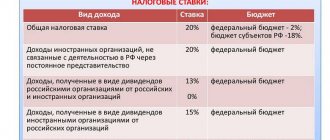
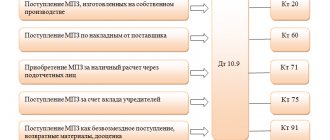
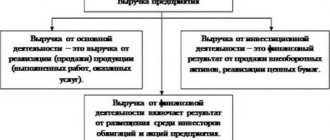
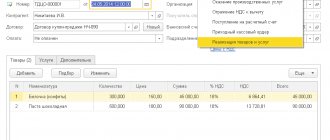
General concepts of business transactions
A business operation consists of a certain action that reflects data on calculations, changes in the composition of equity, and the sources of their formation. Based on it, the accountant draws up an entry. The operation is recognized as completed only if there are supporting documents.
Each economic action will change either the size of the property, or the size and composition of the sources of its formation, or two indicators simultaneously. Their decrease or increase equally affects the total amount of assets and liabilities of the balance sheet.
Classification
There are the following types of business transactions:
- +A-A. This category of events changes the composition of the property, that is, it concerns only the asset. In this case, the balance sheet currency is not adjusted.
- +P-P. These operations influence the sources of formation of the company's material assets. They affect only the passive. In this case also remains unchanged.
- +A+P. This category of events affects both the size of property and the sources of its formation. In this case, the adjustment is made in the direction of increase. The balance sheet currency for liabilities and assets increases by the same amount.
- -A-P. These transactions also affect the property and its sources. But the changes are decreasing.
Main stages of the organization's work
In the course of the enterprise’s activities, 3 processes can be distinguished, which are taken into account by separate operations: (click to expand)
- Supply - takes into account the receipt of goods and materials from third-party companies, repayment of transport and procurement costs.
- Production - inventory items are released into production, wages and taxes are calculated.
- Sales - the revenue received from the sale of goods (provision of services) to counterparties is recorded, the corresponding costs are written off, and profit is determined.
The organization's assets are constantly involved in the production process. To determine their value and economic analysis for a specific date, the accountant draws up a balance sheet. It includes a system of parameters that qualify the financial status of the company, the condition and size of its assets and sources in the same monetary equivalent.
Grade
Each business transaction must have its own cost at the time of completion. The company must evaluate its property in order to reflect it in documents in monetary terms. In accordance with current accounting principles, all liabilities, assets, equity, expenses, and revenues must be reflected in the appropriate amount.
Material assets purchased for a fee are assessed by summing up the actual costs of the purchase. Property received free of charge is accepted at the market price in effect on the date of recording. Material assets created at the enterprise itself are valued at the cost of production.
Types of accounting transactions
Depending on the interaction of assets and sources, there are 4 types of operations.
- Active - affect the composition of funds, i.e., the balance sheet asset, without affecting the results. These include actions to use inventory items, liquidate accounts receivable, receive money from a bank account to the cash desk, issue money on account, etc.
The first type of change is reflected by the formula:
A + ΔI – ΔI = P, where
A - balance sheet asset;
P - passive;
ΔИ - change in property due to economic action.
- Passive operations affect the sources of formation of assets, i.e., the liability side of the balance sheet. The result is constant. Such operations include: deductions from earnings, the formation of reserves or the accrual of dividends from profits for distribution, replenishment of the authorized capital from additional funds, etc.
This type of operation can be reflected as follows:
A = P + ΔI – ΔI.
- Active-passive increasing - increase the asset, liability and currency by an identical amount. These include: repayment of debt on deposits in the authorized capital, accrual of depreciation of fixed assets, advances from buyers, receipt of borrowed funds, etc.
This type of operation looks like this:
A + ΔI = P + ΔI.
- Active-passive decreasing - reduce the asset, liability and balance sheet total by the same amount. This is the payment of earnings, payment of debts to creditors.
A – ΔI = P – ΔI.
Example 1. Type 4 operation
Based on bills and bank statements, 214 thousand rubles were transferred to the supplier. for the materials received. The result of the operation will be a change in two items: the asset account will decrease. 51 by 214 thousand rubles, in liabilities the account will decrease. 62 for 214 thousand rubles. The asset and liability totals changed by an equal amount. The balance identity is preserved.
