Skip to content Kontur.Partner
PRACTICAL ACCOUNTING, TAXES, PERSONNEL
8-800-551-36-30
Free call within Russia
10/14/2018 Lara Bodrova Question and answer
An invoice is the main document for VAT accounting, on the basis of which deductions are made. Therefore, it is extremely important for all payers of this tax to know the subtleties associated with its preparation and recording. Our material today contains a selection of explanations from officials about invoices.
What form of document should I use for correction?
The accountant found out that changes need to be made to the invoice. But at the time of drawing up the initial document, one form was approved, and now another is in effect. Which one should I use to fix it?
To correct in this case, you need to use the old invoice form, that is, the one that was valid on the date of the original document. This explanation was given by Federal Tax Service officials in a letter dated 06/07/2018 No. SD-3-3/ [email protected] The conclusions are based on the instructions for filling out an invoice from Government Resolution No. 1137 dated 12/26/2011. It says that corrections to the invoice are made on the date of their preparation.
When should I issue an invoice for a rental?
Can invoices be issued when renting a property during the period for which the fee is charged? And when should such a document be reflected in the sales book?
Providing for rent - this provision is disclosed in paragraph 5 of Article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is an activity whose results are consumed in the process of providing it.
An invoice for the service should be issued no later than 5 days from the date of its provision (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), that is, after the service is provided. Therefore, issuing an invoice before the end of the rental month is incorrect. But you can generate a document on the last day of the month - this is not a violation. At the same time, the lessor must reflect the invoice in the sales book in the tax period when the tax liability arose.
Such explanations are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 06/05/2018 No. 03-07-09/38397.
Kinds
There are three main types of invoice:
- ordinary, shipping. This document confirms that the goods have been transferred. This is the most common type of invoice, but legislation provides for more than just one;
- advance payment, written out and drawn up upon concluding a contract and receiving an advance payment for work performed or services rendered. This form does not confirm the fact of transfer;
- adjustment, filled in when the price or quantity of shipped products changes.
Is it a violation if there is no individual entrepreneur status on the invoice?
The invoice indicates the name of the buyer - an individual entrepreneur, but does not indicate his status as an individual entrepreneur. Is this a violation? And is it possible to claim VAT deduction on such a document?
The response of the Ministry of Finance is in letter dated 05/07/2018 No. 03-07-14/30461. On the one hand, the invoice must contain mandatory details, including the full or abbreviated name of the buyer in accordance with the documents . That is, there is an error.
On the other hand, according to paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , not every error makes an invoice invalid and prevents VAT from being deducted. In particular, if an error allows one to identify the parties to a transaction, then it should not be a basis for refusing a deduction.
Conclusion : an invoice that contains the buyer’s full name without indicating his status as an individual entrepreneur is not considered to have been drawn up in violation.
Online training in accounting and 1C 8. Document invoice is
DocumentDocument invoice is
Good day! Today I want to talk to you about what an account is, and not a current account, a personal account, a deposit account or something else. The topic of the article today is business accounts.
I’ll say right away that 99% of businesses use invoices, these can be invoices from suppliers to pay for goods you ordered, or vice versa, for example, an invoice issued by you for services provided.
What is an account
As always, I will not write standard descriptions, but will try to explain everything in my own words.
The first thing you need to understand is that an invoice is an internal document of the organization and there is no need to submit and report on it to anyone; for reporting there are invoices and invoices.
The invoice indicates the payment details of the organization that issues it, as well as the goods or types of work for which the invoice is issued. In addition to the seller's payment information, the invoice also contains the buyer's information. In order to prepare an invoice, you must request a company card from the new partner.
The invoice can be made on the organization's letterhead or be standard; this is not important and simply depends on the organization itself. It must have a seal (if any) and the signature of the manager and chief accountant.
The main purpose of the invoice is to indicate to the buyer the details of the current account for payment by the buyer.
Account validity period
Since the invoice is an internal document of the organization, its validity period is determined by the seller himself (entrepreneur or director of the organization).
