What are adjustments and corrections?
When the cost of shipped products (services, property rights) changes, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation obliges taxpayers to issue an adjustment invoice. Such an adjustment is recorded as follows.
First, a document is drawn up indicating the change in the cost of shipped products (services, property rights). In this case, it does not matter why the cost has changed - due to changes in price or due to changes in the volume of shipped products (services, property rights). In both cases, a document (agreement, etc.) is drawn up that confirms that the buyer agrees to such a change.
When the adjustment document is issued, the seller adjusts the invoice and issues it to the buyer.
The further steps of the seller and buyer directly depend on the type of adjustment.
Since legislators approved the preparation of adjustments to invoices, many incidents have accumulated in accounting practice. The reason for this was the misconception of many accountants that any change to a previously issued invoice is documented in an adjustment document. However, it is not.
First of all, you need to learn to distinguish between the concepts:
- adjustment , which is formalized by drawing up an adjustment invoice and a primary document;
- an error that was originally made on the invoice and requires correction. In this case, a corrected invoice will be sent to the buyer.
The basis for the adjustment is a contract or other document that confirms that the buyer agrees to a change in the cost of shipped products (services, property rights). These documents confirm that the change took place after shipment.
But in case of violation of the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation during the initial issuance of an invoice or an error was made, for example, an arithmetic one, the invoice is not adjusted, but corrected. In such a situation, you cannot issue an adjustment invoice.
How to take corrected ESF?
Making changes to an invoice is not a problem, but each additional ESF involves wasting time and unnecessary entries. Practice shows that accounting books full of corrections are of particular interest to inspection authorities. Also, although these are small, they are still unnecessary expenses. Therefore, when accepting an invoice, especially after corrections, it is recommended to carefully check all document details. Moreover, the information should not only be in its place, but also correspond to reality.
At the same time, no one can work without making a single mistake. With digital document management, it is much easier to make changes to documents. In addition, the speed of data exchange increases significantly. This allows you to quickly identify errors and correct them immediately. Our company specializes in the development and implementation of paperless technologies and the implementation of EDI for the exchange of documents with counterparties. If you are interested in their capabilities, contact us by leaving a request on the website or by phone. We will be happy to advise you and offer the best option for cooperation.
Let's sum it up
It is not always possible to draw up an invoice correctly the first time. This is due both to the characteristics of the specific field of economic activity in which the company operates and to the human factor. Moreover, there are often cases when a seller or supplier makes mistakes due to the fault of the counterparty. For example, the buyer made a mistake when entering bank details or missed a number in the tax ID.
Therefore, the legislator is loyal and gives the opportunity to business entities to make amendments on their own. For this purpose, either an adjustment invoice or a corrected one is used. These two types of documents should not be confused, since their purpose is radically different. It is impossible to reflect a change in the price of a product in the form of a correction if it occurred in connection with the signing of an agreement between the seller and the buyer. To do this, you should use a correction invoice, otherwise it is contrary to current legislation. But if we are talking about real corrections of errors, then it is necessary to prepare a corrected invoice.
In addition to the instructions and recommendations described in the article, remember one more rule: each ESF is signed with a qualified digital signature. No matter how many changes you make to the same document, each time it must be endorsed using the CEP.
Features of accounting in one period and in different ones
If the cost of shipped products (services, property rights) increases in the current period (adjustment period):
- in the current period, the seller includes the resulting difference in the tax base, regardless of the period in which the products (services, property rights) were shipped (clause 10 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the buyer makes a tax deduction for the difference between the VAT calculated before and after the adjustment (clause 13 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Kontur.VAT+ takes into account adjustments and corrections and verifies the results with counterparties for all quarters.
Find out more
If the cost of shipped products (services, property rights) decreases in the current period (adjustment period):
- the seller makes a tax deduction for the difference between the VAT calculated before and after the adjustment (clause 13 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the tax base, which was determined at the time of shipment of products (services, property rights), is not adjusted;
- the buyer recovers VAT for the amount of the difference between the VAT calculated before and after the adjustment (clause 4, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- adjustments for reduction are carried out with KVO 18.
The seller and buyer reflect these transactions in their purchase and sales books as follows:
To correctly record adjustments in the books of purchases and sales in different reporting periods, use the following cheat sheet:
Example 1
According to the lease agreement between Sokol (lessor) and Lastochka (tenant), the rent amount is 106,000 rubles.
per month (including VAT). According to the additional agreement concluded in February 2021, the rental payment increased to RUB 112,600. per month (including VAT). According to the additional agreement, this change is effective from October 1, 2021. For the 4th quarter of 2021, rent amounted to RUB 318,000. (including VAT - 48,508 rubles). After concluding an additional agreement in February 2021, rent for the 4th quarter of 2021 increased to RUB 337,800. (including VAT - RUB 51,529).
