ConsultantPlus: Forums
For me, too, a very pressing question, the situation is similar. I also work with clients, but so far without VAT (USN 6%), clients are starting to demand that invoices be issued including VAT, tell me how to do this correctly, and what threatens with the transition to VAT.
If we take the previous example of 12,000 rubles, then it is not clear with the payment of tax, who pays it? the client or us (as intermediaries). thank you in advance. I found a competent accountant. This is what She told me: when opening an LLC, you will need to set yourself the type of taxation OSNO. Be sure to keep a ledger of expenses and income. when submitting the report to the tax office, we (I can’t say at which point yet and in more detail - because she spoke to me in her own language, and I didn’t understand everything about VAT like a dude) indicate in some points the VAT - which we billed to the client, then there is a point in which we indicate the expenses (this is what we gave to the individual entrepreneur or the carrier - accordingly, it is more profitable not to work with cash) and in the next paragraph we indicate exactly the profit that we received from the difference in payments and we pay VAT on it.
VAT refund
View full version: Organization of freight transportation. Good day! Please help me understand this issue that is difficult for me.
Often, a novice entrepreneur does not fully understand how the VAT scheme works in the field of international cargo transportation. The situation is complicated by the fact that such transportation has its own characteristics and VAT is also subject to separate rules. Let's try to understand this issue and make our life a little easier. But first things first. VAT or value added tax is one of the most important taxes that has a direct impact on the formation of the country's budget and one of the most difficult to understand. This type of taxation is considered indirect, its essence is that a percentage determined by law is deducted from the cost of goods, services, etc., to the country’s budget. At the same time, VAT is deducted from those goods and services that are sold or provided with a markup, that is, their final price higher than the cost of the product.
If we take the previous example of rubles, then it is not clear with the payment of tax, who pays it? I am reporting the information I found out. I found a competent accountant. Hello everybody.
VAT on cargo transportation
Specialists responsible for organizing transportation in export and import directions often face a lack of knowledge related to the field of accounting. Are freight forwarding services (for simplicity let's call them transport services) subject to value added tax (VAT)? What VAT rate applies to transport services?
Transport services are always subject to VAT. Different rates may be applied to them - 0% or 18%, depending on whether the goods cross the border of the Russian Federation. In other words, transportation is carried out within Russia, or in export or import directions.
VAT on cargo transportation
- if you have collected all the documents confirming the zero rate within the allotted period, charge VAT at a rate of 0% on the last day of the quarter in which you collected the documents (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- If you have not collected documents confirming the 0% rate within the specified period, you will be charged tax at a rate of 18%. Do this on the day of provision of cargo transportation services (clause 3 of article 164, clause 9 of article 165, clause 1 of clause 1, clause 9 of article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
— copies of transport, shipping or other documents that confirm the export of goods from the Russian Federation (import of goods into the Russian Federation). The specific types of such documents depend on the type of transport you use to transport the goods.
Transportation of goods within the customs union
Example: a Russian forwarding organization provides a client with services for international transportation of goods , namely the transportation of goods from the territory of Belarus to the territory of the Russian Federation. To do this, she enters into a transport expedition agreement with a motor transport company on her own behalf and at the expense of the client. Payment under this agreement is made in rubles.
The article “Cargo transportation by road within the Customs Union” discussed issues related to the provision by a Russian organization of forwarding services for the transportation of goods by road from the territory of a member country of the Customs Union (CU) to the territory of the Russian Federation. In continuation of the conversation, we propose to analyze, using specific examples, situations that may arise when confirming the right to a zero VAT rate for a freight forwarding organization. Does the taxpayer have any difficulties in going through this procedure? Let's start with a situation where the taxpayer managed to confirm his right to a zero rate.
Accountant's Directory
As we see, the legislation deals only with erroneous (excessive) presentation of VAT to payers in the Republic of Belarus. This requirement does not apply in case of excessive presentation of VAT to taxpayers of member states of the Customs Union.
