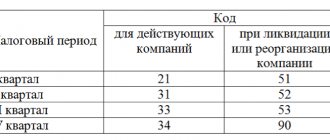
To submit a 2-NDFL certificate, you need to clarify a number of questions: whether it should be submitted, to which inspection, by what time, electronically or on paper. As a general rule, 2-NDFL certificates are submitted to the tax authority at the location via telecommunication channels. The deadline for submitting 2-NDFL certificates depends on the information you submit. If the certificate contains information about all income received by an individual for the year, then it must be submitted no later than April 1 of the year following the reporting year. If this is a certificate stating that personal income tax cannot be withheld, then the deadline for its submission is no later than March 1 of the year following the reporting year. If you miss the deadline for submitting a certificate, you may be charged a fine.
If errors are detected in the 2-NDFL certificates, the tax agent should either correct it or cancel it. However, if the tax office reveals errors in the certificates, it may impose a fine of 500 rubles. for every incorrect certificate.
What is a 2-NDFL certificate?
Certificate 2-NDFL is a document that in 2021 and earlier was drawn up in the form approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] This order established one general form of certificate, which:
- was submitted to the Federal Tax Service by tax agents in order to inform tax authorities about the fact of accrual of personal income tax - in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as for the purpose of informing them about the amounts of personal income tax not withheld - in accordance with clause 5 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- issued to recipients of taxable income (for example, employees) upon their request.
Starting from 2021 (according to reporting for 2021, and then for subsequent years), the certificate is drawn up in accordance with the new order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 2, 2018 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected]
It installs 2 separate types of help:
- compiled according to the form given in Appendix No. 1 to the order (used for the agent’s tax reporting);
- compiled according to the form given in Appendix No. 5 to the order (used for issuing income to recipients).
Thus, starting from 2021, two different 2-NDFL certificates are used: one is intended to be submitted to the Federal Tax Service, the other is intended to be provided to the recipient of the income (employee).
And they should not be confused. We list the key features of the 2-NDFL certificate:
- The certificate shows income for the tax period - that is, for the year. There is no certificate issued for a quarter, half a year or month. But if the certificate is issued at the request of the income recipient, it contains information on his income for the months of the year preceding the date of drawing up the document.
- The most important feature of 2-NDFL is personalization. One certificate is drawn up in relation to one income recipient.
Let's consider in what case and to whom the responsibilities arise for drawing up the first or second type of a new certificate.
What has changed in the order of formation
The key changes that have occurred with the certificate are related to information about the legal successor of the reorganized company. When he submits corrective or cancellation reports for a reorganized company, he must indicate the number of the previously provided certificate, as well as the date of generation of this certificate.
Also, the successor of the tax agent must register the OKTMO code at the location of the reorganized company or its branch.
In the “tax agent” line, the assignee must write down the name of the reorganized company or its branch.
Firms that are on an imputed or patent taxation system in relation to their hired personnel must register the OKTMO code at the place of their registration in connection with the conduct of such activities.
Who submits 2-NDFL and is there a “zero” version of it?
So, the first type of 2-NDFL certificate is the one submitted to the Federal Tax Service by a tax agent. Such an agent is considered to be an individual entrepreneur or a legal entity that has paid income taxable to personal income tax to an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur or as a payer of professional income tax. In addition, the following are considered tax agents for personal income tax: privately practicing notaries; lawyers who have established law offices; separate divisions of foreign legal entities.
Income can be represented by:
- salary;
- payment for work or services under a civil contract;
- dividends.
If an individual entrepreneur or legal entity did not pay taxable income to any individual, then there is no reason to draw up a certificate. There is no zero form 2-NDFL (unlike declarations or reports on insurance premiums). The fact that the company has a valid employment contract with the person does not matter: theoretically, the person could be on very long vacation or sick leave throughout the year and not receive any payments from the employer.
If income is paid by one individual, who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur, to another individual, then the first is not considered a tax agent (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 2, 2010 No. ШС-37-3 / [email protected] , and since then the position of the department has not changed). A typical scenario is the first individual buying an apartment or car from the second. In this case, the recipient of the income must report to the Federal Tax Service independently. Moreover, not with the help of a 2-NDFL certificate, but with the use of a 3-NDFL declaration.
