Characteristics of account 55 (specifics, legislative standards, active or passive)
Accounting for special accounts in banks (cash in letters of credit, checks, bank deposits and other payment documents, except bills) in accounting is account 55 . It is called account 55 - Special bank accounts.
The following funds are reflected in the same account:
- targeted financing with the condition of their separate storage;
- allocated by the company for the current needs of branches/divisions if they have a separate current account;
- in electronic wallets, on corporate cards, etc.
Checkbooks are counted on account 55 only as personal checkbooks issued by the bank directly to the company itself. If the organization receives third-party checks (for example, from a buyer), they are recorded in off-balance sheet account 008.
Maintaining accounting records on account 55 is regulated by several legislative standards: Chart of Accounts and Instructions for its application (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, PBU 23/2011, Regulations Central Bank of the Russian Federation “On the rules for transferring funds” dated June 19, 2012, Civil Code of the Russian Federation, etc.
To the question: is account 55 active or passive? The Chart of Accounts gives the answer that the account is active, that is, by debit there is a replenishment, in this case, the opening of a monetary document or a special account, and by a credit, funds are written off, that is, the closure of this monetary document / special bank account.
What is a special bank account for legal entities
This innovation came with changes that came into force on 07/01/2018. This is a regular current account in which the bank blocks or withdraws money upon request from any of the eight electronic trading platforms for trading under 44-FZ. It is used by government procurement participants on the supplier’s side. And they came up with it to simplify the process of securing applications during competitive bidding, in electronic competitions and auctions.
We talked about how to open a special account for accounting for government orders, what it is and how to work with it in the video.
Subaccounts according to the Chart of Accounts, reflected in the reporting
Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts for account 55 for accounting for each type of monetary document / special account offers the following sub-accounts for accounting:
- letters of credit - 55.1;
- check books - 55.2;
- deposits - 55.3, etc.
If the company also has an electronic wallet and a corporate card, then the next numbered subaccounts are opened. It is important that separate accounting is required for each open letter of credit or check book. To do this, second-order subaccounts should be added to these subaccounts - this is the analytics of account 55.
You can open monetary documents or special accounts in foreign currency. This requires the same separate accounting. In addition, do not forget about converting into rubles on the day of the operation and at the end of the month and taking into account exchange rate differences.
At the end of the period, the debit balance on account 55 in rubles is included in the amount on line 1250 “Cash and cash equivalents” of the balance sheet.
Movement in the account is also reflected in the Cash Flow Report according to PBU 23/2011.
Deposit accounts fit the definition of financial investments and can be reflected in accounting in account 55 or 58 - the company approves its choice in its accounting policy. It also indicates whether the financial investment is classified as cash equivalents. If yes, then they are reflected in line 1250 of the balance sheet (according to PBU 23/2011). If not (in accordance with PBU 19/02), then they are reflected in the amount of financial investments on line 1240.
Account 58 “Financial investments”
Order 94n established the following list of subaccounts of account 58:
- 58.1 - shares and shares;
- 58.2 - debt securities;
- 58.3 - loans provided;
- 58.4 - contributions under a simple partnership agreement.
However, the law does not prohibit enterprises from independently establishing a list of subaccounts in accordance with the goals of their accounting policies. At the same time, Order 94n clearly states that the enterprise is obliged to ensure a breakdown of financial investments into long-term and short-term.
Therefore, if the enterprise has financial investments with a period of up to 12 months or more than 12 months, it is necessary to organize their separate accounting, which allows separating the amounts of long-term financial investments from short-term ones.
More information about the procedure for organizing accounting of financial investments can be found in the article “Accounting for financial investments - PBU 19/02”.
