Advertising ⓘ
If you're reading this, there's a good chance that you're already thinking about starting a business. You may have looked at a few articles about e-commerce and discovered that if you want to use online payment methods, you need the right tools.
First, terms like "payment provider" can be confusing for newbies. This is especially true when many people do not seem to know the difference between a merchant account or a payment service provider - two separate entities.
Today we're going to provide the help you really need to start accepting credit and debit cards online. We'll define what a payment service provider is, how it helps you process different payment methods, and more. Let's start.
Special bank account of a paying agent: purpose and features of use
A special account is used by a paying agent to credit funds received from individuals in favor of a supplier of goods or services as part of the execution of an agency agreement. The legislation provides for a ban on the use of other accounts for this purpose, while the use of the account itself is limited (Article 4 of Law No. 103-FZ dated 06/03/2009).
The following operations are allowed on a special account:
- Crediting funds from individuals to fulfill their obligations to the supplier;
- Transferring funds from another special account of the agent;
- Debiting funds to a special account of another agent or supplier;
- Write-off of funds to current accounts - in cases established by law (for example, agent remuneration).
No other transactions are allowed on this account. Such restrictions were introduced for several reasons:
- Protecting the interests of the supplier - the agent does not have the opportunity to dispose of funds at his own discretion;
- Protecting the interests of individual payers from the actions of an unscrupulous agent in not transferring payment to the supplier;
- Control over the circulation of collected payments and their use;
- Simplification of accounting for the income of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs in terms of its allocation from the total amount of funds received by them.
Thus, legislation with the introduction of special accounts resolved many issues of both a fiscal nature and the economic and legal security of market participants.
Duration of contract with payment service providers
When evaluating your payment acceptance options, you may also need to consider how long you need to stay with your payment service provider. Being tied to a specific deal can make it difficult to change your strategy if you find a better option elsewhere.
On the plus side, with a payment service provider, you usually get a “pay as you go” experience. There is no additional cost to worry about if you decide you want to cancel your service. On the other hand, if you choose a merchant account, it is much more difficult to leave a relationship you no longer want to be in.
While the industry is evolving and more merchant accounts are giving companies much more freedom to grow and pay monthly, you get a discount if you pay for long-term accounts. Annual contracts and other costly termination or termination fees for your accounts will mean you'll have more financial worries to consider as you try to build a successful business. It's definitely a good idea to make sure you don't rush your comparisons.
Advertising ⓘ
Research what's going on in your industry and make sure you know which companies can offer you the best value in the long run. If you're still a relatively new business and aren't sure how quickly your needs will change, a monthly pricing structure may be best for you. Using this approach will allow you to switch accounts if you find something more affordable elsewhere.
Types of special bank accounts
A special account is a separate bank account in which money that is not accountable through a checking account is stored and spent. A special account is designed to separate a company's specific cash flow from the general one for the purpose of:
- spend these funds to solve specific problems, for example, a clearing account;
- separate out amounts that should not belong to the account owner, for example, a debtor's account.
Most often, the source of income for special accounts is payments from individuals or legal entities for services provided to them. The functionality of a special account is the same as that of a current bank account, but all actions with it are subject to certain rules depending on the type of account.
There are many special accounts, and their list is constantly growing. In addition to the 12 accounts listed in the Central Bank Instructions, special accounts also include those specified in various laws, for example, a special account for bankruptcy proceedings.
Select a bank for a special account
When to open account No. 40821: specific examples
First of all, you need to understand what is meant by a special account. A special bank account is an account that has a specific purpose. Its use is regulated by law and is mandatory. If we talk specifically about special account No. 40821, it is necessary for interaction with legal entities that have entered into an agreement with the supplier (online store) to carry out activities for accepting cash.
In what cases it is necessary to open an account and in what cases not, it is better to look at specific examples. If an online store has couriers on its staff, then it acts as an ordinary business entity without intermediaries. This means that invoice No. 40821 is not necessary.
