When receiving an advance payment, this day is considered the date of receipt of funds, and when shipping goods - the date indicated in the delivery note or the certificate of completion of work. The law does not allow issuing an invoice later than this period. In addition, if the seller issues an invoice before the shipment date, the tax authorities may also refuse to deduct VAT for the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 9, 2011 No. 03-07-0 9/39).
But the error in the numbering of invoices may not be corrected. Such an error is not critical and does not interfere with tax deduction (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 11, 2013 No. 03-07-09/42466).
Thus, officials actually confirmed that no matter how the seller numbers his invoices (even if in violation of the established rules), this does not threaten his customers in any way. They have the right to deduct VAT, since any incorrect numbering of invoices (even if it is recognized as an error) cannot prevent tax authorities from identifying the seller, buyer, name of goods (work, services), property rights, their value, tax rate during an audit. and the amount of VAT.
The seller himself, who issued an invoice with an erroneous numbering, especially does not face anything. After all, if he correctly calculated the amount of tax payable to the budget and reflected it in full in the declaration submitted to the inspection, then, even if they made a mistake in drawing up any invoice, there is nothing to punish him for according to the norms of the Tax Code.
If the receipt of the advance payment and the shipment of the goods occurred in the same quarter, then an invoice for the prepayment may not be issued. This conclusion was made by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated January 16, 2012 No. VAS-17397/11. The judges pointed out: since the tax period for VAT is a quarter, an advance payment “closed” by shipment in the same quarter is not an advance payment at the end of the tax period.
The certificate of completion and the invoice are issued with different dates: how critical is this?
The legislation does not require that the dates in the work completion certificate and the invoice coincide. And the date of issuance of such a document as an invoice is not regulated by any regulatory act. This is explained by the fact that the invoice is not recognized as a primary document in accounting, and for tax accounting it has no significance. The contractor delivers it to the customer at his own discretion or within the time limits specified in the contract. That is, a coincidence in the dates of the invoice, invoice and certificate of completion of work is acceptable, but not necessary.
How to get rid of calendar confusion
The date of the invoice affects the timeliness of the customer receiving the VAT deduction for the work. It is determined according to the norms of paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is selected from a segment of 5 calendar days, counted from the moment:
Therefore, if in the situation under consideration, less than 5 days have passed between the date of issuing the act of services provided and the date of issuing the invoice, for example, the act was signed on November 30, 2012, and the invoice was issued on December 3, 2012, there are no violations. It does not matter that the date of the act of services rendered and the date of the invoice fall in different months. In this case, VAT on such an invoice should be deducted in December 2012 (Article 171 and Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In other words, if the difference between the dates in question is more than 5 days, then it is quite possible that the tax authorities may make claims regarding the discrepancy between the dates of the primary document and the invoice. In such a situation, the requirements of tax legislation are actually violated, so the tax authorities in this case may deny the organization the right to deduct VAT.
Let us recall that a primary accounting document is a supporting document with which an organization formalizes each completed business transaction (Part 1, Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 402-FZ). Primary the accounting document must be drawn up when a fact of economic life is committed, and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion (Part 3 of Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ).
According to paragraph 5 of Art. 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a service for tax purposes is recognized as an activity whose results do not have material expression and are sold and consumed in the process of carrying out this activity.
The invoice date is later than the month the service was provided
When preparing invoices by sellers, you can find various options for dating them, which are discussed below.
The invoice is dated by the date of actual shipment of goods, performance of work, provision of services.
According to Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for accepting the presented amounts of tax for deduction or reimbursement from the buyer in the prescribed manner. Invoices drawn up and issued in violation of the procedure established by paragraphs 5 and 6 of this article cannot be the basis for accepting tax amounts presented to the buyer by the seller for deduction or reimbursement.
Based on Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer has the right to reduce the total amount of tax calculated in accordance with Article 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by the tax deductions established by this article. Tax amounts presented to the taxpayer upon acquisition of goods (work, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation in relation to goods (work, services) purchased to carry out transactions recognized as objects of taxation are subject to deductions.
Such tax deductions are made on the basis of invoices issued by sellers when the taxpayer purchases goods (works, services). Subject to deductions, unless otherwise established by Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are only tax amounts presented to the taxpayer after the specified goods (works, services) have been registered, taking into account the features provided for in this article and in the presence of relevant primary documents.