Postings for transactions with financial investments in account 58 may look like this:
| Dt | CT |
| Shares were added to the authorized capital of the enterprise | |
| Received funds for securities (sale of shares) | |
| Purchased bills (debt securities) with cash payment | |
| Debt securities are included in the authorized capital of the enterprise | |
| 58.1(58.2) | The securities were received by the company free of charge |
Postings to account 55
The most frequently used transactions for account 55 (subaccounts 55.4, 55.5 and 55.6.USD are indicated here as an example; any organization can set its own numbering):
| Debit | Credit | Contents of operation |
| 55.1 | 51 | Opened (covered) letter of credit |
| 60 | 55.1 | Goods, works, services paid for (letter of credit executed) |
| 55.2 | 51 | Funds deposited to clear checks |
| 60/76 | 55.2 | Funds are written off for checks presented for payment by the supplier/other counterparty |
| 71 | 55.2 | The money on the check was received by the accountant |
| 51 | 55.2 | Unused checks were returned to the bank, the special check book account was closed |
| 55.3 | 51 | Funds transferred to open a deposit |
| 51 | 55.3 | The deposit amounts were returned by the bank |
| 55.4 | 51 | Electronic wallet replenished |
| 55.4 | 62 | Payment received from buyer via electronic money |
| 76 | 55.4 | Commission for transferring money is taken into account |
| 55.5 | 51 | Funds have been credited to a special card account (corporate card) |
| 71 | 55.5 | Funds were written off to the account from a corporate card (paid by bank transfer, cash withdrawn) |
| 55.5 | 71 | The remaining cash was deposited via an ATM onto the card |
| 55.6.USD | 52.1.USD | Card account opened in dollars |
| 55.6.USD | 66/67.USD | The loan is credited to the foreign currency card account |
| 71.USD | 55.6.USD | The accountant used foreign currency from the card account |
Transfer to a special bank account
The list of banks where you can open a special account for participation in auctions under the Federal Law of 04/05/2013 N 44-FZ and under the Federal Law of 07/18/2011 N 223-FZ (where only small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) participate) is approved by the Order Government of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2018 N 1451-r.
To open a special account, you need to contact any bank from this list. To do this, the Organization must be accredited on the electronic platform. If the Organization already has a current account in one of these banks, then you can use a current account as a special one or open a new one (depending on the conditions of the bank).
To create a special account in the program, go to the organization’s card, follow the link Bank accounts - Create button.
Please indicate:
- Account type - Other .
See how to display hidden fields using the example of the Contractors directory
When moving money between its accounts, the organization does not have any income or expenses; therefore, debiting money from the account and crediting it is not an expense or income of the simplified tax system (Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Reflect the transfer of funds to a special account in the document Write-off from the current account transaction type Transfer to another account of the organization in the Bank and cash desk section - Bank - Bank statements - Write-off button.
Please indicate:
- Date - date of transfer, according to the bank statement;
- According to document No. from - the number and date of the payment order;
- The recipient's account is a special account;
- Debit account - 55.04 “Other special accounts”;
- Expense item - Internal movement of funds ; Movement type - not filled in.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 55.04 Kt 51 - transfer to another account.
To reflect the receipt of funds to a special account, register with the document Receipt to the current account transaction type Transfer from another account in the Bank and cash desk section – Bank – Bank statements – Receipt button.
Please indicate:
- Date - date of transfer, according to the bank statement;
- According to document No. from - the number and date of the payment order;
- Payer's account - the current account from which the transfer was made.
The document does not generate postings; the posting for the receipt of money to the current account is generated in the document Write-off from the current account . But the document Receipt to the current account must be created, otherwise the balances in the context of bank accounts will not match.
If the Use account 57 “Transfers in transit” checkbox when moving funds is selected in the accounting policy settings, then:
- The document Write-off from the current account will generate a posting only for writing off money from the current account through account 57: Dt 57.01 Kt 51 (55.04);
- document Receipt to the current account will generate a transaction for crediting money to the current account:
Dt 51 (55.04) Kt 57.01.
If you use downloading bank statements, then this document will be downloaded to the database automatically.
Examples of letter of credit and deposit accounting
Example 1
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
The company entered into an agreement for the purchase of a car with the installation of additional internal equipment in it, which provides for payment for the delivery (950,000 rubles, incl. VAT 18%), covered by a letter of credit. To do this, the company opened a covered letter of credit with the bank. The car arrived on time, but not all additional equipment was installed, and the bill turned out to be 50,000 rubles. cheaper. All necessary delivery documents have been submitted to the bank for verification. The invoice payment has been made. The bank's commission for servicing a letter of credit is 0.1% of its amount.
Calculations:
- 950,000 – 50,000 = 900,000 - the cost of a car with equipment;
- 900,000 / 118 × 18 = 137,288 - VAT amount;
- 900,000 – 137,288 = 762,712 — cost of equipment excluding VAT;
- 950,000 × 0.1% = 9,500 - bank commission for servicing the letter of credit.
Solution
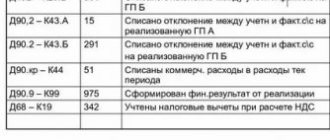
| Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) | Contents of operation |
| 55.1 | 51 | 950 000 | Covered letter of credit opened |
| 08.4 | 60 | 762 712 | The car was delivered |
| 19 | 60 | 137 288 | VAT reflected |
| 60 | 55.1 | 900 000 | Supplier invoice paid |
| 08.4 | 51 | 9 500 | The amount of the bank commission is included in the cost of the car |
| 51 | 55.1 | 50 000 | The balance of unused funds is returned to the current account |
Example 2
The company opened a deposit in a bank of 150,000 rubles. for 6 months at 16% per annum.
