. The document contains information about the seller and buyer
.
How many copies need to be issued? The delivery note must be written out in two copies:
- one copy must remain with the company supplying the goods, since this is the primary accounting document for writing off the goods;
- the second must be with the organization purchasing the products, and is the right to use inventory items.
The paper version requires 5 signatures
:
- three from the supplier side;
- one on the recipient's side;
- another one is placed by the person responsible for the cargo, in the line “The cargo was received by the consignee.”
You can learn how to correctly fill out a consignment note, as well as study the form and a sample of the TORG-12 form at.
Requirements for the electronic version
Generating an electronic version is similar to a paper version
, the only difference is that the electronic TN is created in one copy. It consists of two files: the first file is compiled by the seller, the second - on the buyer’s side, when sending the document.
An electronic signature is used to sign the electronic version. There should be only two signatures on the invoice - one on each side.
Thus, the paper version of the TN does not require an electronic signature; it can be compiled and transmitted without the use of a computer or the Internet.
An electronic version of the TN can be drawn up in cases where both parties have access to the Internet and everyone has an electronic signature.
Who should apply?
This document is prepared by the shipper. How to receive goods? The goods are received by an employee of the purchasing organization
. He must put a stamp and signature on the TN, or provide a power of attorney and sign (read about who should sign the columns “received the cargo”, “received the cargo” and others).
But before putting his signature, the employee must check the inventory items for compliance with the data specified in the invoice, as well as the characteristics of quantity and quality.
If upon acceptance it is discovered that the characteristics of the goods do not correspond to the data in the document, then first of all this is documented - a report is drawn up. After the report is drawn up, a claim is drawn up and sent to the supplier along with a copy of the report.
This procedure must be completed within the time period established by the contract.
(if there is no deadline, then just as quickly as possible).
The buyer may claim in a claim that:
- refuses the product and demands a refund (if payment has been made);
- demands to transfer the missing goods (in case of shortage);
- agrees to a smaller quantity of products and requires a refund of part of the money if payment has been made.
Write-off algorithm
All the nuances of write-off are described in detail in the Methodological Instructions, which were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 49 of June 13, 1995. They note that the rules for writing off non-financial assets are determined by the owner of this property. If this owner is an organization, then in most cases this process occurs as follows:
- An inventory is being taken. As a result, a list of property is identified that is not used, has fallen into disrepair, or for some other reason needs to be written off. They must relate to the company's fixed assets.
- An inventory list is compiled, which includes this list with inventory numbers of non-financial assets.
- A separate commission is being convened on the issue of writing off non-financial assets.
- An act on the write-off of non-financial assets is drawn up, and a package of documents is compiled for reporting to higher organizations.
Accounting
The rules for recording this document are not established by law, therefore the organization has the right to approve the rules for transportation and storage of invoices independently.
In most cases, a commodity report is generated at the warehouse, which is a document on the basis of which the report reflects data on the sale of objects and their cost.
Invoices are attached to the report
. They are arranged in chronological order. When accounting for objects, records are kept in a journal or computer database, reflecting changes in the condition of the products that are taken into account. These entries are called entries.
Postings for receiving goods
:
- Dt 41 Kt 60 – receipt of products.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – reflection of incoming VAT.
- Dt 68-VAT Kt 19 – VAT accepted for crediting.
- Dt 44-TZR Kt 60 – cost of services of third-party companies.
- Dt 60 Kt 51 – transfer of prepayment.
- Dt 41 Kt 42 - reflection of the value of the trade margin.
- Dt 15 Kt 60 – a reflection of the actual cost of materials.
Postings for shipment of goods
:
- In case payment is made later.
- Dt 90.02 Kt 43, 41 – shipment of finished delivered objects.
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01 – reflection of revenue including VAT.
- Dt 90.03 Kt 68.2 – the amount of VAT.
- Dt 51 Kt 62.01 - reflection of the repayment of debt for shipment.