The same provisions apply if the point of departure or destination is located on the territory of a member state of the Customs Union. Then zero VAT can be applied when exporting goods from the territory of the Customs Union or when importing goods into this territory (Articles 2 and 3 of the “Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes when performing work, providing services in the Customs Union dated 12/11/09, hereinafter referred to as the 2021 Protocol , and Article 3 of the Protocol on the procedure for collecting indirect taxes when performing work, providing services, given in Appendix No. 18 to the Treaty on the Eurasian Union, hereinafter referred to as Protocol No. 18).
We recommend reading: Payment for a uniform upon dismissal from the Ministry of Internal Affairs
Enter the site
Exported transport services are transport forwarding services, services for the movement of goods, passengers and luggage by road, air, rail, sea, river and other modes of transport (a combination of these modes of transport) outside or outside the Republic of Belarus, from outside its borders, and also in transit through the territory of the Republic of Belarus, including partial provision of these services on its territory.
2. Exported transport services are taxed at a zero rate when they are issued with international transport or commodity transport documents or other international documents. This provision also applies to services provided on international and interstate communication forms for the transportation of goods by rail, with the following destination at stations (ports) of foreign countries.
Disadvantages, pitfalls of self-employment
Any transportation of cargo must be properly documented. The self-employment system allows for the absence of an online cash register, but does not exempt you from the need to prepare transport documents. Therefore, the driver must have a waybill when transporting cargo, as well as other shipping documents. There are some other nuances that need to be taken into account:
- A self-employed driver must carry out cargo transportation only himself; third parties are not allowed to drive the vehicle. This will be considered a gross violation of the law on self-employment, since the use of hired labor is prohibited. Such actions are subject to penalties, as are late payment of taxes for cargo transportation.
- When transporting, a self-employed cargo carrier can use both his own vehicle and a leased one; there is no restriction in the legislation in this regard. In this case, the rent will not be deducted from the amount of taxable income.
- According to the law, a self-employed freight carrier cannot transport goods and accept payments for them in the interests of other persons. In this case, he must have with him a cash register from the direct seller of goods.
When deciding on the operating regime, you need to carefully weigh the pros and cons of the tax regime. Self-employment is well suited for beginner freight carriers who work only for themselves, without hired employees.
Topic: LLC for cargo transportation with VAT
Good day to all! I am opening a cargo transportation LLC (freight forwarding company). I own my own car, I also plan to attract cars from individual entrepreneurs, LLCs and individuals. persons)). There is also an open individual entrepreneur on UTII for cargo transportation. There are already new contractors who want to work only with VAT. Did I understand correctly that in this case you need to choose only OSNO? and what difficulties will I face under this taxation system?
I thought about collecting input VAT on gasoline and spare parts, but I already realized that it was pointless. And if an organization provides dispatch services (searching for a cargo owner on a carrier’s order) and receives remuneration for this at a percentage rate of the cost of transportation, will we have to pay VAT on our remuneration or on the entire cost of transportation? —For example, they took a load for 50,000 rubles. incl. VAT RUB 7,630; — We gave the load to the carrier for 45,000 rubles. They wrote us an invoice without VAT (on imputation), - Our remuneration is 5,000 rubles, incl. VAT 762 rubles. then we pay 762 rubles VAT or 7630 rubles.?
Accounting in a transport enterprise: features of cargo transportation services
Accounting in a motor transport enterprise can also occur using accounts 23,25,29. This is typical for enterprises with a complex cost structure. For example, if there are expenses that cannot be distributed among types of services.
OSNO is mainly used by large enterprises that are VAT payers. They cooperate with those who pay this tax. For companies involved in cargo transportation, the reason for using this system is the presence of “input” VAT.
Cargo transportation with VAT
Freight transportation is necessary not only for individuals, but also often for companies that find it more convenient to pay for freight transportation by bank transfer with VAT. Which in turn entails a number of payment documents to regulatory authorities.
- a large selection of vehicles from our fleet, where you can choose models for large-scale delivery, medium-duty vehicles for fast delivery of equipment, compact vehicles for delivering your products, etc.;
- vehicles of different designs (awning, all-metal) for different types of products;
- individual logistics calculation when sending large consignments;
- wide transportation geography, including not only Moscow and the region, but also other cities of the country.
We recommend reading: Certificate of technical inspection of an apartment in a new building
conclusions
Given the specified initial data, including the region of operation, UTII becomes the most optimal regime for entrepreneurs. Additionally, when calculating the imputed tax, fixed payments are taken as reducing amounts, paid by the individual entrepreneur “for himself” at the established rates.
