“Paper” VAT scheme
At the end of the quarter, the accountant makes a preliminary VAT calculation and informs the manager of the amount.
He understands that there is not enough money to pay the tax. The company is looking for a “friendly” supplier who, for a certain bonus, is ready to draw up documents for the supply of some goods or services. The supplier issues a fictitious “paper” invoice, it is included in the Purchase Book, the VAT payable is adjusted, and a declaration is submitted.
The most interesting thing begins just after filing such a VAT return. And most often the tax is assessed additionally and fines are imposed. And for concealing taxes in excess of 5 million rubles, the manager faces criminal liability.
Substitution of taxation systems
One of the daily functions of an accountant is to check the counterparty for the applicable tax system. In the case under consideration, I will describe a situation where a legal entity on the general taxation system unknowingly accepted for deduction invoices from a counterparty using the simplified taxation system .
Theory.
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are, as a general rule, not recognized as VAT payers (except for situations expressly defined by tax legislation). In other words, when selling goods, works, services, property rights, “simplified” people do not have the obligation to issue invoices, maintain a purchase book and a sales book. But the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain a direct ban on issuing invoices to “special regime officers”.
In paragraph 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that only VAT payers are required to prepare invoices. In practice, there are often situations where these persons, without receiving any benefit, issue invoices to buyers at their request.
For reference:
The “simplified” cannot take into account the amount of VAT paid in the tax base:
nor as part of expenses (if the single tax is calculated from the difference between income and expenses), since according to paragraphs. 22 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the amounts of VAT paid to the budget on the basis of clause 5 of Art. 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are not subject to inclusion in expenses;
neither as part of income , since according to paragraph 1 of Art. 248, paragraph 1, art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining income, the amounts of taxes that are presented to the buyer are excluded from them.
At the same time, tax legislation does not formally prohibit a “simplified” person from issuing an invoice with the VAT amount highlighted on a separate line and presenting it to the buyer. This means that persons who are not payers of this tax, due to certain circumstances, have the right to independently decide whether to impose an indirect tax on the buyer of goods (works, services) for payment or not. But for such an “expression of will” you will have to pay value added tax to the budget.
Thus, the issuance of a “simplified” invoice with an allocated tax by virtue of clause 5 of Art. 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation entails the obligation to pay tax to the budget based on the results of the tax period, based on the corresponding sale of goods (work, services) for the expired tax period, no later than the 25th day of the month following this period (clause 4 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). In case of non-payment of the VAT shown in the invoice, this will have to be done based on the results of a desk tax audit, with the corresponding penalties and fines. In this case, the “simplified people” will hardly be able to challenge the fiscal sanctions.
Note!
The emergence of an obligation for a “simplified” person to transfer VAT to the budget does not mean acquiring the status of a VAT payer, therefore he does not have the right to apply tax deductions. Clause 1 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that this right applies exclusively to VAT payers (and not to persons who paid the tax on their own initiative).
Practice.
In my work, I came across a situation where the tax inspectorate carried out a desk tax audit of the VAT return with additional charges for a counterparty who turned out to be “simplified.” After all, some “schemists” of paper VAT do not even know the basics of tax accounting; in their work they use any organizations that fall into their hands.
The story was as follows.
The older company was on a simplified taxation system for the entire period of its existence. She did not work for a long time and submitted zero tax and accounting reports. The owners of the enterprise decided on alternative liquidation and sold their share in the authorized capital of the organization to a new participant. In the future, he became the general director, although he turned out to be a nominal one. The “schemists”, without checking the taxation system, considered that it was general (traditional) and included this organization in the paper VAT reporting.
Several operating organizations (as it later turned out, beneficiaries) included transactions with this problematic counterparty as deductions for value added tax.
The result of this work was:
- denial of VAT deductions and subsequent identification of non-payment of value added tax to the budget by an organization that applies a simplified taxation system (despite a significant number of counterparties in the chain and declared VAT deductions). At the same time, revenue did not exceed 100 million rubles;
- denial of VAT deductions and additional tax assessment to be paid to the “beneficiary” counterparty in the context of transactions with the “simplified” counterparty.
What is this, illiteracy of “schemists” or inexperience of an accountant - business owners will have to figure it out. I'll add. This error was identified in the declaration for the first quarter of 2021.
