Fines for violating rules for storing archival documents will increase
The State Duma adopted in the second reading bill No. 759112-7 with amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation on tightening sanctions for improper storage of archival documentation. The author of the initiative was the State Council of the Republic of Tatarstan. Fines will increase for officials and legal entities.
Now the norms of Article 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation provide for administrative liability for violation of the rules:
- storage;
- acquisition;
- accounting;
- use of archival documents.
The punishment for such a violation is a warning or a fine for officials in the amount of 300 to 500 rubles. Organizations are not held liable for this.
Legislators propose maintaining a warning for officials for the first violation, and increasing the amount of the fine:
- for officials - from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for legal entities - from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles.
The new norms will come into effect 10 days after the official publication of the amendments to the Code of Administrative Offenses adopted and signed by the president, that is, still this year.
Normative base
The procedure for compiling files and storing documents generated in the process of activity is determined by archival legislation:
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation, articles 230, 230.1.
- Law “On Archiving in the Russian Federation” No. 125-FZ of October 22, 2004, which obliges the preservation of certain documentation for the period of time established in regulations.
- “Basic Rules for the Operation of Organizational Archives”, approved by the decision of the Board of Rosarkhiv dated 02/06/2002 (are of a methodological and informational nature).
- Order of the Federal Archive No. 236 dated December 20, 2019, which approved the list of standard archival documents indicating the storage time (List), which defines the obligations for all organizations for various types of documentation, including accounting, tax and personnel.
But do not forget that the listed regulations are advisory in nature, the specific storage periods for documents and the list of cases for 2021 are determined by the internal documents of the organization.
IMPORTANT!
02/18/2020 Order of the Ministry of Culture No. 558 dated 08/25/2010 became invalid. Instead, a list appeared, approved by Order of the Federal Archive No. 236 of December 20, 2019. Please take these changes into account in the LNA.
Possible consequences if you refuse to receive an “Administrative” postal item
The limited shelf life of a registered letter at the post office can result in serious problems for the recipient of the letter. It happens that the recipient does not actually live at the registration address. Such letters cannot be sent to other addresses. Therefore, if the addressee does not show up at the post office, the letter is returned to the sender after 7 working days. In this case, the fact of receipt of a postal notification gives the right to an official or authorized person to consider the letter to have reached the addressee. Especially if it is a registered letter with return receipt requested.
Some items, such as notices of fines and taxes, are duplicated in the personal accounts of State Services or the tax office. Citizens who regularly monitor the accrual of taxes and payments and do not forget to repay them on time using modern means of communication do not need to rush to pick up the letter. But such correspondence as subpoenas in administrative cases, summons for drawing up protocols, are subject to mandatory receipt. Failure to appear at the trial will be regarded by the court as a reluctance to protect one’s rights, and may create additional difficulties for the addressee if a decision is made not in his favor.
Storage rules
The employee responsible for maintaining personnel records and storing information is appointed by order of the head of the organization, his functional responsibilities are fixed in the job description.
Personnel information is compiled into files and transferred for storage to the organization’s archive or (in case of liquidation and in some other cases) to the state archive.
Formation of cases should be understood as grouping executed documents into cases (folders) in accordance with the nomenclature of cases.
Below is the order of case formation:
- To avoid the need for additional decoding, the following details must be indicated on the cover of the case:
- name of the organization (in full);
- name of the structural unit (in full);
- case number (in accordance with the nomenclature);
- case title;
- retention periods for the file and numbers of articles according to the list (if necessary).
- The following are filed in the file:
- only completed and executed documents;
- one original, except in a few cases;
- published in the same calendar year.
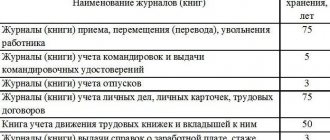
- Inside the file, the papers are filed in order by numbers and dates; if the volume exceeds 250 sheets or volume (4 cm), division into volumes is required. In large organizations, a large number of orders are issued, and as a rule, they are filed in different files depending on the duration of storage. Thus, the storage period for vacation orders is 5 years, and orders for hiring or dismissing employees are already 75, which is why they are assigned to different folders.
How can you find out about the sender of a registered letter?
The content of a customized “Administrative” message will most likely be generated by an official, or his executor in the local administration, or another government agency or body. Only the shipping address will be indicated based on the location of the mailing sorting center to which the government agency’s order for bulk mailing was sent. Just some of them are located in such automatic sorting points or post offices: Moscow-473, Volgograd-66, Troitsk, Kaluga 9. Usually, taking into account the location of the delivery point, the nearest post office is determined, which will carry out the order of the government agency. That is, trying to get clarification about a registered letter to these addresses makes no sense.
The addressee can be identified by the 14-digit notification number on the Russian Post website.
Thus, if you are confident that the contents of the “Administrative” letter awaiting receipt at the post office are insignificant, especially if the sender is determined by the notification code, you do not have to pick it up. If you do not know what may be in the shipment, it is better to receive it in a timely manner so as not to waste precious time to eliminate administrative violations.
Shelf life
In state and municipal organizations, documentation is completed in the prescribed manner for transfer to the archive. But in commercial things it’s not so simple. The organization's LNA will help answer the question of how the storage periods for personal data and other information and documents are determined. They are compiled on the basis of existing regulations and established office practices.