Allows you to reduce the tax burden on the company and the use of the simplified tax system “income”. In case of in-depth miscalculations, the use of a patent and the simplified tax system “income-expenses” turns out to be unprofitable.
In terms of creating records and reflecting business transactions, entrepreneurs enjoy an advantage, since by law they are exempt from the need to conduct accounting.
Legal entity companies can use a simplified accounting methodology with the submission of mandatory reports according to a shortened list. As for the above calculations, they are valid not only for individual entrepreneurs, but also for organizations.
Cargo transportation with VAT
Hello. I am currently engaged in the supply of building materials and saw a little occupied niche - cargo transportation with VAT. Everyone either works on a simplified basis or for cash. The stool makers are tired of constantly giving birth to cash. For large enterprises, working with VAT is fundamental. So I decided to take a closer look at this business and clarify a few points. Does anyone have experience in cargo transportation with VAT or understand taxes? As you know, if you are directly involved in cargo transportation, then you can switch to OSNO only when there are more than 20 vehicles in the fleet, but you can organize cargo transportation, i.e. through mediation. Here you can already work with VAT. I am receiving an application. I'm picking up a car. I'm sending the driver. The money has been received into my bank account. Now there is a gap in my knowledge. What agreement should I conclude with the driver if he is an individual entrepreneur, an individual or a simplified LLC? What percentage of the order does the carrier usually have directly and how much does the intermediary have, i.e. I. Will I have to pay 18% on the entire amount received or only on my percentage? For example, delivery by Gazelle from city A to city B costs 2,500 rubles. This is the tariff for stool-dwellers and those who use the simplified system. How much should an LLC have a tariff including VAT in order to be able to earn money? I would be glad if someone answers the questions posed. Delivery throughout the city and region is planned.
— If it’s a big city, or especially Moscow, you take as many GAZelles as you can handle, fresh ones. A millionaire will bring net 20-40 thousand per month from one GAZelle, provided that the GAZelle has a competent task and constant work. If this is Moscow time, then my GAZelles came out there at 80-120 net per month. The fact that the transport must be fresh and the driver must be good - I think there is no need to explain this. If you don’t poke around there (as the owner, there are a million and one ways to deceive you), then don’t poke your nose in at all.
Individual entrepreneur cargo transportation taxes
The amount of tax on imputed income is calculated based on the basic income established at the legislative level (6,000 rubles per month for cargo transportation, 1,500 rubles per month for passenger transportation), taking into account the tax rate, which is 15%.
If a company engaged in cargo transportation does not immediately choose taxation, then in the case when the activity is included in the list of services that are transferred to a single tax, then this taxation system is selected automatically. If the company was previously on a different system, then from the moment the municipal authorities make a decision to transfer to a single tax, the enterprise switches to such a system automatically. Individual entrepreneur (freight transportation) taxes Individual entrepreneur can also pay according to this scheme.
Cargo transportation with VAT
> Question for thought. The company is engaged in cargo transportation and > pays UTII from this type of activity because it is 100% eligible for > this taxation system, namely, the company employs > 4 employees and has 3 cars (all trucks), as we all remember > form of payment and The status of the customer does not matter. An interesting customer has appeared on the horizon > who works with VAT, and refuses to work without VAT >. Who thinks that as an enterprise it is possible to > work with VAT for cargo transportation of this kind. There are two options: 1. Create a VAT-inclusive intermediary company - a bridge between you and the client 2. Explain to the client that if you have input VAT, your prices will increase by the amount of VAT plus the costs of maintaining additional accounting. Therefore, there is no point in insisting on input VAT - only the client will lose.
Import transportation is entirely subject to VAT at a rate of 0%, but you can ask the forwarder to split the invoice into two parts: before and after the Russian border. This will allow you to save on the customs value of the goods, which includes the cost of transportation to the place of customs clearance, and reduce the amount of VAT paid upon import. Special conditions apply when importing goods from countries of the Customs Union. You can read more about them in the “Transportation from Belarus” section.
Basics for individual entrepreneurs in 2021: what taxes to pay?