In general, the standard account validity period is 3 days. It is believed that during this time there cannot be any significant changes in the cost of goods or services for which this invoice is issued.
Sample invoice for payment
I will post one of my organization’s invoices so you can see it live:
How to issue an invoice for payment
If you sell something or provide services to legal entities or entrepreneurs, as a rule they make payment by bank transfer (from their current account).
It is for this that you will need to issue an invoice for payment with your details.
In fact, you can also pay your invoice in cash, but in this case the essence of issuing an invoice is lost.
There are many ways to issue an invoice:
- Account form. You can simply download a blank invoice form from the Internet in EXEL or PDF format and enter all the data there manually (I once did this myself, about 10 years ago), this method of issuing an invoice is simply a relic of the past, and if you seriously decide to do business, then this method will not work;
- Using free programs. There are many free programs and services on the Internet for creating invoices; if you issue invoices very rarely, then this method is quite suitable. I will not specifically make any links so as not to advertise to anyone;
- Using paid programs. As you probably know, there are paid programs for accounting, the most common and simple in my opinion are programs from 1C. With the help of these programs, you can completely automate your business from the accounting department. Invoices in these programs are generated almost automatically. In general, I recommend it, especially if you need to issue invoices regularly. Just choose what suits you best, since the range of 1C accounting programs is quite wide.
Is it possible to deduct an invoice issued late?
The invoice must be issued no later than 5 days from the date of shipment of goods, performance of work, provision of services. What if the seller completed the document later than the deadline? Is it possible to deduct VAT on this basis?
The Ministry of Finance answers this question positively (letter dated April 25, 2018 No. 03-07-09/28071). The rationale is the same as in the previous question. That is, the fact that the invoice was issued late does not prevent us from identifying the important parameters of this document. Namely:
- buyer and seller;
- the object of the transaction and its value;
- rate and amount of VAT.
Therefore, the buyer can deduct VAT on an invoice issued after the five-day period.
Why is an invoice required?
The invoice does not have a strictly regulated form, but it is of great importance in the relationship between the seller and the buyer.
When issuing an invoice, you must provide the following information:
- seller details;
- buyer details;
- subject of the transaction (name, quantity, cost);
- details of the agreement on the basis of which the invoice for payment was issued;
- serial number;
- date of document generation.
In addition to the specified information, the invoice may contain the following information:
- the exchange rate on the basis of which the invoice was issued;
- due date;
- conditions under which the paid goods will be shipped to the buyer.
Thus, an invoice for payment is a document, guided by which the buyer pays for goods, work, or services. The transfer of goods is most often carried out after payment of the invoice.
How do I register a late invoice?
The supplier issued the invoice late, in particular, after the end of the tax period to which the transaction related. How can an intermediary record this document in the journal of received and issued invoices?
The Ministry of Finance responded to the question in a letter dated April 26, 2018 No. 03-07-09/28450. Based on the provisions of the instructions from Resolution No. 1137 , officials came to the conclusion: if in the current period it is discovered that there is no entry in the journal about an invoice that was received in the past period, then such an entry must be made in a new line of the journal for that period in in which the document was drawn up. The rule applies to both the original and adjustment invoices.
Best Invoice Designs to Inspire You
If you think that documents are not a place for creativity, then we are ready to demonstrate examples of invoices where the numbers work well together and have an interesting design. Check out some interesting accounts to get inspired to create your own.
Source: by Dawar Mir
Source: by Michael Cullinan
Source: by Pontus Börjesson
Source: by Social Media Templates
Source: by PANTER
Source: by Michael Volkwijn
Source: by Dario Vaccaro
Source: by Charlie Bob Gordon
Source: Stefan Devai
Source: by Ben Dixon
Source: by Samuel Nudds
Source: by Omega Labs
The technological process simplifies everything. And if recently this simplification was called a calculator, now even this is not needed for accounting calculations. After all, now online tools can automatically carry out all the calculations based on your documentation. Therefore, draw up invoices for each transaction and conduct your affairs competently.