- If prepayment has been made
- Dt 51 Kt 62.02 – crediting of prepayment.
- Dt 76.AV Kt 68.02 – VAT calculation.
- Dt 90.2 Kt 43.41 – shipment of products.
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.1 – revenue including VAT.
- Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 – crediting the advance to the shipment account.
- Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AB – the amount of VAT is credited from the prepayment that was made earlier.
Postings for sales of products (wholesale)
:
- Dt 51 Kt 62.02 – payment is credited.
- Dt 76.AV Kt 68.02 – preparation of an invoice for advance payment.
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 – accounting for revenue from the sale of products.
- Dt 90.03 Kt 68.02 – VAT calculation.
- Dt 90.02.1 Kt 41.01 – write-off of sold units.
- Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 – crediting the advance.
- Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AV – deduction of advance VAT.
Postings for the supply of products
:
- Dt 90.2 Kt 41 – reflection of disposal of goods.
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.1 – reflection of revenue on the sale price of objects including VAT.
- Dt 90.3 Kt 68.2 – reflection of the amount of VAT.
Read about the important rules for filling out TORG-12 with and without VAT, and from there you will learn how to correctly fill out a delivery note for an individual entrepreneur.
What should I do if the buyer does not return the signed TN?
After the document is stamped and signed, the buyer must return the technical specification to the supplier. This is done in order to record receipt of the goods by the customer.
If the buyer does not return the invoice, the supplier has every right through the court to demand the execution of a product acceptance certificate from the recipient.
To do this, it is necessary to competently approach the evidence of the fact of delivery of the goods to the buyer. It is better to engage a lawyer to file a claim for return to court
. To file a claim yourself, you need to adhere to the rules established by law.
The statement of claim is submitted exclusively in the form of a written document. The claim must indicate:
- Name of the court where the application is being filed.
- Full official name of the plaintiff.
- Full official name of the defendant.
- What are the violations of rights? Plaintiff's claims.
- Cost of claim.
- Circumstances on the basis of which claims are made.
- Proof.
- Documents attached to the application.
- The date the document was compiled.
Inventory list of fixed assets
One of the documents drawn up based on the results of the inventory is a document in the INV-1 form - inventory list of fixed assets.
The inventory is drawn up in two copies, one of which remains with the person bearing financial responsibility, and the second is transferred to the accounting department for the formation of a matching statement.
Before conducting an inventory, all employees responsible for the safety of assets write a receipt. It is included in the header part of the form.
The inventory is printed with loose-leaf sheets similar to the second page of the form, the number of which is determined by the head of the organization.
If automated processing of information on accounting for inventory results is carried out, the inventory form is issued to members of the commission with completed columns from the first to the ninth. The responsible employee fills out the tenth column regarding the actual availability of valuables.
If during the inspection, valuables were discovered that were not reflected in the records, responsible employees must enter information about these objects into the inventory. By decision of the inventory commission, they must be capitalized. In such a situation, their initial price is calculated based on market prices.
Inventory records are drawn up separately by asset groups (non-production and production purposes).
For assets that were leased, an inventory is drawn up in triplicate separately for each lessor. The rental period must be specified. One copy is sent to the landlord's address.
Rules for filling out an inventory list
The fixed assets inventory form consists of three pages.
The first page is the title page. It displays the following information:
- Full name of the organization or its structural divisions;
- Reasons for conducting an inventory (based on the relevant order);
- The dates when the inventory will begin and when it will end;
- Name of objects that will be checked;
- Last names, first names, patronymics, as well as positions of responsible employees;
- If the fixed assets are listed as leased, in the “lessor” line it is necessary to enter the name of the organization that owns the objects.
At the end of the sheet, responsible employees put their personal signatures.
The second page is the main one; it contains a table with the following fields to fill out:
- Record number in order;
- The name of the OS object, as well as its main features;
- Number, as well as date of the certificate of acceptance and transfer of the OS for registration;
- Year of manufacture of the object;
- Factory and inventory numbers, passport;
- Actual availability in quantitative terms;
- Price.