In February 2021, after signing the additional agreement, Sokol issues an adjustment invoice to Lastochka and indicates:
- the previous amount of lease payment for the 4th quarter of 2021 (RUB 318,000, including VAT - RUB 48,508);
- new rental payment amount for the 4th quarter of 2021 (RUB 337,800, including VAT - RUB 51,529);
- difference (increase) (RUB 19,800, including VAT - RUB 3,020).
In this situation, Sokol increases the tax base for the 1st quarter of 2019 by registering an adjustment invoice in the sales book for this period by 16,780 rubles. (without VAT).
Lastochka has the right to deduct VAT in the amount of RUB 3,020 in the 1st quarter of 2021. according to the adjustment invoice received from Sokol, registering this invoice in the purchase book of the 1st quarter of 2021.
Example 2
In September 2021, Sokol shipped products worth RUB 96,000 to Lastochka.
(including VAT - RUB 14,644). In February 2021, the parties agreed to reduce the cost of shipped products. The cost after reduction was 82,400 rubles. (including VAT - 12,569 rubles).
In February 2021, Sokol issues an adjustment invoice to Lastochka, indicating:
- the previous cost (96,000 rubles, including VAT - 14,644 rubles);
- new cost (RUB 82,400, including VAT - RUB 12,569);
- difference (decrease) (RUB 13,600, including VAT - RUB 2,075).
In this situation, in February 2021, Sokol has the right to claim VAT in the amount of 2,075 rubles. according to the adjustment invoice issued to Lastochka. To do this, Sokol registers the adjustment invoice issued to Lastochka in its purchase book for the 1st quarter of 2021.
Lastochka in February 2021 must restore VAT in the amount of 2,075 rubles indicated in the adjustment invoice received from Sokol. In this regard, in February 2021, Lastochka must make a restoration entry in its sales book for the 1st quarter of 2019.
Registration of corrections depending on the period occurs according to the scheme presented below.
The practice of drawing up adjustment invoices has shown that adjustments to the cost of goods, services or property rights can be carried out repeatedly.
Please note: When a re-adjustment occurs, the seller will issue an adjustment invoice. It records the data from the previous adjustment invoice. This is how the next adjustment invoice includes the difference between the new data and the data from the previous adjustment.
In this case, the new adjustment invoice includes the date and number of the previous one. It is registered by the parties in the books of sales and purchases in the generally established manner for the amount of the difference indicated in it. In this case, the records of the previous adjustment invoice are not canceled (they remain in the form in which they were reflected when it was issued).
Let's learn how to work correctly with VAT in 1C. Corrected invoice
We are starting a series of lessons on working with VAT in 1C: Accounting 8.3 (edition 3.0).
Today we will look at the topic: “Corrected invoice.”
Most of the material will be designed for beginner accountants, but experienced ones will also find something for themselves.
Let me remind you that this is a lesson, so you can safely repeat my steps in your database (preferably a copy or a training one).
So let's get started.
A little theory
Unlike a corrective invoice, a corrected invoice is used to correct errors made when filling out the original invoice.
Corrections are made only in cases where filling errors are detected, for example:
- typos,
- incorrect details,
- tax rates are mixed up.
The corrected invoice is drawn up by the seller in 2 copies, one of which remains with him, and the second is transferred to the buyer.
The number and date of the corrected invoice completely coincide with the primary document, but it additionally indicates the number and date of the correction.
Corrections are numbered within the primary invoice from 1 to infinity.
Let's look at possible situations using examples.
Seller side fix
On January 1, 2016, we (VAT LLC) shipped 2 air conditioners to Buyer LLC at a price of 15,000 rubles each (including VAT).
At the same time, we issued the buyer a primary invoice No. 1 dated 01/01/2016, in which we made a typo, indicating 3 air conditioners instead of two.
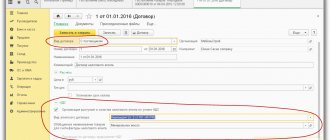
We issue the initial invoice
Go to the “Sales” section and select “Sales (acts, invoices)”:
We create and fill out a new document “Sales (goods)”:
We carry it out, and then issue an invoice (button at the bottom of the document):
The error was discovered in the same tax period (by the seller)
We discovered our error on January 10, having issued the buyer a corrected invoice No. 1 (correction 1) dated 01/01/2016 (correction 01/10/2016).