Published byNatalia Shpitula Updated May 24, 2021 Posted inHow To, Tools and services
Blog editor at Logaster, content marketer. Web marketing and branding expert. He knows how to write simply about complex things. Using her articles, you can build a successful brand and start successful promotion on the Internet.
Can I claim a deduction if there is a mistake in the address?
Quite a lot of questions are related to inaccurate spelling of addresses on invoices. How to correctly indicate the address? And is it possible to claim a deduction if it is written in violation?
In response to such questions, the Ministry of Finance, in letter dated April 25, 2018 No. 03-07-14/27843, reports the following. According to the rules, the address must match the one indicated in the state register of legal entities or individual entrepreneurs. However, many address errors do not prevent VAT from being deducted.
In particular, an invoice containing abbreviations, for example, “g” instead of “city”, “d” instead of “house”, and so on, will not be considered incorrect. Moreover, the words “house”, “street” and other similar ones may be completely absent - such an error will not be considered critical. It’s also not scary if the document contains an abbreviation of this type - instead of “Bolshaya Dmitrovka,” “Dmitrovka B.” is indicated. And finally, the fact that the address is written in lowercase or lowercase and uppercase instead of capital letters will not affect the deduction. All these inaccuracies do not require correction of the invoice.
ASK VAT invoice
Definition of each concept
- An invoice is an accounting document certifying the actual shipment of goods or provision of services and their cost. Issued by the seller of goods (works, services), who, in accordance with the Legislation of the Russian Federation, is responsible for paying VAT to the budget. Serves as a basis for the buyer to accept for deduction the VAT presented by the seller of goods (works, services) and property rights (clause 1).
- An invoice is a document containing the seller’s payment details, which gives the buyer grounds to pay for the purchased goods (works, services).
Check
A document containing the details of the supplier, seller, including bank details, a list of goods and services, work to be paid. The payment amount is calculated in the tabular part of the invoice, in accordance with the agreed prices and volumes.
An invoice is an optional document, but it is used everywhere in business because it allows:
- monitor the fulfillment of contractual obligations by the parties;
- make correct payments to the supplier;
- track changes in essential details of the counterparty, avoiding errors in accounting data.
The invoice is issued:
- for the amount of delivery already made;
- for the amount of the advance payment.
An invoice may itself constitute an offer. Acceptance of the invoice means that the contract between the parties is concluded. Most often, acceptance is expressed in payment of the invoice. (Chapter 28 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 438, 435-432).
In order for an invoice to be recognized as an offer, it must include essential data inherent in contracts as such. A properly executed invoice can serve as evidence of contractual relations in controversial situations, including litigation.
The terms according to which invoices are issued are fixed in the contract. The form of the invoice for payment is not strictly regulated, and does not have a unified form that is mandatory for use.
Typically the document contains the following details:
- name of the supplier (organization or individual entrepreneur), usually in full form;
- full legal address;
- full actual address at which the counterparty operates;
- TIN and KPP - for an organization, TIN - for an entrepreneur;
- number, date;
- bank details used to make the payment;
- basis for payment: details of the contract or name of goods, works, services;
- amount to be paid;
- payment deadline, invoice validity period;
- name and full name of the responsible persons, including the head of the company, individual entrepreneur, chief accountant, executor directly preparing the account, their contacts and signatures.
The invoice contains an indication of the supplier's tax treatment. For example, organizations using OSNO must highlight and indicate the amount of VAT in calculations, and counterparties using special tax regimes make an appropriate note about this in the invoice. The invoice can be issued either for payment by bank transfer or for cash.
Why is an invoice required?
The invoice does not have a strictly regulated form, but it is of great importance in the relationship between the seller and the buyer.
When issuing an invoice, you must provide the following information:
- seller details;
- buyer details;
- subject of the transaction (name, quantity, cost);
- details of the agreement on the basis of which the invoice for payment was issued;
- serial number;
- date of document generation.