Note that an individual who has received income from a tax agent, in turn, is not required to draw up a 3-NDFL declaration, just as the agent himself is not required to do this for the recipient of the income. This declaration will need to be drawn up if a person needs to apply for a tax deduction - moreover, he will have to do this himself or by contacting a specialized company. The main source of data for the declaration is the 2-NDFL certificate. At the same time, the tax agent-employer can help the employee in drawing up a “voluntary” (optional) 3-NDFL declaration, but has the right to refuse this.
The second type of 2-NDFL certificate is the one issued by the tax agent directly to the recipient of the income upon his request (for example, when he applies for a bank loan, a visa abroad, or for the purpose of filing a tax deduction). Such a request can be made as often as desired - and in all cases the employer is obliged to satisfy it within the time limits established by law.
An employee has the right to ask the employer to issue several identical 2-NDFL certificates at the same time, without explaining the reasons why they are needed.
Of course, the employer is also obliged to comply with all deadlines for submitting 2-NDFL to the tax office.
General procedure for issuing a certificate: payer code
The deadline for submitting 2-NDFL directly depends on the attribute entered in a special field of the form. It is an encrypted code that explains information about the payer and the tax to regulatory authorities. The attribute is expressed in the numbers “1” or “2”, and the deadline for submitting the document depends on which of them the employer puts in the “Attribute” field. The field for indicating the taxpayer's characteristics is located in the center of the form on the line located after the date of the certificate.
Sign “1” denotes a block of information about the amount of income of an individual and the amounts of withheld and transferred personal income tax.
Code “2” informs the Federal Tax Service that it is impossible to withhold the amount of calculated tax.
Such a distinction makes it possible for the Federal Tax Service to establish:
- The number of employees of a company or individual entrepreneur, the amount of taxable income received and the amount of accrued and withheld tax;
- The amount of personal income tax debt and the number of debtors.
How to correctly fill out 2-NDFL and calculate withheld tax
A detailed procedure for filling out the form, approved by the Federal Tax Service, is presented here.
The most problematic tasks when filling out a certificate—those that should be given special attention—are:
Filling out the fields:
- by income (the “Total amount of income” field on the Title Page - on the 1st page of the certificate, as well as the “monthly” fields in the Appendix to the certificate - on the 2nd page);
- “Tax Base” on the Title Page;
- “Tax amount calculated” on the Title Page;
- fields where data on deductions is reflected (they are available both on the Title Page and in the Appendix to the certificate).
They are all connected.
Deductions according to the 2-NDFL certificate - it is appropriate to start the story with them - are classified into 2 categories:
- Those related to standard, social and property. These deductions, in correlation with the codes established by Appendix No. 2 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] , are shown on the Title Page (and only there).
- Other. They, in correlation with the codes in the same Appendix No. 2 to Order No. MMV-7-11 / [email protected] , are shown in the Appendix to the certificate (and only there).
All amounts of both specified types of deductions are summed up, after which the resulting total is subtracted from the “Total Amount of Income” indicator. The result is recorded in the “Tax base” field.
The “Total amount of income” indicator on the Title Page must be equal to the amount of income “scheduled” monthly in the Appendix to the certificate. Income in the Appendix to the certificate is shown in relation to the codes established by Appendix No. 1 to the same order No. MMV-7-11 / [email protected]
The calculated personal income tax (the “Calculated tax amount” field) is the rate multiplied by the indicator in the “Tax base” field.
And if there were no deductions, then, obviously, the fields “Total amount of income” and “Tax base” will be equal to each other.
The amount of deductions reflected on the Title Page is not equal to the amount of deductions in the Appendix to the certificate. Moreover, both indicators are in no way related to each other, since deductions belong to different categories.
You can download deduction codes for 2-NDFL here.
Filling out the field “Tax amount withheld”
First of all, let’s say a few words about the correlation between “calculated” and “withheld” taxes. Tax is generally considered calculated when taxable income is handed over to an individual or transferred to a bank account. An exclusive rule is established regarding wages. Regardless of when the salary (in terms of the advance or the main amount) is paid out, income is considered received on the last day of the month for which the salary was accrued (clause 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, even if the employer delays wages, it is nevertheless considered the employee’s income, and tax is calculated on it. In the certificate, such income is shown in the Appendix (and affects the amount of income on the Title Page) for the month in which it is payable in accordance with the employment contract.
