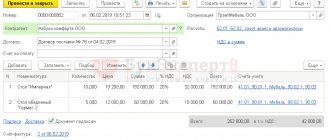
Upper part of the Invoice (header)
- Number and Date . The number must correspond to the numbering of documents approved in the accounting policy of your organization. The date indicated is current at the time of creation of the Invoice.
- Correction and Date . The correction number must correspond to the document numbering approved in the accounting policies of your organization. The date indicated is current at the time the Invoice is corrected. When drawing up an Invoice, before making corrections to it, a dash is placed in this line.
- Column Seller , the full and abbreviated name of the legal entity or individual entrepreneur (seller) is indicated.
- Column Address , the full address (with index) of a legal or individual entrepreneur (seller) is indicated.
- The seller's TIN/KPP column indicates the TIN and KPP of the legal entity (seller). An individual entrepreneur indicates only the TIN.
- The column Shipper and his address indicates the full and abbreviated name of the legal entity or individual entrepreneur (shipper), as well as his full address (with index). If the Invoice is drawn up for services performed (rendered) or property rights, then a dash is placed in this line.
- Column Consignee and his address , the full and abbreviated name of the legal entity or individual entrepreneur (consignee), as well as his full address (with index) is indicated. If the Invoice is drawn up for services performed (rendered) or property rights, then a dash is placed in this line.
- Column For payment and settlement document No. , indicates the number and date of the payment and settlement document (payment order) or cash receipt.
- Column Buyer , the full and abbreviated name of the legal entity or individual entrepreneur (buyer) is indicated.
- Column Address , the full address (with index) of a legal or individual entrepreneur (buyer) is indicated.
- The TIN/KPP column indicates the TIN and KPP of the legal entity (buyer). An individual entrepreneur indicates only the TIN.
- Column Currency: name, code , indicates the name of the currency and its code in accordance with the OKV classifier. The specified currency must be the same for all listed goods (works, services), property rights.
- Column Identifier of government contract, agreement (agreement) , indicates the identifier of the government contract, agreement or agreement. If there is no government order in the invoice, then a dash is added.
Invoice for services If the Invoice is drawn up for services performed (rendered) or property rights, then the two columns “ Consignor and his address ” and “ Consignee and his address ” are not filled in, you can put a dash (“–”) or a triple dash (“- — -“). If, when drawing up an invoice for services, you still fill in these two columns, then this will not be a mistake. In this case, this information will be additional information to the required details and cannot serve as a basis for refusing to deduct VAT.
When is a document needed?
First of all, you need to decide in what situations you need to issue a consolidated invoice. A consolidated invoice is a conceptual document that has never been introduced into use by regulations.
The need for this document arose when the growth rate of construction with the attraction of investor funds became very high. Then the Ministry of Finance of Russia (see letter dated May 24, 2006 No. 03-04-10/07) suggested that developers issue a consolidated invoice to investors when transferring to the latter his share and the associated costs and VAT on construction. This form of document flow was supposed to be carried out under investment agreements. According to such an agreement, the developer (a person who has ownership or lease rights to the site being developed) attracted funds from third-party investors to finance the construction, while undertaking the obligation to transfer to them a share in the constructed facility in accordance with the terms of the agreement. At that time, these agreements were qualified as an independent type of agreement, despite the fact that the Civil Code of the Russian Federation did not provide for such qualification. Agreements for shared participation in construction are essentially similar to investment agreements. However, their content, procedure for concluding and implementing, in contrast to investment agreements, were regulated by Federal Law No. 214-FZ of December 30, 2004 “On participation in shared-equity construction of apartment buildings...”. The economic similarity of equity and investment agreements has made it possible to extend the practice of issuing consolidated invoices to equity participation agreements in cases where the shareholder is a legal entity.
Thus, a consolidated invoice is a document introduced into use by business customs. Hence the problems that arose when filling it out, related to the lack of regulatory regulation of the procedure for its compilation and the inability to fill out individual positions. As a result, developers draw up consolidated invoices based on their own ideas, risking that tax authorities, referring to the general rules for filling out invoices, will consider these documents to be issued in violation of current rules. Theoretically, such a risk still exists, although in most cases tax authorities are loyal to consolidated invoices.
List of goods and services in the Invoice
The table with the list of goods and services is filled with data in accordance with the column headings.
- Column 1 - Product name , indicates the name of the product, work and service.
- Column 1a - Product type code , when exporting goods abroad, indicates the HS code, otherwise a dash is added.
- Column 2 and 2a - Unit of measurement , indicate the name and code of the unit of measurement of the product or service, in accordance with the OKEI classifier. If there are no indicators, a dash is added.
- Column 3 - Quantity (volume) , indicates the quantity of goods, works and services. If there are no indicators, a dash is added.
- Column 4 - Price (tariff) per unit of measurement , indicates the price per unit of goods without VAT. If there is no indicator, a dash is added.
- Column 5 - Cost of goods (work, services), property rights without tax - total , indicates the amount of goods without VAT.