Checking VAT chains at the tax office
The tax office checks the continuity of VAT chains using the ASK VAT-2 software package. Compares purchase and sale transactions from supplier and buyer declarations, their deductions and sees exactly where the tax gap occurs. The program also sets the size of the gap and determines which company to start audits with and uncover possible tax violations.
Schemes for bypassing the VAT-2 ASK, which are used by fraudsters (for example, lengthening the chains of “paper” VAT), in any case cannot hide the VAT gap, but often provide a delay in its detection.
What could innovation be like for business?
According to law enforcement officers, the most common tax crime today is illegal reimbursement of value added tax from the budget. Any given crime is classified as the creation of artificial document flow for the purpose of inflating profit expenses and inflating deductions for value added tax. Isn’t this what the concept of “paper” VAT includes for entrepreneurs today?
The main tax article in the Criminal Code for legal entities is 199 “Tax evasion.” As soon as entrepreneurs receive at least one budget ruble, they become defendants in a more serious article - 159 “Fraud”. (The article is relevant for cases with illegal VAT refunds).
Practice today. Law enforcement officers continue to actively identify and suppress criminal activities in the field of taxes. This is especially true for persons providing formal document management services (including sellers of “paper” VAT). These are the so-called “VAT optimization platforms”. Criminal cases are being initiated against these persons under Art. 173.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (Illegal formation (creation, reorganization) of a legal entity), Art. 173.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation (Illegal use of documents for the formation (creation, reorganization) of a legal entity). In addition, the police are establishing a circle of alleged “beneficiaries” who, in order to minimize tax liabilities, took advantage of unjustified VAT tax deductions. The intended “beneficiaries” face punishment under Art. 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Tax evasion.”
Development of events: conversation at the tax office
If the company's supplier, who provided a “paper” invoice, does not submit a VAT return, or the tax office rejects his return, or easily identifies a VAT gap, then the purchasing organization is required to submit an update on unconfirmed tax amounts.
Regardless of whether the company submits the clarification with supporting documents or not, the directors may be summoned for questioning by the tax office. Most likely, here he will be told that his counterparty is a suspicious and unreliable organization and it is better to voluntarily refuse “paper” invoices and pay additional VAT. Otherwise, a trial is possible, and along with it fines and penalties.
Such arguments do not always work on the director: he believes that the tax office only has a program for coloring organizations in the colors of traffic lights and the subjective opinion of the inspector, based on the instructions of the Federal Tax Service. And the director has well-executed documents, contracts, invoices, acts, payment slips and invoices.
Invoice with VAT confirmation!
Privacy Policy
The administration of the site (hereinafter referred to as the Site) respects the rights of Site visitors.
We unreservedly recognize the importance of confidentiality of personal information of Site visitors. This page contains information about what information we receive and collect when you use the Site. We hope this information will help you make informed decisions about the personal information you provide to us. This Privacy Policy applies only to the Site and information collected by and through this site. It does not apply to any other sites and does not apply to third party websites that may link to this Site. Information We Receive
The information we receive on the Site can only be used to facilitate your use of the Site.
The Site collects only personal information that you provide voluntarily when visiting or registering on the Site. The term “personal information” includes information that identifies you as a specific person, such as your name or email address or telephone number. Sharing of information The Site Administration under no circumstances sells or transfers for use your personal information to any third parties. We also do not disclose the personal information you provide, except in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation. Disclaimer
Remember, the transmission of personal information when visiting third-party sites, including the sites of partner companies, even if the website contains a link to the Site or the Site has a link to these websites, is not covered by this document. The Site Administration is not responsible for the actions of other websites. The process of collecting and transmitting personal information when visiting these sites is regulated by the document “Protection of Personal Information” or similar, located on the websites of these companies.
Article on VAT reduction
Entrepreneurs know how important it is to fill out an invoice correctly, because it not only confirms the shipment of goods or the provision of certain services, but also plays a strategic role in the process of calculating VAT payments. In this article we will talk about the features of the document and answer the burning question for many: is it possible to reduce VAT? If so, what role does the invoice play in this?
Who will need a VAT invoice? People who are faced with incorrectly filling out a document, have lost paper, and also those who want to reduce VAT tend to buy an invoice with confirmation from the tax office. Note that the invoice is a kind of sales receipt for large enterprises; it has a standard form defined in Russia and a mandatory list of information entered - for example, the cost of work performed, transferred property rights, units of measurement, digital information about the manufacturer, currency calculation.
