To organize his business activity, if retail trade is chosen as its activity, an entrepreneur has many ways. He does not necessarily need to rent a large retail space or buy a tent or kiosk. A merchant can sell his products directly from the warehouse, having in his own arsenal several couriers who will deliver them according to orders. In the event that trade is carried out without a specialized point of sale, then the code applied to it is OKVED 47.99 .
What are the consequences of the decisions “the more codes, the better” and “if there’s anything, I’ll add it later”
Such options are often offered in various instructions for determining OKVED codes. They can be guided, but wisely.
How many OKVED codes can you choose? As many as you like - there are no restrictions. But acting “in reserve”, it would be nice to make sure that additional codes will not become an obstacle to choosing a preferential tax regime, that due to them the contribution rates will not increase or that you will not have to issue a license.
Relying on the ability to add the necessary codes later is also not always justified. If you do not yet conduct activities whose code is not registered, that’s one thing. But if the situation is the opposite, problems are possible:
- Exactly the same consequences may occur as if the activity does not comply with the declared OKVED codes (the next section of the article is devoted to them).
- Adding new codes may lead to the need to reconsider an already established business model. It happens that changes have been made, but it turns out that now you can’t use the preferential tax regime. For example, a newly registered individual entrepreneur provides household services to the population without hiring employees and enjoys tax holidays for two years after registration. If he begins to provide services to legal entities, he will lose the right to tax holidays. It also happens that due to changes it is necessary to increase the size of the authorized capital (for example, in the retail trade of alcoholic beverages, each subject of the Federation sets its own), but the owners do not give consent, or the company does not have the resources. Or a new registered type of activity requires obtaining a license or changing the status of an individual entrepreneur to a legal entity, but funds have not been allocated for this. For example, an individual entrepreneur does not have the right to engage in the production and sale of alcoholic beverages, or organize and conduct gambling.
Which OKVED code to choose
You can select one or more OKVED codes. If there are several codes, one should be defined as the main one (indicated first), and the rest - additional. The main activity is considered to be the type of activity that occupies (will occupy) the main place in the volume of work, services, production, sales or brings (will bring) the greatest profit.
Code definition scheme:
- We determine what we want (plan) to do.
- We open the classifier where you can select OKVED codes. Let's look or.
- We choose which field of activity (section of OKVED) our direction belongs to. Sections are designated in the classifier by the Latin letters A, B, C, and so on.
- In the appropriate section of OKVED we select a suitable grouping, in this grouping - a suitable subgroup, and in it - a suitable type of activity, the digital designation of which will be the code.
Let's say you want to open a retail grocery store. Find in OKVED section G “Wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles.” Since you don’t plan to trade in cars and motorcycles, choose group 47 “Retail trade, except trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles.”
It remains to determine the codes. If the assortment is wide or you have not yet decided, you need to choose codes for both a non-specialized and a specialized store. You can limit yourself to the following codes:
- main
- 47.11 (food products and tobacco products) - additional:
- 47.21 (fruits and vegetables)
- 47.22 (meat and meat products)
- 47.23 (fish, crustaceans and molluscs)
- 47.24 (bread, bakery and confectionery products)
- 47.25 (drinks)
- 47.26 (tobacco products)
- 47.29 (food products).
In addition, if appropriate for the planned activity, codes can be included:
- 47.81 (retail trade in non-stationary retail facilities and markets of food products, drinks and tobacco products)
- 47.89 (retail trade in non-stationary retail facilities and markets of other goods)
- 47.91.2 (retail trade via the Internet)
- 47.99 (other retail trade outside shops, stalls and markets)
- 47.99.2 (trading through machines).
Didn't find an exact match in the classifier? Look for the option that suits you best. There may be several of them, even in different sections and groups. In this case, you can indicate all suitable options (codes) or stop at some.
Don't have the time or desire to understand the classifier? Order the “Registration or LLC” service in Finguru, and we will select the appropriate codes for you, based on many years of experience!
Order service
After all the codes have been defined, you need to see which of them should be the main one and which ones should be additional. Then you need to analyze how the selected set of codes will affect aspects of the planned activity:
- will there be any problems with registering a legal entity or individual entrepreneur - is it possible to conduct the selected types of activities in the selected status (individual entrepreneur, LLC, JSC, etc.);
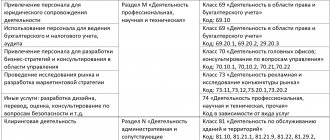
- Is it necessary to obtain a license, which one, or, for example, to join a self-regulatory organization (SRO) of builders, designers, auditors, appraisers, etc.;
- what tax regime can be chosen;
- what rates will be on mandatory payments;
- whether it will be possible to have tax and other benefits;
- what reports will need to be submitted, and so on.
