand what wage taxes are set in 2019.
The Tax Inspectorate monitors the timely payment of tax deductions from wages of employees of all organizations registered in the Russian Federation.
123 of the Tax Code for underestimating the tax base (incomplete transfer or withholding of the corresponding mandatory payment) provides for a fine of 20% of the unpaid amount.
Next year, the payment calculation mechanism will remain the same as in 2021. The scheme for establishing the amount to be paid to the tax authority works according to the following mechanism.
The accountant determines whether a tax deduction is provided for a specific employee, for example, for the purchase of housing. The amount of this deduction reduces the tax base - i.e. the amount of the employee's official salary.
The result is multiplied by the current rate: the funds received are transferred to the current account of the tax office.
Rates vary depending on whether the employee:
- resident - for this category of citizens the tax is 13% of earnings;
- non-resident – 30%.
Note! According to Part 2 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a resident of the Russian Federation is a person who has been on the territory of our state for 183 calendar days over the last calendar year.
An exception is provided for specialists from abroad working on the basis of a patent, as well as for residents of the Eurasian Economic Union. Taxes for these categories of citizens are charged at a rate of 13%.
According to Part 6 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to transfer the corresponding deduction amount no later than 1 day from the date of payment to the employee.
As for individual entrepreneurs, a deduction is provided for these legal entities depending on the applicable taxation system:
- with UTII its size is 13%;
- with the simplified tax system – 6 or 15%, depending on the chosen method of taxation, i.e. from the difference between income and expenses, or imputed income.
Insurance premiums
The size of the Federal Tax Service is regulated by Art. 426-429 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the tariff is set at 30%, excluding regional increasing coefficients.
In 2021, preferential tariffs for individual entrepreneurs working under the simplified tax system - production workers and social workers - will be abolished. Also, low rates will not apply to pharmacies operating under UTII and individual entrepreneurs that work with patents.
FSS - insurance premium for occupational diseases and industrial accidents will remain the same. There are 32 tariffs in total, the value of which is in the range of 0.2-8.5%. The average percentage is set at 0.51%.
In total, organizations are required to pay 30.51% of insurance premiums by the 15th day of each month for the reporting period. For example, if the salary was accrued for March 2021, then it must be paid before April 15, 2019. If the payment date falls on a weekend or holiday, then payment can be made on the next working day after the holiday.
There are many changes in payroll tax rates in the new year. For a complete table with all tax contributions for 2021 and interest rates on them, see the article. Also in the article are the interest rates of additional contributions to pension insurance.
The employer, as a tax agent, withholds personal income tax from the salary. We have given the percentage rates in the table below. The size differs depending on the status of the income recipient - resident or not. For non-residents the penalty is higher. But there are more residents in the country, so most salary calculations are carried out using the already classic rate of 13%.
Personal income tax rates in 2021
The income of individuals is taxed at rates of 9%, 13%, 15%, 30%, 35% - depending on the type of income of the individual and his tax status. Let's look at the tax rates in order.
At a rate of 35% personal income tax in 2021, tax agents most often withhold from such income as:
- winnings and prizes received by individuals during advertising campaigns, if their value during the year exceeds the non-taxable minimum - 4,000 rubles;
- interest on bank deposits in the part exceeding the key rate of the Bank of Russia for ruble deposits, increased by 5%, and for foreign currency deposits - 9% per annum. The calculation takes into account the key rate that was in effect during the period for which interest on the deposit was accrued.
| Date from which the rate applies | Key rate, % per annum |
| From 03/26/2018 | 7,25 |
| From 02/12/2018 | 7,50 |
| From 12/18/2017 | 7,75 |
| From 10/30/2017 | 8,25 |
| From 18.09.2017 | 8,50 |
| From 06/19/2017 | 9,00 |
| From 05/02/2017 | 9,25 |
| From 03/27/2017 | 9,75 |
| From 09/19/2016 | 10,00 |
| From 06/14/2016 | 10,50 |
| From 01/01/2016 | 11,00 |
At a rate of 30%, income tax in 2021 is withheld from the income of tax non-residents. They are considered citizens of the Russian Federation and foreigners who, at the time of payment of taxable income to them, were in Russia for less than 183 days within 12 continuous months. Although for some remunerations in their favor the personal income tax rate is 13%, read about this below.
At a rate of 15%, personal income tax in 2021 is withheld from dividends paid to tax non-residents, regardless of their citizenship.