Each OS is listed on a separate line.
After all the data is entered, the total cost of the objects is calculated. It is displayed on a separate line.
On page 3, all responsible employees, as well as inspectors, affix their signatures. By this they confirm that all objects have been checked and the information has been entered into the table.
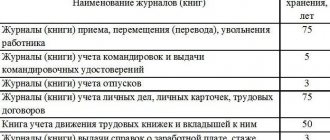
Storage period in the organization
Since the technical document is a primary accounting document, it must be stored for 5 years after the reporting year. Accordingly, this document must be stored in a safe environment.
, where it will be protected from changes:
- access should be allowed only to a certain circle of persons;
- proper environmental parameters must be created and fire protection conditions must be ensured.
Such requirements are imposed by Federal Law.
A document such as a delivery note is used to certify the fact of the transfer of ownership of a particular product from the seller to the buyer. In accordance with the importance of this document, it is subject to strict adherence to the structure during execution and proper storage after the transaction.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
.
Each organization must be guided by Federal Law 125-FZ of October 22, 2004, according to which it is necessary to ensure the correct storage of primary documentation for a specified period. The duration of deadlines for certain groups of documents may be regulated by various federal laws, as well as other legal acts of the Russian Federation, lists and regulations. We will tell you in the article what is the legal storage period for invoices and other documents at an enterprise.
When determining the storage period, you must be guided by the Accounting Law, according to which primary accounting documentation must be stored five years after the year in which it was compiled. Certain laws and regulations may require longer retention periods. If different legal acts establish different time periods for the same document, then you need to focus on the longer one.
Invoice retention period
For paper and electronic invoices, the minimum retention period is 4 years.
This time period is counted from the quarter that follows the period of the last use of the document for tax purposes - for calculating tax and preparing reports. Thus, the following deadlines are relevant for the seller forming the s/f:
- Advance s/f - 4 years from the end of the quarter in which the s/f is registered in the purchase book, and the tax deduction for this s/f is shown in the VAT return;
- Shipping s/f - 4 years from the end of the quarter in which the s/f is registered in the sales book, and the accrued VAT on it is shown in the declaration.
For the buyer receiving the s/f, the following terms apply:
- Advance income tax – 4 years from the end of the quarter in which the income tax is entered into the sales book, and the restoration of the tax accepted for deduction on the advance payment is shown in the declaration;
- Shipping s/f - 4 years from the end of the quarter in which the s/f is registered in the purchase book, and the tax deduction on it is shown in the declaration.
If the buyer did not direct the tax on the listed prepayment for deduction, then the advance tax does not need to be stored.
How expense reports are destroyed
Sooner or later, documents on advances stored at the enterprise for longer than 10 years have to be destroyed. They are sent from the archival department for review by experts. The examination will help select documentation for subsequent destruction that does not violate legal norms in Russia.
The following officials can become members of the expert commission:
- from the category of managers, economists, accountants;
- The presence of a representative of the state archive on the commission is mandatory.
Determining the shelf life of delivery notes and invoices in non-standard situations
If the right to deduction is used later
The right to deduct tax is valid for three years after the end of the period for receiving the invoice. If the company decides to exercise its right later, then the storage periods are shifted, since the four-year storage period of the s/f begins to count from the end of the period in which the refundable VAT is included in the declaration.
For example, if the company received goods in the second quarter. 2021, and VAT on them was deducted in the II quarter. 2021, then the beginning of the storage period for c/f and invoices for tax purposes is shifted by one year.
If the s/f is received later than the goods with the invoice
If goods with an accompanying invoice are received in one period, and an invoice for them is received later in another period, then the shelf life is shifted. Moreover, not only the storage period of the s/f is shifted, but also the invoice used as the basis for confirming the acceptance of values for accounting.