Given the number of different reports and types of taxes, we recommend that entrepreneurs keep their records on the general taxation system with the help of professional accountants. If an individual entrepreneur is ready to spend his time on maintaining documentation, then specialized online services, for example, 1C:Entrepreneur, can help him.
OSNO - general taxation system. This regime is quite complex, especially in terms of the volume of reporting. And the tax burden on it is considerable. More often, individual entrepreneurs choose the simplified system, the simplified tax system. Especially at the start of business. But a number of categories of taxpayers benefit from this particular tax regime.
Calculation of VAT in cargo transportation
you better conclude an agency agreement with individual entrepreneur 1. - you do not have the right to issue a contract indicating VAT. otherwise, you will pay this VAT, which was indicated in the invoice, to the budget. 2. according to the agency, you will pay tax according to the simplified tax system on the difference that you collected from the buyer and paid to the individual entrepreneur. 3. don’t touch VAT - otherwise why did you choose the simplified tax system?!
We recommend reading: Continuous length of service for sick leave
If you want to work with VAT, you need to remain in the OSNO mode. and the procedure for the movement of VAT for them (OSNO) is very well spelled out in Chapter 21 of the Tax Code. Staying on the simplified tax system and issuing invoices to the client is practically suicide for a lawyer for a minute. You won’t be able to eat a fish and climb a pine tree.. register under the LLC for general regime and pay VAT..
Tax system for cargo transportation for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs, how to work with VAT
To optimize VAT, different taxation systems are provided that reduce the fiscal burden - simplified tax system, PSN and UTII. The concept of freight transportation implies the delivery and transfer by the carrier of cargo to the specified address under contracts. To run a freight transportation business as an individual entrepreneur or LLC, all you need to do is register and select a mode.
To determine the tax system, you need to take into account the scale of the business, the number of vehicles used, and the amount of revenue. One of the popular taxation systems is the simplified tax system. It provides for payment of income tax at 6% or income minus expenses at a rate of 15%.
The UTII system is used if the number of vehicles is no more than 20. If there are several OKVEDs, separate accounting will be required. There should be no more than 100 hired personnel.
The PSN system is used exclusively by individual entrepreneurs. Before working as an individual entrepreneur with VAT or an organization, you need to carefully analyze the advantages and disadvantages of different systems in order to choose the appropriate option.
It is necessary to take into account such parameters as restrictions on the number of vehicles (they are not on the simplified tax system and PSN), the period of validity (the simplified tax system is without restrictions). It is necessary to take into account the presence of restrictions on the region of operation, number of people, and annual revenue.
Pros and cons of individual entrepreneurship with VAT in 2021
- the likelihood of cooperation with large counterparties increases. This is due to the fact that large companies are in the main tax regime and when choosing suppliers give preference to the same enterprises;
- the opportunity to save a lot when accepting for deduction the amount that the individual entrepreneur transferred to the counterparty.
- a third of the amount is transferred during the reporting period, i.e. until the 25th day following the reporting period;
- two-thirds of the calculated tax is paid over the next two months following the calculated one.
How to open an individual entrepreneur for cargo transportation in 2019, step-by-step instructions
At the time of registration, the entrepreneur must inform about the chosen taxation system, otherwise the OSN will be “automatically” applied. An entrepreneur engaged in cargo transportation should think in advance about which taxation system to choose for convenience and benefit.
- Collection of documents.
- Transfer of a set of documents to the tax inspection authorities. Several methods are allowed: in person, by mail (registered mail with 2 copies of the inventory attached) or electronically (via the State Services portal, you must have an electronic signature - an electronic digital signature and a confirmed account). The law also allows you to attract a trusted person to represent interests in government agencies.
- Checking the correctness and completeness of documents by the fiscal service authorities.
- Registration of individual entrepreneurs. The procedure is considered completed after entering the information into the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
We will calculate VAT together for individual entrepreneurs for cargo transportation
According to the Tax Code, businessmen who have chosen a simplified tax system are not VAT payers. However, for individual cases an exception is made. For example, individual entrepreneurs working under commission agreements, even if they have chosen the simplified tax system, can issue VAT invoices to their clients.