In general, personal income tax is withheld upon actual payment of income (clause 4 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, simultaneously with the calculation of personal income tax. But if the income is a salary, then the situation is special.
As a rule, the salary consists of 2 parts: an advance for the 1st half of the month - paid after the 15th, and the main part (for the 2nd half of the month) - paid on the first days of the next month. Both parts of the salary are considered paid on the last day of the month. This means that personal income tax on both the advance and the main part of the salary:
- calculated on the last day of the month;
- is withheld on the day of payment of the main part of the salary (since it cannot be withheld from the advance payment - due to the fact that at the time of its payment it is not yet recognized as taxable income).
Section 1
In this section, information about the individual who is the recipient of the income is filled in. Rules for filling out section. 1 are established in clauses 3.1 – 3.9 of the Procedure for filling out the form . For clarity, we present them in table form.
| Field name | Filling procedure |
| TIN in the Russian Federation | The TIN of the individual is indicated, confirming his registration with the tax authority of the Russian Federation. If the institution does not have information about the TIN of the individual receiving the income, this detail is not filled in |
| Full Name | The surname, first name and patronymic of the individual taxpayer are indicated without abbreviations, in accordance with the identity document. The patronymic may be absent if it is not reflected in the taxpayer’s identity document. For foreign citizens, the surname, first name and patronymic may be indicated in letters of the Latin alphabet |
| Taxpayer status | The number is indicated: – 1 – if the taxpayer is a tax resident of the Russian Federation (except for taxpayers carrying out employment activities in the Russian Federation on the basis of a patent); – 2 – if the taxpayer is not a tax resident of the Russian Federation; – 3 – if the taxpayer, a highly qualified specialist, is not a tax resident of the Russian Federation; – 4 – if the taxpayer, a participant in the State program to assist the voluntary resettlement of compatriots living abroad to Russia, is not a tax resident of the Russian Federation; – 5 – if the taxpayer is a foreign citizen (stateless person), recognized as a refugee or granted temporary asylum on the territory of the Russian Federation, and is not a tax resident of the Russian Federation; – 6 – if the taxpayer, a foreign citizen, carries out employment activities in Russia on the basis of a patent |
| Date of Birth | The date, serial number of the month, year are indicated by sequentially recording data in Arabic numerals |
| Citizenship (country code) | The code of the taxpayer’s country of which he is a citizen is indicated according to the All-Russian Classifier of Countries of the World (OKSM). Russia – 643. If the taxpayer does not have citizenship, the code of the country that issued the document proving his identity is entered in this field |
| Identity document code | The codes are given in Appendix 1 to the Procedure for filling out the form |
| Series and number | The details of the taxpayer’s identity document are entered without the N sign |
Sample of filling out certificate 2-NDFL for 2018
Let's look at how to apply for 2-personal income tax using an example.
Employee Stepanov V.S. During 2021, I received a salary in the amount of 610,000 rubles. At the beginning of the year, he brought a notice from the Federal Tax Service for a property deduction in the amount of 106,000 rubles. Personal income tax in the corresponding amount in 2021 was not calculated from Stepanov’s salary on the basis of this notification. In December Stepanov V.S. received financial assistance of 4,000 rubles from the employer, for which a full deduction was applied.
The example documents:
- Income
| Month | Amount of income (RUB) | Type of income | Revenue code |
| January | 40 000,00 | Salary (salary) | 2000 |
| February | 40 000,00 | ||
| March | 40 000,00 | ||
| April | 40 000,00 | ||
| May | 40 000,00 | ||
| June | 40 000,00 | ||
| July | 40 000,00 | ||
| August | 40 000,00 | ||
| September | 80 000,00 | ||
| October | 80 000,00 | ||
| November | 70 000,00 | ||
| December | 56 000,00 | ||
| 4 000,00 | Financial assistance from the employer | 2 760 | |
| Total (total income) | 610 000,00 | ||
- Deductions
| Month | Deduction amount (RUB) | Type of deduction | Legal basis for deduction | Deduction code |
| January | 106 000,00 | Property deduction | subp. 3 p. 1 art. 220 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 311 |
| February | ||||
| March | ||||
| April | ||||
| May | ||||
| June | ||||
| July | ||||
| August | ||||
| September | ||||
| October | ||||
| November | ||||
| December | ||||
| 4 000,00 | Deduction for financial assistance | clause 28 art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 503 | |
| Total | 110 000,00 | |||
You can view a sample certificate filled out in accordance with the example discussed (submitted to the Federal Tax Service) here.
