Free legal consultation by phone:
8
In some cases, it is necessary for employees to work more than the time specified in the employment contract. An employee cannot be forced to perform more duties than required. However, if there is consent on his part, this option is possible. Any overtime and overtime must be paid. If this condition is not met, then the employee will be able to defend his rights in the labor inspectorate.
Save money on “workaholics”: paying “underovertime”
Perhaps the main changes were made to Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - “Payment for overtime work.” It clarifies that when calculating overtime hours, work on holidays and weekends performed in excess of the standard working hours, which was paid at an increased rate, should not be taken into account. The developers emphasize that it is already paid in a larger amount.
note
For an employee who works part-time, an irregular working day can be established only if the agreement of the parties to the employment contract establishes a part-time working week, but with a full working day or shift.
Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation – “Payment for work on weekends and non-working holidays” – also included an addition: increased payment for work on weekends and holidays should be made to all employees only for hours actually worked.;
This rule will also apply if part of the work shift falls on a holiday.
In other words, if only part of the working day (shift) falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, then the actual time worked on the weekend or non-working holiday will be paid at an increased rate. Currently, overtime work is paid for the first two hours of work at least one and a half times the rate, and for subsequent hours at least twice the rate.
The project developers in this case were guided by the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated November 30, 2005 No. GKPI05-1341, according to which, when calculating overtime hours, work on weekends and non-working holidays performed in excess of working hours should not be taken into account, since it has already been paid in double amount .
Payment for overtime hours with summarized recording of working hours
During work, it is possible that an employee will have to perform work beyond the established period of working hours. For this purpose, labor legislation provides for a corresponding concept - overtime work. Normal working hours are determined by shift. If the enterprise has summarized accounting, then the normal number of working hours is taken as a basis.
With summarized accounting, longer accounting periods are taken compared to the general procedure. For summarized accounting, processing is best illustrated using a specific example. If the accounting period was equal to one month, then let’s assume that the normal amount of time for an employee was 176 hours.
Let’s imagine that during this period the employee was at the workplace for only 180 hours. With a salary of 100 thousand rubles. per hour a person receives: 100 thousand / 176 = 568 rubles. With summary accounting, one and a half sizes for the first 2 hours and double for the rest of the time remain relevant. Since the overtime was 4 hours, for the first two hours the employee will be entitled to: 1,704 rubles (1.5 * 2 * 568), and for the remaining two – 2,272 rubles (2 * 2 * 568). As a result, the employee will receive 100 thousand + 1704 + 2272 = 103,976 rubles.
Read further: Calculation of vacation pay upon dismissal: online calculator.
How is overtime pay calculated?
Under a normal schedule, an employer cannot force an employee to be at work more than 40 hours in a week. If it turns out that, due to the needs of the employer, the citizen spent more time than established, then we are talking about overtime.
According to the general rules, for the first 2 hours the employee is charged 1.5 times more than usual, and for all subsequent hours - 2 times more. If a person is at work on a holiday, then he must be paid twice as much for the entire period spent at work. Other increasing factors are not applied.
Particular attention should be paid to the case when processing occurred at night. When processing overnight, a person should receive at least 20 percent more than usual.
Read further: Curfew in the Chelyabinsk region.
Calculation of overtime pay for hourly wages
This calculation is simpler, because there is no need to calculate the average hourly payment. Here, the tariff rate is initially established, in accordance with which the calculation is carried out.
Therefore, if, according to an employment contract, a person receives 200 rubles/hour, then it is obvious that for the initial 2 hours of overtime he will be entitled to pay 300 rubles (1.5 x 200), and for the entire subsequent period - 400 rubles/hour (2x200). The calculation was made in accordance with the minimum values specified in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Employers have the right to negotiate higher amounts with employees.
Read further: Examples of payments when moving from maternity leave to maternity leave.
Don’t make a cult out of food: who will be left without lunch?
In accordance with the amendments, employers will be able to stipulate in internal regulations or in employment contracts with employees the possibility of working without breaks for rest and food. It will be possible not to provide lunch breaks to those employees for whom the established duration of daily work or shift does not exceed four hours.
Currently, in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a break for rest and food should last no less than 30 minutes and no more than two hours. Its duration is not included in working hours and work without a break is not provided for by law. So all employment contracts must have a corresponding clause, regardless of the working hours, length of the working day or shift. After the amendments are adopted, employers will be able not to include this break in the employment agreement, and in some cases, save on unnecessary lunch breaks. Corresponding changes have been made to Part 1 of Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
What to do if overtime hours are not paid?
Anything worked overtime must be paid accordingly. If a person is forced to work overtime without pay, then this is a direct violation of the Labor Code on the part of the employer.