Thus, the taxpayer has the right to tax deductions subject to three conditions:
· goods, works, services must be accepted for accounting;
· the specified goods (works, services) are used in activities subject to VAT;
· We have an invoice for purchased goods, works, and services.
If all the above conditions are met, VAT can be deducted during the tax period.
If the invoice date coincides with the shipment date, then this option is the most preferable for both the seller and the buyer, since both primary documents (invoices, certificates of work performed) and invoices have the same number, which does not cause disagreements when reconciliation between counterparties, and there are also no claims from the tax authorities. This is ideal. However, in practice this ideal state of affairs is often not observed.
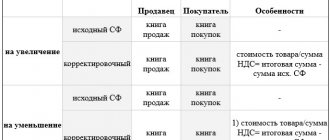
When maintaining a purchase book, in column 2 you should indicate “the date and number of the supplier’s invoice.” Clause 8 of the Maintenance Rules requires that invoices received from sellers be registered in the purchase ledger in chronological order as purchased goods (work performed, services rendered) are registered. Moreover, neither the date of issuance of the invoice by the seller, nor, especially, the date of its receipt by the buyer, based on the text of paragraph 8 of the Rules, are involved in determining the order of registration of invoices in the purchase book. Although for the buyer these dates are the basis for making an entry in the purchase book.
Often, with a significant document flow of an enterprise, situations often arise when an invoice arrives at the enterprise far beyond the deadline established by law for its preparation to the buyer. The culprit for the delay may also be the supplier, who did not consider it necessary to bring the issued invoice to the buyer, especially for periodic services, sometimes this can also happen due to the fault of the post office, and what is most offensive is that the delay of such invoices necessary for the accountant to deduct is carried out by themselves company employees who forget to deliver documents to the accounting department on time. The result is that the required chronological order of recording invoices as they are accepted cannot be maintained.
The invoice is dated later than the date of service
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, invoices are issued no later than five days from the date of shipment of goods, provision of services or performance of work. The term “issuance” means the preparation of an invoice by the supplier, and the date of the invoice should not exceed five days from the date of shipment of the goods or provision of the service. For example, the shipment of goods occurred on May 25, 2006, therefore, the invoice must be dated no later than May 30, 2006. With regard to services, paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation says the following: “when selling services, invoices are issued no later than five days, counting from the date of provision.” Thus, if a property lease agreement is concluded with monthly rental payments, then the date of service provision will be the last day of each month. The lessor, following the norms of tax legislation, has the right to issue an invoice on the fifth day of the next month. Let us note that this procedure for preparing invoices is disadvantageous for the tenant, since he will be able to submit VAT for deduction not in the month of service provision, but only in the next month, when the mandatory condition for submitting VAT for deduction regarding the presence of an invoice is met. To avoid such undesirable consequences for the tenant, it can be recommended that when concluding contracts, indicate what date the landlord should date the invoice and within what time frame it should be issued to the tenant.
It must be taken into account that if the seller nevertheless insists on such an option for drawing up invoices, then it is not possible to change his point of view, only rely on his consciousness, since he acts in accordance with the law. But what to do with invoices that can be drawn up on a date later than 5 days from the date of completion of work or provision of services?
The invoice was drawn up later than 5 days from the date of completion of work or provision of services
In this case, as in the previous version, the right to deduction will arise in the month of presentation of the invoice. And if the supplier is located in another city, there is a high probability that the invoice will arrive significantly late. The taxpayer will be able to submit VAT on such an invoice for deduction when it arrives at the organization. To confirm the date of receipt, you must register the invoice by stamping incoming correspondence in accordance with the rules of document flow. There are cases when tax authorities tried to challenge such a procedure for deducting VAT, but the courts do not support them in this (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated June 7, 2004 in case No. KA-A41/4545-04). The position of the tax authorities was that since the disputed invoice was dated in February, the organization had no right to claim it for deduction in March, despite the fact that the organization actually paid a large amount of tax to the budget. But the court rejected this position, citing the fact that in the absence of an invoice, “even if the taxpayer complies with other conditions (payment of VAT, capitalization) with which the law associates this right, there are no grounds for claiming VAT amounts for deduction.”