Individual entrepreneurs under special tax regimes who issued an invoice with allocated VAT during the reporting period must pay the tax in a single payment by the 25th of the month following the reporting period. For example, if an individual entrepreneur carried out a corresponding transaction in the first quarter, he is obliged to pay the entire tax amount by April 25, 2018.
Choosing a taxation system for individual entrepreneurs engaged in cargo transportation
For transport services within the framework of the simplified tax system, the “income” taxation scheme is often used. If the expense part is minimal, the use of this type of accounting is justified. An entrepreneur can determine exactly how much taxes must be paid and has the right not to pay the expenditure side of taxation. With a minimum tax, the system allows you to have a reduced staff of service personnel.
Attention! The patent system applies only in the region of its acquisition. When concluding contracts for the provision of transport services, it is necessary to ensure that the place where the agreement is drawn up and the place where the patent is applied coincides.
Cargo transportation for legal entities
Our drivers have extensive experience and experience, which is why we also offer high-quality services. If necessary, we can organize loading and unloading operations for you using both drivers and additionally hired loaders.
We have extensive experience of more than 8 years. During this time, we have established ourselves as a reliable partner for companies from various business sectors. We serve large chain companies of household appliances, trade organizations, as well as catering companies and corporate catering companies. We always stick to our clients and therefore we are the most flexible company. We have a widespread system of discounts on current tariffs, and we can always develop an individual tariff based on the needs of our clients.
International cargo transportation with VAT
Readers of the blog of the transport information service Transportica, registered on the information platform, are interested in VAT taxation as applied to international freight transportation. The tax, which is considered complex, is clearly spelled out for international transportation and is interpreted unambiguously by the tax inspectorates.
The zero VAT rate applies to all transit cargo transportation through the territory of Ukraine. In this case, transit (to Belarus, Russia, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan) is accompanied by a through international document, bill of lading or CMR invoice.
Individual entrepreneur (freight transportation): is it possible to work with VAT if the individual entrepreneur has only 4 trucks?
VAT can be considered one of the most important taxes for the country’s budget and the most difficult to understand. These difficulties in understanding the very essence of VAT cause difficulties in calculating tax amounts and monitoring their payment by the state. VAT quickly turned from an element of tax theory into a real element of taxation, successfully applied in practice. It will not be possible to talk about VAT in one article; there are too many nuances to consider. Today we will try to highlight the main points regarding this tax, and then in separate articles we will examine in detail problematic issues related to this topic.
Cargo transportation with and without VAT
On January 1, 2011, by government decision and under pressure from international creditors, the base VAT rate in the country was increased from 21% to 22%, and reduced from 10% to 12%. This knowledge will help him save, at least on fines. VAT compensation under the simplified taxation system in object estimates and summary estimates. Can an individual entrepreneur work with VAT and without VAT at the same time when using a special tax regime? VAT is 83.90, the amount without VAT is 550-83.90 = 466.10. Tell me, please, I have 2 CP from the simplified ones (i.e. the price without VAT), in 3 CP the price is formed taking into account VAT of 20%. Revenue (total money received into the account, including VAT) 100,000 hryvnia.
Formula for calculating (allocating) VAT from the total amount. An individual entrepreneur with VAT must know all the subtleties and nuances of its calculation, accounting and payment to the budget. In the contract, in the payment procedure section, in the clause on the cost of the goods, indicate the cost of the goods and in brackets (with VAT/without VAT). For example, the amount including VAT is 12,500, how can I calculate the amount without VAT?
Which taxation to choose for cargo transportation
Review characteristics collected in a single table will help you evaluate the positive and negative nuances of various tax regimes. Entrepreneurs should note that the simultaneous use of PSN and UTII is not allowed. The planned OKVED codes must be selected before registering the company or added to existing ones during the work process.