In addition to the specified information, the invoice may contain the following information:
- the exchange rate on the basis of which the invoice was issued;
- due date;
- conditions under which the paid goods will be shipped to the buyer.
Thus, an invoice for payment is a document, guided by which the buyer pays for goods, work, or services. The transfer of goods is most often carried out after payment of the invoice.
Invoice
A document closely related to the application of OSNO and VAT calculations. Based on the invoice, VAT is accepted for deduction in the amount presented by the seller (Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 169-1). The buyer has no right to claim tax deduction in the absence of this document. The invoice must be issued strictly within the framework established by law, otherwise the tax authorities may consider the amount of VAT deductible to be unlawful.
Attention! The electronic version of the document is valid only if transmitted via electronic communication channels using a qualified digital signature.
The invoice contains the following details:
- date and account number;
- corrections (if made, the details for making corrections are indicated, if not, a dash);
- TIN and addresses of counterparties;
- consignor and consignee (if the data matches the data of the buyer and seller, indicate “the same person”);
- payment document, if there was a transaction with prepayment;
- government contract, if any;
- document currency with encoding;
- name of the goods, works, services, property rights that are the subject of settlements;
- units of measurement, volumes;
- price without tax;
- amount without tax;
- excise taxes, if we are talking about excisable goods;
- value added tax rate;
- cost calculation of VAT charged to the buyer;
- invoice amount plus tax;
- product type code – for products exported to the countries of the Eurasian Union (EAEU).
Attention! EAEU countries – Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Armenia. If there are no contracts with these countries, a dash is placed in column 1a of the invoice (see Government Decree No. 981 dated 19-08-17).
A group of details characterizing goods produced outside of Russia and cleared customs for use in the economic zone of the Kaliningrad region:
- foreign country code;
- its name;
- TD registration number.
Attention! If the product was manufactured in Russia, dashes should be placed in columns 10 and 10a. At the same time, it is not prohibited to put the code of Russia (643) and the name of the country (see letter from the Ministry of Finance dated 10-01-13 No. 03-07-13/01-01). If the goods are not produced in Russia, but are subsequently divided for sale in such a way that the country of origin of its individual batches cannot be determined, then the country of origin and the customs declaration in the invoice are not filled out (see letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 27-11-17 No. 03-07 -09/78220).
There are a number of points to consider when working with invoices:
- If services appear in the document, a dash is placed in the information about the sender and recipient of the cargo.
- When filling out the document, they write “without excise tax”, similarly - if the product is not excisable.
- Names of goods, works, etc. in the contract and in the invoice must match.
- The document is issued on the day of delivery or no later than 5 days after.
- Addresses of counterparties are entered in exactly the same way as they are recorded in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRIP). If a different address is indicated in the contract, it is written down in additional lines (letter of the Ministry of Finance 21-12-17 No. 03-07-09/85517).
- All invoices, regardless of their type (including advance, adjustment), are accounted for chronologically and not separately. For convenience, you can enter alphabetic characters into the account number.
- The document is signed by the head of the organization, individual entrepreneur, chief accountant or their authorized representatives.
Attention! The rights of authorized persons and the legality of their signatures must be formalized by a power of attorney or order if we are talking about an organization and a single power of attorney if the authorized person represents an individual entrepreneur.
Who should issue an invoice?
When selling goods, services, works, etc. primary documentation is required.
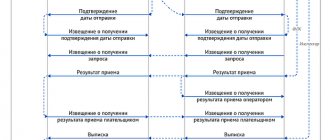
So, according to invoices, they are issued under certain conditions:
| Conditions for issuing an invoice | Invoice deadline |
| No later than five calendar days, counting from the day:
|
Why is an invoice needed?
In accordance with this, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the buyer to accept the goods (work, services), property rights presented by the seller (including the commission agent, agent who sells goods (work, services), property rights on their own behalf) tax amounts to deduction.
In other words, VAT can be deducted only on the basis of an invoice. Neither an invoice, nor a delivery note, nor a cash receipt, nor other documents serve as the basis for issuing a tax deduction.