Consideration of four types of business transactions led to the following conclusions:
- Each fact of activity is reflected in at least two balance sheet items;
- Changes to the asset (types 1, 2) do not change the currency of the document;
- Changes in assets and liabilities (types 3, 4) change the currency by the same amount;
- Any operations maintain equality of balance sheet totals.
Table. Examples of postings by type of operation.
| Content | Debit | deviation | Credit | deviation |
| Type 1. | ||||
| Raw materials transferred to production | 20 | + | 10 | — |
| Payment received from buyer | 51 | + | 60 | — |
| Received money in cash | 50 | + | 51 | — |
| Type 2. | ||||
| Personal income tax withheld from salary | 70 | — | 68 | + |
| The reserve is replenished from profits to be distributed | 84 | — | 82 | + |
| Advance paid to supplier using borrowed funds | 60 | — | 66 | + |
| Type 3. | ||||
| Received materials from supplier | 10 | + | 60 | + |
| Salary accrued | 20 | + | 70 | + |
| The loan amount has been credited to the account | 51 | + | 66 | + |
| Type 4. | ||||
| Loan repaid | 66 | — | 51 | — |
| Employees' salaries transferred | 70 | — | 51 | — |
| Payment has been made to the supplier for the goods | 51 | — | 60 | — |
Returning goods to the seller
The seller receives the goods that were returned by the buyer who is not a VAT payer
1. The seller makes a record in the sales book about the issued invoice with KVO 26. The fields “Name of the buyer” and “TIN/KPP of the buyer” do not need to be filled in.
2. When a buyer who is not a VAT payer returns the goods, the seller makes an entry in the purchase book with KVO 16. In the fields “Name of the seller” and “TIN/KPP of the seller” he indicates his own details (only data on the TIN/KPP is included in the declaration , name not given).
The seller receives the goods that were returned by the individual buyer who paid for the purchase in cash
If an organization sells goods, work, or services to customers exempt from VAT obligations, at the end of the day it generates a report with the total cost of sales and the amount of VAT.
Based on the report, one invoice entry is made in the sales book for the total cost of sales and the amount of VAT. One entry can also be made based on the results of the month (quarter), the data for which is compiled in a summary document.
1. The seller makes a record in the sales book about the issued invoice with KVO 26, but does not fill in the fields “Name of buyer” and “TIN/KPP of buyer”.
2. If the goods are returned by an individual, the seller makes an entry in the purchase book with KVO 17. In the fields “Name of the seller”, “TIN/KPP of the seller”, he indicates his own details (the declaration includes only data on the TIN/KPP, the name is not indicated), in the field “Number and date of document confirming payment of tax” - the number and date of the document confirming the return of funds to individuals.
How to determine the type of operation?
To understand which of the four types discussed above a transaction belongs to, you need to determine which accounts are involved in the posting and what happens to the balance sheet currency.
| Type of transaction | Corresponding accounts | Changes in Debit and Credit values | Balance sheet |
| Active | Both active | Dt increases, Kt decreases | Doesn't change |
| Passive | Both are passive | Dt decreases, Kt increases | |
| Mixed to increase | Dt - active, Kt - passive | Dt and Kt increase | Increases |
| Mixed on decline | Dt - passive, Kt - active | Dt and Kt decrease | Decreases |
To have a good understanding of the types of accounts, you need to know their layout and balance sheet design. An asset refers to the company's property, and a liability refers to sources. There are mixed type accounts that can be present in both the assets of the balance sheet and the liabilities. It depends on the state of the settlements. These include: 40, 60, 62, 68, 69, 71, 73, 75, 76, 79, 84, 90, 91, 99.
Features of reflecting accounting entries
Each production action must be documented. Changes arising from the operation are of a dual nature and occur in two interrelated accounting objects. A characteristic feature of the operation is that it is shown on the accounts twice: in debit and credit. This relationship represents the correspondence of accounts.
Transactions are reflected on accounts at the time of their occurrence, i.e., as they are completed. Double entry reveals the opposite nature of the asset and liability accounts, linking them to the form of the balance sheet. On the left they reflect the balances of the property (debit), on the right - the sources of its appearance (credit).
Correspondent accounts and balance form a single system, connected by double entry, which is based on three principles: (click to expand)
- Duality of reflection;
- Fixation of amounts for Dt and Ct accounts;
- In both accounts, changes are shown in the same amount.
For control, the registration of the action in accounting is repeated twice. First of all, it is reflected as a fait accompli confirmed by documents, then - by the distribution of amounts among correspondent accounts.