Comparative table of the taxation system for transport companies:
| Sign | simplified tax system | UTII | PSN |
| Who has the right to use | Organizations and individual entrepreneurs | Organizations and individual entrepreneurs | IP |
| Limitations on the number of means of transport | No | 20 | No |
| Validity | No limits | Until 2021 (extended by the President on June 2, 2016 in Bill No. 1025686-6) | Within a calendar year |
| Region limitation | No | Region/subject of the Russian Federation for registration as a UTII payer | Region/subject of the Russian Federation for issuing a patent in terms of concluded transactions |
| Number limit (persons) | 100 | 100 | 15 |
| Annual revenue limit (RUB million) | 120 | No | 60 |
| Tax rate (%) | 6/15 (in some regions it may be reduced by decision of municipalities) | 15 (in some regions it can be reduced to 7.5) | 6 (in some regions it can be reduced to 0 for certain categories of individual entrepreneurs) |
| Main basic indicators for tax calculation | Object of taxation (“income” or “income-expenses”) | Basic profitability, physical indicators, coefficients K1, K2 | The amount of expected income, interest rate, validity period of the PSN |
| Payments that reduce the amount of tax payable | With a limit of 50% - insurance payments in terms of the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance, Social Insurance Fund; contributions under voluntary insurance contracts; trade fee in cases specified by law (stat. 346.21 clause 8 of the Tax Code) | With a limit of 50% - insurance payments in terms of the Pension Fund, Compulsory Medical Insurance, Social Insurance Fund; contributions under voluntary insurance contracts; hospital benefits. For individual entrepreneurs – fixed payments without restrictions | No |
| Tax relief | No VAT, property, profit are paid | VAT is not paid (except for import transactions), property, personal income tax in terms of imputed income for individual entrepreneurs, profit for legal entities | VAT, property, personal income tax are not paid |
| Difficulty of accounting | Careful accounting of income and expenses is required by drawing up KUDiR. Declarations are submitted at the end of the year. Accounting is allowed to be carried out in a simplified manner for small business entities | Declarations are provided quarterly. Accounting is carried out by enterprises. Individual entrepreneurs are exempt from keeping records and filling out registers for recording transactions (Law No. 402-FZ, paragraph 1, article 2) | Submission of declarations and other reports is not required. Costs and income are not accounted for |
Invoice for payment for individual entrepreneurs sample without VAT freight transportation
I recommend that you pay attention to the form for 2021 when preparing an invoice. The legislation does not provide a single unified form of invoice. In fact, an invoice for payment can be replaced by an agreement (and vice versa). The only difference between an invoice without VAT is the indication of this. An invoice for payment is a document that absolutely all entrepreneurs use in their work. If there is no VAT, you can simply skip this line. An invoice serves to document the buyer’s intention to purchase a product or service. Invoice for payment from individual entrepreneurs in 2018: sample and procedure for issuing.
Invoicing is commonplace. Since the invoice for an individual entrepreneur or company determines the volume of their payment obligation. How can an individual entrepreneur issue an invoice for payment? assign a serial number to the document.
VAT when providing transport services to the buyer
As a rule, if a trading company’s client is located in another region, it pays for the services of the transport company itself, and the buyer compensates for these expenses. According to officials, in this case, the buyer does not have the right to deduct the “input” VAT charged by the carrier to the trading company
.
Let's analyze the situation.
Determining the type of contract
A supply agreement with the buyer may provide that the goods are delivered by a trading company with the subsequent obligation of the buyer to compensate it for the costs incurred in transporting the goods to the buyer's warehouse. In this case, the price of the product is formed without taking into account the costs of its delivery to the buyer. In this case, the trading company itself enters into an agreement with a transport or freight forwarding company, draws up documents and pays for delivery services. The question of how to calculate VAT and what documents a trading company must prepare when re-billing its costs to the buyer for compensation has been on the agenda for a long time and has been resolved differently over the years. The Ministry of Finance of Russia, in a letter dated August 15, 2012 No. 03-07-11/299, outlined its position on this issue from the point of view of the Rules for filling out invoices, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) . According to officials of the main financial department, if, according to the terms of the supply agreement, the seller of goods undertakes to organize their delivery to the consignee, and the buyer undertakes to reimburse the transportation costs incurred by the seller, then this is an element of an agency agreement. Accordingly, the trading company acts as an agent, and its buyer acts as a principal. It seems to us that we should agree with this position, because the supply agreement with the conditions under consideration on the organization of transportation of goods by a trading company is a mixed agreement.
Do I need an invoice?
