What documents are considered cash registers?
Cash register documentation is used to carry out settlements with counterparties and within the organization. These include:
- receipt order (PKO): it is issued when money is received;
- expense order (RKO): formed upon disposal of funds;
- register of PKO and RKO: it keeps records of incoming and outgoing orders;
- advance reports: used to account for accountable funds;
- announcement for cash deposit: fill out when depositing money into the bank to replenish the current account;
- Cash book: used to reflect all income and expense transactions and cash balances;
- a book of accounting for received and issued funds: kept if the company has several cashiers and a senior cashier, transactions on the issuance and receipt of money between them are recorded in it;
- Cashier-operator's journal: operations on the receipt and expenditure of cash for each cash register in the enterprise are entered into it.
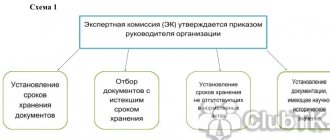
Cash register documentation is maintained in both paper and electronic form. The manager appoints a responsible employee for conducting operations and generating documents for the cash desk by a separate order:
Accounting and tax regulations indicate how long documents confirming cash settlements with customers and financial transactions at the cash register must be kept. The storage period for such documentation includes:
- 402-FZ of December 6, 2011 (Article 29); Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 8, part 1, article 23);
- Order of Rosarkhiv No. 236 of December 20, 2019 (clause 277).
In addition, the storage period for cash receipts in the organization and other bank registers is prescribed in the Directives of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014. According to the standards of the Central Bank, all payment registers for the bank and cash desk are stored for 5 years.
What is a cash register Z-report and how to make it
To switch to compilation mode, you will need the “MODE” button. You will need to press it again. The number of times depends on the settings. In the menu that opens, you need to start forming. To do this you will need the “IT” key. When pressed, the procedure is initiated. But user details are required to log in. If they are not installed in advance, you can enter . Or the one that is used at a given point.
There are practically no differences with the previous paragraph. Only the button that will lead to the menu changes to the new “AN/RE”. The rest of the process is organized according to the same scheme.
This is perhaps the easiest option for working specifically on the stated task. We will need a third mode for printing. Find the appropriate option change button and double-click on it. The display will show your selection. All that remains is to click on “enter” and agree with the chosen solution.
It is necessary to open the main window with the definition of the procedure mode. There you will find the note “CCP reports”. This is the section we need. In the window that appears, close the shift by double-clicking the enter button.
Types of Z-reports
Z-reports come in several types.
- The main Z - report is the main report that is taken at the end of the shift. It clears all “registers” on the cash register for the current shift (resets the daily revenue to zero). It MUST be removed every shift, otherwise the cash register will be blocked.
- Z – report by department – this report shows how much money was spent for each department, after the previous withdrawal of the Z – report by department. It resets the accumulation of department counters. It doesn't have to be removed every day.
- Z – report on cashiers – this report shows how much money was entered by a particular cashier. If this report is removed, the cashiers' savings will be reset to zero.
- Z – report on goods – this report shows how many goods were sold if a database of goods (or services) is programmed in the cash register.
Accumulations in the report are the total amount of all money entered for the entire period of operation of the cash register.
Sometimes savings may be reset, for example in the following cases:
- re-registration of a cash register
- replacing fiscal memory
- other cash register repairs
The amount of savings itself does not mean anything in a legal sense. That is, the tax inspectorate cannot and does not have any claims regarding savings. But out of old habit, when resetting savings, some tax inspectors ask to fill out the KM-2 form.
Despite the fact that these two reports are similar, they have significant differences. The difference between these two documents is that the first is designed to close the shift and reset the sales registers, increasing the shift counter by one point. After all these steps, the cash register is ready for the next cashier to work. The second document opens the shift and shows the amount of cash and revenue from the moment of its opening, recording this in the fiscal registrar. It can be printed as many times as you like to verify the amount of money in the cash register. Another difference is in the list of details contained in each of them, but more on that in the next section.
The X-report helps to determine the correctness of entering information into CCP, as well as to analyze trade turnover, both in general and specifically for a specific product.
What is their storage period?
The order of safety of cash registers is regulated by both accounting and tax legislation. In Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation explains the storage period for cash documents for cash transactions: organizations are required to retain documentation with accounting and tax information for 5 years. At the request of tax authorities, income and expense registers are kept for the same amount of time.
