“Gift” personal income tax
A gift is income in kind, which is taken into account when determining the tax base for personal income tax (Clause 1, Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation exempts from taxation gifts received by individuals from organizations whose value does not exceed 4,000 rubles per year. It is unlikely that a children's New Year's gift will cost more. This means that the employee most likely will not have any obligation to withhold personal income tax. In this case, the organization is required to keep personalized records of these incomes (see, for example, letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 20, 2017 No. 03-04-06/2650). Important! Recommendation from ConsultantPlus The transfer of the gift must be documented, otherwise the income will not be considered a gift (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/28/2020 N 03-04-06/14371, dated 08/12/2014 N 03-04-06/40051). Such documents are... For more details, see K+. Trial access is available for free.
If a gift costs more than 4,000 rubles, or the organization gives gifts not only to children, but also to the employees themselves, and not only on New Year, but also on other holidays, and the total cost of gifts for the year exceeded the tax-exempt amount, for this income the organization becomes a tax agent (clause 1 of article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But only in relation to the excess amount, from which the tax must be calculated.
An example of calculating personal income tax when issuing several gifts in a calendar year from ConsultantPlus Situation: An organization gave three gifts to an employee (tax resident of the Russian Federation) during the calendar year: the first gift - by March 8 in the amount of 1,500 rubles; the second gift in June for a professional holiday in the form of a vase worth 2,000 rubles; the third gift in December for the New Year in the amount of 1,000 rubles. The issuance of each gift is formalized by order of the manager. Calculation of personal income tax can be viewed in K+. Trial access to the system is free.
See also “Are gifts under 4,000 rubles reflected in 6-NDFL?”
Do I need to withhold income tax?
The need to charge personal income tax depends on the market value of the gift set. Tax is not withheld if the cost of incentives for an individual does not exceed 4,000 rubles. The amounts of all gifts from the beginning of the reporting period are taken into account on an accrual basis, so separate records of gifts should be kept for each employee.
According to the letter from the Federal Tax Service dated July 21, 2017, the company has the right not to display the value of gifts below 4,000 rubles in the 6-NDFL declaration. If during the year the amount of incentives exceeded 4,000, then the organization is obliged to reflect information on Form 6 for income tax.
Case Study #1
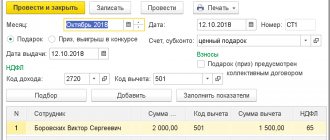
The management of Cactus LLC encouraged employee Petrov for high performance throughout the year - in May he was given a gift certificate in the amount of 3,800 rubles. At the end of November, the company gave a New Year's package to his child, the market value of which was 2,000 rubles. During the reporting period, employee incentives reached 5,800 rubles. Since the set was given to Petrov’s child in kind, the accountant was able to withhold personal income tax only when issuing wages for the month.
(3800 + 2000) – 4000 = 1800 rubles – the amount of exceeding the limit of gifts not subject to personal income tax.
Dt70 Kt68
234 rubles – 13% personal income tax was withheld from Petrov’s salary.
Dt68 Kt51
Personal income tax was transferred to the Federal Tax Service of Russia no later than the next working day after payment of wages.
In addition: more about accounting account 68.
Should insurance premiums be charged?
There is no need to calculate insurance premiums, including for injuries, from the cost of children's gifts. If only because there is no labor relationship between the children of employees and the organization, and therefore there is no object for taxation of contributions (clause 1 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1 of Article 20.1 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ, see . also letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2010 No. 1239-19).
In addition, paragraph 4 of Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly provides that payments under civil contracts, within the framework of which the transfer of ownership of property occurs, do not relate to the object of contributions. And a gift agreement is just such an agreement.
See also “You may not have to pay fees on holiday gifts even in the absence of a gift agreement.”
How to arrange the transfer of children's gifts?
The transfer of New Year's gifts to children of institution employees is regulated by Ch.
32 “Donation” of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 572 under a gift agreement, one party (the donor) gratuitously transfers or undertakes to transfer to the other party (the donee) an item of ownership or a property right (claim) to himself or a third party, or releases or undertakes to release it from a property obligation to himself or a third party. The institution may enter into such an agreement orally.
A written conclusion of an agreement is necessary only in the cases provided for in Art. 574 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
What about VAT?
It is better to pay VAT on the cost of gifts. And not only because this is the position of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation (Resolution No. 1001/13 dated June 25, 2013) and the regulatory authorities.
For more information, see our material “Do I need to pay VAT when giving gifts to employees?”