But how to reduce VAT based on an invoice? The fact is that when paying for the transaction, the seller is charged value added tax (VAT). It is the invoice in this case that will act as a confirmatory check; it is registered by the buyer in a special book.
Attention! VAT deduction on the invoice occurs after entering the indicators into the VAT return - every citizen has this right by default, the main requirements are the correct filling out of the document and the correct execution of other papers.
If you are looking for information on how to reduce VAT without breaking the law, consider that you have come to the right place. It is in the invoice that you can indicate expenses that reduce VAT. Another way is to indicate an amount less than what was actually paid to the seller. This way we will reduce VAT payable while maintaining business relationships with customers. It is possible to reduce VAT for 1 transaction by correcting just a few documents.
Restoring VAT (the invoice has already been filled out) is another operation that can result in losses.
It consists of paying the tax previously accepted for deduction. If such a situation occurs, we recommend that you contact specialist economists who will help you at least so that such troubles do not occur in the future activities of the company.
VAT is highlighted on the receipt, but there is no invoice: what to do? An invoice is not always 100% proof that a certain product was shipped or services provided.
In some cases confirmation is required. Suppose we are interested in reducing VAT, then we should additionally provide a delivery note or a work acceptance certificate. We would like to note that our company does not confirm invoices, but we know reliable partners that you can contact.
We understand how important it is sometimes to find a company with which cooperation will be comfortable. In order not to waste your time searching, you can come to us and get the coordinates of companies with an excellent reputation. VAT refund on invoices, production of confirmation documents, consultations, correct filling of invoices and other services in the shortest possible time - this is what our time-tested partners offer.
Conclusions The tax issue has always been acute for domestic entrepreneurs. There are many ways to reduce the burden of paying the state, everyone knows that salaries reduce VAT, as well as how the amount of payments is affected by specific invoices for certain transactions. If you are also interested in legal ways to reduce VAT, be sure to contact us for advice. We will tell you how you can save money and who to contact.
Development of events: desk audit and trial
If, during a desk audit, the inspectorate sees unreliable counterparties in the purchase book, it may refuse to accept VAT amounts on them for deduction. And also impose a fine and penalties. The justification for this step is the tax office’s conclusion that the company generated fictitious documents to obtain an unjustified tax benefit.
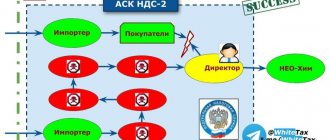
Courts readily consider the data provided by the tax inspectorate software package ASK NDS-2, especially if this data is supported by other evidence about the fictitiousness of the transaction with a dubious counterparty. And banking control helps clarify the situation.
The tax office can initiate an in-depth audit and request from the company not only acts, invoices and contracts, but also transport documents, as well as any other evidence that confirms the purchase of goods or services and their delivery to the company’s warehouse. If the required quantity of goods is not found in the warehouse, or shortage reports are not seen, then this will work against the company claiming the deduction.
The director of a dubious supplier usually does not come to the tax office for questioning. Inspectors can also check the financial flows of an unreliable counterparty and see the receipt of certain amounts from the accounts of the defendant company, which then went to the accounts of individuals. If the number of employees of a dubious company is zero, the court will side with the tax authorities.
The tax office's approach to desk audits and the Federal Tax Service's tools are being technically improved. Therefore, simple schemes such as “paper” VAT are being disclosed more and more often, and the tax office is increasing VAT collection. Taxpayers lose in court, even if all the documents requested are completed correctly. An example is the resolution of the AAS dated February 27, 2018 No. 11AP-618/2018 from Kazan.
“Paper” VAT prospects and consequences
Businesses are interested in easy and simple ways of tax optimization. For a long time, the scheme with fly-by-night companies was used to this, which solved four pressing problems at once: 1. reducing VAT; 2. reduction of income tax; 3. “optimization” of salary taxes; 4. receipt by the business owner of cash that could be freely disposed of.
RMS ASK VAT-2 has changed the situation since 2015: automatic control of VAT declarations, invoices, sales books and purchase books made it possible to identify gaps in VAT payments, and judicial practice on schemes using “one-day scams” made it possible for tax authorities to increase the level of tax winnings disputes up to 84%. The number of on-site tax audits has decreased: from 29,393 in 2015 to 7,398 at the end of 7 months of 2021. At the same time, the average amount of additional charges increased from 9.1 to 21.9 million rubles.