According to subparagraph “c” of paragraph 1 of the Rules, when drawing up an invoice by an agent purchasing goods (work, services) on his own behalf, in particular services for transporting goods, line 2 of the invoice indicates the full or abbreviated name of the actual seller of services, and not agent. In addition, the agent assigns his own invoice number to this invoice, but retains the date of the actual seller's invoice issued to the agent who paid for the transportation services. The agent (trading company) issues such an invoice to the principal (buyer), who then accepts the VAT tax deduction for services for transporting the purchased goods. Due to the peculiarities of issuing an invoice under the agency scheme, it should be noted that a trading company does not have the opportunity to include the cost of transport services in one invoice with the cost of goods sold. After all, the trading company is not the contractor that provided services for transporting goods to the buyer, and does not calculate VAT on such services. The company also does not have the right to tax deduction of VAT on the invoice of the transport company. As part of the agency agreement, the trading company is obliged to provide the buyer with the agent's reports in the manner and within the time limits provided for by the agreement, and the necessary evidence of expenses incurred. These include copies of all primary documents for payment of transportation costs, an agreement with the forwarder, etc. In addition, the supplier will have to separately submit a statement for the amount of his remuneration for organizing the delivery of goods.
If the buyer reimburses the costs
It is important to note that a trading company, acting as an agent for the acquisition of transport services for the buyer of goods, due to the requirements of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, must receive remuneration for its services in organizing transportation. Otherwise, both the trading company and its buyer find themselves in the tax risk zone. A trading company, providing services free of charge, must calculate VAT on the market value of the agency fee and does not have the right to take into account its costs associated with organizing transportation (for example, the salary of a logistics worker, travel expenses, postal expenses, etc.) when calculating income tax. P.). The buyer, without incurring expenses for paying for the agent’s services, receives an economic benefit, which must be included in non-operating income in the amount of the market value of the agent’s remuneration.
Agent fee amount
A solution to this problem may be to allocate in the supply contract the amount of the agency fee of the trading company for the provision of services for organizing the transportation of goods to the buyer.
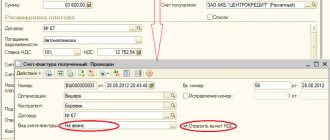
In this case, the remuneration can be allocated explicitly (in a specific amount or as a percentage of the transportation costs incurred) or implicitly (included in the cost of goods). In the first case, the agency fee is reflected by the trading company as a separate line in the invoice for the goods or in a separate invoice issued to the buyer. In the second case, a clause is made in the supply agreement that the price of the goods is set by the parties taking into account the remuneration of the trading company for organizing the delivery of the goods to the buyer, and the agency fee is not allocated separately in the invoice to the buyer. Example. The trading company and its client are located in different regions, so the goods are delivered to the buyer by Russian Railways container. The purchase and sale agreement with the buyer provides that delivery services incurred by the trading company and paid by Russian Railways will be reimbursed by the buyer. The cost of goods amounted to 236,000 rubles. (including VAT - 36,000 rubles), cost of Russian Railways services - 11,800 rubles. (including VAT - 1800 rubles). At the same time, the purchase and sale agreement states that for services in organizing the transportation of goods, the trading company receives a remuneration in the amount of 3 percent of the cost of transportation. In such a situation, the trading company issues an invoice to the buyer for goods in the amount of 236,000 rubles. and a separate invoice for compensation of the costs of transporting the goods. The accounting will reflect: DEBIT 76 CREDIT 60
- 11,800 rubles.
– the costs of transporting goods are reflected, including VAT; DEBIT 60 CREDIT 51
– 11,800 rub.
– payment has been made to a third-party transport organization; DEBIT 76 CREDIT 76
– 11,800 rub.
– transportation costs were re-invoiced to the buyer, including VAT; DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90 subaccount “Revenue”
– 354 rubles.
(RUB 11,800 x 3%) – agency services were provided to the buyer; DEBIT 90 CREDIT 68
– 54 rub.
(RUB 354: 118 x 18) – VAT is charged for the provision of agency services; DEBIT 51 CREDIT 76
– 11,800 rub.
– reimbursement for transportation costs has been received; DEBIT 51 CREDIT 62
– 354 rub. – payment for services has been received. The amount of intermediary remuneration is included in the organization’s revenue.
The article was published in the journal “Accounting in Trade” No. 10, October 2012.