Updated January 5, 2021
Hello, dear readers of the KtoNaNovenkogo.ru blog. The world of economics for a person far from business seems incomprehensible and mysterious. But is he really so incomprehensible?
Today I will explain in simple words one of the fundamental economic concepts - working capital (current assets). Let's look at what working capital (CA) is, how it differs from fixed assets, and how its efficiency is calculated.
What does "current assets" mean?
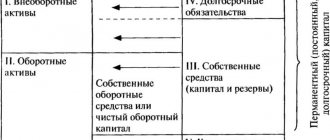
The active part of the balance sheet of each company contains information about the property assets at its disposal. All company assets can be divided into two conditional groups: current assets and non-current assets . The first group includes various property assets of the company used in the course of business activities. This category includes production equipment, vehicles and a number of other material assets. Asset turnover involves three distinct stages during which the above values change their own economic structure:
- First stage. At this stage, the company's financial resources are transformed into the production capacity of the enterprise. An example of this stage of turnover is the acquisition of raw materials, production equipment and other resources necessary for the operation of the company.
- Second phase. At this stage, working capital transfers its value to the price of manufactured products. It is important to note that this process is carried out only once. As a rule, this stage involves the introduction of new technologies for the production of commercial products.
- The final stage. At the final stage, finished products are sold through various markets, which brings new financial resources to the production company.
Current assets are a certain category of resources owned by a company that can be converted into cash within a certain period of time.
Carrying out activities aimed at assessing the amount of working capital allows us to determine the amount of resources that can be used during the production cycle. The results of this assessment form the basis for the company's working capital creation strategy . Proper optimization of such funds allows one to identify assets with the highest liquidity. Such funds can be used in the production process and can be converted into financial resources.
What do they include
For detailed information on the state of other current assets, it is assumed that there is a specially designated line 12605 “Deferred expenses”.
This line reflects income from the sale of property, the right to ownership of which has not yet been registered in the name of the buyer. To clarify the situation, an accompanying note or a note in the form of an additional line with a transcript is allowed as an attachment.
Also, line 12605 takes into account the value added tax, which was accrued on the amount of revenue received, but cannot be temporarily taken into account due to the following circumstances regulated in PBU 9/99. Conditions for revenue recognition that must be met simultaneously:
- The right to receive revenue for an organization is legally secured and has a legal basis, i.e. it arose when concluding the relevant agreement or in another way.
- The amount of money received is determinable.
- When there is a guarantee that from specific actions, the enterprise will receive an increase in economic benefits. For example, when a firm has received payment for an asset or its receipt is certain.
- Ownership of certain products has been transferred from the organization to the buyer, customer, and also if the service has been provided in full and accepted.
- The expenses that the company has made or plans to make have a cost determination.
If at least one condition is not met, then the cash and other assets that were transferred to the company will not be taken into account in the revenue column, but will be taken into account in the balance sheet in the accounts receivable group.
However, there are exceptions:
- Lease or provision for temporary operation of any asset owned by the company.
- Providing intellectual property products – registered patents – for remuneration for temporary use. They can be for inventions, samples of industrial equipment and other types.
- Taking part in the authorized capital of other enterprises.
To recognize the revenue of such organizations, it is necessary to simultaneously fulfill only the first three items from the list.
- The amount of damage caused due to property damage or shortages, the culprit of which has not yet been identified or a decision has not been made to write them off as expenses for the production process or sales expenses.
- VAT and excise taxes refundable in the near future.
- The price determined by the contract, which has been calculated but not yet issued.
- The amount of shares that were purchased from other companies for further resale.
What shapes enterprise resources
Current assets of an enterprise are a separate category of financial resources and material assets that can be used in the production process. The main component of working capital is cash and cash equivalents. This balance sheet item can include both cash stored in the company's cash desk and funds available in the company's current account. Cash equivalents are financial assets of a short-term nature. Funds belonging to this group must meet certain criteria. As a rule, such tangible assets should be sold at a price equal to their fair market value. The period for disposal of assets should not exceed three months.
Current assets include accounts receivable that are short-term in nature. It is important to note that in the case of these assets, it is very important to consider the volume of promised payments. In addition, the loan term should not exceed one year. This condition for providing an installment plan or loan is a mandatory criterion for classifying receivables as working capital.