A significant reduction in the use of schemes with shell companies has led to an unexpected consequence. According to the head of the legal department of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation Oleg Ovcharov: tax authorities won 66.3% of tax disputes in the first half of 2021 (previously - 84%). The number of legal disputes itself has also decreased - by 6.4% compared to 2021 (to just over 7,300). And no, the point is not that Federal Tax Service lawyers have become worse at their work or that the courts have begun to support business: most taxpayers submit “clarifications” on disputed counterparties voluntarily after a “cordial” conversation with the tax office. Litigation regarding business fragmentation, the use of agency, tolling schemes, simple partnerships, etc. much more complicated, which causes a drop in the percentage of tax authorities winning in the courts.
Judicial practice on the application of Article 54.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has not yet been formed (valid for inspections from August 19, 2021), and the first court decisions that appear are ambiguous. For example, the AS of the Kaluga Region in case No. A23-8752/2017 indicated that the provisions of clause 2 of Article 54.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not provide for negative consequences for taxpayers for unlawful actions of counterparties of the second, third and subsequent links, and tax claims are possible only if proven by the tax authorities body of the fact that the transaction (operation) was unrealistic to be executed by the taxpayer’s counterparty and the taxpayer’s failure to comply with the conditions established by clause 2 of Article 54.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (the decision has not been appealed).
If judicial practice develops on the basis of the above logic, then schemes with fly-by-night companies in the 3-100 link may appear again. However, we should not forget that the concept of holding the actual beneficiary of the scheme accountable is well established, which means that they will be looking for him, excluding “technical” organizations from the chain.
But as the demand for “optimization” of VAT continues, a new VAT was born. There are two options here: 1. the counterparty simply “draws” the invoices necessary for the customer and enters them into the sales book; 2. the counterparty actually has VAT to deduct. In any case, the transaction is not real, funds are not transferred to the counterparty, but invoices are issued and registered in the book of purchases and sales of the parties to the contract. In the diagram it looks like this:
If the documents are completed correctly and registered, the VAT-2 ASK does not detect the VAT gap (at least in the next quarter), but the customer has a whole bunch of problems that he, having happily submitted the VAT return, does not think about.
The first problem is obvious - the scheme is illegal and contrary to Art. 54.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The second is that if the counterparty “supplies” the goods, then the customer has virtual inventory balances. Third - as Cat Matroskin said: “in order to sell something unnecessary, you must first buy something unnecessary”, the counterparty in 99% never bought what he sold to the customer, which means he did not transport it, did not reflect it in accounting and etc.
If payment is made for a service, then in the vast majority of cases the counterparty cannot provide it (there are no necessary employees, permits, etc.), and even if it potentially can, interrogations of the performers will put everything in its place (the list of questions is directly indicated in the letter from the Federal Tax Service RF dated July 13, 2021 NED-4-2/ [email protected] ). Fourth, the customer develops a debt to the counterparty, who can go to court: formally, the delivery has been made, the primary documents have been drawn up, invoices have been registered, but the delivery has not been paid for. They try to pay off the debt in two ways: either with a bill of exchange or with an assignment, when the debt is assigned to a person controlled by the customer:
This example shows a “greedy” scheme when the counterparty assigns the debt to the customer’s founder. In this case, a cover-up scheme is created: the counterparty writes a claim to the customer, the latter does not have money in his account to repay the debt, the founder comes to the rescue, buying out the debt of his organization, after which the customer transfers the debt to the founder, who cashes the money.
The obvious weakness of this solution is the lack of confirmation of payment by the founder of the assignment agreement, because the counterparty does not receive money in cash (otherwise the scheme is further complicated by the need for the counterparty to cash out funds for the customer, and with a circular scheme of returning money from the counterparty to the customer through technical organizations, adverse tax consequences arise) . If the assignment is paid by the founder in cash, then the counterparty must apply the cash register (Article 1.1 54-FZ, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 18, 2021 N ED-4-20 / [email protected] ).
Fifth - if the debt to the counterparty is ongoing - this is the first sign of an unusual transaction for tax authorities and the police, who, according to the data indicated on the website of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, did not detect fewer tax crimes.