Determines the period for which cash register documents are stored in the organization, and 402-FZ. In Art. 29 of the Accounting Law establishes a minimum period of preservation of primary accounting registers. It is 5 years after the end of the reporting year, which coincides with the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The company independently organizes storage and provides the conditions required for the safety of documentation. If necessary, the company creates an archive and transfers all registers of previous years there (clause 2 of Article 13 125-FZ of October 22, 2004).
If a company conducts an audit of the cash register, a special audit act is drawn up. 402-FZ does not have a separate provision regarding how long the audit report of the main cash register is kept and how to store it. But the accounting law clearly defines the storage period for cash documents. All registers related to cash discipline are kept by the company for 5 years.
Confirms the minimum storage period for the cash book in the organization (and other cash register documents) and the order of the Federal Archive No. 236. Clause 277 of the order No. 236 provides the storage period for bank registers and cash register documents, counterfoils of cash check books, orders, time sheets and other forms.
In accordance with paragraph 277 of list No. 236, the storage period for a cash receipt order is 5 years. RKO, cash book, cashier's journals and checks are stored for a similar period.
Is it necessary to store Z-reports of an online cash register?
When using an online cash register, the machines must be equipped with fiscal drives, which are an analogue of a secure electronic control tape (ECT), but the essence of an online cash register is that all information on transactions performed is encrypted and cannot be corrected. And one of the documents stored in the financial storage is the shift closing report (a modern analogue of the Z-report). Based on this document, you can also generate cashier reports (upon delivery). But the online cash register itself sends all the required reports to the Federal Tax Service.
It is allowed to capitalize the proceeds the next day after the fiscal report is issued, for example, when the operating hours of the company (from 12.00 to 24.00) and the administration (from 10.00 to 19.00) do not coincide.
Expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT, professional accountant
I. Bashkirova
For organizations and individual entrepreneurs, Rules for working with cash registers are formed regarding the movement of funds, their storage and work with cash registers in general.
The order sets a balance limit for organizations, the rest is handed over to the bank (if there is no order, then the limit = 0), the individual entrepreneur can store cash in as much as necessary. Exceeding the limit is allowed on paydays, weekends and holidays.
For cash payments to organizations and individual entrepreneurs, a limit of 100,000 rubles is established; there are no restrictions for individuals.
When introducing online cash registers, the use of forms No. KM-4 and No. KM-6 is not necessary.
A Z-report or a report with cancellation is the final document (check), which the cashier displays from the cash register when closing the shift. The results are summed up, the data is reset, and after that you cannot perform cash transactions: returns, cancellations, etc.
The cashier-operator takes out the cancellation report at the end of each shift, but at least every 24 hours, taking into account the following factors:
- When there is a day off and/or a pre-holiday day and the organization is not operating, reporting is not removed.
- If no trading operations were carried out on a certain business day, reporting is generated even with zero indicators. The cashier-operator puts dashes in the journal for the whole day. Does not make entries in the cash book.
Since all individual entrepreneurs and legal entities have switched to online cash register equipment, the new Z-reporting is slightly different from usual.
Cash register for UTII in 2018
Online cash registers from July 1, 2021
Cash issues
Online cash registers for cafes
Nomenclature in online cash registers
Z-reports when using online cash registers are not compiled in the form in which they were generated on the old-style cash register with EKLZ. The main task of Z-reports was to reset data based on the results of a worked shift and record information about all operations performed (arrivals, returns, cancellations, discounts). This made it possible to obtain correct information on the volume of revenue for each shift and fill out cash reports.
Amendments to Law 84-FZ affected not only the scope of use of cash register equipment, the generation and transmission of checks, but also basic reports. The Z-reports familiar to cashiers are a thing of the past, but they have been replaced by shift closure reports. The main difference between the new fiscal document is the need to send it automatically to the Federal Tax Service. But there are a number of other features of its formation and storage.
After the loss of force of Government Resolution No. 470 from July 1, 2017, which is reflected in paragraph 3 of PP No. 1173 of November 12, 2016, regulating the use of CTT using paper control tapes, the question logically arose about the forms of primary documents.
Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-01-15/3482 dated January 25, 2017 explains that Goskomstat Resolution No. 132 dated December 25, 1998, which reflects the provisions on the forms of primary documents, as well as Federal Law-402 “On Accounting”, regulating since January 2013, the form of primary accounting documentation used to create unified journals and albums has lost force and is not mandatory.