At a rate of 9%, personal income tax is withheld from interest received by individuals on mortgage bonds issued before January 1, 2007.
At a rate of 13%, personal income tax in 2021 is withheld from the remaining income of individuals, including:
- from payments to tax residents of Russia;
- from payments under employment contracts to foreigners who have issued a patent;
- from payments under employment contracts to foreigners - highly qualified specialists, if they are listed as temporarily staying in the Russian Federation.
Today, personal income tax rates seem quite shaky, as do the KBK for personal income tax, standard tax deductions for personal income tax or personal income tax refunds for past years, but you shouldn’t worry so much right away. No one can say for sure what changes await us, not even the state itself and its numerous representatives, represented by the State Duma or, for example, the Ministry of Finance.
For now, the country has established a moratorium on any increase in tax rates, as this will greatly change the tax burden of Russia as a whole. Personal income tax consists of five rates established for all types of income that the taxpayer receives. The Tax Code establishes all the basic principles of tax management. But still, in the near future we can still expect a sharp increase or decrease in the rate by a couple of percent.
Let’s look at all the rates separately in order to have at least some idea of personal income tax and the differences between various tax penalties in Russia.
Rate 9%
This is the smallest of all rates, its size is only 9 percent of the total income of an individual. It applies to cases such as:
- making a profit, such as any dividends;
- all interest payments on various bonds that were issued before 2021;
- the constituent income of a mortgage-backed trust that was received under certificates issued before 2007.
Rate 13%
This rate is slightly higher than the previous one and its size is only 13 percent for individuals who are tax residents of the Russian Federation. Taxable income includes:
- various dividends;
- official salary of a citizen;
- any monetary rewards under contracts;
- all profits received from the disposal or sale of one's personal property.
There are no tax deductions for income received as a result of a citizen’s share participation.
If the taxpayer is still not a citizen of the Russian Federation, but receives income on its territory, then the NFDL also applies to him. Here the taxable income is:
- official income received from various activities;
- all remunerations of crew members of ships flying the flag of the Russian Federation from labor relations;
- payments for the work of a qualified specialist who is not a citizen of Russia;
- all income of individuals who have moved and permanently reside abroad.
The entire 13% rate is paid by any citizens of other states, persons without citizenship at all and temporary citizens of any country who officially conduct some kind of activity in Russia and receive the corresponding official income.
Rate 15%
This tax rate is established for most individuals who receive wages in the form of dividends from domestic organizations. Only these persons must be foreign citizens.
Rates 30%
All other income that is not included in the list available to tax residents of the Russian Federation must be taxed at a rate of 30%.
Rate 35%
But the highest rate in personal income tax is as much as 35%, which is quite a lot, considering what kind of income is taxed. Eligible income is:
- prize money and various winnings;
- interest payments on various bank deposits;
- interest on borrowed funds that goes beyond the norm;
- payment to a credit consumer cooperative.
In general, it is very important to consider that any individual who receives official income taxed at a rate of 13 percent can greatly help himself. This assistance is called deductions, which is understood as an amount that reduces the amount of all income for the reporting period. And the Tax Code defines all deductions as “the return of a certain part of the personal income tax already paid.”
For yourself: procedure and deadlines for paying personal income tax
When receiving funds from other sources (not through tax agents), the individual must independently pay the treasury. Such cases include, for example:
- winning the lottery;
- sale of real estate, the tenure of which does not exceed 3 years;
- cash prizes worth more than 4,000 rubles. and etc.
In 2021, the tax is paid no later than July 15 for the reporting period of 2017 (clause 6 of Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From January 1, 2021, winnings up to 4,000 rubles. are not subject to personal income tax. Tax on winnings from 4,000 to 15,000 rubles. the individual pays independently. Tax on winnings over 15,000 rubles. withheld by the tax agent.
Also see “Changes to personal income tax in 2021“.
Changes
For deductions in 2021, the codes in form 2-NDFL have been clarified. The new deduction code – 619 – is used by brokers when reflecting an individual’s profit in his individual investment account. This innovation should have been taken into account, starting with reporting in Form 2-NDFL for 2021.
Well, now it’s time to talk about those very tax changes that may be awaiting us in the near future. Because even now there is some information or guarantors that confirm the possible fears of all Russian citizens. Let's look at the main upcoming changes to personal income tax.
