Regular interaction of business entities with partners, employees, budgetary structures and other persons is inevitably accompanied by the emergence of financial obligations.
Their repayment is often made by non-cash transfer of money from a bank account. In order for the servicing financial institution to execute the corresponding payment, the business entity must formalize and provide it with an order of proper content.
If such payments are made by the payer in several directions, it is necessary to take into account the order of transactions performed when drawing up a series of payments.
It is noteworthy that the clear sequence in accordance with which debits and non-cash transfers of funds for certain needs are carried out is strictly regulated by the norms of current legislation.
What is the order of payment in a payment order?
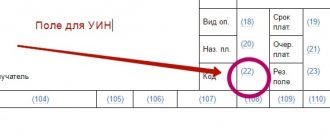
One of the fields that the payer must fill out when drawing up a payment order is called “payment order” and has the number 21. As follows from the explanations for the procedure for filling out payment orders (Appendix 1 to the Bank of Russia regulation dated June 19, 2012 No. 383-P), in the props “Och.
payment." The number indicates the order of payment in accordance with federal law. The general sequence of writing off funds from the account is established in paragraph 2 of Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (note that part two of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation was put into effect by Federal Law No. 14-FZ of January 26, 1996).
According to this norm, payments are made first of all on the basis of writs of execution, which order the withholding (collection) of alimony or funds for compensation for harm to life and health.
Calculate your salary for free with deduction of alimony and standard deductions for personal income tax
The second stage of payments are transfers within the framework of executive documents for the transfer of wages, severance pay or royalties.
“Ordinary” wages (including debts paid voluntarily, and not under a writ of execution) are transferred from the account in third place. Also, in the third place, money will be written off based on collection orders from the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund.
The fourth priority consists of payments under enforcement documents providing for any other penalties (debt under contracts, fines, penalties, etc.).
All other payments are transferred in fifth place.
Important
Within one queue, payment orders are executed in the order they are received by the bank.
Fill out a payment form for free in the accounting web service
Here is OKTMO
The OKTMO code is given in field 105 in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Municipal Territories (approved by Order of Rosstandart dated June 14, 2013 No. 159-ST). It replaced the OKATO code.
This code can consist of 8 or 11 characters:
- 8-digit is indicated when taxes either go entirely to the regional budget, or partially or completely to the budgets of municipalities (urban or rural settlements);
- 11-digit is given if taxes are distributed between settlements included in municipalities.
The distribution procedure can be found from regional regulations or from the Federal Tax Service.
The OKTMO in the payment order must correspond to the OKTMO specified in the tax return.
We talked about the nuances of indicating OKTMO in payments here.
Why indicate the order of payment in a payment order?
Paragraph 1 of Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states: if there is enough money in the account to fulfill all the requirements presented to the account, funds are written off in the order in which payments are received. A similar rule is contained in paragraph 2.10 of Regulation No. 383-P. It says that if there are sufficient funds in the payer’s bank account, orders (payment orders) are subject to execution in the sequence of their receipt by the bank.
Accordingly, establishing the order of payments is necessary, first of all, in case the account at some point does not have funds to execute all payments. Then the bank will transfer money not in calendar sequence, but taking into account the sequence indicated in field 21.
In addition, recording the order of payment in the payment order is necessary in case of arrest or blocking of the account. In such situations, the bank has the right to make payments that occupy a higher step in the queue than those for which the account was arrested (blocked). For example, a decision by tax authorities to suspend operations due to non-payment of taxes (Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) will not prevent the bank from transferring alimony and wages according to executive documents.
Payer's bank details
IMPORTANT! Be careful when specifying your bank! If you make a mistake, the tax (contribution) may be declared unpaid (clause 4 of article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that penalties will be charged.
After the bank details, information about the recipient is provided: his name, TIN and KPP (fields 16, 61 and 103).
READ MORE: Payroll tax Russia
In payments for taxes and contributions, those organizations that administer them appear as recipients. In this case, the abbreviated name of the Federal Treasury body and in brackets the abbreviated name of the administrator are indicated, for example: “UFK for Moscow (Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. 16 for Moscow).” The name must be contained in 160 characters - this length of the details is provided for in Appendix 11 to Regulation No. 383-P.
The TIN and checkpoint can be found on the websites of the Federal Tax Service of Russia and the Social Insurance Fund.
Read about where to find out the details for tax payments here.