We issue a corrected invoice in the same tax period (from the seller)
Again go to the “Sales” section and select “Sales (acts, invoices)”:
Select the previously created implementation with the left mouse button, and then select the “Create based on” item (can be hidden in the “More” item) and then the “Adjust implementation” item:
Fill in the implementation adjustment:
Please note a few points:
- Type of operation “Correction in primary documents”.
- Correction No. 1 dated January 10, 2016.
- Quantity 2.
We post the document and issue a corrected invoice (button at the bottom of the document):
We look at the sales book in the same tax period (from the seller)
We create a sales book for the 1st quarter:
And we see that the primary invoice has been canceled (by the reversal method):
The corrected invoice was included in the sales book:
At the same time, the number and date of the correction are also indicated:
The error was discovered in another tax period (at the seller)
We discovered our error on April 1, having issued the buyer a corrected invoice No. 1 (correction 1) dated 01/01/2016 (correction 04/01/2016).
We issue a corrected invoice according to the same scheme (as above), only with the date 04/01/2016:
In this case (issuing a corrected invoice in a different tax period), the correction is made through an additional sheet of the 1st quarter sales book.
Opening the sales book for the 1st quarter:
Click on “Show settings”:
About for the current period:
We create a sales book and, instead of the main section, indicate “Additional sheet for the 1st quarter of 2021”:
Here is the cancellation of the original invoice:
And here is the corrected invoice indicating the number and date of correction:
Buyer side fix
On January 1, 2016, we (VAT LLC) received 2 air conditioners from Supplier LLC at a price of 15,000 rubles each (including VAT).
At the same time, we received the primary invoice No. 1 dated 01/01/2016, in which there was a typo (3 air conditioners are indicated instead of 2).
Entering the initial invoice
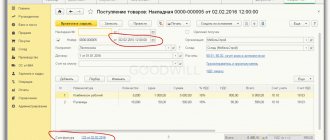
Go to the “Purchases” section and select “Receipts (acts, invoices)”:
We create and fill out a new document “Receipt (goods)”:
We register the primary invoice at the bottom of the document:
The error was discovered in the same tax period (by the buyer)
The seller discovered his mistake on January 10, having issued us (the buyer) a corrected invoice No. 1 (correction 1) dated 01/01/2016 (correction 01/10/2016).
We enter the corrected invoice in the same tax period (from the buyer)
Again go to the “Purchases” section and select “Receipts (acts, invoices)”:
Select the previously created receipt with the left mouse button, and then select the “Create based on” item (can be hidden in the “More” item) and then the “Receipt Adjustment” item:
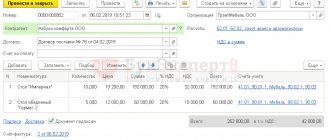
We fill out the receipt adjustment as follows:
On the “Products” tab, indicate the correct quantity:
We post the document and register the corrected invoice:
We make an entry in the purchase book in the same tax period (from the buyer)
Go to the “Operations” section and select “VAT Accounting Assistant”:
We indicate the period “1st quarter” and then open the formation of purchase ledger entries:
Click the “Fill out document” button:
The “Purchased Values” tab will be automatically filled in with our receipt, indicating the date of receipt of the invoice 01/10/2016 (date of correction):
We post the document and then create a purchase book for the 1st quarter:
The original invoice is cancelled, a new (corrected) invoice is entered.
The error was discovered in another tax period (by the buyer)
The seller discovered his mistake on April 1, having issued us (the buyer) a corrected invoice No. 1 (correction 1) dated 01/01/2016 (correction 04/01/2016).
We enter the corrected invoice according to the same scheme (as above), only with the date 04/01/2016:
In this case, the cancellation of the primary invoice is made through an additional sheet of the purchase book for the 1st quarter:
And the corrected invoice is entered into the purchase book for the 2nd quarter through entries in the purchase book.
To do this, open the “VAT Accounting Assistant” for the 2nd quarter:
And open the operation “Creating purchase ledger entries”:
In the form that opens, click the “Fill out document” button:
The “Purchased Assets” tab was automatically filled in with the corrected invoice dated 04/01/2016:
We post the document and then create a purchase book for the 2nd quarter:
The corrected invoice is entered into the 2nd quarter purchase ledger.
We're great, that's all :-).