These assets require reimbursement upon consumption, and their use implies future economic benefits.
One of the sources of enterprise resources is raw materials and consumables. Such materials are used in every production cycle. This category includes fuels and lubricants, spare parts and consumables, packaging and other containers. It is important to note that unfinished goods and semi-finished goods also fall under the category of current assets. Many enterprises use technologies that are based on a certain stage when an unfinished product is moved to a warehouse. Unfinished products cannot be offered for sale or used as raw materials. It is this factor that forces these funds to be indicated in a separate line of the balance sheet.
All of the above sources are the company's own resources. In addition to them, financial loans or investments received from third-party investors can be used as working capital. It is important to note that using your own sources can significantly reduce the risk compared to using third-party resources.
Are current assets and current assets the same thing? This question is asked by many newbies in business. “Current assets” is a term often used in accounting, and “current assets” in economic research. Despite some specific differences between these concepts, they reflect those property values of the company that can be converted into financial resources.
Financial structure of the bank
The bank, like other organizations operating on the market, has its own assets. Bank working capital is unique in its own way.
Did not you find what you were looking for?
Just write and we will help
All banks work with money, so we can say that banking products are funds that are used for lending.
Definition 1
A bank is an organization that operates in the field of financing through the issuance of financial assets to the borrower on mutually beneficial terms.
Note 2
Banking assets are all present economic resources used by a banking institution to generate profit.
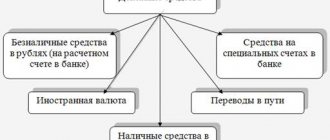
Regarding current banking assets, they are the majority of all bank assets and are reflected in the total amount of money, including securities.
An important component of working bank funds is money; it is they that are needed for the effective functioning of the bank.
Components of assets on the balance sheet
The balance sheet contains important information about the value of the property assets of a particular company. This information is generated on the basis of financial statements, valuation activities and other documents. In simple terms, a balance sheet asset is a kind of list listing the company’s material assets that are at its own disposal.
Current assets
The working capital item of each enterprise includes six components. The first component is accounts receivable, which are urgent. The next part of this group is the financial investments made by the company itself. The validity period of these investments should not exceed one year. In addition to accounts receivable and financial investments, “input” VAT is included in the working capital item, which has not yet been accepted by regulatory authorities.
One of the important parts of current assets are financial resources. This part of this group includes several items:
- Cash kept in the cash register of a particular institution.
- Money placed in the current account of a banking organization.
- Funds credited to the company's foreign currency account.
The fifth component of working capital is the company's reserves. This category includes raw materials and inventory, products being prepared for sale, unfinished goods, semi-finished products and those valuables that will be used for resale. The last part of working capital is other assets that can be converted into cash.
Current assets - refers to material assets directly used to carry out the production process
Other current assets
Other current assets include a debit balance, that is, the amount of VAT accrued during the shipment of marketable products. This article also includes value added tax received when making an advance payment. This group of funds also includes manufacturing defects, shortages and financial losses. The complete list of resources related to this group is as follows:
- Damaged property that has not been written off from the company’s accounts.
- Costs associated with fulfilling unfinished orders.
- VAT on shipped products, advance payments, as well as excise taxes, which will be reimbursed in the next reporting period.
In addition to the resources listed above, this group may include securities and funds invested in the authorized capital of third-party companies. The main criterion for selecting resources in this group is their implementation period. According to the established rules, other working capital is recorded in the second section of the balance sheet, in line number 1260.
Low liquid current assets
Before examining the question of what falls into the category of assets with low liquidity, it is necessary to consider the meaning of the term “liquidity”. This economic analysis tool displays the rate of transformation of property values into financial resources. In simple words, this indicator demonstrates the speed of asset sales. According to experts, asset liquidity is of paramount importance in generating revenue. In order to gain full control over the financial condition of the company, you need to develop a strategy that allows you to quickly identify the most liquid assets that can be used to overcome the crisis.
Experts also note that the risk level of an entrepreneur is inversely proportional to the liquidity of the asset. Thus, financial resources and liabilities of a short-term nature have the highest level of liquidity and the minimum degree of risk for the entrepreneur. Inventories and finished goods also have high liquidity. The only caveat associated with these funds is the need for a quick sale. The risk level of these assets is low.