In payments for taxes and contributions, fields 104–110 are also required to be filled in. In this case, you need to be guided by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n. Let's look at these fields further.
What order of payment should I indicate in 2021?
When filling out field 21 of payment orders in 2021, you must adhere to the following order.
To transfer payments for taxes, fees, and contributions, you should enter 5 (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2014 No. 02-03-11/1603). The same figure must be indicated in field 21 of the payment slip for the transfer of state duty, since it is a federal fee. This code also indicates penalties and fines that the payer pays based on the requirements of the tax authorities.
When transferring wages, you must enter the number 3. This code is also indicated in the case of voluntary repayment of wage debt. If the debt is paid according to a writ of execution or a decision of the Labor Inspectorate, then 2 is entered in field 21 of the payment slip.
For alimony payments, indicate 1. This code applies regardless of the basis for withholding alimony (writ of execution, court order or notarial agreement).
For payments under writs of execution, the order may vary: 1st, 2nd and 4th orders are possible. It all depends on the essence of the payment specified in the writ of execution. For example, as already mentioned, money under writs of execution for the collection of alimony should be written off first. The first priority also includes payments under a writ of execution, which establishes obligations to compensate for harm to life and health.
Payments under writs of execution for the recovery of wages, severance pay and royalties require the number 2 to be indicated in field 21. And payments under all other writs of execution are made in the fourth place.
Attention
A credit institution does not have the right to refuse to accept a payment order if it incorrectly indicates the order of payment (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 4, 2017 No. 05-07-06/64623).
Fill out a payment form for free in the service, where the current KBK and other details are entered automatically
Insurance premiums
Since 2021, responsibility for insurance premiums has been assigned to the tax authorities. Previously, it was carried by foundations. But the changes in question did not change the queuing code. If a scheduled payment is made, code 5 is indicated. If the payment is made on the basis of a collection request, a fine is imposed, code 3 is indicated. If the contribution for the company is made by a third party, code 5 is indicated.
Penalties and fines
What to do if the tax office has received demands regarding the payment of fines and penalties? Tax payments are made according to code 3. But the regulations do not say anything regarding penalties and fines. What to do? There is a letter from the Ministry of Finance No. 02-08-12/22232 dated May 8, 2014. It states that fines and penalties transferred on the basis of a tax order are assigned to code 3. If the company pays fines voluntarily, code 5 must be entered.
The account may be blocked by decision of the tax office. In this case, almost all calculations are suspended. However, some payments will continue. In particular, these are the following payments:
- Taxes paid on the basis of a collection order.
- Current payments of taxes, penalties.
Tax payment code is 3. Even when the account is blocked, requirements with codes 1-3 are fulfilled.
An organization can send orders to the bank for an amount that exceeds the amount in the account. It works like this: a banking institution receives an order from a company and then checks the amount of money in the account. Is it enough to carry out the assignment? If the money runs out, these are the possible ways the situation could develop:
- Orders with order 5 are immediately rejected (cancelled).
- Orders with a different order are placed in the queue.
Payments are executed as money arrives in the account. It must be borne in mind that the organization can at any time withdraw a payment in the queue.
Sequence of payments when seizing an account
The seizure of funds in an account (for example, as a measure to secure a claim or to execute a decision to collect taxes) in itself cannot violate the order of write-offs established by Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. This means that it does not prevent the transfer of payments that have a higher priority than the requirement due to which the account was blocked (Section II of the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 1996 No. 6).
For example, if an organization’s account is seized based on a decision of the Federal Tax Service in connection with non-payment of taxes, then payments that belong to the first and second stages can still be made on it. And if the blocking comes from bailiffs who have a writ of execution to transfer payments of the fourth stage, then the current salary can also be paid from the seized account.
Generate payments automatically according to the electronic request data from the Federal Tax Service Generate for free
What to do if there is money in the current account to pay off the debt to the state
It happens that an organization is unable to pay taxes or fees. In this case, you will have to repay the debt with the organization’s property.
The law establishes two grounds for debt collection using non-monetary property:
- the organization does not have enough money in its current account;
- The tax office does not know how much money is in the taxpayer’s current account.
Tax authorities have two months to formalize the collection of property in an indisputable manner. If this time is missed, recourse must be made through the courts.
After the decision is made, the resolution is transferred to the bailiff service.