The form for providing an invoice can be:
- in paper form;
- in electronic form (by mutual agreement of the parties to the transaction and if these parties have compatible technical means and capabilities for receiving and processing these invoices).
In the event of an error in invoices, which does not prevent the tax authorities from conducting a tax audit, identifying:
- seller;
- buyer of goods (works, services);
- property rights;
- name of goods (works, services);
- price;
- tax rate;
- the amount of tax presented to the buyer is not a basis for refusing to accept tax amounts for deduction.
The invoice issued for the sale of goods (work, services), transfer of property rights must indicate:
- serial number and date of invoice;
- name, address and identification numbers of the taxpayer (tax agent) and the buyer;
- name and address of the shipper and consignee;
- number of the payment and settlement document in case of receiving advance or other payments for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
- name of the goods supplied (shipped) (description of work performed, services provided) and unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it);
- quantity (volume) of goods (works, services) supplied (shipped) according to the invoice based on the units of measurement accepted for it (if it is possible to indicate them);
- name of currency;
- identifier of the government contract, agreement (agreement) (if any);
- price (tariff) per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) under the agreement (contract) excluding tax, and in the case of applying state regulated prices (tariffs) that include tax, taking into account the amount of tax;
- the cost of goods (work, services), property rights for the entire quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights without tax;
- the amount of excise duty on excisable goods;
- tax rate;
- the amount of tax imposed on the buyer of goods (works, services), property rights, determined based on the applicable tax rates;
- the cost of the total quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, taking into account the amount of tax;
- country of origin of the goods;
- Number of customs declaration;
- code of the type of product in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the Eurasian Economic Union.
The invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization.
When issuing an invoice by an individual entrepreneur, the invoice is signed by the individual entrepreneur or another person authorized by a power of attorney on behalf of the individual entrepreneur, indicating the details of the state registration certificate of this individual entrepreneur.
An invoice drawn up in electronic form is signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature of the head of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization or individual entrepreneur.
According to this, when selling goods (works, services) by taxpayers who are exempt from fulfilling their duties as a taxpayer, invoices are drawn up without allocating the corresponding tax amounts. In this case, the corresponding inscription or stamp “Without tax (VAT)” is made on these documents .
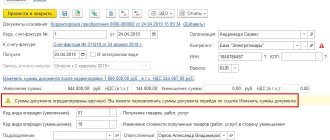
When issuing an invoice, the seller makes the following accounting entry:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation |
| 90.3 | 68/VAT | VAT calculation |
The buyer paying VAT, based on the received invoice, makes the following accounting entries:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation |
| 19 | 60.1 | Input VAT |
| 68/VAT | 19 | Tax deduction statement |
Procedure for filling out an invoice
The invoice contains information about the name and details of the seller and buyer, the list of goods or services, their price, value, VAT rate and amount, and other indicators.
Line (1) indicates the date of the invoice and its serial number.
Lines (2), (2a), (2b), (6), (6a), (6b) indicate the name, address of the seller and buyer, their tax identification number and checkpoint. Names and addresses are given in accordance with the constituent documents of the seller and buyer. In this case, names can be indicated both full and abbreviated.
Lines (3), (4) indicate the name and postal address of the consignor and consignee of the goods. If the goods are shipped by the seller himself, then in line 3 you can write “He.” If the invoice is compiled for works (services), a dash is placed in these lines.
Line (5) indicates the number and date of the payment document if an advance was received for the supply. If the advance was not monetary, then a dash is added.
Line (7) indicates the name of the payment currency and its digital code according to OKV.
In the tabular part, you need to fill in the following columns sequentially:
Column 1 indicates the name of the goods (description of work, services), as indicated in the contract (invoice, act).
Columns 2, 2a, 3, 4 indicate the code and national designation of the unit of measurement of goods (work, services) according to OKEI, the quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) and the price per unit of measurement excluding VAT.