If materials are received according to the invoice, but not paid for
In this case, a debt arises that can be written off after three years due to the expiration of the statute of limitations. The invoice must be stored for 4 years. from the end of the limitation period, a total of 7 years.
If an act of reconciliation with the debt specified in it is drawn up annually with the counterparty, which is signed by both parties, then the three-year limitation period begins to count anew from the moment of signing this act. Accordingly, the storage period for the invoice and invoice confirming this debt is shifted.
If the reconciliation act is signed annually, then the limitation period will constantly shift, and at the same time, the end period for the need to store documents will be postponed every year. In this case, the storage period can increase indefinitely, and storage of the invoice must be ensured by both the buyer and the seller.
An example of determining the shelf life of delivery notes and invoices
In the third quarter 2021 The company received a delivery note and an invoice from the seller. According to the invoice, the company received goods that were delivered to the receipt in the same period. Based on the s/f, the added tax on these values in the same quarter is sent for deduction, and the s/f itself is entered using a registration entry in the purchase book.
Sales of income received in the third quarter. valuables were produced in the next IV quarter, their value in the IV quarter. included in tax expenses.
| Document | Storage period | The number from which the period is calculated | Last day of the storage period |
| Invoice | 01.10.2016 | 30.09.2020 | |
| Consignment note, when used as a basis document for accepting valuables for accounting and confirming the presence of the right to deduct tax | 4g. from the end of the quarter in which the tax was deducted | 01.10.2016 | 30.09.2020 |
| Consignment note, when used as a basis document to confirm the value of the value of valuables for inclusion in tax expenses | 4g. from the end of the year in which this cost is included in tax expenses | 01.01.2017 | 31.12.2020 |
| Consignment note used as a primary document for accounting purposes | 5l. from the end of the year in which the received values are delivered to the parish | 01.01.2017 | 31.12.2021 |
Thus, if the period is unambiguously determined by the invoice, then for the delivery note you need to choose the longest period. In this example, the last day of the storage period for c/f is 09/30/2020, for the invoice – 12/31/2021.
Accounting certificate (form code 0504833)
Accounting certificate ( f. 0504833
) is intended to reflect by the institution transactions carried out in the course of business activities, as well as transactions carried out by the body providing cash services, financial authorities, which do not require documents from payers and accounting entities.
In addition, based on the Accounting Certificate ( f. 0504833
) accounting entries are made related to the correction of errors identified by the accounting entity. In this case, corrections are recorded in the corresponding correspondence on the accounting accounts and reference is made to the number and date of the document being corrected, and (or) the document that is the basis for making corrections.
In order to reflect in accounting the transactions reflected in the Accounting Certificate ( f. 0504833
), the chief accountant of the accounting entity (the head of the structural unit) fills out
the “Note on the acceptance of the Accounting Certificate for accounting”
while simultaneously reflecting the accounting entries in the relevant accounting registers.
In the article, we examined the most frequently used, in our opinion, primary documents in accounting to reflect transactions with non-financial assets of institutions. Almost all of the forms considered have undergone changes. Almost all documents must indicate the type of property to which the object of accounting belongs (real estate, especially valuable movable, other movable). Since transactions with the property of institutions often require their approval by the founder or other bodies, many documents provide fields for putting the appropriate marks. Accounting records about ongoing transactions with property are also made in specially designated places.
O. Lunina
Journal expert
“Institutions of physical culture and sports:
accounting and taxation”
Retention period for work completion certificates
Acts are drawn up in addition to civil contracts, for example, contracts. In accordance with the act, the contractor reports to the customer on the actions performed. That is, the act acts as the primary document on the basis of which work is transferred and accepted.
For primary accounting documentation, a storage period of 5 years is established. Thus, acts of completed work must be kept for five years from the end of the period of validity of the contract or agreement, in addition to which this act is drawn up.
conclusions
An inventory card is the main tool for accounting for fixed assets entering, moving and leaving an organization.
