Organizations daily face situations where it is not possible to reflect property on balance sheet accounts. In accounting, off-balance sheet accounts are used to reflect transactions with valuables that are not objects of balance sheet accounting. It should be noted that information for off-balance sheet accounting, in the same way as for balance sheet accounting, is reflected in the reporting (certificate of off-balance sheet accounts f. 050730, f. 0503130 and f. 050830), and therefore it is necessary to maintain the correctness of the entered data so as not to distort reporting.
- How off-balance sheet accounts work
- Lease of non-financial assets
- Obtaining non-exclusive rights to use software products
- Accounting for property transferred for use
Material assets of the company in accounting
According to the current Russian legislation, the property of each individual organization exists separately from the property of other organizations and owners.
Property accounting is regulated by Russian PBU. Property assets of organizations are divided into categories:
- fixed assets - include real estate, transport, technological equipment;
- intangible property assets - intangible objects that bring income to the organization (inventions, computer programs);
- cash, non-cash funds of the organization in any currency;
- investments in valuable assets, authorized capital of other organizations;
- inventories for production (raw materials, goods, finished products, etc.);
- accounts receivable - finances that are the debt of counterparties.
The reporting of property assets of companies is based on the strictest principle: the company's property in money is equivalent to the sources of its formation. The increase in sources is recorded on credit accounts. Expenses are shown by account debits.
Property rental: postings
The rental price of premises often consists of fixed and variable costs. The price per square meter rented is constant, utility payments are a variable part. Rental costs at the end of the month are included in expenses. The choice of accounts depends on the purpose of the area.
For example, a company rented office space of 42.5 sq.m. for 1000 rubles. per sq. m. The entries made by the accountant look like this:
| Dt | CT | Wiring | Sum |
| 26 | 60.01 | Rental payment taken into account | 42 500 |
| 60.01 | 51 | Money transfer | 42 500 |
| 19 | 60.01 | VAT presented | 6483 |
| 68 | 19 | VAT is accepted for deduction | 6483 |
Displaying the company's property assets in accounting
To briefly clarify what the accounting of an organization’s property is based on, it is worth highlighting three main positions from this category:
- financial resources (cash, non-cash, at the cash desk, in bank accounts);
- intangible assets;
- tangible assets (not of particular value, fixed assets).
Any property object of an organization has its own localization on the established balance sheet account, which depends on many criteria, primarily on price.
Property assets worth up to 40 thousand rubles, but with a period of operation of more than one year according to the calendar, are not of particular value. Their accounting is kept on accounts 10, 11, 15. Such property is accounted for by regular posting in the accounting department D10-K60. Assets considered to be fixed assets of a company, which are not classified as low-value, differ in certain properties:
- such property assets are used for the production of products subject to further sale or for the provision of services;
- operation of this category of property items is expected for a long period of time (more than one year);
- book value of material assets from 40 thousand rubles.
Capitalization of fixed assets is carried out by posting:
- debit account 08 - credit account 60 (purchase from a supplier - entry to fixed assets).
After this, the value of property related to fixed assets is debited to account 01. Materials that are not of particular value are classified as tangible assets. These are property values that have a material expression, which can be reflected spatially, they can be observed, felt, and applied.
But there are such assets that are also valuable for the company, capable of bringing it profit, sometimes quite good, but they do not have a substantive form. This type of asset is considered intangible, for example:
- company reputation;
- intellectual rights;
- rights to use natural resources;
- organizational costs.
Intangible assets do not have a substantive form, but at the same time they can bring economic benefits to the organization.
How off-balance sheet accounts work
Instruction 157n provides for thirty-one off-balance sheet accounts. We remind you that the accounting entity has the right to use additional off-balance sheet accounts. To use additional accounts, they must be included in the working chart of accounts and approved when developing the Accounting Policy.
The movement in off-balance sheet accounts is reflected as follows: the debit account takes into account the increase in the values of the account, and the credit account for the decrease, since all accounts are active. Recording on accounts, unlike balance sheet accounts, is simple; a corresponding account is not needed to generate postings.
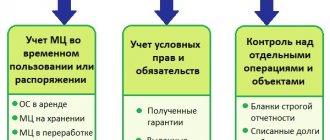
The main business situations in which an institution, in accordance with current legislation, needs to make entries on off-balance sheet accounts.
How are the sources of property of enterprises reported?
Reporting of a company's property assets involves identifying the sources of organization of such property.
Accounting for the sources of formation of an organization's own property provides for the division of material assets into two key categories: own assets, borrowed funds. Often, an LLC acquires property through the use of its own funds. The company creates equipment, and with money from the sale of the product, it updates the production line: it adds to the list of fixed assets, thanks to which it subsequently receives income. As a rule, to develop large-scale activities, one’s own finances are not always sufficient, especially at the initial stage of development of the company’s activities. Therefore, organizations often attract third-party resources, that is, they enter into contractual agreements with business partners and credit institutions.