Sixth, the counterparty must “remember” to register the invoice in the sales book; to minimize this risk, customers play it safe and do not pay the VAT itself until a desk audit of the declaration has taken place. In this case, the counterparty can submit an updated declaration later, excluding from it “supply” to the customer (in fairness, it should be noted that such a risk potentially exists in relationships with real counterparties). At the same time, we should not forget that the VAT return can be canceled if the counterparty has signs of being ephemeral (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 10, 2018 N ED-4-15/13247).
The courts do not agree with this approach, pointing out that “based on the analysis of the norms of the current tax legislation, circumstances such as the fact that the LLC has the characteristics of a “transit” organization, does not actually conduct financial and economic activities, is not located at its legal address, etc. d. (as indicated by the tax authority) do not entail a refusal to accept tax reporting” (Decision of the Tomsk Region AS dated January 31, 2018 in case No. A67-9224/2017), but not every counterparty will be ready to sue the tax office.
Business owners ask us: “One-day transactions” are not allowed, “paper” VAT is not allowed, but what is possible, how to live?” This question itself implies a simple answer about the “secret” way to optimize taxes, simple and understandable. But there is no such way, safe tax optimization now is a set of many schemes and combinations that allow you to legally reduce the tax burden and defend your position, if not during an on-site tax audit, then at least in court and be among the 33.7% of taxpayers, winning tax disputes. And above all, the business owner himself must be ready to delve into not only the basics of sales, marketing and production, but also tax optimization, without replacing his accountant and without becoming a tax expert, but understanding the basic methods, their correspondence to real business processes and the consequences of his decisions .
Source: https://www.buhgalteria.ru/article/n167886
Signs of a justified tax benefit
There are formal requirements for recognizing the legality of a tax deduction; they are listed in Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The business transaction that entitles the company to the deduction must be real. The buyer must have documents that demonstrate this reality: an agreement with a transport company, the purchase of containers, etc. Also get ready to demonstrate the warehouses. The tax office is not always ready to believe only documents.
Another requirement is due diligence when choosing a counterparty. Proof of such diligence is provided not only by the standard list of documents, but also by the company’s motives when choosing a supplier, and also by the circumstances under which the contract was concluded and executed. If you can explain and comment on all of this in a consistent manner, it will demonstrate your due diligence.
To work with VAT carefully and apply all legal deductions, we recommend the Kontur.Accounting web service. The system calculates preliminary VAT, gives recommendations on how to reduce the amount, suggests which documents are missing in accounting and what errors need to be corrected. Accounting provides simple accounting, payroll, reporting and other tools for accountants and business managers. The first 14 days of the service are free.
Working with an organization where the general director is disqualified
Theory.
Disqualification is a type of administrative punishment.
Disqualification consists of depriving an individual of the right to occupy leadership positions in the executive management body of a legal entity, to join the board of directors (supervisory board), to carry out entrepreneurial activities to manage a legal entity, as well as to manage a legal entity in other cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
For a more detailed study, I recommend reading the article on the disqualification of a director.
Practice.
In my work, I encountered a situation where the tax inspectorate carried out a desk tax audit of a VAT return with additional charges for a counterparty whose sole executive body was disqualified by a court decision. In this case, the “schemists” of the paper VAT did not properly assess the activities of the sole executive body of the organization (general director) in earlier periods.
The future disqualified person was the owner and director of two organizations created in different periods of time. As it turned out over time, it was nominal. In this context, I will mention the data and LLC “Tulip”.
According to the previously created), the court made a decision to disqualify the head of the LLC for a period of 6 months. The question arises. Can a disqualified manager hold leadership positions in other LLCs? (In this case, Romashka LLC). The answer is simple. The disqualification of a director automatically applies to all legal entities under his leadership.
“Schematozniki”, in turn, included Romashka LLC in the paper VAT reporting. The result of this work was the denial of VAT deductions for transactions with a company where the director was disqualified.
This error was identified in the declaration for the fourth quarter of 2019.
You can check your counterparty for director disqualification on the official website of the tax service. But even here there are pitfalls. Information about the disqualification of a director may appear with a significant delay. Here I would like to note that disqualification can be different. This is both a full disqualification with a ban on holding a leadership position by a court decision, and disqualification for registration actions. (Both existing organizations and newly created ones).