When giving gifts, including to children of employees, ownership of the goods is transferred free of charge. And by virtue of paragraph 1 of Art. 39 and paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such transfer is subject to VAT. Consequently, the organization must calculate the tax on the market value of gifts (clause 2 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and pay it to the budget. You also need to draw up an invoice - in one copy, with dashes in lines 6-6b. One invoice is enough for all gifts.
If the gift seller also pays VAT, then there are no special problems here. By calculating the tax for this transaction, the purchasing organization receives the right to deduct the “input” tax (Clause 1, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The market value of gifts, from which in this case VAT payable must be calculated, will be the price of their acquisition. Thus, the amount of tax accrued will be equal to the amount of the deduction. This means that the organization will not lose anything.
At the same time, failure to pay taxes may result in:
- claims from regulatory authorities;
- impossibility of deducting “input” VAT (clause 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the need for separate accounting (clause 4 of article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If gifts were purchased from a VAT evader (for example, from a “simplified person”), you will actually have to pay the tax at your own expense. If the amounts are significant, it is better to avoid such suppliers.
Business gifts: asking price
According to the law, the value of the gift should not exceed 3,000 rubles, since donations of a larger amount in relations between commercial organizations are prohibited (subclause 4, clause 1, article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
There are no penalties for violating this requirement. Moreover, according to the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a gift in circumvention of this prohibition may lead to the invalidity of the transaction (Article 168 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). But in a situation with a New Year's gift, this is difficult to imagine. Therefore, if you do give something more valuable, any adverse consequences are unlikely. As for the taxation procedure, the cost of the gift does not affect it - an expensive gift is taxed on a general basis.
Gift accounting
Based on the Chart of Accounts and instructions for its use (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), the acquisition and issuance of children's gifts can be reflected in accounting as follows:
Debit 41 Credit 60 - children's New Year's gifts were capitalized;
Debit 19 Credit 60 - reflects the VAT presented by the supplier;
Debit 68, subaccount “Calculations for VAT”, Credit 19 - “input” VAT is accepted for deduction;
Debit 73 Credit 41 - reflects the transfer of gifts to employees;
Debit 91 Credit 73 - the cost of gifts is included in other expenses;
Debit 91 Credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for VAT” - VAT is charged on the cost of gifts.
Due to the fact that these expenses do not reduce taxable profit, organizations applying PBU 18/02 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n) will have a permanent tax difference and a corresponding permanent tax liability (PNO):
Debit 99, subaccount “Permanent tax liability” Credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - for the amount of PTI.
Income tax on gifts
A gift, regardless of who it is intended for, an employee or his child, is recognized in accounting as company property, which is subject to gratuitous transfer. Consequently, accounting and taxation of New Year's gifts for children of employees is carried out according to special rules. Expenses for the purchase of souvenirs cannot be taken into account as expenses that reduce the tax base when calculating the corporate income tax. Such instructions are contained in paragraph 16 of Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If a company applies a simplified taxation system in the “Income minus expenses” form, expenses for gifts to employees’ children for the New Year cannot be taken into account as expenses (Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Results
As you can see, keeping track of children's New Year's gifts is not so difficult. Follow our simple recommendations, and these pre-holiday chores will only be a joy for you.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n
- Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 25, 2013 No. 1001/13
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
A written agreement is required
If the value of a gift from a legal entity exceeds RUB 3,000.
If the contract contains a promise of a gift in the future
If the object of the donation is real estate
The issuance of gifts should be accompanied by a corresponding statement, the form of which is arbitrary and is developed by the institution independently.
Let us remind you that any form, including a statement for the issuance of children's gifts, must contain the mandatory details of the primary accounting document:
- Title of the document;
- the date of its preparation;
- name of the economic entity that compiled the document;
- content of the fact of economic life;
- the value of the natural and (or) monetary measurement of a fact of economic life, indicating the units of measurement;
- the name of the position of the person who completed the transaction, operation and is responsible for its execution, or the name of the position of the person responsible for the execution of the accomplished event;
- signatures of persons indicating their surnames and initials or other details necessary to identify these persons.
For your information:
The requirements for the “primary” are established in Part 2 of Art. 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402‑FZ “On Accounting”, as well as paragraph 7 of the Instructions for the application of the Unified Chart of Accounts for public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state academies of sciences, state (municipal) institutions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 157n).
Restrictions
No matter how good-hearted an employer is, the law limits the amount of gifts that can be given per year of service. More precisely, it does not limit, but tries to regulate this process in such a way that giving gifts does not become a systematic method of payment.