The bailiffs perform their actions:
- in relation to individual entrepreneurs - at his place of residence;
- in relation to an organization - at the place of its registration.
Bailiffs are required to execute the decision to foreclose on property within two months from the date of the decision.
Sequence of payments in bankruptcy
If the paying company is at the stage of bankruptcy, then additional requirements are imposed on orders for the transfer of current payments. They are contained in paragraph 2 of Article 134 of the Federal Law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)”.
Thus, first of all, requirements for current payments related to legal costs in a bankruptcy case are satisfied; payment of remuneration to the arbitration manager; collection of arrears in payment of remuneration to persons who performed the duties of an arbitration manager in a bankruptcy case.
The first priority also includes payment in favor of persons whom the arbitration manager is obliged to involve in the bankruptcy case on the basis of the law (for example, payment for the services of a servicing bank). At the same time, payment for the activities of other specialists attracted by the manager at his own discretion is included in the third priority.
Secondly, the requirements for payment of wages of persons working or who worked (after the date of acceptance of the application for declaring the debtor bankrupt) under an employment contract, and the requirements for payment of severance pay are satisfied. This same line includes the transfer to the budget of personal income tax withheld from current wages (clause 41.1 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2009 No. 60).
In fourth place, utility bills, fees under energy supply contracts and other operating expenses are transferred. Finally, the fifth priority includes claims for all other current payments.
Attention
In field 21 of the payment order, the “bankruptcy” order is not reflected. Control over its compliance is carried out by the credit institution directly when spending funds from the bankrupt’s account. It conducts a check on formal grounds, determining the order of payment based on the information contained in the order or documents attached to it (resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga District dated October 8, 2018 No. F06-37700/2018).
Features of the most popular codes
What does payment order 3 mean?
Indicating the number 3 in field 21 of the payment order means that this is a document for the transfer of wages that the employer pays on a voluntary basis. If the organization’s account does not have enough funds to satisfy all requirements, or it is seized, then the money based on such payment will be debited in third place. Namely: after money under writs of execution for the payment of alimony, funds as compensation for harm to life and health, wages, severance pay and royalties. But before the bank begins to fulfill the requirements for other executive documents and for payment orders for the transfer of payments assigned to the fifth stage.
Accordingly, if an organization’s account is arrested as part of enforcement proceedings initiated on the basis of a writ of execution, which provides for the recovery of funds in favor of counterparties, then the payment order with the number 3 in field 21 must be executed without any delays. The salary for such a payment will be transferred even if the Federal Tax Service issued collection orders to this account, but they arrived at the bank later than the payment from the company (clause 2 of Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
What does payment order 5 mean?
A payment order with the number 5 in field 21 means that the bank is entrusted with the transfer of current payments that are not wages and are not related to the fulfillment of requirements under executive documents. The bank must accept such a payment if there is enough money in the organization’s account to satisfy all higher-level requirements available on the same date. And also provided that the account is not blocked, including collection orders from the Federal Tax Service. Payments with the number 5 do not compete with each other - the bank executes them in the order they are received.
In conclusion, we note that correct determination of the order of payment will allow you to correctly fill out the payment order and promptly transfer it to the bank for execution. This will make it possible to make payments without delays, and in some cases, make payments from a blocked account.
Please note: errors when filling out payment slips can be eliminated if payment documents are generated automatically. Some web services for submitting reports (for example, “Kontur.Extern”) allow you to generate a payment in 1 click based on data from the declaration (calculation) or the request for payment of tax (contribution) sent by the inspectorates. All necessary data (recipient details, current BCC, account numbers of Federal Treasury departments, codes for payer status) are promptly updated in the service without user participation. When filling out a payment slip, all current values are entered automatically.
Legislative justification
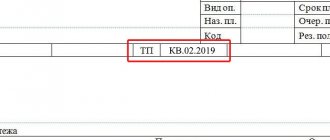
Field 106 indicates a 2-digit payment basis code. The main codes are as follows:
- TP - payments of the current year;
- ZD - voluntary repayment of debt for expired tax, settlement (reporting) periods in the absence of a requirement from the tax authority to pay taxes (fees);
- TR - repayment of debt at the request of the tax authority to pay taxes (fees);
- AP - repayment of debt according to the inspection report.
If the value 0 is indicated in field 106, if it is impossible to unambiguously identify the payment, the Federal Tax Service will independently classify the received money as one of the grounds.