- Column 6 - Including the amount of excise tax , indicates the amount of excise tax on excisable goods. If there is no indicator, “without excise tax” is indicated.
- Column 7 - Tax rate , indicates the tax rate (for example, 0%, 10%, 18%). For operations specified in clause 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is indicated “without VAT”.
- Column 8 - Amount of tax presented to the buyer , indicates the amount of VAT. For operations specified in clause 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is indicated “without VAT”.
- Column 9 - Cost of goods (work, services), property rights with tax - total , indicates the amount of goods, work, services including VAT.
- Column 10 and 10a - Country of origin of the goods , indicate the name and code of the country of origin of the goods in accordance with the OKSM classifier. For goods produced in the Russian Federation, a dash is added.
- Column 11 - Registration number of the customs declaration , indicates the number of the customs declaration. For goods produced in the Russian Federation, a dash is added.
Total payable - the sums of the numbers in columns No. 5, 8 and 9 are summed up.
Design rules
Based on the above, it can be assumed that those positions that cannot be filled out in the consolidated invoice (for example, payment and settlement documents) do not need to be filled out - a dash is placed in them.
In addition, the consolidated invoice must be accompanied by copies of all the invoices on which it was compiled, so that information that is missing in the consolidated document can always be found. It is recommended to consolidate these invoices into a register. Based on the total sum of the documents included in it, it is also possible to calculate the share of the tax that is transferred to a specific investor, relative to the cost of the share of the constructed object being transferred.
Bottom of the Invoice (footer)
The lower part contains the signatures of the responsible persons:
- Head of the organization or other authorized person - the full name is indicated and the signature of the head of the organization or other authorized person is affixed.
- Chief accountant or other authorized person - the full name and signature of the chief accountant or other authorized person is indicated.
- Individual entrepreneur - the full name and signature of the individual entrepreneur are indicated, and the details of the certificate of state registration of the individual entrepreneur are indicated.
In organizations, in addition to the manager and chief accountant, a “other” authorized person can sign, but only with a valid intra-organizational order with the right to sign accounting documents.
An individual entrepreneur signs only one column, Individual Entrepreneur .
How to issue a consolidated invoice in 2021
When and how a consolidated invoice combines transactions and payments, consider the options.
One invoice for several contracts
In financial and economic activities, enterprises use contracts to regulate the conditions between the parties to the transaction. Agreements are concluded both for individual transactions and for long-term cooperation, the stages of which are recorded by several separate primary documents confirming the shipment of goods or the provision of services at each stage.
If an enterprise has entered into two contracts with the same counterparty, is it possible to issue one invoice for both contracts? Yes, if, for example, the same counterparty delivers the goods at the same time or no later than 5 days according to the calendar. The consolidated invoice indicates the combined number of units of goods supplied under contracts or services provided under the terms of contracts. The date of the consolidated invoice in this case will be the date the parties signed the first primary documents.
Consolidated invoice for heterogeneous transactions
It happens that under an agreement or several agreements, the seller of goods and the performer of the service provided to the buyer, for example, delivery of products or installation of equipment, are one legal entity. In this case, the seller has the right to issue a consolidated invoice for the shipment of goods, services provided and work performed. When filling out a consolidated invoice, the seller indicates the product and service in one consolidated invoice on different lines, combining their costs into one total amount.
Advance invoice for several payments under one contract per day
Some buyers make an advance payment under contracts to the seller's bank account by transferring funds for goods or services in several payment orders per day. That is, if you have two payments on one day, you can make one advance invoice. In this case, when issuing a consolidated invoice for advances, the seller indicates in it the consolidated amount of advances deposited into the seller's current account, listing the numbers of payment orders separated by commas in the highlighted line of the consolidated invoice. An important condition for issuing a consolidated invoice in this case is a five-day period combining transfers. The Tax Code does not prohibit such an operation; tax authorities also do not object, provided that when issuing a consolidated invoice, the procedures and rules provided for by law are followed.
Invoice “Without VAT”
Goods and services not subject to VAT From January 1, 2014, when performing transactions that are not subject to VAT, in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, there is no need to issue Invoices, keep logs of received and issued Invoices, purchase books and sales books. Changes have been made to clause 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note that 0% VAT and “No VAT” are not the same rate, and each is applied for its own purpose. When performing transactions with a zero rate, indicating 0% VAT in the Invoice is mandatory.
Thus, there is no need to issue invoices for goods from January 1, 2014. But at the request of the counterparty, you can issue an Invoice “Without VAT”; this is not a violation. The requirement to issue an Invoice “Without VAT” can be presented by budgetary and government institutions. According to the specifics of their work, the treasury cannot make a payment without presenting an invoice.
What are the consequences of mistakes?
Errors and inaccuracies may be accidentally made in any document; their price may vary depending on the significance of the paper. What are the consequences of errors in the invoice?