It turns out that with the transition to online versions of cash registers, organizations and entrepreneurs do not have to generate the usual Z-report, information from which was previously entered without fail into the Cashier's Certificate Report (form No. KM-6), as well as into the Cashier-Operator's Journal ( f. No. KM-4).
How then can entrepreneurs record data at the end of a working day or shift? Clarity is provided by clause 4 of Article 4.1 of the Federal Law No. 84, which sets out the list and requirements for the formation of mandatory fiscal documents.
When using an online cash register, closing is carried out with the appropriate report, the mandatory details of which are reflected in table 32 of Chapter II of Appendix 2 of FSN Order No. ММВ-7-20/229 dated March 21, 2021.
The usual Z-report and the new cash register closure report are essentially analogues. But there is a certain difference in their formation and tasks.
Table 1. Difference between closing a shift at the online cash register and the Z-report
| Name | Shift closing report | Z-report |
| Formation | At new online cash desks at the close of the operating period | On old samples of KKM |
| Legal data requirements | Stipulated in the FSN Order No. 229 dated March 21, 2021. | Not defined, depends on the cash register itself |
| Requisites |
|
|
*in offline mode they are not included in the report;
**are not mandatory details, formation depends on the type of cash register;
***the report can be printed if desired by the cash register owner
As you can see, the old and new reports will differ slightly in practice. Therefore, cashiers should not have difficulty generating them.
Work with the online cash register begins with the generation of a report on the opening of a shift. After completing all calculations, it is necessary to run a report on the closure of the shift.
Important! In accordance with clause 2 of Article 4.3 of Federal Law No. 54, the generation of an online cash register receipt for sales cannot occur later than 24 hours after the closing of the previous shift.
Accordingly, the duration should not exceed one astronomical day.
Such requirements are related to the characteristics of fiscal drives. Clause 1 of Article 4.1 of Federal Law No. 84 focuses on the impossibility of displaying fiscal characteristics on generated receipts if the shift duration exceeds 24 hours.
Reference! A shift can open on one calendar day and close on the next, but cannot exceed one day.
Since no other recommendations are specified in the Law, the exact time for generating the report and reducing the duration of the shift are regulated by the management of the organization using the online cash register.
After the transition to the new cash discipline, the need for maintaining a journal and a cashier’s certificate report disappeared. But no one forbids entrepreneurs from maintaining such cash documentation on their own. The new shift closing report has all the data to fill out such documents.
A mandatory requirement for the new document is the automatic transmission of data to the Federal Tax Service. The FN built into the online cash register does an excellent job of this task. The generated document must be stored in the memory of the FN for at least 30 days. Therefore, if there are problems with the Internet, data is transferred automatically when a connection is established.
Reference! If checks are not transferred for more than 30 days, the cash register is blocked.
You can avoid such an incident if you regularly check the number of checks not sent to the OFD. And this opportunity is provided precisely when generating a report on the closure of a shift.
Below the part “State of exchange with OFD”, during normal data transfer, zeros should be displayed in the following lines:
- date and time of the first FD not transferred;
- number of unsent checks.
[3]
A Z-report or a report with cancellation is the final document (check), which the cashier displays from the cash register when closing the shift. The results are summed up, the data is reset, and after that you cannot perform cash transactions: returns, cancellations, etc.
The cashier-operator takes out the cancellation report at the end of each shift, but at least every 24 hours, taking into account the following factors:
- When there is a day off and/or a pre-holiday day and the organization is not operating, reporting is not removed.
- If no trading operations were carried out on a certain business day, reporting is generated even with zero indicators. The cashier-operator puts dashes in the journal for the whole day. Does not make entries in the cash book.
A canceled report is a special report that is taken from the cash register at the end of each shift. It contains all transactions performed during the working day. Its formation occurs no later than 24 hours from the moment you start working on the device. The document is removed even if the cashier has not entered a single check for the whole day.
There is another report called the uncancelled report. What an X report is will be discussed in this section.
X report without cancellation is another document generated by the cash register device. It contains information about all the cash that was processed on it during the shift. This document can be generated at any time, it is not recorded anywhere and does not require sending to the Federal Tax Service.