Example 2. Posting
Contents of the operation: materials worth 85 thousand rubles were received from the supplier.
Reasoning:
The changes affected two accounts: account. 10 — balances of inventory items and invoices increased. 60 - the debt to the supplier has increased.
Account 10 - active, takes into account assets, growth is put in Dt;
Account 60 - passive, height - according to Kt.
The increase in assets and liabilities corresponds to operations of the third type. The posting is written as follows: Dt 10 Kt 60.
Simultaneous sale (purchase) of own goods and goods under a commission agreement
An intermediary providing services under a commission agreement may, simultaneously with fulfilling obligations under the contract, sell his own goods to the principal or purchase goods from the principal for himself.
1. Sale by an intermediary of goods under a commission agreement and its own goods.
The intermediary must make the following entries on invoices:
- in the journal of received invoices with KVO 01, which reflects data on goods sold as part of intermediary activities;
- in the journal of issued invoices with KVO 15, which reflects data on goods sold as part of intermediary activities;
- in the sales book with KVO 15, which reflects data on the own goods sold to the buyer simultaneously with the goods of the consignor, indicating: the cost of sales obtained by adding the cost of the goods of the consignor and the consignor’s own goods;
- the amount of VAT only for your own goods.
2. Purchase by an intermediary of goods for the principal and his own needs.
The intermediary must make the following entries on invoices:
- in the journal of received invoices, an entry with KVO 15, which reflects data on goods purchased for the principal. Indicate: the purchase price, obtained by adding the cost of goods for the principal and own goods;
- the amount of VAT only for goods for the consignor.
- in the journal of issued invoices, an entry with KVO 15, which reflects data on goods purchased for the principal;
- in the purchase book, an entry with KVO 15, which reflects data on goods purchased for yourself. Indicate: the purchase price, obtained by adding the cost of goods for the principal and own goods;
- VAT amount only for own goods.
Documentary evidence of records
Entries in accounts are made according to documents, so all papers received by the accountant are subject to processing. Documents are established for homogeneous groups of operations. For each action, they create correspondence accounts. The text indicating the correspondence and amount is called a posting. It is compiled directly on the document, in a statement, or in a special journal.
To facilitate data entry, each account is assigned a number. The control function of double entry of information is to check the equality of debit and credit turnover for the period. Inequality indicates the presence of an error in the wiring. The cognitive function of double registration is that it is easy to formulate the content of the operation using correspondent accounts.
Example 3. Formulation of the contents of correspondent accounts
The entry is given: Dt 69 Kt 51 in the amount of 15,300 rubles.
Explanation:
Dt sch. 69 - passive, a decrease in the sources of the company’s funds is recorded;
Kt sch. 51 - active, the cost of funds is decreasing.
The values in these accounts decrease, which means that the operation belongs to the fourth type.
The content of the posting will be as follows: “reflects the transfer of funds to extra-budgetary funds in the amount of 15,300 rubles.”
Adjustment invoice for reduction
The company issues or receives a reduction adjustment invoice if the price has changed, the quantity of the product has changed, or the product has been partially returned.
What to consider when issuing an adjustment invoice:
- The consent of the parties to change the price is required. It can be drawn up in the form of an additional agreement (as a two-sided document), in the form of a notification (a one-sided document) or a primary document (for example, an act on an established discrepancy).
- A correction invoice is issued for a specific original invoice. You can create one adjustment invoice for several original invoices from the same business partner. This document is called a “Unified Adjustment Invoice”.
- An adjustment invoice must be issued within five calendar days from the date of signing the document indicating a change in the value of the invoice, including due to a change in the price or quantity (volume) of goods shipped. If the parties agreed on changes before the seller issued a shipping invoice, then within five days from the date of shipment he issues a regular invoice for the new price/quantity of the goods. In this case, it is not necessary to issue an adjustment invoice.
- Issued in two copies.
The difference between the tax amounts calculated based on the cost of goods shipped before and after such a reduction is taken by the seller as a deduction, and the buyer must restore it.
The buyer selects the recovery period according to the earliest date:
- obtaining primary documents to reduce the cost of goods;
- receiving a corrective invoice.
Let's consider this situation in more detail.