The form is drawn up according to the unified OS-6 form and reflects all the necessary information about the object. If the organization has a small volume of fixed assets, then it is permissible to use a consolidated inventory book.
The responsible accountant is responsible for filling out and maintaining the accounting card. After five years, the document can be destroyed.
Source
The procedure for storing documents at the enterprise
Registers and primary documentation can be stored in both paper and electronic formats. The storage procedure is determined by the Regulations approved by Letter of the Ministry of Finance 105 dated July 29, 1983. First of all, the storage space must meet certain requirements:
- Be inaccessible to a wide range of people;
- Have suitable parameters for the state of the ambient air;
- Have a high degree of safety and fire resistance.
The storage room must be specially prepared. The ideal option would be a fireproof metal safe or cabinet with a secure lock.
A responsible person must be appointed who is charged with ensuring the safety and security of the entrusted archival documentation throughout the entire storage period. After the established deadlines, documents may be destroyed.
At the same time, a commission is assembled to evaluate the documentation regarding the expiration of their storage periods. Papers to be destroyed are transferred under a transfer deed to a specialized company engaged in processing these raw materials. The destruction of documents with an expired storage period is subject to mandatory documentation.
Have the retention periods for invoices changed since October 1, 2017? How to organize the storage of electronic invoices? Is it necessary to keep copies? Where should documents be kept? Let's figure it out.
How to view data about an OS object for a specific date
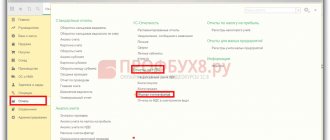
The card reflects data about the object as of the current date. But there is a need to see what the data was before any changes, on a certain date. To do this, in the inventory card, by clicking the “More” button, select the “Change form” command.
Fig.6 Select the “Change Shape” command
Having opened the form settings, we see that among the form header details there is an unchecked “Information date” attribute.
Fig.7 Information date
By checking this box, in the form of an OS directory element we will see an additional field where we can set the date for which we want to view information about our object.
Fig.8 Setting the date
Storing Invoices: The Basics
Every organization and entrepreneur is required to keep accounting documents. This is required by Article 29 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. The director of the organization must ensure the storage of documents. And an individual entrepreneur is responsible for this independently (Article 7 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Invoices, incl. electronic, must be stored for at least four years after the end of the quarter in which the document was last used to calculate tax and prepare tax reporting (clause 8, clause 1, article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1.13 of the Procedure for issuing and receiving invoices electronically form).
Results
In most cases, an organization will have to store expense reports for at least 5 years. But they may need to be retained longer if they are used to support expenses carried forward to other periods. The corresponding period in correlation with the transfer of losses of the organization can be 10 years.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ
- Order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Changes from October 1, 2021
This document puts into effect:
- invoice form;
- sales book form;
- purchase book form;
- form of a journal for recording received and issued invoices.
However, in addition to this, amendments were also made to the rules that relate to the storage of invoices. Let's tell you more about them.
Storing invoices in chronological order
Storage periods for invoices
From October 1, 2021, you will still need to store invoices for 4 years. During this period, it is necessary to organize storage:
- to the principal (principal) - copies of invoices that were given to him by the intermediary. The intermediary receives them from sellers when purchasing goods (works, services) for the principal (principal);
- to the customer of construction work (investor) - copies of invoices that were handed over to him by the developer (customer performing the functions of a developer). He, in turn, receives them from sellers when purchasing goods (works, services) for the buyer (investor);
- to the customer of forwarding services - copies of invoices that were handed over to him by the forwarder. He receives these invoices from sellers when purchasing goods (works, services) for the customer.
It is required to store all types of invoices: primary, adjustment and corrected. Copies of paper invoices received from intermediaries must be certified by their signatures (principals, principals, developers or forwarders).