It should be noted that such cases are quite rare. If such disagreements arise, taxpayers may be advised to provide the inspectors with explanations from the financial department. For example, letter No. 03-03-11/107 of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 23, 2004 provides the following explanations: “the right to deduct the paid amounts of value added tax arises for the taxpayer if the three above conditions coincide. In connection with the above, for paid information services, invoices for which were received late, the deduction of value added tax is made in the tax period in which the invoice data were actually received.”
Thus, when registering invoices in the purchase book according to the date of their actual receipt by the accounting department from the supplier, it is advisable for each fact of discrepancy between this date and the date of provision of services, shipment of goods, performance of work for more than five “permitted by law” days, to have a supporting document , for example, an envelope with a stamp indicating the date of receipt at the organization's post office. In the event that it is impossible to prove that an invoice arrived at the enterprise on a later date through no fault of the buyer, then be guided by the principle of caution, recognizing what happened as a distortion that arose in the previous tax period, and accept the requirements established by Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for making corrections in accounting and filing updated tax returns.
The invoice was issued earlier than the date of service
This situation may occur when the buyer has made an advance payment and asks the seller to draw up documents. If the seller meets the buyer halfway, then he provides a disservice to his client, since in this case one of the necessary conditions for the deduction is not met - the service has not yet been provided, therefore, VAT cannot be claimed for deduction in the current tax period, and only after registration. During an audit, tax authorities may notice such a discrepancy, which will cause additional penalties and sanctions.
The most interesting thing is that the buyer cannot force the seller to issue an invoice properly, and even more so cannot force him to take all measures to timely deliver the invoice to the buyer. Receiving an invoice is a headache for the buyer. These conclusions can be drawn from the current legislation.
Paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges the seller to draw up an invoice and keep logs of received and issued invoices when performing transactions recognized as an object of taxation. Moreover, as can be seen from the text, the invoice is drawn up in one copy. The Rules of Maintenance, which are approved by Government Decree, require two copies to be made. Although subparagraph 8 of paragraph 1 of Article 6 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that those normative acts that change the content of the concepts defined therein or use them in a meaning different from the meaning established therein do not comply with it.
Thus, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the seller can draw up an invoice and take it into account in his journal; for some reason, the Tax Code does not prescribe it, nor does it set deadlines for this. Moreover, the Tax Code does not oblige the seller to keep the invoice. Subclause 8 of clause 1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges to preserve for four years documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes, but the invoice does not apply to those of the seller, since according to the definition of an invoice, which is given in paragraph 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code Russian Federation, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for deducting VAT from the buyer. Therefore, it is he who must store such documents to confirm deductions in the event of a tax audit. For the absence of invoices on which VAT was claimed for deduction, the tax authorities can only fine the buyer under Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for a gross violation of accounting rules.
Consequently, the seller bears no responsibility for failure to present the invoice to the buyer on time. In order to avoid difficulties in obtaining invoices in practice, the contract should include a clause on the mandatory preparation of the invoice within the period specified in the contract and sanctions for late submission by the seller, thereby making it possible to discipline the seller.
Sale at a discount
Invoice in conventional units
27.06.2010 11:44
Accounting and legal services
Lines 11 and 16 fill in the dates of shipment (transfer) and receipt of goods (work, services, property rights), respectively. VAT in the invoice in 1C in the document Receipt of goods and services needs to be unchecked in the Prices and Currency tab in the VAT box included in the price. Look at the acts of Russian Railways, they generally give them in summary for the entire month for all shipments. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not indicate that the numbers and dates of delivery notes and invoices must match. But what date should appear in the act and the invoice for it? In 1C there are 3 dates on the invoice and this is often confusing. If the dates are different. then options are possible. In addition, it is recommended to reflect other details in the act.
Invoice from January 1, 2021
At the same time, for profit tax purposes, when defining the concept of an error, one should be guided by the provisions of PBU 22/2010 (clause 1 of Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 13, 2016 N 03-03-06/2/21034, dated November 4, 2014 N 03-03-06/1/62348, dated 10/17/2013 N 03-03-06/1/43299, dated 08/13/2012 N 03-03-06/1/408).
Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 168. The amount of tax presented by the seller to the buyer: 3. When selling goods (work, services), transferring property rights, as well as upon receiving payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer property rights, the corresponding invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), from the date of transfer of property rights or from the date of receipt of payment amounts, partial payment on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services) services), transfer of property rights.
Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 146. Object of taxation 1. The following operations are recognized as the object of taxation: 1) sale of goods (work, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation, including the sale of collateral and transfer of goods (results of work performed, provision of services) under an agreement on the provision compensation or novation, as well as transfer of property rights. For the purposes of this chapter, the transfer of ownership of goods, results of work performed, and the provision of services free of charge is recognized as the sale of goods (work, services);
Theme Options
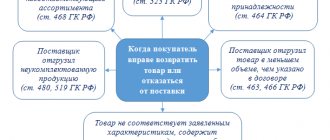
Civil Code of the Russian Federation Article 753. Delivery and acceptance of work 1. The customer, who has received a message from the contractor about the readiness for delivery of the result of the work performed under the construction contract or, if provided for by the contract, of the completed stage of work, is obliged to immediately begin its acceptance... 4. Delivery of the result of the work by the contractor and its acceptance by the customer are formalized by an act signed by both parties. If one of the parties refuses to sign the act, a note to this effect is made in it and the act is signed by the other party. A unilateral act of delivery or acceptance of the result of work can be declared invalid by the court only if the reasons for refusing to sign the act are recognized by it as justified.
When maintaining a purchase book, in column 2 you should indicate “the date and number of the supplier’s invoice.” Clause 8 of the Maintenance Rules requires that invoices received from sellers be registered in the purchase ledger in chronological order as purchased goods (work performed, services rendered) are registered. Moreover, neither the date of issuance of the invoice by the seller, nor, especially, the date of its receipt by the buyer, based on the text of paragraph 8 of the Rules, are involved in determining the order of registration of invoices in the purchase book. Although for the buyer these dates are the basis for making an entry in the purchase book.
You may like => Notice under clause 1 of Article 93 44 Federal Law in 2021
It turns out that the discrepancy in dates is a normal situation limited by time frames. What happens if you violate the 5-day deadline or issue a non-advance invoice before the work is completed and accepted by the customer? Such calendar leapfrog, if it occurs at the border of tax periods, can cause claims from controllers and become a reason for a fine.
Your rights in the section
Quote (Sweet raspberry): Quote (Julia79): Good afternoon! When services are provided, the corresponding invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the date of provision of services. Were the services actually provided to you on July 31? Then the deadline has not been missed. yes, 31 were provided. But it's a day off. Is it normal if documents are posted on a weekend? What stresses you out? A lot of organizations work seven days a week and on a rotating schedule.
Therefore, if in the situation under consideration, less than 5 days have passed between the date of issuing the act of services provided and the date of issuing the invoice, for example, the act was signed on November 30, 2012, and the invoice was issued on December 3, 2012, there are no violations. It does not matter that the date of the act of services rendered and the date of the invoice fall in different months. In this case, VAT on such an invoice should be deducted in December 2012 (Article 171 and Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The date in the work completion certificate is an important element that affects the reliability of the formation of information in accounting. On this date, the customer’s accounting recognizes expenses in the amount of the cost of work performed, agreed upon by the parties. In the contractor's accounting on the same date, revenue from the implementation of work is reflected and expenses associated with the fulfillment of obligations under the contract are recognized.
Invoice, invoice and certificate of completion of work
In earlier letters, the tax department explained that the day of provision of services is the date of signing by the contractor and the customer of the act on the provision of services (letter of the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated September 7, 2004 No. 24-11/57756).
An organization is not obliged to use electronic document management, but it has such a right if the other party to the transaction also agrees. The consent of the parties can be expressed in any way, but in any case it must be documented.
Calendar days for invoice
Y. Nikerova, expert at the “Practical Accounting” berator
The presence of an invoice is one of the conditions for applying the value added tax deduction. The supplier must issue an invoice to the buyer within five days from the date of shipment of goods (work, services). That is, an invoice can be issued only five calendar days later than shipment. But it often happens that the buyer waits a long time for this important document. What are the consequences of a “late” invoice and how to reflect such an invoice in accounting, we will tell you in this article.