Semi-finished and unfinished products have average liquidity and average risk. Low liquidity assets include unused capacity, overdue accounts receivable and unfinished goods (assuming high volume). It is important to note that this group has the maximum level of risk.
As a rule, the category under consideration includes those assets where the turnover rate in cash equivalent is more than twelve months. A striking example of such assets is commercial products stored in a company's warehouse for a long time. This category also includes loans issued with a repayment period of more than one year. Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that working capital with a high degree of risk is included in the group of low-liquidity resources.
Analysis of current assets displayed in the balance sheet allows us to identify the provision of the production cycle with the necessary resources
Line 1210 “Inventories”
Line 1210 should reflect information about materials, goods, finished products and work in progress. Inventories also include household equipment, inexpensive office furniture, stationery and other property of the organization that has not been written off at the end of the reporting period.
The data on line 1210 primarily includes the debit balance on account 10 “Materials”. Here the cost of materials, purchased semi-finished products, components, fuel, packaging and spare parts that are not written off for production is indicated.
An organization can keep records of raw materials and supplies on account 10 at accounting prices. Then actual costs are reflected in the debit of account 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”, and the deviation of actual costs from accounting ones is reflected in account 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets”.
With this accounting procedure, when filling out line 1210, to the balance of account 10, you must either add the debit balance on account 16 (if the actual cost of materials exceeds the accounting one), or subtract the credit balance on this account (if the actual cost of materials is lower than the accounting one).
If an organization creates a reserve for the depreciation of inventories, then when filling out line 1210 from the debit balance of account 10, the credit balance of account 14 “Provisions for the reduction of the value of material assets” is subtracted.
Line 1210 reflects the cost of products that have not gone through all stages of processing, as well as work that was not accepted by customers. To fill out this line, manufacturing firms summarize their account balances:
— 20 “Main production”; — 21 “Semi-finished products of own production”; — 23 “Auxiliary production”; — 29 “Service industries and farms”; — 44 “Sales expenses”; — 46 “Completed stages of unfinished work.”
Trading companies show on line 1210 transportation costs that relate to the balance of unsold goods. If the accounting policy provides that transportation costs are included directly in the cost of purchased goods, then such expenses are reflected in account 41 “Goods” and are also included in these lines 1210 of the balance sheet, but as part of the cost of goods.
To reflect balances of finished products and goods in the balance sheet, the debit balance of accounts 41 “Goods” and 43 “Finished Products” is transferred to line 1210. If an organization accounts for goods at sales prices, then from the debit balance in account 41 the credit balance in account 42 “Trade margin” is subtracted. That is, in line 1210 of the balance sheet, goods are reflected at actual cost.
Manufacturing enterprises indicate in line 1210 the actual or standard cost of finished products.
In addition, line 1210 reflects the cost of products or goods transferred to customers, the proceeds from the sale of which cannot be recognized in accounting. For example, if the transfer of ownership of goods occurs not at the time of shipment, but after payment. On the same line, the cost of valuables that are transferred to other organizations for sale under a commission agreement is recorded. Thus, the debit balance of account 45 “Shipped Goods” is entered in line 1210.
How to calculate the liquidity ratio of available resources
To identify the amount of time required for the full turnover of the company's own funds, a formula is used to calculate the current liquidity ratio. This economic instrument clearly displays the financial condition of the company and the ability to repay current debt obligations using its own funds. From all of the above, we can conclude that identifying a high coefficient makes it possible to determine the effectiveness of decisions made by management.
When making calculations, the formula is used: “Current assets / short-term debt obligations.” All the data needed for the calculation can be found in both the financial documents and the balance sheet. When considering the methodology for calculating the liquidity of working capital, it is necessary to mention the procedure for determining net assets. Net assets represent the totality of financial assets owned by the company and long-term loans minus the total amount of non-current assets.
Working bank funds and their role
Working capital serves as the foundation for a bank. They are the source of issuing loans, opening deposits, and issuing money.
Credit is the most common banking product.
Definition 2
A loan is a loan of money for a short or long term on banking terms.
When issuing a loan, an exchange of working capital occurs, that is, the bank gives its funds to the borrower, and the borrower returns the working capital.