Its other names are: morning reporting or zero check. It is called that way because previously the tax office required its removal at the very beginning of the shift, that is, in the morning. This was done in order to make sure that there was no cash in the cash register and to show that revenue at the beginning of the shift was zero. Today, this document is not required to be withdrawn every morning, since all the necessary information can now be stored in a secure electronic cash tape.
Both of these documents look like checks printed by cash register machines. The only difference is in the data and details provided.
For the z-report, the order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation approved the following list of details, the presence of which is mandatory in the report:
- The name of the organization or the full name of its founder;
- Taxpayer identification number;
- Legal address of location;
- Full name of the cashier operating the device;
- Name and number of the document;
- The sum of all settlements for various operations;
- Receipt and return amounts;
- Number of checks printed per day;
- Information about the cash register: registration number and serial number;
- Fiscal storage number;
- Shift number, date and time;
- Fiscal sign.
Important! There is an optional field “Individual Entrepreneur Revenue Amount”, but some cash register companies have it and can fill it out. You can find out detailed information about this on the websites of fiscal data operators.
The X report provides the following data:
- Date and time;
- Number of checks printed;
- Total sales amount;
- Amount of cash in the cash register;
- Information on returns;
- Number of sales for the current shift;
- Type of payment: cash or non-cash.
It will not be possible to obtain this data for other shifts electronically, since the X-report makes it possible to take readings only of the current shift and record them on paper.
Z-reports are not very diverse, but they come in several types:
- Basic. The main document removed at the end of the shift. He clears all registers of the cash register, that is, he resets the revenue for the working day and ends the shift. It must be carried out, otherwise the cash register will be blocked;
- By department. The paper shows everything the same, but specifically for each sales department. The report resets the department accumulation counter to zero. It is not necessary to withdraw every day;
- By cashiers. Determines the amount of money entered by one or another cashier. Removing it means that cashier savings will be reset to zero;
- By goods. Displays the number of products sold if the device contains a database of all products.
In addition to daily and aggregated data, you can also receive documents based on narrower indicators. They are not much different from the types of Z-reports discussed earlier and include:
- Basic paperwork for checks and cash. It reflects the number of receipts per shift and the amount of cash in the cash drawer;
- By cashiers. All revenue data is grouped for each individual cashier;
- By department. Similar to the grouping by cashiers, the information reflects the grouping of the main document by sales departments;
- By goods. Used to control inventory balances and group data by product;
- Checking sales activity. Sales analytics are performed over time to determine the highest buyer activity.
- The main document is the cashier’s main document, which must be removed every day at the end of the shift. Removing the report allows you to reset the device counters and clear the registers. If the cashier forgets and does not remove the Z-report, the machine will be blocked and will not work.
- By cashiers - this document is intended to summarize data separately for cashiers and shows how much revenue a particular responsible employee generated. When withdrawing, the cashier's information is also reset to zero.
- By department – allows you to determine how much revenue each department earned.
Accumulations of counters are also reset when the report is taken, but this is not necessary to do every day. - By goods - this type of reports is available if the device is programmed to collect data on a database of goods or services.
Important! Removing a Z-report ALWAYS resets the data on the cash register in the current operating mode.
In addition, resetting occurs in the event of re-registration of equipment; during repairs or after replacing fiscal memory.
7 of the Law of July 3, 2021 No. 290-FZ.
On old and current cash registers, the Z-report is a daily report of the cash register with information being reset in RAM and entering it into fiscal memory, while new machines immediately write everything into fiscal memory. Therefore, with the introduction of online cash registers, cashier-operator logs will become a thing of the past, and there will be no need to store Z-reports. After all, the online cash register will quickly transmit data to tax authorities via the Internet.
Important: In new machines, before the cash register starts making payments, a report on the opening of a shift will be generated, and upon completion of payments, a report on the closure of a shift.
At the same time, a cash receipt cannot be generated later than 24 hours from the moment the report on the opening of the shift is generated. Let me remind you about the stages of transition to online cash registers: 1) from July 15, 2021, according to paragraph.
5 tbsp. 7 of the Law of July 3, 2021
“Online cash register” Z-reports come in four types:
- The main one is the main document of the cashier, which must be generated at the end of each day. Thanks to the generation of such a report, it is possible to reset the cash register counters and clear the registers. If the cashier forgets to take this report, the cash register will stop functioning.