- In 2021, a significant extension of the exemption from personal income tax is provided for all payments or monetary objections to citizens who are self-employed and do not conduct business activities. This will also affect employers, who are exempt from paying all insurance premiums received as a result of payments to self-employed citizens of the Russian Federation.
- They are also considering a new bill that will lead to the abolition of personal income tax next year for the sale of household waste paper. If the documents for this project are approved and signed on time, then from January 2021 we will see it in action.
- From the State Duma, the Communist Party faction sent the Chairman of the State Duma a certain bill, which is intended to change Chapter 23 of the second part of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They put forward an initiative to set absolutely different rates. This could also be implemented by early next year.
- Already on April 23, 2021, a law came into force that regulates personal income tax payments for each month. However, this will only be carried out at the birth of children: the first and second.
The President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin himself instructed those responsible to develop and implement a variety of numerous proposals related to reforms of the state tax system. Now in 2021, work is already underway on future changes in 2021.
If you believe the president’s words, the main goal of all future reforms will be to stimulate the economy and move towards business activity of the entire population of the country. Analysts say that all important changes will concern personal income tax rates. But it's not that simple.
Tax agents
The obligation to pay income tax is assigned to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who have hired personnel. In this case, they act as tax agents, so they must:
- charge tax monthly (with an accrual total);
- withhold the required amount when paying staff;
- make timely payment of personal income tax to the budget.
All of the above requirements are regulated by paragraphs. 3 and 4 tbsp. 226 Tax Code. In this case, funds received by the payer from other organizations are not taken into account in the calculation.
Salary
According to Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the tax agent is obliged to issue wages every 15 days. But deductions to the personal income tax budget are made only once during this time - after the final calculation of the amount of the employee’s remuneration. And then almost immediately the tax is withheld and paid (see table).
| Payment method | When to pay personal income tax on salary in 2018 | |
| Cashless | Funds are credited to a bank card | On the day of transfer |
| Spot | 1. The cashier of the enterprise hands out the money personally | No later than the date following the day of issue |
| 2. Funds are received from the bank | On the day of receipt | |
These deadlines are established in paragraph 6 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, there are special rules. If you have any difficulties, ask our experts on the forum.
Economic justification
up to a certain limit, the tax rate will provide high budget revenues, but if this limit is exceeded, tax revenues will decrease, since the excessive tax burden will reduce the desire of civil society subjects to engage in this taxable activity. Accordingly, in order to effectively collect fiscal payments, the state chooses a certain tax policy.
For example, if legislation establishes a low tax rate, then an expanded tax base is simultaneously established, and vice versa. In the current economic situation, when Russians are becoming poorer, increasing the tax rate on already economically declining incomes would lead to a significant deterioration in the situation of the bulk of the population.
While the material was being typed up, the news spread across all news channels that the government was planning to introduce a system of individual pension capital, the amount of contributions to which could amount to up to 6% of Russians’ income, and what is this if not a hidden increase in income tax? Read about this in the article “Will citizens be included in the individual pension capital system automatically?”
Payment for rest and illness
Since 2016, when accruing vacation pay and temporary disability benefits to an employee, the deadline for transferring personal income tax has become the last day of the month in which such funds were provided.
EXAMPLE accrued to K.V. Ivanov received vacation pay in the amount of 37,000 rubles, which were transferred to his account on February 8, 2018. The enterprise is obliged to pay income tax to the treasury no later than 02/28/2018.
Also see “Personal Income Tax Payment Deadline”.
How to calculate tax
If suddenly, behind all these complex changes, taxpayers will have questions like: “How will personal income tax taxes be calculated then?” or “What is this, recalculating everything now?”, then you shouldn’t rush to conclusions. Maybe even big changes will not affect the rates themselves, but will only change some aspects.
So for now you don’t have to worry about calculation formulas and spreadsheet accounting systems. If there are any changes in this area, then the Ministry of Finance will certainly inform about this in advance in order to prepare all organizations, entrepreneurs and employees themselves.
If there are those who are still wondering about the calculation of personal income tax without changes, then all the detailed information can be easily found on the Internet, without even having difficulty finding what you need. Why are there examples and diagrams? There are even online calculators that should accurately calculate all taxes. So there was no need to worry about the availability of information, and there is no need to worry in the future.
In general, in order to understand how much all the upcoming changes will affect ordinary citizens of the state, we must wait and see what the state will come to in these matters. So you shouldn’t judge too hotly; maybe many reforms will only bring sweet fruits.