To do this, a tax (specifically, personal income tax) is imposed on material assets transferred free of charge if their value is more than 4 thousand rubles. per employee for one calendar year. Of course, this will also depend on the form of the gift. All cases where exceptions are made to this rule are spelled out in detail in paragraph 8 of Article 217 of the Tax Code.
How to take into account New Year's gifts that a company gives to its employees, contractors and clients?
The fabulous time of New Year's gifts is coming soon. You need to do a lot: congratulate colleagues, buy gifts for counterparties, not offend important clients, show signs of attention to everyone who is dear to your company or your business. It is important to know that the law sets restrictions on gifts, and it is also important to correctly take into account these expenses.
How to arrange gifts?
In order to purchase gifts, you must first understand who to give gifts to. Therefore, the first step is to make a list of people to whom gifts will be given. At the same time, companies often share gifts with company employees, contractors, and government officials. Companies prefer to give different gifts to different categories of people. For example, a company will not give the same gifts to important contractors with whom multimillion-dollar contracts have been concluded, and to employees of a courier service that, working as a contractor, transports parcels and correspondence on an irregular basis.
After this, you need to draw up a cost estimate. Often the initial cost estimate is adjusted several times, unnecessary costs can be removed from it, and the number of people to whom gifts need to be given can be adjusted. It is also important to make an estimate of expenses because it is customary to give different gifts to different categories of people. For example, it is customary to give gifts to contractors with company logos so that the gift does not get lost among others. But an employee does not have to give a gift with a logo.
After calculating the preliminary costs, an order is drawn up, which defines:
- responsible persons;
— timing of donation;
- funds allocated for the purchase of gifts.
To purchase gifts, you must draw up an agreement with the selling company. In such an agreement, it is advisable to provide for the possibility of returning gifts, the procedure for payments, and a list of supporting documents. Such supporting primary documents may include:
— waybills;
- checks;
— acts of acceptance and transfer.
In this case, the transfer of a gift to both the employee and the counterparty can be carried out both in writing and orally. However, probably no one has encountered the situation where gifts, for example, for the tax office, were handed over against signature. A written agreement is required only if the value of the gift exceeds 3,000 rubles. (Clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, it is recommended to purchase gifts for a smaller amount to avoid the need to formalize a gift agreement.
But when a company employs a large number of employees, as well as in cases where gifts are provided not only to the employees themselves, but also to their children, it is recommended to organize the presentation of gifts according to the statement. In this way, it is possible to understand who has received gifts and who has not yet.
How to avoid getting into trouble?
It should be remembered that it is not always possible to give gifts to everyone. Especially when it comes to expensive gifts.
Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation talks about the prohibition of donations. Thus, gifts are prohibited:
1) on behalf of minors and citizens recognized as incompetent, their legal representatives;
2) employees of educational organizations, medical organizations, organizations providing social services, and similar organizations, including organizations for orphans and children without parental care, citizens who are in them for treatment, maintenance or upbringing, spouses and relatives these citizens;
3) persons holding government positions in the Russian Federation, government positions in constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipal positions, civil servants,
4) in relations between commercial organizations.
Thus, if your organization wants to congratulate an employee of the tax service or a municipal body, such a gift may not be accepted. However, this ban does not stop either accountants or inspectors: the former give gifts, the latter accept them with pleasure.
In order to comply with the law, it is advisable to limit yourself to inexpensive gifts in the amount of up to 3,000 rubles (Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax accounting of gifts
Regardless of who the gifts were purchased for, it will not be possible to include them in expenses.
In accordance with paragraph 16 of Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses in the form of the cost of gratuitously transferred property (work, services, property rights) and expenses associated with such transfer are not taken into account when determining the taxable base for income tax.
The Ministry of Finance adheres to the same position in letter dated October 19, 2010 N 03-03-06/1/653.
In addition, VAT will have to be charged on the cost of the gift. The transfer of gifts to employees of an organization is subject to value added tax. In this case, the tax base for this operation is determined in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which when selling goods free of charge, the tax base is determined as the market value of these goods. This opinion was expressed by the Ministry of Finance in a letter dated January 22, 2009 N 03-07-11/16.
The courts also believe that operations for issuing New Year's gifts for children indicate the transfer of ownership of them free of charge, therefore, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are recognized as sales and are subject to VAT (Resolutions of the FAS VSO dated September 27, 2011 N A33-13342/2010, FAS VVO dated February 11, 2010 N A29-3055/2009). In this regard, the company will have to charge VAT and at the same time not recognize expenses for gifts in tax accounting.