Salesman
1. The seller reflects the sale of goods by making an entry in the sales book about the invoice with KVO 01.
If you need to reduce the amount of a previously registered sales invoice, you should create an adjustment invoice on its basis with KVO 18. An entry about it must be made in the purchase book, indicating:
- in the field “Number and date of the seller’s invoice” - the data of the original invoice;
- in the field “Number and date of the seller’s adjustment invoice” - details of the adjustment invoice;
- in the fields “Name of the seller”, “TIN/KPP of the seller” - your own details (information from the purchase book includes only data on the TIN/KPP, the name is not indicated);
- in the fields “Cost of purchases on the invoice, the difference in the cost on the adjustment invoice (including VAT), in the currency of the invoice”, “VAT amount on the invoice, the difference in the amount of VAT on the adjustment invoice accepted for deduction, in rubles and kopecks” - amounts by which similar amounts of the original invoice were reduced.
Buyer
1. The buyer reflects the purchase of goods by making an entry in the purchase book about the received invoice with KVO 01.
2. Having received an adjustment invoice to reduce the amount of a previously registered invoice, the buyer makes an entry about the adjustment invoice in the sales book with KVO 18, indicating:
- in the field “Number and date of the seller’s invoice” - the data of the original invoice;
- in the field “Number and date of the seller’s adjustment invoice” - details of the adjustment invoice;
- in the fields “Name of the buyer”, “TIN/KPP of the buyer” - your own details (only data on the TIN/KPP is included in the declaration, the name is not indicated);
- in the fields “Cost of sales according to the invoice, difference in value according to the adjustment invoice (including VAT), in the currency of the invoice”, “Cost of taxable sales according to the invoice, difference in value according to the adjustment invoice (without VAT) in rubles and kopecks at the rate”, “VAT amount on the invoice, the difference in the VAT amount on the adjustment invoice, in rubles and kopecks, at the rate” - the corresponding amounts by which similar amounts of the original invoice are reduced.
Basic balance postings
Postings for some business activities are presented in the table.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| Wage | ||
| 20 (25) | 70 | Salaries accrued to the main workers (administration) |
| 70 | 68 | Personal income tax withheld from employees' earnings |
| 76 | Child support withheld from salary | |
| 50, 51 | Salary paid | |
| 20 (25) | 69 | Contributions to extra-budgetary funds accrued |
| 68, (69) | 51 | Personal income tax (insurance contributions) transferred |
| Cash desk and bank | ||
| 50 | 51, (52) | Money has been received from the account to the cashier |
| 62 | Advance received from buyer | |
| 70 | Refund of excess amounts paid for salaries | |
| 71 | Return of the balance of accountable money | |
| 75 | Contribution to the authorized capital has been received | |
| 70 | 50 | Salary paid |
| 71 | Money was issued for reporting | |
| 94 | The lack of money in the cash register has been taken into account | |
| 73 | A loan was issued to an employee | |
| 51 | Proceeds handed over to the bank | |
| 51 | 62, (76) | Paid for goods by buyer (debtor) |
| 66, 67 | Loan received | |
| 75 | 51 | Dividends paid |
| 60 | Money was transferred to the supplier for the goods | |
| 66, 67 | Loan interest paid off | |
| 81 | Shares purchased | |
| 91.2 | Payment to the bank for cash management services | |
| Fixed assets (FPE) and intangible assets (IMA) | ||
| 08 | 60, 71, 75, 76 | Received OS (intangible assets) |
| 01, (04) | 08 | Assets were accepted for accounting (intangible assets were put into operation) |
| 20, 23, 25, 26, 44 | 02, (05) | Accrued depreciation on fixed assets (intangible assets) |
| Inventories | ||
| 10, (11) | 60, 75, 76 | Received MPZ (animals) |
| 20, 23, 29 | Production waste has arrived | |
| 20, 23, 25, 26, 44 | 10 | MPZ written off |
| 90, 91 | MPZ sold | |
| 08 | 11 | Young cattle were transferred to the main herd |
| 20, 23, 29 | Costs of slaughtering animals are taken into account | |
| Expenses | ||
| 20 | 23, 25, 26, (28) | The costs of other production (losses from defects) are distributed among the main products |
| 21 | Own semi-finished products were released into production for processing | |
| 20, 23, 25, 26, 44 | 60, 76 | Works (services) of third-party organizations are reflected |
| 68, 69, 70 | Taxes and salaries accrued | |
| 21 | 20 | Semi-finished products (own) are taken into account |
| 90 | 44 | Sales expenses are written off to the cost of products sold |
| Calculations | ||
| 62 | 90 | Products sold |
| 20, 25, 44 | 66, 67 | Interest accrued on the loan |
| 10, 20, 41 | 71 | Accountable amount spent |
| 73 | 94 | The shortage is attributed to the culprit |