In this case, dashes are placed in these columns:
- if the contract provides for a unit of measurement that is not in Section. 1 or sec. 2 in OKEY;
— if the contract does not specify a unit of measurement, for example, when implementing works (services);
— if the unit of measurement cannot be specified, for example, when renting or leasing.
Column 6 reads:
- if the sale of goods is not subject to excise tax - “without excise tax”;
- if the sale of goods is subject to excise tax - the amount of excise tax.
Columns 7, 8 indicate the tax rate (0%, 10%, 18%, 10/110, 18/118, “excluding VAT”) and the amount of VAT presented to the buyer. The VAT amount must be indicated in rubles and kopecks - it cannot be rounded.
Columns 5, 9 indicate the total cost of goods (work, services) supplied according to the invoice without VAT and including VAT.
Columns 10, 10a, 11 are filled in only when selling imported goods. When selling imported goods, these columns indicate the digital code and short name of the country of origin of the goods according to OKSM and the number of the customs declaration under which the shipped goods were imported into the territory of the Russian Federation. If the organization resells imported goods, then these columns indicate information from the supplier’s invoice.
In this case, dashes are placed in columns 10 - 11:
— if Russian-made goods are shipped;
- if the invoice of the supplier from whom the imported goods was purchased does not contain the necessary information.
The invoice is signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant (or other persons authorized by a power of attorney or by order of the head).
An invoice drawn up on paper can be filled out on a computer or by hand, or partly on a computer and partly by hand.
VAT and invoice
When paying for the transaction, the seller is charged value added tax. It is the document that we consider (invoice), as confirmation of VAT payment, that is registered by the buyer in a special book. Based on this document, he fills in the corresponding indicators in the VAT return. According to the law, the buyer has the right to a tax deduction under this taxation article (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), if everything is completed correctly and accurately.
There are situations when VAT is not charged, for example, for entrepreneurs working under the simplified tax system. But often the buyer, despite this circumstance, asks for an invoice, even without VAT. This is not the seller’s responsibility, but sometimes it is still worth meeting the buyer’s request and issuing an invoice, just indicate in the document that it is without value added tax, without filling out the corresponding line of the form.
IMPORTANT! If you are not a VAT payer, you should not indicate a 0% rate on your invoice instead. Even zero percent shows the real rate to which you are not entitled in this case. Specifying a rate that does not correspond to reality can create many problems for the recipient of the document, starting with a fine and ending with the accrual of the standard 18% rate.
Types of invoices found in accounting
There are only two of them. The first is called the standard SF. It is created when a shipment has been shipped or work has been completed for which the buyer now owes money. It is necessary when the products are fully paid for. Time for preparation and sending is 5 calendar days from the date of transfer. The same is given if the products were returned back to the supplier.
The second type is advance payment. It should be prepared if prepayment is required or has been credited to the account for future shipments. Here you do not need to fill out fields such as:
- shipper;
- cargo receiver;
- volume of goods or services received;
- units in which everything will be measured.
But be sure to include everything that will be needed later for calculations.
In what cases is an invoice not needed?
There are situations when issuing an invoice is not necessary, and the transaction is confirmed by other documents: an invoice for payment, invoices, etc. You don’t have to worry about an invoice if:
- the transaction is not subject to VAT (Articles 149, 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the enterprise sells goods to individuals at retail for “cash” (for such transactions, a strict reporting form or a receipt from the cash register is sufficient);
- entrepreneurs are under special tax regimes (simplified taxation, imputation, unified agricultural tax, have a patent);
- a legal entity gives the goods to its employee free of charge (based on letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 8, 2021 No. 03-07-09/6171);
- delivery of goods is planned, and an advance has been received for it (in this case, this product is produced no longer than six months, or the buyer does not pay VAT, or the transaction has a zero rate for this tax, for example, the product is being exported).
Invoice: what are the characteristic differences of this document?
To understand how an invoice differs from an invoice, you need to have a clear understanding of exactly what characteristics are inherent in each of the documents in question. We will begin this review with an invoice - a document, all aspects of the use of which are regulated by law:
- Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation>;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137>;
- clarifications from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
The invoice serves as the basis for accepting VAT as deductions. The absence of this document makes it impossible to exercise this right.