If this document is filled out with inaccuracies, the buyer may be denied a VAT tax deduction. Naturally, in the future the buyer will no longer want to deal with the seller who caused him such a loss.
Error error discord
Not every mistake leads to dire consequences. Let's consider the most common variants of incorrectness in the invoice, on the basis of which the tax office has the right to refuse to reimburse VAT (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Unknown authorship. If it is difficult to determine from the document who exactly is the buyer and who is the seller, such an invoice will be considered invalid. This is quite likely. If the details of both parties are incorrectly specified or missing, such as:
- Name of the organization;
- address;
- TIN.
- Wrong product or service. If the invoice does not clearly indicate which product was purchased or service was provided, or this information contradicts other documents, VAT will not be refunded. For example, according to the invoice, “Romashka” candies were shipped (this name of the product is indicated in column 1), but in fact “Red Poppy” candies were sold.
- Inaccuracies in monetary figures. Problems associated with incorrectly indicating the cost of products (services) or the advance received for them also neutralize the value of the invoice. This may be related:
- with an incorrect indication of the payment currency (pay attention not only to the name of the currency, but also to its code);
- with omission or incorrect information regarding the quantity of goods (units of work or services);
- with errors in prices;
- incorrect calculation of cost (quantity multiplied by price does not result in the indicated figure in the “cost” column).
- Incorrect VAT calculation. In the column where VAT is indicated, one rate is indicated, and the amount is calculated using another, or a standard percentage is calculated when the rate should have been zero.
- Unknown VAT amount. If the required number is not in the corresponding column, although it is indicated in the “rate” column, and also if the given number is not obtained by multiplying the rate and the amount paid for goods (services).
When mistakes are not fatal
Tax authorities do not have the right and usually do not refuse a tax refund if there are other deficiencies in the invoice, for example:
- lowercase letters are used instead of capital letters or vice versa;
- quotation marks missing;
- missing or extra characters such as periods, dashes, commas, parentheses;
- there is no checkpoint or it is indicated incorrectly;
- there is no description of the work performed or services provided (information in column 1);
- there is no justification of the invoice by the contract number;
- errors in specifying payment details;
- numbering with inaccuracies;
- information about the consignee is not duplicated if he and the buyer are the same (the same goes for the seller and the consignor).
An error was made, what should I do?
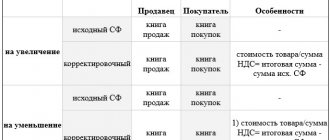
If the seller who issued the invoice finds errors in it, he has the right to make the necessary adjustments. The buyer does not have this right, but he can point out the error to the invoice issuer and ask for corrections. For this purpose, a special operation is provided - adjusting the invoice.
Deductions on consolidated invoices: claims of tax authorities and arguments of judges
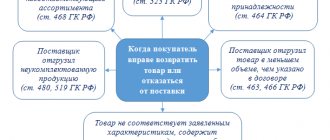
Taxpayers often have to defend their right to receive a VAT deduction under a consolidated tax return in court. Particularly indicative are the legal proceedings regarding the illegality of denial of deductions to taxpayer-investors.
What most often becomes the subject of litigation regarding consolidated invoices, see the figure:
A well-drafted agreement, as well as the ability of the taxpayer to prove its legality in court after the end of the three-year period, helps to defend VAT deductions under the consolidated s/f.
Regular long-term supplies: the Ministry of Finance has allowed to optimize VAT document flow
The Ministry of Finance does not object to the execution of consolidated financial statements if a long-term agreement for the continuous supply of products is concluded between the customer and the contractor (letter dated September 13, 2018 No. 03-07-11/65642).
Officials considered a situation where bakery products are supplied monthly on a continuous basis to the same buyer. In this case, you don’t have to draw up an invoice for each supply of bread, but issue a consolidated invoice at least once a month: no later than the 5th day of the month following the end.
Find out how to account for costs in a bakery enterprise from this material.
The Ministry of Finance recommends that this procedure for issuing invoices be fixed in the accounting policy for tax accounting purposes. The supplier must agree on its desire to arrange shipments with a consolidated s/f with the buyer. It is better to do this in writing by including in the contract or additional agreement a description of the document flow scheme.
The following materials will tell you how to organize and improve document flow:
- “Personnel document flow is ordered to be transferred to electronic form”;
- “Maintaining document flow for warehouse accounting of materials.”
Results
An invoice - regardless of whether it is drawn up by an individual entrepreneur or a company - is a document that allows the buyer to receive a VAT deduction. If an individual entrepreneur is a VAT payer, he is required to prepare invoices for each sale. If an entrepreneur applies a special regime, he is not recognized as a VAT payer and is not required to issue invoices (except in certain situations). Tax legislation does not prohibit him from issuing a VAT invoice, but in this case he must pay the tax to the budget and report.
Since 2021, companies and individual entrepreneurs applying the Unified Agricultural Tax have become VAT payers.
In this case, it is possible to obtain an exemption under Art. 145 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But you will still have to issue invoices, albeit without tax. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.