Features of accounting for rent
When receiving fixed assets for rent, the company does not acquire ownership of these assets. Consequently, leased properties are not reflected in balance sheet accounts. Such assets should be accounted for in off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets”. For example, the receipt of equipment under a lease agreement should be reflected in accounting by a one-sided entry in the debit of account 001.
But there may be exceptions. The rules for accounting for leased property are determined by the terms of the agreement. If the assets are assigned to the balance sheet holder, then the equipment received on lease or rent is reflected in off-balance sheet account 001. If the property is transferred to the recipient’s balance sheet, then reflect the assets on the balance sheet.
What does the equity capital of an LLC consist of?
Any company has certain material assets on its balance sheet.
But they are not always paid for by it, that is, some of the organization’s property is accounted for in accounting as acquired with borrowed funds. To determine the equity capital of an LLC from the price of real estate/movable property, it is necessary to subtract debt obligations. The organization's equity capital includes:
- Authorized capital is the investment of the founders. It is created at the initial stage of company formation. The amount and percentage of investors' investments are not established by current legislation, but the authorized capital should not be less than 10 thousand rubles, otherwise the owners of the organization will not be able to register it.
- Additional capital represents a unit formed after periodic additional assessment of non-current assets, carried out as part of accounting for the company's property assets.
- Reserve capital is funds accrued by reserve funds intended to cover shortfalls and repurchase own shares. An LLC can create such a fund if this provision is specified in the constituent documentation. The fund is replenished with funds from net profits. Often, LLCs specifically create reserve funds to pay annual bonuses, carry out repairs, and other activities.
- Profit is the finances that remain after calculating the necessary expenses and taxation from income. Profit, as a rule, accumulates during the operation of the enterprise. Therefore, in accounting there is the concept of profit for the period of the current year (January 1 is the date of calculations), profit for previous years (accumulations from the moment the enterprise began operating until December 31 of the previous annual period).
- Targeted financing is money intended for established events, coming from special funds, companies, and authorities. It is possible to allocate budget money, for example: for scientific research, organization of an international conference, construction of a socially important facility, and other needs. Targeted financing is possible in the form of subsidies and other income from third parties and government agencies.
- Borrowed capital is credit funds that are used for the development of a company in the event of a lack of own funds. The company's liabilities are also borrowed funds.
Important! According to accounting, property assets acquired through borrowed funds also include property acquired by the company on terms of deferred payment by installments. That is, when the counterparty credited the enterprise for the amount of the cost of services provided or items of property.
It is quite difficult to engage in entrepreneurial activity without attracting third-party funding. In practice, there are no companies that would not use borrowed funds for their own development and expansion of production lines.
Company property and its types
The legislation clearly defines what should be classified as a company's property. Key definitions and classification are provided not only by Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”. Also, the regulatory regulation of the issue is enshrined in the Civil and Tax Codes and in the PBU.
It is normatively established that the property of an organization is accounted for according to the principle of property separation. This means that a company's assets must be accounted for separately from those of its founders and third parties.
Types of property in accounting
| Property category | Concept and example | Legal acts regulating the rules of accounting | Which account is the property accounted for (Order of the Ministry of Finance 94n) |
| Fixed assets | These are company facilities used in the company's core business. The period of use is more than a year. Not for sale. Buildings and structures, offices, equipment vehicles. | PBU 06/01. Guidelines for maintaining OS records. | 01 |
| Intangible assets | An object that has no physical shell or characteristics. But it is used by the company in its activities to make a profit. The period of use is more than 1 year. Inventions, software, trademarks. | PBU 14/2007. | 04 |
| Inventories | Objects used in the economic activities of the organization. Use life is less than a year or one production cycle. Goods and products for resale are also included in the inventory. Raw materials, materials, goods. | PBU 05/01. Methodological recommendations for accounting for MH. | 10 41 |
| Money | This is all the company's cash held in cash on hand or in current accounts. Moreover, not only ruble amounts are taken into account, but also money in foreign currency. | PBU 3/2006. Instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U. Law No. 54-FZ. | 50 51 52 |
| Financial investments | Investments in securities, shares, authorized capital of other companies. They are classified into short-term (up to 12 months) and long-term (more than a year). | PBU 19/02. | 58 |
| Accounts receivable | Amounts transferred to counterparties for future supplies or services. That is, those funds that counterparties owe the organization. | PBU 21/2008. | 60 62 76 |
These categories of objects are subject to mandatory inventory. The rules for checking the actual availability of property and property are determined by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49.