But personal income tax may not be charged if the amount of the gift is not very large, up to 4,000 rubles. Clause 28 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for exemption from personal income tax on income received for various reasons in kind or in cash, the amount of which does not exceed 4,000 rubles. for the tax period. But even if the value of the gift is symbolic, it is recommended to keep personalized records of gifts. In Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 20, 2010 N 03-04-06/6-155, the department notes that the organization should keep personalized records of such income received from it by individuals.
Regarding insurance premiums, the following should be noted. Gifts, prizes, including those given to employees in cash, as payments and other remunerations accrued by an organization in favor of an individual who has an employment relationship with this organization on the basis of an employment contract, are subject to insurance premiums. They are not subject to insurance premiums, according to Part 3 of Art. 7 of Law N 212-FZ, payments and other remuneration made within the framework of civil contracts, the subject of which is the transfer of ownership or other real rights to property (property rights), and contracts related to the transfer for use of property (property rights) , with the exception of copyright contracts, contracts on the alienation of the exclusive right to works of science, literature, art, publishing license agreements, license agreements on granting the right to use works of science, literature, art (Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2010 N 1239-19). Thus, gifts to employees will be subject to insurance premiums. But gifts to counterparties will not be subject to Law 212-FZ.
Accounting for expenses of gifts with company symbols
A very good option in terms of accounting for gifts is to purchase gifts with company symbols. Such gifts have a number of advantages compared to ordinary gifts:
- the recipient will not confuse who the gift is from;
- gifts are well remembered;
- and most importantly, they can be taken into account in expenses.
Expenses for souvenir products with the company logo are recognized as advertising costs, having previously drawn up documents that will confirm that the souvenirs were distributed among an indefinite circle of people (clause 28, clause 1 and clause 4, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These gifts can be given:
- counterparties;
- clients;
— representatives of government bodies;
- notaries;
— and even the employees themselves.
The possibility of accounting for such expenses without taking into account any standards is confirmed by judicial practice. The courts believe that the legislation does not establish standards for providing employees with stationery if they contain the organization’s advertising symbols (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated January 31, 2011 N A40-55061/10-99-250).
However, if expenses on gifts are taken into account as advertising, disputes with the tax authorities are possible. An important feature of advertising is that it is intended for an indefinite number of people, which means that the advertisement does not contain any indication of a certain person or persons for whom the advertisement is created and to whose perception the advertisement is directed (Letter of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of Russia dated 04/05/2007 N ATs/4624). However, if gifts are intended to be transferred to certain partner organizations or company employees, then the circle of recipients is defined and limited. But if the company distributes the same products at exhibitions, training seminars, or gives out to contractors as advertising, then it can be proven that these products are intended for an unlimited number of people.
Companies can use this feature of tax accounting to account for expenses. But there is another opportunity to take into account costs.
Accounting for gifts in the form of alcoholic beverages in expenses
Well, what New Year would be complete without a bottle of champagne? And many companies prefer to use alcoholic drinks as gifts: strong drinks for men, champagne for women. In this case, the cost of alcoholic beverages is written off for the official reception. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to take into account expenses for holding official receptions, without specifying the list of expenses that can be classified as such expenses (clause 2 of Article 264). The Ministry of Finance and the courts also support companies in recognizing expenses as part of entertainment expenses.
Thus, in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 25, 2010 N 03-03-06/1/176, the financial department explains that the costs of purchasing alcoholic beverages for organizing an official reception can be taken into account when taxing profits as part of entertainment. The courts also supported the companies, pointing out that tax legislation does not detail the list of foods and drinks that are included in entertainment expenses. Therefore, the organization’s expenses for the purchase of alcoholic beverages are legally included in expenses (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga Region dated January 15, 2013 in case No. A55-14189/2012). The court came to a similar conclusion in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated November 10, 2010 N F09-7088/10-C2 in case No. A60-2408/2010-C6. The court indicated that the list of entertainment expenses is not exhaustive; they may include expenses for the purchase of alcoholic beverages.
Thus, gifts in the form of alcoholic beverages are much more profitable for the company than other gifts. However, the following must be taken into account:
— entertainment expenses are regulated;
These expenses are normalized in an amount not exceeding 4% of the taxpayer’s expenses for wages for the reporting period (clause 2 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
— it is necessary to document the official reception, including preparing an order and an estimate.
Accounting for food package expenses
Drinking tea at work or good coffee is probably what most workers love. This is a good reason for a gift. Thus, employers write off the cost of tea, coffee and sweets in accordance with clause 4 of Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as the cost of food for employees.