Rule common to all To apply input VAT deductions, you must simultaneously meet the following three conditions:
- you have a properly executed supplier invoice;
- you have registered goods (work, services) or property rights;
- goods (work, services) purchased by you for transactions subject to VAT.
The procedure for issuing invoices is the same for everyone. The supplier is obliged to issue an invoice to the buyer no later than five days from the date of shipment of the goods (performance of work, provision of services). This is the requirement of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In other words, the supplier's invoice can be dated not only on the day the goods were shipped, but also on any other of the next four calendar days. For example, the supplier shipped the goods to you on July 21, and issued an invoice on July 23. But this is just one of the cases when the invoice is “late”. In reality, there can be many different situations. Here are some of the possibilities:
- the invoice was issued with the date of shipment. However, the buyer received it a few days later;
- the invoice has the “wrong” date: later than five days after shipment or earlier than this date (this can also happen).
Let's look at these situations in more detail and try to answer the following questions. How will this affect the VAT deduction? What can be done to mitigate the negative consequences of these events? Ideal situation If the invoice was issued on the date of shipment, and you received it on the same day along with the invoice, then there are no problems with crediting the “input” VAT. The main thing is to comply with the conditions for applying the VAT deduction. The accountant will make the following entries in accounting:
Debit 41 (10, 26, etc.) Credit 60 – reflects the cost of the values received (work performed, services rendered); Debit 19 Credit 60 – VAT is taken into account on the cost of values received (work performed, services rendered); Debit 68 Credit 19 – VAT on purchased assets (work, services) is credited.
Five Day Difference If the invoice is issued within 5 days of shipment, one of two things can happen:
- the invoice date falls within the same tax period in which the shipment was made;
- the invoice date falls within the next tax period.
Let us remind you: the VAT tax period is not the same for everyone. To determine it, the size of the company's revenue is important. Typically, for large and medium-sized companies, the tax period is a month. And for small businesses, as a rule, a quarter. Let's look at both situations using an example.
Example: Astra CJSC purchased goods from Tyulpan LLC in the amount of 236,000 rubles, including VAT - 36,000 rubles. The tax period for VAT for Astra is a month. Situation 1. Astra received the goods on August 17. "Tulip" issued an invoice and handed it over to "Astra" five days later - on August 21. The buyer's accountant will make the following entries: August 17 Debit 41 Credit 60 - 200,000 rubles. – reflects the cost of goods received; Debit 19 Credit 60 – 36,000 rub. – VAT on goods received is taken into account; August 21 Debit 68 Credit 19 – 36,000 rub. – VAT on purchased goods has been credited. CJSC Astra will show the VAT tax deduction in its return for August. Situation 2. Astra received the goods on August 31. "Tulip" issued an invoice and handed it over to "Astra" five days later - on September 4. The buyer's accountant will make the following entries: August 31 Debit 41 Credit 60 - 200,000 rubles. – reflects the cost of goods received; Debit 19 Credit 60 – 36,000 rub. – VAT on goods received is taken into account; September 4 Debit 68 Credit 19 – 36,000 rub. – VAT on purchased goods has been credited. Astra will receive the right to a tax deduction not in August, but a month later. The tax deduction amount will be included in the September return. In August, Astra will have to pay a larger amount of VAT, which may not be beneficial for it at all.