Another option is also possible. Products purchased from an online store are delivered by a third-party delivery service. This service takes a certain amount from the buyer and then transfers it to the store. This means that this service can be considered an intermediary. And just in order to pay with such an intermediary (paying agent), the online store needs a special account No. 40821. It is impossible to interact with such a courier service in any alternative ways.
Electronic wallet systems (for example, PayPal and Webmoney) can also play the role of payment agents. For mutual settlements with them, you also need a special account.
And finally, online stores themselves sometimes act as intermediaries, accepting funds from customers. This happens when the goods do not belong to this online store, but to someone else. Here, the online store also needs a special account for mutual settlements with different parties (and the store must register as a paying agent).
Payment service provider vs merchant accounts
The biggest difference between a payment service provider and a merchant account is how it handles accounts. With PSP, there are multiple users in a collection, group, or sellers. On the other hand, the merchant account provider provides each merchant with their own divi dual accounts. The verification process for each merchant is also more thorough with merchant account models.
Merchant accounts also differ from payment systems in other ways. Merchant accounts are very focused on payment processing. A third-party processor, on the other hand, can provide a more complete solution for companies. In addition to the payment processor, you can access things like ordering tools and hardware.
The benefit of accepting card payments through a payment service provider is that you usually don't have to pay additional security fees. Things like PCI compliance are already available in your account.
Another big bonus of payment service providers over merchant services is that you are buying an entire platform of tools. The support an acquirer receives with a PSP is often much more comprehensive for payment processing. Tools like Square, Shopify, and Stripe all include invoicing and reporting tools, for example.
Additionally, many of these solutions come with a unique gateway that makes it easier for people to start selling online. Square and PayPal users could easily accept payments using American Express and other payment methods, while also offering things like fraud protection and loyalty options from within their payment solution.
Businesses that don't have significant budgets to spend on their accounts and points of sale can certainly benefit from a payment service provider. However, you won't get much support if you need help starting from scratch.
Important information about invoice No. 40821
Those who are going to open a special bank account No. 40821 should know the following information: in accordance with Article 86 of the Tax Code of Russia, the bank must notify the tax office of the opening, change of details and closure of special accounts for taxpayers.
Art. 86 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Accounts starting with 40821 are certainly subject to these requirements - this is clear from paragraph 2 of Article 11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. By the way, the tax inspectorate has the right to receive all the necessary information on them directly from the bank, without sending requests and notifications to the online store itself.
By the way, accounting for funds in special bank accounts is also carried out in a special way - for this purpose, there is a special account 55 in the accounting plan.
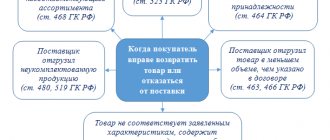
And one more interesting and significant fact. In relation to the special account of the paying agent, the bank can only carry out the following debit transactions:
- transfer of money received from end consumers to the supplier selling goods (carrying out work, providing services);
- payment for utilities and rent of premises;
- transfer to the ordinary settlement account of the paying agent of the amount of remuneration in accordance with the agreement between the agent and the supplier (online store).
That is, the list of possible operations is strictly regulated. However, there is good news: forced collection does not apply to special accounts.
Pros and cons of using a payment service
There are many reasons why you might choose to use a PSP rather than trading accounts. Payment systems are much more flexible than their counterparts. For smaller companies, you will have the freedom to change services as you wish and explore the different options that may be available to you. Pay as you go prices also mean you're not stuck with anything.
Much of the popularity associated with payment service providers stems from the fact that you get a lot of convenience for a small fee. Payment service providers are great for growing businesses and smaller businesses. You get things like payment security and various advanced tools built into your package. This means you can easily find what you need.
Also, remember that payment service providers are great for quick setup. You can fill out an application and start accepting payments almost immediately. There are no intimidating contracts to worry about or sign-up processes where you might not be accepted. Additionally, even though merchant account providers provide businesses with more options today, they still have a hard time getting their foot in the door.