At the same time, the courts support taxpayers both in terms of recognition of costs and in terms of non-accrual of VAT (Resolutions of the Moscow Federal Antimonopoly Service dated 04/06/2012 N A40-65744/11-90-285 and Volgo-Vyatka district dated 07/19/2011 N A29-11750/2009 ). In the above decisions, the court came to the conclusion that since the applicant attributed the listed expenses to labor costs and accepted them for profit tax purposes, there is no taxable base for VAT in this case.
However, it should be remembered that if it is possible to personify persons who received income in kind in the form of food, then in this case personal income tax will have to be charged,
When an organization purchases food (tea, coffee, etc.) for its employees, as well as during corporate holiday events, these persons can receive income in kind, as established by Art. 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and the organization providing the specified food (holding corporate events) must perform the functions of a tax agent provided for in Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
For these purposes, the organization must take all possible measures to assess and take into account the economic benefits (income) received by employees.
Thus, if the company does not charge personal income tax on the cost of food packages, then legal disputes are possible.
VAT exemption
Companies often give contractors or regular customers some “symbolic gifts.” This could be a refrigerator magnet, a pen or a notepad. Please remember that VAT can be saved on such gifts.
The fact is that operations involving the transfer of goods for advertising purposes, the cost of acquiring (creating) a unit of which does not exceed 100 rubles, are exempt from taxation with value added tax. In order to be exempt from value added tax on goods distributed for advertising purposes, including by placing them on the premises of third-party organizations, the cost of purchasing (creating) a unit of these goods should not exceed 100 rubles. taking into account the tax amounts presented by suppliers of such goods or goods (works, services) purchased for their creation. If the cost of purchasing (creating) a unit of goods transferred for advertising purposes exceeds 100 rubles. taking into account the value added tax, then transactions for the transfer of such goods are recognized as subject to taxation under this tax. In this case, the tax base for value added tax is determined in the manner established by clause 2 of Art. 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, based on the full cost of goods transferred for advertising purposes, based on market prices (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 27, 2010 N 03-07-07/17).
This feature should be taken into account to optimize taxation when purchasing low-value gifts and souvenirs.
Gift accounting
Gifts can be reflected in accounting in two ways:
— using accounts 41 “Goods”, 10 “Materials”;
— with the cost of gifts included in other expenses: account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
Let's give an example
Example
purchases gifts for employees for a total amount of 118,000 rubles, including VAT of 18,000 rubles.
The company employs 30 people. There are also 10 gifts for contractors.
Since the cost of one gift is 2950 rubles, including VAT, in this case personal income tax is not charged.
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Operation |
| 41,10 | 60 | 100 000 | Gifts purchased |
| 19 | 60 | 18 000 | Input VAT reflected |
| 68 | 19 | 18 000 | Input VAT is accepted for deduction |
| 73 | 41,10 | 100 000 | Gifts were given to employees |
| 91-2 | 68 | 18 000 | VAT is charged on the transfer of gifts |
| 91-2 | 73 | 100 000 | The cost of the gift is included in other expenses |
In conclusion, it should be noted that, of course, the New Year cannot do without gifts. It is gifts that create a unique atmosphere of miracle and fairy tale. But for managers and accountants it is very important to choose the right gift, as well as arrange it in such a way that expenses can be taken into account for tax purposes. Therefore, choose gifts wisely!
note
This article was a useful guide at the time it was written and published. The nuances of taxation change regularly, and therefore, in order to get out of difficult situations without losses, you need to be aware of the latest information.
Auditors and lawyers at Korn-Audit are always ready to help and offer an individual, most comfortable solution. With us you will forget about problems with taxes.
Call! Glad to help.
You might be interested in our services:
Calculate the cost of accounting services.
Why register
It would seem that a gift is a noble gesture that does not require documentary evidence. However, for legal entities everything is more complicated. It is imperative to confirm the fact of the transfer of valuables, since the tax service may raise questions regarding the good intentions of the employer. After all, unscrupulous managers may require labor costs from employees in return. And this is already going beyond the law, “gray” wages. Which, naturally, will lead to administrative penalties during inspections.
Special cases
If an employer decides to give gifts to an employee individually on the occasion of, for example, a birthday, then no one has the right to prohibit him from doing so. However, it would be illogical to start a statement in such a situation. A donation agreement will be sufficient. According to clause 2 574 of Article of the Civil Code, such an agreement must be drawn up if the total amount of the gift exceeds 3 thousand rubles.
Attention! The gift agreement should not contain references to the regulatory acts of the organization, the position or any professional achievements of the employee.
Otherwise, tax control officials may classify this as a reward for work and collect the applicable taxes (plus penalties for non-compliance).