| 75 | 80 | Authorized fund accrued |
| 10, 51, 50,11, 41 | 75 | Funds contributed to the contribution to the authorized capital |
| Capital | ||
| 81 | 50, 51 | Securities purchased |
| 84, 75 | 82 | The reserve fund has been replenished |
| 82 | 84 | Losses are covered using reserve capital funds |
| 75 | 83 | Increased price of securities |
| 75 | 80 | Authorized fund accrued |
| 83 | 75 | Additional capital is distributed among the participants of the JSC |
| 50, 51 | 86 | Special-purpose financing |
| Financial results | ||
| 90 | 10, 21, 41, 43 | The cost of inventory items is written off |
| 62 | 90 | Sales revenue taken into account |
| 90 | 68 | VAT charged on products sold |
| 20, (44) | Actual sales expenses are written off (cost of sales) | |
| 99 | Sales profit taken into account | |
| 40 | The deviation of the actual cost from the planned cost is reflected | |
| 99 | 90 | Loss on sales by main activities |
| 91.2 | 10 | Spare parts written off for repairs |
| 03 | The value of property leased is written off | |
| 20 | Main production services written off | |
| 94 | Shortage written off (no culprit) | |
| 99 | Profit from sales written off | |
| 99 | 91.2 | Other expenses written off at the end of the year |
| 10 | Spare parts from car disassembly are taken into account | |
| 20, 23, 91 | 96 | A reserve has been created for future expenses |
| 99 | 68 | Profit tax accrued |
| 84 | 99 | Uncovered loss identified |
| 99 | 84 | The final result of the work is reflected - profit |
Prepaid transactions
The seller, upon receipt of payment for the future delivery of goods (performance of work, provision of services), is obliged to issue an advance invoice within five working days.
An advance invoice is not issued if:
- an advance was received against the future supply of goods with a long production cycle;
- the advance was received against the future supply of goods taxed at a rate of 0%.
The seller must register the advance invoice issued in the sales book. The amount of the advance received by the seller must be reflected in the VAT tax return in column 3 of line 070 of section 3, and the amount of calculated VAT on the advance - in column 5.
After shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), the seller has the right to deduct VAT calculated from advance payments. In this case, the seller must issue a shipping invoice. When recording the shipping invoice in the sales ledger, the seller can exercise the right of deduction and record the advance invoice in the purchase ledger. In the “Name of Goods” column when issuing an invoice, you must correctly indicate information about the goods so that the delivery of the goods can be identified.
The advance invoice should indicate that this is an advance payment for the goods. A supply agreement (a contract for the performance of work or the provision of services) must contain conditions on the transfer of an advance payment, its amount and the timing of delivery of goods (performance of work, provision of services).
Amounts of VAT on advances accepted for deduction when shipping goods (performing work, providing services) must be indicated in column 3 of line 170 of section 3 of the declaration. The shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) is reflected on line 010 (020) in column 3 of section 3, and the VAT amount is reflected in column 5.
Let's look at this transaction from the perspective of the seller and the buyer.
Salesman
1. The seller issues an invoice for the advance payment with KVO 02, making an entry about it in the sales book. In this case, the following fields are not filled in:
- “Cost of taxable sales according to the invoice, the difference in value according to the adjustment invoice (excluding VAT) in rubles and kopecks, at the rate”;
- “The cost of sales exempt from tax according to the invoice, the difference in value according to the adjustment invoice in rubles and kopecks.”
2. Sales of goods are reflected by an entry in the sales book with KVO 01:
3. The seller returns the advance payment (previously paid to the VAT budget), making an entry in the purchase book with the data of the original (advance) invoice with KVO 22. In the fields “Name of the seller” and “TIN/KPP of the seller” indicates his own details (in information from the purchase book is included only TIN/KPP, the name is not indicated).
Buyer
1. The buyer makes an entry in the purchase book about the received invoice for the advance payment with KVO 02.
2. Receipt of goods from the seller is reflected in the form of an invoice entry for receipt with KVO 01 in the purchase book.
3. The buyer restores the VAT (returns the previously received deduction to the budget) by making an entry in the sales book with the data of the original (advance) invoice with KVO 21. In the fields “Name of the buyer” and “TIN/KPP of the buyer” he indicates his details ( The declaration includes only data on the TIN/KPP, the name is not indicated).