- By cashiers – such a report is intended to summarize information separately for cashiers. It reflects how much profit a particular cashier employee received.
- By department - thanks to this report, you can find out how much profit each department of the company received.
- By goods - this type of report will be available only if the cash register device is programmed to collect information on a database of services or goods.
It is worth noting that removing any of these types of reports always resets the information on the cash register in the current operating mode.
At webinars and conferences for small businesses, experts from the “” and “” services answer many questions about the transition to online cash registers, the choice of equipment and the rules for its use. Today Buhonline presents you with a selection of their answers to the most common questions. From July 1, 2021, the use of cash registers is mandatory for the following entities:
- Individual entrepreneurs on UTII who have employees and are engaged in retail or catering.
- LLC on UTII, which are engaged in retail trade or provide catering services.
- Individual entrepreneurs on PSN who are engaged in retail and catering.
Also see about the timing of application of CCP for other segments of trade and services.
The Z-report (today called the shift closing report) is a daily report on the operation of the cash register, carried out at the end of the cashier’s shift (it is not reset to zero in online cash registers). The use of online cash registers in work is aimed at reducing paper reporting and exchanging information between the entrepreneur and the Federal Tax Service in electronic format.
Today, entrepreneurs, regardless of the applicable tax regime, are required to switch to online cash registers, but conducting cash register transactions directly on site remains the same.
The printed check with the final report must be pinned or glued to the “Cashier-operator’s certificate-report”. The following information is entered into the cash register as a separate line:
- date of each document;
- his number;
- gross total (sum at the beginning and at the end of the shift);
- amounts of sales, returns, discounts, etc.
Together with the recorded revenue, the cash register at the end of the shift (working day) is handed over to the senior cashier, to the accounting department or personally to the manager (depending on how this is established by the internal procedure of the organization).
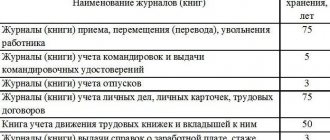
The collected Z-reports, as well as used EKLZ, must be stored for at least 5 years; the manager is responsible for the timing and safety.
IMPORTANT! Take care of these documents, do not lose or throw away the taken Z-reports, even if they were carried out by a foreman when setting up the cash register, contain zero indicators, or were taken as a test. Absolutely all canceled reports must be recorded in a journal.
“Zetka” is a document of strict financial reporting.
It must be removed after a shift or working day, but at least once every 24 hours. If this is not done, the cash register will be blocked. All cash registers, as required by law, are equipped with an automatic locking system when a 24-hour shift is exceeded. Until the Z-report is removed, the cash desk will not be able to perform any operations.
The SFSU letter dated February 10, 2015 clarified that zero reports do not need to be printed if not a single cash transaction has been completed within 24 hours. However, often internal documents of an enterprise require opening and closing a shift, regardless of the passage through the cash register. In addition, in practice, small money is most often stored in the machine, and this is also finance that must be carried out daily through the cash register (“service deposit”), and this is an operation that will be reflected in the Z-report.
- Each cancellation report has its own serial number, so there should be no gaps in the cashier’s journal.
- It cannot be removed or canceled again, since it is recorded in the fiscal memory of the device and on the control tape.
- If no cash transactions were made within 24 hours, you can issue a zero Z-report.
- During a shift or working day, you can take any number of Z-reports; each must be issued separately and filed with the operator’s certificate.
- After printing the Z-report a second time, it cannot be withdrawn until any cash transaction is carried out.
NOTE! The very first report with cancellation, taken to the INFS when registering the cash register, will remain there: its absence will not in any way affect the correctness of the cash register. But with all the subsequent ones you should be especially careful.
In life, anything can happen, and even an irreplaceable report with cancellation may, for some reason, not be documented in the journal as it should be. This most often happens:
- with inexperienced employees who unknowingly throw away such an important check;
- due to the repair of the device, when the report is punched out by the master for verification, they do not always think to save it;
- if the receipt was not printed due to a breakdown of the cash register, problems with the ribbon or paper, or a power outage;
- if the check is lost;
- when the document is torn, worn out, flooded, or damaged in some other way.
The absence of a Z-report threatens the company with large fines. To avoid them, you need to immediately follow the procedures prescribed by law when you discover the loss of the socket.