So why shouldn't anyone get a PSP account?
Well, there are downsides too. As mentioned above, the payment service provider is a third party processor. There are some risks with this approach to selling. For example. It's easy to open an account, so there's a good chance someone will cancel your account if things about your purchases start to change.
Another common problem with a payment processor is that there is always a risk that something will happen to your account and you won't be able to get the support you need to get back on track. When you register for this type of account, you need to understand that your account can be suspended or deleted with little to no warning.
While there are people you can contact to find out what's going on, it often takes some time before you can get the money you're owed.
Special paying agent account: opening procedure
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are required to open this type of account, both those accepting payments in favor of third parties - suppliers, and the suppliers themselves. According to the current procedure for opening accounts in credit institutions, special accounts have a separate designation: 40821 - “Special bank account of the paying agent, bank paying agent (subagent), supplier,” which allows them to be identified when used in settlements (clause 4.43 of the “Regulations on the Chart of Accounts” accounting for credit institutions", approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on February 27, 2017 No. 579-P).
This type of account can be opened in any bank, but in most cases there is a requirement that it is opened only in the credit institution where the agent or supplier has a valid current account.
To open an account with the bank, you must provide an application in the prescribed form and attach to it a copy of the agency agreement with the supplier or other paying agent, as well as a standard package of documents that is used to open a simple current account. After checking the submitted documents, the account will be opened - on average it takes 2-3 days.
The agreement on a special account provides for the obligation of the agent to promptly inform the bank about the termination of the agreement with the supplier, or about the conclusion of new agreements both with previous counterparties for accepting payments and with new ones. In addition, the agent is obliged to notify the credit institution of the termination of activities for accepting payments in favor of third parties.
Accounts for bank payment agents are opened in a similar manner with the only difference being that instead of an agency agreement with a supplier, it is necessary to submit an agency agreement with a money transfer operator or another bank payment agent.
Note that in most Russian banks, opening an account for 40821 paying agents involves high tariffs. Credit institutions explain this by the fact that the activities of payment acceptance agents carry many risks for the bank and high tariffs partially protect them from possible fraudulent schemes.
Problems with using payment systems
Using a PSP to service payment card services provides many benefits, from PCI DSS to other advanced features for online transactions. However, the PSP also has its disadvantages. For example, you don't get much customer service to help with your online transactions. You can deal with the issuing bank if you have direct banking problems. However, there are not many ways to get help from your PSP.
Some payment systems provide technical resources so you can find your own answers to questions about global payments or chargebacks, for example. However, your aggregator will not be able to help you. There may be a need to do a lot of Google searching.
On the other hand, with a merchant account, you get much more support with credit card processing features. Because trading accounts are designed to support divivid dual users, you receive more personalized support.
Another downside of the PSP is how easy it is to get an account. While it may sound great that you can set up an account immediately, it also means that you have a higher risk of someone suddenly canceling or blocking your account if something goes wrong. The additional verification process you go through with a merchant account may seem annoying, but it increases your chances of staying on top of your account.
Merchant accounts give you the benefit of the doubt when something changes in your account. On the other hand, with a payment service provider, if you suddenly changed a large credit card transaction or something else made you look suspicious, your account would often be frozen instantly. Since there are not many people around who can help you, if something goes wrong, you will have to struggle alone.
There is a risk that once your account is frozen, you may have to wait a few weeks before you can set everything up again.
How much does a payment service provider cost?
One of the first things many business owners will look at when using online payment providers is how much the account will cost. Things can get tricky at this point because the best solution for your business may not be the same as for every other business owner you know. Fees will depend on the size of your company, the average transactions you need to process, and so on.
Pricing for a merchant account or PSP can sometimes go against you when you consider factors such as price per transaction, volume of business, compliance fees, hardware costs, etc. The pricing structure of a merchant account also needs mentioning.
Most payment service providers use a single rate structure for pricing. Essentially, this ensures that you pay the same amount for every transaction, regardless of card type. There are no monthly fees to worry about, and other costs other than transactional ones are generally non-existent.