What are OKVED codes and why are they needed?
OKVED in decoding is the All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities, approved by Rosstandart. It lists all activities grouped into classes, subclasses, groups and subgroups. Each is assigned a six-digit code, which has the format XX.XX.XX. Decoding the OKVED code allows you to determine not only the type of activity, but also the subgroup (ХХ.ХХ.Х), group (ХХ.ХХ), subclass (ХХ.Х) and class (XX) to which this type belongs.
OKVED provides a unified approach to the names of types of activities, and a specific code is a kind of economic identifier of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur. It allows government agencies to see what activities a company plans to conduct or is conducting, as well as collect, analyze and evaluate static data linked to a specific code.
Using OKVED codes, a legal entity or individual entrepreneur is identified in the tax authority (FTS), in extra-budgetary funds (PFR, MHIF, FSS), in Rosstat, in the banking sector, among other companies and individual entrepreneurs. It doesn’t matter how a businessman describes his activities, officially his activities are what is indicated and registered in the form of OKVED code(s).
Selected OKVED codes affect many aspects of activity:
- the possibility/impossibility of legally conducting business in the current conditions (existing organizational and legal form, license, amount of authorized capital, etc.);
- the presence/absence of an obligation to notify about the commencement of activities of certain government bodies;
- available tax regimes, tax rates, deductions and benefits;
- presence/absence of benefits on insurance premiums, the size of the tariff on contributions for injuries;
- scope of reporting;
- the ability/impossibility of making transactions that require approval (verification, approval) from government agencies.
Accordingly, errors deprive the company or individual entrepreneur of the benefits that they could receive, or, conversely, entail unreasonable costs, losses, and sanctions that might not have existed.
Consequences of non-compliance of OKVED codes with actual activities
- Administrative liability (warning or fine up to 10,000 rubles) for failure to submit, untimely submission of information contained in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities/Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs, for the provision of inaccurate or unreliable information.
- Refusal or prohibition in the use of the simplified tax system or other special regime, if there are factual grounds for the use of such a regime, but according to OKVED codes there are no.
- Refusal to deduct VAT, the application of which includes, for example, goods that are not related to the registered activity.
- Refusal to provide benefits, deprivation of rights to benefits on insurance premiums, increased rates of contributions for injuries. LLCs must confirm OKVED annually. If one type of activity is declared (for example, trade), then if an application for confirmation of OKVED is not submitted, the rate will not be raised above 0.2%. If several types of activities are open (for example, trade and construction), and the main type is trade, then if an application for confirmation of OKVED is not submitted, the FSS will set a rate for the most “dangerous” type of activity - construction, which is 0.9%.
The biggest risk is negative tax consequences. Many entrepreneurs are subject to special tax regimes: simplified tax system, patent, UTII, unified agricultural tax. Their specificity is a limited list of activities. And although the regimes can be combined (except for the simplified tax system with the unified agricultural tax), it will be necessary to differentiate between accounting by type of activity - this is difficult. If it turns out that the types of activities fall under 2 incompatible special regimes, the tax office may prohibit both. The result is that businesses will face a serious tax burden associated with the general taxation regime and a huge volume of all kinds of reporting.
All employers, except individual entrepreneurs, must annually confirm their main type of activity in order to maintain a “low” accident insurance rate. Through Gosuslugi it costs 3,000 rubles, and through Fingura - 1,000.
Find out more about the service
- Counterparties have doubts about the reliability of a company or individual entrepreneur who is trying to conclude a deal in an area of activity that is not listed in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities/Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
How to remove or add codes correctly
- We fill out the application form (for individual entrepreneurs), (for a legal entity) or (for legal entities in case the charter needs to be changed due to a change in activities).
- If we make changes to the charter, we pay a state fee of 800 rubles, attach to the application copies of the payment document, the new edition of the charter and the decision to approve the changes (minutes of the meeting).
- We send the application and additional documents to the tax authority with which you are registered. If you send by mail, courier or through a representative, you will need to notarize the application.
- We are waiting for the decision of the Federal Tax Service within 3 working days.
It is important to first understand how the changes will affect those aspects of the activity that you do not want to change, but they will be affected. For example, will it be possible to remain on the simplified tax system, will it be necessary to increase the authorized capital or obtain a license in the absence of funds for this.
Let's sum it up
OKVED codes are your officially registered activities. The tax regime, the size of insurance premium rates, types of reporting and other conditions of state control and regulation depend on them.