Next, we will look at examples of typical mistakes when preparing a 2-NDFL certificate and consider what consequences they can lead to.
What happens if the 2-NDFL certificate is filled out incorrectly?
Despite the relatively simple structure of the help, mistakes can be made in almost any part of it. So, common mistakes:
- When filling out the field “Tax amount over-withheld by the tax agent.” The only reasons for excessive tax withholding are an accountant’s error or a software glitch, as a result of which personal income tax is deducted from an individual’s income in a larger amount than it should be. In this case, the excessively withheld amount of personal income tax must be returned to the individual (clause 1 of Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If such a return was made before submitting the certificate to the Federal Tax Service, then the field in question is not filled in. If not, fill it out and indicate the corresponding amount of personal income tax overpayment. At the same time, as soon as the return is issued, an adjustment certificate 2-NDFL must be sent to the Federal Tax Service without the completed field regarding excessive tax withholding (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 13, 2014 No. PA-4-11/15988).
- When indicating in the certificates the personal data of individuals - passport numbers, full name, INN. Passport numbers and full names tend to change - and it can be difficult for an accountant, especially at a large enterprise, to track this. A person can change his passport due to expiration date, due to its loss, change of name upon marriage, etc. The main tax identifier of an individual - TIN - never changes. But it is important not to mistakenly “attribute” the TIN of one person to another - for example, if they have similar last names and initials.
- When specifying the OKTMO code (in comparison with the code shown in the tax payment order). The certificate shows the OKTMO code: of the municipality where the tax agent-legal entity is located, or of the municipality where the tax agent-individual entrepreneur resides. The code entered in 2-NDFL and the one shown in the tax payment slip (field 105) must match, even if the tax agent has several OKTMOs. The Federal Tax Service, having discovered that the codes in the payment slip and the certificate are different, may classify the payment as uncleared receipts, and it will have to be clarified.
It should be borne in mind that absolutely any inaccuracy in the 2-NDFL certificate can become a reason for tax authorities to charge the tax agent with reporting “untrue information” and fine him 500 rubles for each certificate with an error (Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It does not matter what the error is: its importance is assessed by the tax inspector independently based on significant circumstances (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 21, 2016 No. 03-04-06/23193). The Federal Tax Service honestly admits that there are no universal criteria here, and, indeed, any mistake can be qualified as serious (letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 08/09/2016 No. GD-4-11/14515, dated 11/16/2016 No. BS-4-11/ [ email protected] ).
However, if errors in 2-personal income tax did not lead to an understatement or non-transfer of personal income tax to the budget, then the tax authorities will most likely not fine the tax agent (letter No. GD-4-11/14515). But the use of such a soft approach is the exclusive right of the tax authorities themselves. There are no guarantees here for the tax agent.
Adjustment 2-NDFL: when and how to submit?
The 2-NDFL correction certificate must be submitted on the “as soon as possible” principle. There will be no fines only if the adjustment is provided before the Federal Tax Service itself discovered the error (Clause 2 of Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But it is impossible to accurately calculate the moment of such detection.
The correction form is submitted not only if errors are detected in the certificate, but also if the data reflected in the original (previous) document changes - for example, in the case of compensation for an overpayment of personal income tax to an employee. For some changes, however, adjustment is not required: for example, if before submitting the certificate to the Federal Tax Service, the recipient of the income had one last name, and then it changed (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 29, 2017 No. GD-4-11 / [email protected] ).
There is a special subtype of adjustment for 2-personal income tax - a cancellation certificate. In it, code 99 is entered in the “adjustment” field. Such a certificate is used if the tax agent recognized that a person received income (and the subsequent calculation and withholding of tax) erroneously, as he subsequently erroneously reflected it in the primary 2-NDFL.
Of course, there will be strict sanctions against the tax agent even if he does not submit the form to the Federal Tax Service in principle or submits it late. Legal consequences are also possible if the document is not provided to the employee.