“Late” invoice If the buyer receives an invoice dated August 30th on September 15th, this is common. For example, a letter with an invoice took a long time to arrive in the mail. But you will be able to deduct VAT only when the invoice is in your hands (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). How to act in such a situation? On the one hand, the norm of Article 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation can be applied here. Namely: you have the right to make the necessary changes and additions to the declaration of the tax period to which the transactions relate. In other words, having received a “late” invoice, submit an updated declaration to the tax office, showing the “late” deduction. This deduction will need to be reflected “retrospectively” in accounting. Article 54 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to do this. It says here: “If errors (distortions) are detected in the calculation of the tax base relating to previous tax (reporting) periods in the current (reporting) tax period, tax liabilities are recalculated in the period of the error.” In other words, if you find an "August" distortion in September, you correct the error with "August". In this case, corrections will also need to be made to the purchase book. In it you will show the “late” invoice with the date indicated in the document. Moreover, additional sheets of the purchase book “will not help” here. After all, these sheets show only those “incoming” invoices that were previously registered erroneously and should be cancelled. On the other hand, employees of the main financial department take a completely different position. In their opinion, the buyer claims for deduction the amount of VAT on a “late” invoice in the tax period in which this invoice was actually received (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 23, 2004 No. 03-03-11/107). It turns out that both the entry for VAT offset and the entry in the purchase book must be made on the day the invoice is received. It must be said that there is a rational grain in the reasoning of financiers. After all, by and large, the provisions of Articles 54 and 81 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation relate specifically to “errors and distortions.” That is, those situations where an accountant, for example, accepted VAT for deduction without having the right to do so. And I discovered the error only in the next tax period. Our case is different: the “correct” invoice with the “correct” date was simply “late” a little. And we are not talking about any mistakes here. In addition, if you act as the Ministry of Finance orders, then there will be fewer problems: you don’t need to correct anything and submit “clarifications”. Invoice with the “wrong” date Anything can happen in our lives. Including a supplier invoice with the “wrong” date. For example, the seller may put a date on the invoice that is beyond the five days required by the code (i.e., well after shipment). How to be in this case? Of course, the ideal option is to convince the supplier to redo the invoice and put the correct date on it. What if this fails? Then you will have to register the document on the date on which it was issued (if the date of issue and the date of receipt coincide). Or the day you actually received the document (if you received it later). Accordingly, the VAT offset posting must be done on the day the invoice is registered. Does the company have the right to such an offset? In our opinion, yes. Let's explain why. Mandatory requirements for an invoice are listed in paragraphs 5 and 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And paragraph 2 of the same article states that the buyer loses the right to deduct VAT if at least one of these requirements is violated. Among the mandatory details listed here are the serial number and date of issue of the invoice. Moreover, what exact date (within five days from the date of shipment, earlier or later) is not stated in paragraphs 5 and 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But this is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the code. Now let’s return to paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Code. There is a wording here that literally “sounds” like this: “Failure to comply with the requirements for the invoice, not provided for in paragraphs 5 and 6 of this article, cannot be grounds for refusal to accept for deduction the tax amounts presented by the seller.” It turns out that the “wrong” date is not a reason to deny a company a VAT deduction. In conclusion, advice: to avoid friction with the supplier, establish a condition on the timing of issuing invoices in the contract with him. And don’t forget to indicate the sanctions for violating these deadlines.
Let's turn to the law Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 163. Tax period 1. The tax period (including for taxpayers acting as tax agents, hereinafter referred to as tax agents) is established as a calendar month, unless otherwise established by paragraph 2 of this article. 2. For taxpayers (tax agents) with monthly amounts of revenue from the sale of goods (work, services) excluding tax during a quarter, not exceeding two million rubles, the tax period is established as a quarter.
for reference Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 2, 2000 No. 914 “Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax” was recently amended (see Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 11, 2006 No. 283). And now there are additional sheets in the purchase and sales books. They need to correct errors made when filling out books. Corrections must be made for the tax period in which the error occurred.
for reference To avoid disputes with tax authorities regarding the deduction of “input” tax in the current month, which relates to previous periods, we advise:
- keep a log of incoming documentation;
- record all “late” invoices in this journal;
- establish the rules for registering documents in the accounting policy or in the order.
Postal papers, such as an envelope, can also confirm the date of receipt of documents.
Features of using electronic invoices
Consequently, primary documents independently developed by the organization and approved on the basis of Part 4 of Art. 9 of Law No. 402-FZ, including the mandatory details provided for in Part 2 of Art. 9 of Law No. 402-FZ are documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05.08.2021 No. 03-03-06/1/31261).
When is an invoice issued?
Despite the ambiguity of the situation, in this case you should be guided by the general rule - issue an invoice within 5 days from the first event. In this situation, the goods were originally shipped, that is, you need to count 5 days from the date of the invoice and issue an invoice during this time. The explanations given by the Ministry of Finance in letters indicate that the terms of the contract regarding ownership of the goods do not affect the timing of invoicing. In any case, the invoice must be issued within 5 days from the date of one of the operations - shipment (provision of services) or receipt of an advance - based on which of these operations was completed first.