Clarification of deadlines affected not only invoices
Also, Government Decree No. 981 dated August 19, 2017 clarifies that from October 1, 2021, certain other “accounting” documents on various transactions must be stored for 4 years. We list the shelf life in the table.
| Operation | What to store |
| Import from EAEU countries | Applications for the import of goods and the payment of indirect taxes, their certified copies, copies of bills of lading and other documents confirming the payment of VAT. |
| Import from other countries | Customs declarations, their certified copies and other documents on payment of VAT at customs. |
| Travel expenses for rental accommodation and travel | strict reporting forms (copies thereof) with the VAT amount highlighted as a separate line. |
| according to VAT, which is restored by the shareholder, participant or shareholder | Documents with which the parties formalize the transfer of property, intangible assets, property rights (clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - in the form of notarized copies. |
| according to VAT, which is restored when the value decreases (subclause 4, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | accounting certificate-calculation (Article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
| – according to VAT, which is restored upon the purchase or construction of fixed assets | accounting certificate-calculation (Article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). |
Also, for 4 years it is necessary to store primary and other documents with summary (summary) data on transactions of each month or quarter, which are recorded in the sales book.
The subtleties of accounting and storage of primary documents of the financial and economic activities of an enterprise: document retention period - TTN - read the article.
Question:
What is the storage period for waybills when transporting goods in a legal entity, such as a Limited Liability Company? 2. Are TTN mandatory if, for example, waybills are already being issued?3. What can you refer to if the court, as part of a civil case, requests TTN data, but it is not advisable to provide them, for example. What can be indicated, loss or anything else, so that it would be convincing and believable.
Answer:
1) it is safer to store TTN for at least five years.
Alexander Sorokin answers,
Deputy Head of the Operational Control Department of the Federal Tax Service of Russia
“Cash payment systems should be used only in cases where the seller provides the buyer, including its employees, with a deferment or installment plan for payment for its goods, work, and services. It is these cases, according to the Federal Tax Service, that relate to the provision and repayment of a loan to pay for goods, work, and services. If an organization issues a cash loan, receives a repayment of such a loan, or itself receives and repays a loan, do not use the cash register. When exactly you need to punch a check, see the recommendations."
Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the organization must store documents necessary for the purpose of calculating taxes (including accounting documents) for four years (subclause 8, clause 1, article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This requirement applies to all accounting and tax documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes.
Part 1 of Article 29 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ states that primary accounting documents must be stored for the period established by the rules of archival affairs. But not less than five years.
Thus, in order not to be punished for violating the rules established by the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, keep the invoices for at least five years.
2) Waybill and TTN are not interchangeable documents. Only if you have a waybill, then a TTN is not needed. To confirm the fact of concluding a contract for the carriage of goods by road, a bill of lading is sufficient. This follows from Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008, part 1 of Article 8 of the Law of November 8, 2007 No. 259-FZ, paragraph 2 of Article 785 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 6 of the Rules , approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 15, 2011 No. 272. A similar conclusion is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/36.
If the cargo is delivered by a transport organization (road transport), a TTN is issued in Form No. 1-T. When transporting using its own vehicles, the seller also issues a consignment note. This document can serve as the basis for reflecting received goods in the buyer’s accounting.
In addition, the TTN (Form No. 1-T) is a document intended to record the movement of inventory items and payments for their transportation by road. Therefore, if the buyer simultaneously acts as a customer for the transportation of goods, he must have a consignment note (form No. 1-T) (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 18, 2009 No. ShS-20-3/1195).
3) In cases where the law or contract requires one party to provide the other party with any information, then failure to provide information will be considered, among other things:
- providing information late,
- providing incomplete information,
- providing incorrect information.
Failure to provide information (information) or untimely submission to a state body (official) entails a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine on officials - from three hundred to five hundred rubles; for legal entities - from three thousand to five thousand rubles (Article 19.7 of the Administrative Code)
The rationale for this position is given below in the materials of the Glavbukh System