The preparers of the invoice are:
- sellers of goods (works, services) carrying out transactions subject to VAT;
- tax agents.
There are three types of this document, the use of each of which is determined by the situation requiring its execution:
- for sale - it is compiled when selling goods (performing work, providing services) or transferring property rights;
- for advance payment - it is applied when the seller receives an advance payment from the buyer;
- adjustment - is compiled when there are changes in the cost or volume of shipped goods.
Each type has a set of required details and design features. But there are only two approved forms of forms:
- main (regular) - documents are generated on it for sales and when receiving advances, taking into account the presence of special requirements for preparation valid for these two situations;
- adjustment - it is used if changes need to be made to an already issued original document regarding changes in price or quantity shipped.
Prices and values in the invoice may be reflected in foreign currency if this meets the conditions of the transaction.
The document can be drawn up either on paper or electronically. In the latter case, it must be signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature of an authorized person.
More materials on the topic
Electronic document management of invoices: new requirements
17.05.2021
Changes to the invoice form
14.05.2021
Explanations of the court on the issue of obtaining a VAT deduction using a “fax” invoice
12.05.2021
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Reporting
- FTS 2-NDFL
- Certificate of income
- 6-NDFL
- Declaration according to the simplified tax system (income-expenses)
- Declaration according to the simplified tax system (income)
- Information about the average salary
- VAT declaration
- Declaration on UTII
- Declaration on Unified Agricultural Tax
- Single (simplified) declaration
- Income tax
- Property tax
- Calculation of insurance premiums
- Form 1. Balance
- SZV-STAZH
- 4-FSS
Last thing
Zero reporting
05/20/2021 Vladlena Vladlena
Do I need to submit zero reporting? Zero reporting of LLC on the simplified tax system and OSNO. Penalties for failure to submit zero reports.
Read more
Most read
- 3-NDFL sample filling
- Employee income certificate for social security: how to prepare
- Form SZV-TD: instructions for filling out
- Form SZV-KORR in 2021 - instructions and examples of filling out
- Guide to filling out the 2021 DAM form
- For a beginning individual entrepreneur: what documents do you need to document business transactions?
- Are you late with the delivery of SZV-M? Find out how to avoid a fine
- 2-NDFL for 2021 - sample filling
- Property tax return for 2021
- A complete list of industries most affected by coronavirus infection
Themes
2-NDFL 6-NDFL ASK VAT Restoration of VAT On-site inspection Deduction of VAT EAEU UTII Wages Foreign companies Desk audit Kontur.Extern Minimum wage SME VAT VAT 0% Personal Tax Taxes Property tax Income tax Violations Wages Reporting PSN Pension Fund Pension contributions Check of counterparties DAM VAT calculation Self-employed Insurance contributions Work book Labor relations USN Tax payment Federal Tax Service Federal Tax Service VAT return VAT calculation VAT taxation letter from the Ministry of Finance letter from the Federal Tax Service invoice electronic reporting
Contour.VAT+
The “VAT+” module in the Kontur.Extern system allows you to reduce risks at every stage of working with VAT: assess the reliability of counterparties, eliminate errors and discrepancies in data, correctly prepare a declaration in consultation with experts, and quickly respond to the Federal Tax Service’s request for clarification.
Menu
- News
- Articles
- Legislation
- Question answer
- Site Map
- Extern
- VAT+
- EP for service stations
Search
Relevance
The 2021 sample invoice is a transfer document that must be drawn up taking into account the above rules. It must take into account changes made since 10/01/2017.
Let's summarize: invoice - what is it in simple words? In short, this is confirmation of payment and payment of VAT. There are peculiarities of filling out this form, advance or corrective, but the essence does not change. It is in this form that there are signatures of authorized persons who actually confirm the execution of the contract. Therefore, this is an extremely important document that it is advisable to include in contractual obligations. Payers on the general taxation system will also need proof of payment of value added tax.