In this case, the employee has two options:
- contact the Labor Inspectorate;
- write statements of claim to the court.
The second step is more radical, which is why they often resort to the help of the labor inspectorate. The main profile of this body is resolving labor-related disputes. The option with an inspection is also more convenient due to the fact that its employees respond faster to requests, and there are not as many requirements as the courts.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself with: The procedure for medical examination for intoxication.
Incomplete and irregular - time and day
Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on part-time work is set out in a new edition. The concept of “part-time working day (shift) or part-time working week” is replaced by “part-time working time (part-time working day (shift) and (or) part-time working week, including with the division of the working day into parts).” It is indicated that part-time working time can be established either without a time limit or for any period agreed upon by the parties to the employment contract.
note
In general, these changes are quite logical and will undoubtedly appeal to many employers, as they will reduce unreasonable labor costs. At the same time, the Minister of Labor of the Russian Federation Maxim Topilin is convinced that the proposed changes will also be beneficial for workers and will not worsen their situation in the least. For example, he noted that increased wages for the time actually worked for those citizens who work shifts will be even more profitable than now.
The second sentence of the first part of the above article (about the employer’s obligation to establish part-time working hours for certain categories of employees at their request) “moved” to a separate second part. The norm is supplemented by the thesis that in this case, part-time working time is established for a period convenient for the employee, but no more than for the period of existence of the circumstances that were the basis for the mandatory establishment of part-time working time. And the regime of working time and rest time, including the duration of daily work (shift), the start and end time of work, the time of breaks in work, is established in accordance with the wishes of the employee, taking into account the production (work) conditions of the given employer.
Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which now defines the concept of “irregular working day”, is supplemented by the clause that an employee working on a part-time basis can have an irregular working day only if the agreement of the parties to the employment contract establishes a part-time working week, but with full time (shift).
What is overtime
Overtime is considered to be work in excess of the established working day (Article 62 of the Labor Code). Overtime work under the hourly wage system is paid at double the hourly rate.
Under the piecework wage system, for overtime work, an additional payment is paid in the amount of 100% of the tariff rate of an employee of appropriate qualifications, whose labor is paid on an hourly basis, for all overtime hours worked.
At enterprises where, due to production (labor) conditions, the daily or weekly working hours established for a given category of workers cannot be observed, it is permitted to introduce summarized recording of working hours so that the duration of working hours during the accounting period does not exceed the normal number of working hours. In the case of cumulative accounting of working hours, all hours worked in excess of the established working hours in the accounting period are paid as overtime. Compensation for overtime work by providing time off is not permitted.
My address is the Soviet Union
To complete the picture, we will provide a list of “legal addresses” of the norms that have migrated to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, since soon mention of them, apparently, will remain only in the memoirs of old honored personnel workers, knights of signature, seal and blank form. So, the following was transferred to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
— the norm of part 1 of paragraph 8 of the resolution of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Secretariat of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated April 29, 1980 No. 111/8-51 “On approval of the Regulations on the procedure and conditions for the employment of women who have children and work part-time”;
— the provisions of paragraph 4 of the resolution of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated 08.08.1966 No. 465/P-21 “On approval of clarification No. 13/p-21 “On compensation for work on holidays””;
— the provisions of part 2 of paragraph 2 of Explanation No. 13/p-21 “On compensation for work on holidays”, approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated 08.08.1966 No. 465/P-21.
Payment for processing according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The Labor Code, or more precisely in its 152nd article, defines the rules for calculation in cases where an employee, for certain reasons, has worked more than the norm. For the first two hours of performing duties after the end of working hours, a person will receive at least one and a half times more.
All subsequent hours are paid even more - at least twice as much as the regular salary. The exact numbers are specified either in the labor agreement or in the collective agreement.
This article allows employees to replace monetary compensation with additional rest. Moreover, the duration of this rest should be no less than the time that was worked in excess of the norm.
Recommended reading: Vacation before the wedding according to the RF IC.
How to register for processing
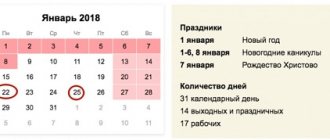
Working time standards are approved by the Labor Code in Art. 91. The normal length of working time is 40 hours per week (in some cases - 36 hours). Payment for overtime work according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2021 is made within 120 hours per year. Exceeding this figure is considered an offence. Over a two-day interval, processing cannot exceed 4 hours. For part-time workers, overtime is calculated daily.
To attract an employee to work after the end of the shift, the company management must obtain the written consent of the employee. Overtime work is paid based on the order. Consent and instructions are drawn up in any form. It is prohibited to employ workers who are under 18 years of age to work beyond the normal length of time. The ban also applies to pregnant women.