There are two ways to issue loans:
- Short-term loan for up to one year. This type of lending is suitable for those organizations where the shortage of working capital is insignificant, and the production cycle is quite short, which leads to the rapid release and sale of finished products, and therefore a quick return of funds. This type of loan is issued quite quickly, but its peculiarity is a fairly high interest rate. It is possible to repay the loan ahead of schedule, but this also occurs under certain conditions. Obtaining this type of loan is not profitable for the borrower due to the fact that a high interest rate leads to an increase in the price of manufactured products. Therefore, before taking out such a loan, it is necessary to calculate how profitable it is from a financial point of view;
- Long-term loan, for a period of more than a year. This means issuing a bank loan for a long time with an acceptable interest rate. Such lending does not provide for early repayment or offers absolutely unfavorable conditions for the borrower. Long-term lending is relevant in this case. If the company receives several large-scale orders at once. If the financial benefits are correctly calculated, such a loan is quite profitable.
Is it difficult to figure it out on your own?
Try asking your teachers for help
Solving problems Tests Essays
Conclusions (+ video)
Current assets on the balance sheet are resources that can be used by the company to improve its financial condition. Timely and competent use of such resources allows us to overcome the economic crisis with minimal negative consequences. Each company must independently determine the size of its working capital based on its needs, production capacity and business size. It is important to pay attention to the fact that a lack of assets in circulation can cause a stop in the production process and an increase in current debt. An increased number of such assets indicates an incorrect allocation of resources and an ill-chosen business development strategy.
Line 1240 “Financial investments (except ...)”
In line 1240, reflect data on short-term financial investments. Here we are talking about assets with a circulation or maturity period of no more than 12 months. For example, these are loans issued for a period of less than a year, bills or bonds with a maturity of no more than 12 months. Data on long-term investments are indicated in line 1170 of the first section of the balance sheet.
In line 1240 enter the debit balance of account 58 “Financial investments” (in terms of short-term investments). If a company creates a reserve for reducing the cost of financial investments, then the indicator in line 1240 of the balance sheet is reflected minus contributions to this reserve. That is, when filling out line 1240, the credit balance of account 59 “Provisions for impairment of financial investments” is subtracted from the debit balance of account 58.
Information about interest-free loans is not indicated in line 1240. Such loans are not financial investments. Therefore, their amount is taken into account as part of accounts receivable on line 1230 of the balance sheet.
And further. Line 1240 does not reflect information about cash equivalents. Their amount is given in line 1250 of the balance sheet.
Line 1260 and count
On line 1260, transactions are carried out on those current assets that cannot be attributed to any item in the main section 2 in the balance sheet.
Example:
- Debit balance on account 45 “Shipped goods”, including here the amounts of VAT accrued upon shipment of products.
- Debit balance for account 46 “Stages completed for work in progress.”
- Debit balance with entry to account 62. Settlements with clients and customers are indicated here. The display finds VAT accrued on the product and advance payment or partial payment of the amount.
- The debit balance of account 69 is payment of taxes and fees. The amounts of excise taxes deducted, but overpaid and not offset, but for which a decision was not made to return them to the company’s budget, are noted. This also includes excessive payments of social insurance and security contributions, which have not been taken into account, but have not yet been entered into the budget balance.
- The debit balance of account 76 is payment of debt to debtors and creditors. In particular, the amounts of VAT, accrued advance payments and preliminary calculations of a full or partial nature.
- Debit balance on account 81 – shares and interests in other organizations, purchased and owned by the enterprise for the purpose of their further sale on more favorable terms.
- The debit balance of account 94 is losses from property damage, defects and shortages.
Line 1260 may take into account the value of assets, the size of which is not significant for assessing the financial and economic condition of the enterprise.
Thus, when compiling line 1260 in the balance sheet, the debit balance of the following accounts can be used:
- 45 – Goods that have been shipped;
- 46 – Stages that have been completed for unfinished work;
- 62 – Settlement operations with customers, buyers and clients;
- 68 – Payment of tax assessments and fees;
- 81 – Shares and equity participation in other companies owned by the enterprise;
- 94 – Losses incurred due to identified shortages, defective goods and damage to property.