Calculations:
150,000 × 16% / 12 × 6 = 12,000 – Interest amount when closing the deposit
Solution:
| Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) | Contents of operation |
| 55.3 | 51 | 150 000 | Deposit opened |
| 51 | 76 | 12 000 | Interest on the deposit is credited after six months |
| 76 | 91.1 | 12 000 | Deposit income taken into account |
| 51 | 55.3 | 150 000 | Deposit closed |
Accounting for financial investments in accounts 55.3 and 73.1, standard transactions
Account 55.3 reflects the enterprise's deposits - funds provided to financial institutions for the purpose of receiving interest income. They can also be short term or long term. Account 73.1 reflects loans provided by the enterprise to its employees.
Here are some typical entries when accounting for financial investments in accounts 55.3 and 73.1.
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| Account 55.3 “Deposit accounts” | ||
| Funds were transferred to the deposit account | ||
| Interest accrual on deposit | ||
| Interest is transferred to a deposit account (if the company does not withdraw it) | ||
| Interest transferred to the company's current account | ||
| Closing the deposit | ||
| Account 73.1 “Settlements with personnel for loans provided” | ||
| A loan was issued from the company's cash desk to an employee | ||
| The loan is transferred to the employee’s card | ||
| The company has accrued interest on the loan issued to the employee (if the loan agreement provides for this) | ||
| Withholding interest or loan amount from the employee's salary | ||
| Repayment of a loan by an employee to the company's cash desk | ||
| The company has written off the employee’s loan debt (if such a decision has been made) | ||
***
The article describes account 55 in accounting. The account is used for settlements with counterparties using monetary documents (letters of credit, checks) and the use of special accounts (deposits, electronic wallets, corporate cards, etc.).
Account 55 is active, the debit is replenishing funds (opening monetary documents and special accounts in the bank), and the credit is writing off (the bank closes monetary documents and special accounts).
The debit balance is reflected in line 1250 of the balance sheet.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Main types of special accounts in Russia
- Special accounts
- About special accounts
- Main types of special accounts...
- Bank special accounts
- Accounting special accounts
First of all, you need to understand that bank accounts and accounting accounts are two different concepts. Therefore, the types of special accounts can be divided into two semantic groups independent of each other:
- special bank accounts;
- special accounting accounts.
Bank special accounts
The types of bank accounts that banks have the right to open, as well as their purpose, are briefly described in the instructions of the Central Bank of Russia No. 153-I. In accordance with this law, there are the following types:
- current – for individuals;
- settlement – for entrepreneurs and legal entities;
- budgetary – for government organizations;
- correspondent - for banks;
- special – used in cases established by law and for specific types of operations;
- and other rarer types.
Since a special account refers to one of the types of bank accounts, and their essence is to provide non-cash payment services for individuals and legal entities, the main functions of bank accounts also apply to special ones.
The same law additionally specifies ten types of special accounts themselves:
- Bank payment agent or subagent. By becoming bank payment agents (by concluding an agency agreement with the bank), individual entrepreneurs and legal entities can take on part of the functions of a bank. They can work either independently or involve subagents. For example, the law allows them to accept and issue cash, including using terminals. It is logical that a special account is a mandatory requirement for them.
- Paying agent. The activities of a paying agent, unlike a banking agent, are more limited. A payment agent is an intermediary in the form of an individual entrepreneur or legal entity who accepts payment from individuals for services provided to them by third-party supplier companies. The most common when paying for housing and communal services. Funds from individuals should be accepted not into a regular account, but into a special one.
- Supplier. We are talking about supplier companies that provide services to the public – individuals. To receive payment, payment agents with whom an agency agreement has been concluded are used. Most often they represent the housing and communal services sector, but not only. They are also required to have special accounts to which their payment agents transfer funds from their special accounts.
- Trade. Opens during clearing transactions. Clearing can be called a type of barter, when companies mutually offset goods supplied or services provided to each other. The remaining difference (if any) is the balance, paid by one of the parties. Clearing participants are required by law to open a special trading bank account.
- Clearing. In clearing transactions, participants often seek the assistance of a clearing organization, which plays the role of a regulator. To carry out this complex activity, a clearing organization requires a license and the opening and operation of a clearing bank account.