- Draw up an act of loss of the Z-report (it must be signed by the shift cashier, the senior cashier, if there is one, the company’s accountant and a representative of the administration).
- Oblige the cashier to provide an explanatory note, which will highlight the time and circumstances of the loss of the report, as well as the reasons why the required information was not entered in the cash register.
- Achieve receipt of a fiscal receipt according to EKLZ data, confirming revenue for a shift with a lost Z-report. To do this, you will have to call a technician from the KKM service center.
- The fiscal report taken for the required period should be drawn up in the cashier's journal instead of the lost Z-report.
IMPORTANT! The manager has the right to impose punishment on the cashier guilty of losing a strict reporting document, if he deems it necessary based on the results of his explanatory note. There is no dismissal for such an offense, but a reprimand or verbal warning is quite likely.
At the end of the shift, they didn’t remove the cap, but performed this action at the beginning of the next day? This often happens, however, this is a violation that, once caught, the tax authorities will not skimp on fines. The reason will be that, according to the documents, the proceeds will be untimely capitalized.
You should not rely on the fact that the tax office will not compare the dates of reports and the posting of money to the cash desk. It may well happen that a violation “comes to light” as a result of servicing representatives of a legal entity. Having received a check for a product or service stamped on a certain date, he can submit it to the accounting department of his organization for a report on the finances spent. A counter-check is quite possible, as a result of which it will become clear that the money received according to the presented check was capitalized not on the day of receipt, but later.
There is a special situation with entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system, who are required to show revenue in KUDIR on the exact date when it ended up in the cash register. If a check for a purchase or service is issued today, and the Z-report on it is going to be taken out only tomorrow, then in KUDIR there will be a discrepancy: you will have to indicate today’s check against a “z” that has not yet been taken out, according to which the checks will already be from yesterday.
NOTE! Isolated cases of untimely withdrawal of a canceled report can go unpunished: after all, they can also be caused by technical problems, this can be reflected in the explanatory note. It is important not to allow such cases to become a regular practice.
Z-report (or report with cancellation) - this is the name of the final report for previously used cash registers equipped with an EKLZ (electronic control tape). It is intended:
- to reset sales data for a shift;
- summarizing revenue per shift;
- recording data on sales results in fiscal memory;
- reflection of refunds and discounts, cancellation of checks;
- substantiation of information entered into the cashier's reporting on the cash register for posting to the operating cash desk (certificate report and journal of the cashier-operator).
A Z-report at old-style cash registers had to be generated at least every 24 hours (otherwise the cash register operation would be blocked) and had to be printed out.
Read about what unified forms can be used to generate cash reporting in the following materials:
- “Cashier-operator’s journal - sample filling (2020)”;
- “Unified form No. KM-6 - form and sample.”
The Z-report is a report from cash desks equipped with ECLZ that are almost a thing of the past. The online cash register provides an analogue of this report - on the closure of a shift, the set of tasks for which has been adjusted in accordance with changes in the technical characteristics of cash registers. One of the important new functions of the shift closure report is its prompt sending to the controlling Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service.
Sources:
- Law “On the use of cash register equipment when making payments in the Russian Federation” dated May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ
- Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 21, 2017 No. ММВ-7-20/
Are there penalties for failure to comply with storage deadlines?
Tax and administrative liability is provided for violation of the safety of primary operating documentation. Legislative regulations stipulate how long cash documents of LLCs, non-profit organizations and budgetary institutions should be kept. The shelf life is 5 years. If the company violates the statutory period, it will have to pay:
- from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles per official - for the first violation (Part 1 of Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles per official or disqualification for a period of 1 to 2 years - for a repeated violation (Part 2 of Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
For violation of the rules for storing and compiling archival documents, the fine is (Article 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- from 1000 to 3000 rubles - for individuals;
- from 3000 to 5000 rubles - for officials;
- from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles - for organizations.
Tax liability is also provided. For a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income and expenses, the company will pay from 10,000 to 30,000 rubles (clauses 1, 2 of Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The instructions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U separately explain how long to keep cash documents of individual entrepreneurs - for 5 years, but only if entrepreneurs decide to keep cash documentation (clauses 4.1, 4.6 of instructions No. 3210-U). An individual entrepreneur has the right not to keep accounting records, not to draw up a cash book and receipt and expense documentation.