In some cases, transaction prices are deducted from each transaction in a simple strategy to help small business owners manage expenses. Large companies also benefit from the payment service provider's fixed pricing structure.
The costs that are often associated with using a primary trading account can be much more difficult to understand. This is why business leaders take a lot of time to properly review the terms and conditions of their services.
With a merchant account you may need to pay the following structures:
- Interchange-plus Basically this means that your payment processor delivers the card network's interchange fees to you along with a small markup.
- Subscription Cost : With this strategy, merchants pay a monthly fee for their trading account membership. There is also another small fee to pay with transactions too. This cost often comes at a flat rate, making it easier to budget for.
- Tiered Pricing : Transactions here are often grouped into unqualified and qualified categories, with qualified transactions costing less. This model often simplifies payment processing and results in merchants paying more in the long run.
In addition to the basic costs, pricing structures may also include other additional fees, such as PCI compliance costs to ensure the security of your payment system and reporting fees. If you're a small company and don't spend a lot of money, you'll typically get a much cheaper experience by working with a payment service provider. On the other hand, if you make a lot of money every month from your company and need additional support, then a merchant account provider may be your best option.
Bank payment agent or subagent account
You must open this special account if you take on part of the banking functions, for example, loan payments. Namely, on behalf of the bank you accept payments from individuals. persons (including using self-service devices), give them cash or provide electronic means of payment.
Available operations on this account:
- crediting cash received from individuals. persons;
- accepting non-cash transfers from special accounts of operators;
- transfers to recipient accounts.
You can open several such special accounts in any banks.
Payment system guarantee fund account
Banks working with payment systems, for example, MIR, must form a special fund from personal contributions to a separate account (to cover possible risks). For this purpose, the payment system operator opens a payment system guarantee fund account. He also sets the size of the transfers. If the bank stops working with the payment system, its payment is returned.
Such special accounts can only be located in banks or non-banking organizations that do not have the right to place raised money to generate income, for example, in the Central Bank. Accounts are not subject to seizures, restrictions or penalties due to debts of the operator or system participants.
We recommend: Rating of banks by cash settlement services for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities with customer reviews.
What about card network prices?
There's another cost you need to think about when you're setting up your business with the right payment provider. Card brand networks act as an intermediary between the issuing bank and the service provider. There are credit card associations and PIN-free networks.
Every business that needs to accept credit and debit cards will need a service to process those payments. Some of these connections require additional third-party payment gateways, which result in increased fees. Payment gateways offer a point of communication between point-of-sale systems and platforms. Gateways, on the other hand, offer connectivity options for businesses that want access to a payment processor that suits them.
Gateways are a suitable option for a wide range of in-store and online business configurations. Payment services are often included as part of a broader selection of services. Some e-commerce platform providers also provide you with support for the payment processor you want to use.
There are also independent merchant organizations that work with payment providers to handle trade relationships. These companies resell services and products from payment processors and service providers. ISOs also receive commissions from the processors they sign up merchants to.
Another option is to work with a value-added reseller, which works in partnership with one or more payment processors to provide services to merchants. VARs offer additional features that complement payment processing options such as point-of-sale hardware, inventory management, etc.
Finally, banks also play a role in your system's overall costs. The issuing bank will deliver the credit or debit card to your consumers. In addition, acquiring banks process credit and debit payments for merchants. You will need to enter into an agreement with an acquiring bank with your merchant account or through a payment service provider.
Escrow account
To insure against the risk of non-payment when concluding an agreement for the supply of products/provision of services, you can use an escrow account. The work flow is as follows:
- The buyer opens a special account and deposits the agreement amount into it.
- The bank is blocking the money.
- The seller fully fulfills its obligations.
- The money is transferred in his favor.
If the terms of the transaction are violated, the money is transferred back to the buyer. Unless otherwise agreed, neither party can dispose of the account.