- Payment system guarantee fund. A rare type that is used by payment systems. For example, the national payment system "Mir" is required by law to use a guarantee fund formed by its participants - banks that make their deposits into this type of special account.
- Nominal. It is used when one person uses the funds of another. One of the cases is when a relative is in another city and there is no opportunity to constantly transfer funds. The advantage of this type is that the owner of the funds can monitor the expenses of another person and even prohibit certain categories of expenses.
- Escrow. It is a kind of insurance for both parties to the transaction. First, the funds are credited by the owner to the escrow account. Then the bank blocks them for a certain period. Next, he waits for the terms of the transaction specified in the escrow agreement to be fulfilled. If they are completed, the funds are paid to the other party, otherwise they are returned to their owner. In 2021, escrow funds are used by equity holders when purchasing apartments in new buildings.
- Collateral. This type of special account is suitable for enterprises on the verge of bankruptcy. If the company has deposited funds into a collateral account, which is opened jointly with the supplier, then he can be confident in payment for his goods and services, since the money is pledged to the bank. A collateral account at the legislative level provides protection of funds from seizure by the state.
- Debtor. Used in bankruptcy proceedings. After the sale of the bankrupt’s property, the proceeds are temporarily transferred to a special account of the debtor, which he is prohibited from disposing of. The money is then distributed to creditors.
The above list is not closed and may be supplemented by individual regulations. Relatively recently, for example, the following were added to it:
- according to 44-FZ “On State Procurement” - a special account of a participant in public procurement, necessary to secure the tender application;
- according to 214-FZ “On participation in shared construction” - a special account of the developer, required by the authorities to control the targeted expenditure of shareholders’ funds;
- according to Article 170 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation - a special account that is opened by a homeowners association, residential complex or management company for accumulating funds from owners for major repairs of apartment buildings (MCD).
What many types of special accounts have in common is that the law imposes some of the same restrictions on them:
- prohibits tax authorities from writing off funds in case of debt;
- establishes a ban on certain types of transactions on them.
Why is this necessary?
Most enterprises have many different accounting objects that constantly change in value and quantity:
- All property (or assets): cash, land, buildings, furniture, raw materials, equipment, even stationery.
- All obligations (in other words, liabilities): to counterparties, clients, employees, banks, budget, etc.
So that all this can be taken into account and analyzed at any time, the accounting department opens a separate accounting account for each of the above types of objects (buildings, land, transport, settlements with personnel, loans, etc.). Their list with numerical numbers is approved by the accountant in a document called the “chart of accounts.”
If the information were not structured, it would be difficult to keep records of property and liabilities.
The concept of “Special Account”, its purpose and types
Currently, non-cash transactions are an integral part of the work of almost every business entity. In this connection, organizations use bank accounts to make payments. For enterprises, in addition to current accounts, credit institutions (banks) can open special accounts into which funds are credited for certain business purposes.
A special account is an account opened by an organization in a credit institution (bank) for the purpose of storing and collecting funds in Russian currency or foreign currency for carrying out transactions using letters of credit, check books and other payment documents, as well as for reflecting transactions on the movement of funds of the target financing
To open special bank accounts, you must fill out an application for opening. The application form is determined by the type of special account. For example:
- Application for a letter of credit;
- Application for registration of a settlement check book;
- Application for opening special accounts
Financial investments in the balance sheet structure
In the structure of the balance sheet, financial investments are assets recorded in lines 1170 and 1240. Line 1170 is located in the first section of the balance sheet “Non-current assets”, and line 1240 is in the second section (“Current assets”). In line 1170 the amounts of long-term financial investments are recorded (for a period of more than a year), and in line 1240 - short-term (for a period not exceeding a year).
In accounting, a breakdown of financial investments by the period for which they are formed must be carried out, as this is provided for by the instructions for using the chart of accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, hereinafter referred to as Order 94n) and PBU 19/02.
The main part of the financial investments reflected in lines 1170 and 1240 of the balance sheet is recorded in accounting in the form of a debit balance of the account. 58, on which financial investments are recorded. To it is added the debit balance of financial investments in accounts 55 and 73 (in terms of deposits and loans to employees of the enterprise, respectively). In addition, the amount of debit balances of accounts 58, 55, 73 should be reduced by the credit balance of account 59 (formation of reserves for financial investments).
IMPORTANT! It is advisable to account for assets reflected in accounts 55 and 73, classified as financial investments, in separate sub-accounts depending on the investment period. Then, when creating a balance, there will be no problems filling out lines 1170 and 1240.