ConsultantPlus experts analyzed the storage periods for personnel documents in an organization where all employees are remote. Use these instructions for free.
Example:
Federal Law No. 152-FZ of July 27, 2006 (as amended on April 24, 2020) “On Personal Data” limits the period of processing (including storage) of personal data to the achievement of the purpose of their processing. After the task for which they were requested has been completed, the PD must be destroyed. The specific period is determined by law or by the organization’s specialists, if such standards are not established.
It is necessary to take into account the special role of the expert commission when establishing the period during which it is necessary to store files in the personnel service. In Scheme 1 we will see the tasks solved by the above-mentioned body.
The regulations on the work of such a commission, as a rule, are developed on the basis of the Order of the Federal Archive No. 2 of January 19, 1995 “On approval of the approximate regulations on the permanent expert commission of an institution, organization, enterprise.”
When setting time, marks of this type are sometimes used:
- according to the protocol (EC), if there is none, an order is used on the period of storage of documents in the organization, which fixes the decision on the need to store documents or destroy them;
- “until the need passes” or “until replacement with new ones”, i.e. The time is set by the organization independently (at least 1 year).
The storage period for documents according to the nomenclature of cases begins on January 1 of the next calendar year. Cases with expired shelf life are prepared for destruction.
IMPORTANT!
Reducing the storage periods stated in lists or regulations is unacceptable. If two regulations set different retention periods for the same type of information, the choice is made in favor of the longer one.
For clarity, here are approximate lists of documents with storage periods:
| Table of storage periods for personnel documents in an organization in 2020 | ||
| Permanent | ||
| Statement on the protection of personal data | Clause 8, part 1, art. 86 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Regulations on remuneration (bonuses and material incentives) | Art. 21 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Regulations on certification | ||
| Regulations on the training system | Art. 196 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, art. 197 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Orders on main activities | ||
| Long-term | ||
| Orders on admission, transfer, dismissal, leave without pay | Art. , 72.1, , part 1 art. 80, clause 6, part 1, art. 81 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 75 |
| Personal cards of employees (T-2) | Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 1 of 01/05/2004 | 75 |
| Journals, books of registration of orders for admission, transfer, dismissal | 75 | |
| Time sheets | Part 3 art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation |
|
| Employment contracts, agreements thereto | Art. 16, art. 56, art. 57, art. 67 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 75 |
| Limited | ||
| Minutes of meetings, resolutions of certification and qualification commissions | 10 | |
| Orders on granting regular and educational leaves | Art. 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 173 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 5 |
| Calculations, analyses, certificates on the revision and application of production standards, prices, tariff schedules and rates, improvement of various forms of remuneration | Art. 135, 144, 147 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 5 |
| Applications, information, correspondence about the need for workers, reduction (release) of workers | 5 | |
| Correspondence about the establishment and payment of personal rates, salaries, allowances | 5 | |
| Orders on personnel (professional development, bonuses and incentives for employees, maternity leave or without pay, etc.) | Art. 6 list of Rosarkhiv dated 10/06/2000 | 75 |
| Orders on business trips, on duty | 5 | |
| Orders of disciplinary action | 3 | |
| Books, magazines, leave cards, issuance of certificates of wages, length of service, place of work | 5 | |
| Time logs | 1 | |
| Vacation schedules | Art. 123 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 3 |
| Internal labor regulations | Part 4 art. 189 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | 1 |
| List of professions with hazardous working conditions | Art. 221 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | DZN (before replacement with new ones) |
| Storage period for incoming and outgoing correspondence | 5 | |
| Table of storage periods for contracts in an organization in 2020 | ||
| Name | List item | Shelf life |
| Civil contracts on the performance of work, provision of services by individuals, acceptance certificates of work performed, services provided | 301 | 50/75 years |
| Documents (calculations, conclusions, certificates, correspondence) for agreements, agreements, contracts | 5 years | |
| Founding agreements of a company, business partnership | Constantly | |
| State and municipal contracts for the purchase of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs | 224 | 5 years EPC after expiration of the contract, termination of obligations under the contract |
| Treaties, agreements, contracts not specified in individual articles of the List, documents (acts, protocols of disagreements) to them | 5 years EPC after expiration of the contract, after termination of obligations under the contract | |
| Table of storage periods for accounting documents in an organization in 2021 | ||
| Name | List item | Shelf life |
| Annual reports | 269 | Constantly |
| Quarterly reports | 269 | 5 years. In the absence of annual reports, they are stored permanently |
| Monthly reports | 269 | 1 year provided that the company prepares quarterly and annual reporting. If not, then store it permanently. |
| Audit reports | 287 | 5 years
|
| Accounting policy documents | 268 | 5 years. The countdown begins on the first day of validity of the new |
Any primary, in particular:
| 278 | 5 years. The countdown begins from the end of the reporting year |
Accounting registers, including:
| 277 | 5 years, if an audit was carried out |
| Information on accounts receivable and payable | 267 | 5 years from the moment the debt is repaid |
| Information about shortages, embezzlement, thefts | 277 | 10 years
|
| Statements for the issuance of salaries, benefits, financial assistance and other payments | 295 | At least 6 years. In the absence of personal accounts:
|