In this case, for the purposes of applying value added tax, the date of shipment of goods is recognized as the date of the first drawing up of the primary document issued in the name of the buyer or carrier for the delivery of goods to the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 28, 2011 No. 03-07-09/23, dated November 1 .2012 No. 03-07-11/473).
The invoice was issued later than 5 days from the date of sale: what are the consequences?
There are also a number of “continuing” services, the ongoing provision of which does not require registration with primary accounting documents. For example, this is a lease (remember, for the purposes of calculating VAT, rent is a service): the lessor and the tenant enter into a lease agreement, sign an acceptance certificate of the leased object and, accordingly, the lease lasts until the termination of the lease agreement and (or) the return of the leased object to the lessor by the tenant . Monthly acts on the provision of rental services are not required. What to do in this case, given that the tax period for VAT is a quarter (Article 163 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)?
Accounting and legal services
- separate divisions (the document number separated by a slash is supplemented by the digital index of the OP, fixed in the accounting policy);
- participants of partnerships or trustees (the company’s transaction index for a specific agreement is also indicated through a slash).
Arguments that enable the performing company to issue an invoice for the provision of work before the fact of presentation and in the absence of prepayment (advance payment) are considered to be those that the supplier companies do not have any fundamental values for the timing of presentation of such documentation.
Buyers maintain a log of received original invoices from sellers. Clause 8 of the Rules obliges to register received invoices in the purchase book as the right established by Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - tax deduction.
Actions after invoicing
Do not discount the fact that when providing work, an invoice cannot be issued before it is provided . But this does not apply to prepayment (advance payment) for work.
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: An invoice for payment can be issued later than the acts for the work performed or the delivery note are signed, unless otherwise provided by the terms of the agreement or contract.
If the invoice is issued next month
The legislation provides the basis for drawing up this document. A mandatory precondition is a contract. An act drawn up in the absence of such a document may be recognized by the tax authorities as erroneous and invalid. The contract mostly specifies what document will be used to record acceptance. Articles of legislation provide for cases where the agreement and transfer and acceptance of services or work can be formalized in one document drawn up in a free format.
Results
If one of the parties refuses to sign the act, a note to this effect is made in it and the act is signed by the other party. The invoice is issued within 5 days from the date of completion of the work. What date should the certificate of work performed (services rendered) and an invoice be issued for when the service is provided? as it should always (well, practically) I receive iakt and sf in the next month.
When receiving an advance payment, this day is considered the date of receipt of funds, and when shipping goods - the date indicated in the delivery note or the certificate of completion of work. The law does not allow issuing an invoice later than this period. In addition, if the seller issues an invoice before the shipment date, the tax authorities may also refuse to deduct VAT for the buyer (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 9, 2011 No. 03-07-0 9/39).
Printable document forms
The document Invoice received is not intended for generating printed forms, however, if necessary, you can use the Print to print the following forms from it:
- Invoice for supplier; PDF
- Envelope. PDF
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Document Invoice received In this article we will talk about the purpose of the document Invoice received. Let's find out...
- Document Invoice received for advance payment Document Invoice received for advance payment is intended for registration of invoices received…
- Analysis of the status of tax invoices for VAT - message There is no invoice received for the Northern Federation without VAT for previous periods Good afternoon. Help clean up the messes of past years. Making a report: REPORTS...
- How to fix it if there is an extra invoice for an advance payment received for the last quarter in 1C Good afternoon. How (step by step, with what documents) to prepare an adjustment document in 1C...
The certificate of completion and the invoice are issued with different dates: how critical is this?
So, above I outlined my vision of the situation, and I tried to substantiate it with references to regulatory documents. This, as they say, is a dry theory. But in practice, I did not give my client a lecture, I advised him to simply fulfill the wishes of the counterparty. 20 years of experience in auditing tells me that attempts in any way and without fail to prove that you are right in business often bring negative results (namely, this situation is not that case). After all, issuing two invoices instead of one is a completely legal option. It’s just that my client – the chief accountant – will have to come to terms with the waste of paper. It’s a small thing, but you shouldn’t annoy your client.