Business lawyer > Accounting > What is deduction code 501: features of reflection in certificate 2 – personal income tax
The legislation provides for personal income tax (NDFL). It is calculated as a percentage of the wages of officially employed workers minus the tax benefits provided. The Tax Code has approved certain codes for each type of income and deductions. The deduction code 501 also has its own characteristics. We will talk about it in this article.
What income can be reduced due to tax deductions?
Certificate 2-NDFL is a comprehensive document that reflects all categories of income received by an individual during the reporting period. These may be:
- basic and additional wages;
- income from transactions with securities and foreign currencies;
- interest on deposits, dividends from other investments;
- material assistance in the form of cash or property (in-kind) payment;
- winnings from participation in sweepstakes and lotteries, casinos and sweepstakes, received not only in monetary but also in property form;
- royalties;
- income from rental activities.
Since there are quite a lot of types of income, and different tax deductions can be applied to them, a special coding system is used to identify each item in the 2-NDFL certificate, as well as in accounting registers, to avoid confusion.
What is personal income tax
To understand why the 2-NDFL certificate is used, you must first understand the meaning of the required abbreviation that appears in its name after the number 2.
What is the certificate in question?
So, personal income tax is a tax levy withdrawn from income received by individuals. The list of these incomes is determined by law. Not all money a citizen can receive is subject to this tax. For example, funds donated by a close relative are not subject to partial deduction to the state treasury.
Most often, the state expects to receive funds for personal income tax from citizens when they:
- receive wages at the place of employment;
- receive bonuses from their superiors;
- accept the provision of financial assistance;
- sell an apartment, house or other housing, or maybe just a share in it;
- rent out their own living space;
- sell a car and other property belonging to them;
- receive royalties for the literary work they publish;
- in many other situations.
This fee is otherwise called income tax. The rates on it are fixed. There are two of them in total. One is relevant for so-called tax residents of the Russian Federation, the other for non-residents.
Possession of this status implies staying on the territory of Russia for a certain period of time - at least 183 days a year. If a citizen has been within the Russian borders for at least a day less, he is not assigned resident status.
Who is a tax resident of the Russian Federation? Our article will help you figure this out. In it we will look at what the tax status depends on, documents for confirmation, as well as the regulatory framework for residents and non-residents.
At the same time, depending on the number of days “on the account” of each citizen, the tax rate will also change. Thus, residents have the opportunity to transfer funds to the treasury at the standard rate for the country: they give only 13% of the funds received. The named value is considered, however, to be quite acceptable. Non-residents are forced to share a huge part of their own income with the state - as much as 30%!
To make it clearer, we will give you an example. Imagine that two friends, Ivan Petrov and Demid Sidorov, decided to sell their home at the same time. Ivan Petrov is in Russia for at least 250 days a year, the rest of the time he goes on business trips or vacations with his family. Demid Sidorov stays within the borders of his homeland no more than 175 days a year. When the time came to sell the apartment, Ivan Petrov put it up for sale at a price of 2 million Russian rubles, and after selling it, he paid 260 thousand in tax to the state treasury (2,000,000 * 13% = 260,000). Demid Sidorov sold the apartment for the same price, however, instead of 260 thousand, he had to give as much as 600 thousand to the state treasury, that is, almost two and a half times more.
Selling an apartment and a car rarely happens in the lives of ordinary people. We will tell you how to calculate and pay taxes on these transactions in our articles: “Tax on the sale of a car” and “Tax on the sale of an apartment.”
As a rule, Russians pay the most income tax in their own lives from the wages they receive at their place of employment. It is issued every month in a certain amount. On the day the salary is issued, a specific part (usually 13%) is deducted from it and transferred to the state treasury on behalf of the taxpayer from whom the money was calculated. The tax agent is involved in this procedure. This, as we have already found out, is the employer organization. In addition to the transfer of wages and tax deductions, the company also provides so-called deductions to citizens by decision of the tax service.
A tax deduction is a certain amount of money by which it is possible to reduce the monetary base taxed in favor of the treasury. In other words, the tax is always calculated from a certain value. Funds deducted from wages are calculated based on its original amount. So, if an employee is promised to be paid a salary of 20 thousand rubles, it means receiving 2 thousand 600 rubles less, that is, only 17 thousand 400 rubles. The difference not received is the part that is due to the state. Its value can be reduced by reducing the wage itself, however, not by demoting the employee or applying any sanctions to him.
It is possible to carry out the procedure using a tax deduction. It is provided to citizens as a result of relevant situations arising in their lives. Most often, deductions are provided through the employer:
- social, for treatment or training of an employee or his family members;
- property, issued when purchasing housing;
- standard, for child support and other types of compensation.
By the amount of the deductions provided, it is possible to reduce the monthly deduction of personal income tax in favor of the state budget, taken directly from the employee’s salary. This reduction will be made until all funds due have been provided in full to the employee.
Types of tax deductions
Depending on the conditions of provision and economic essence, tax deductions are divided into the following categories:
- Standard. They are provided to the majority of the population to provide benefits for the amounts spent on maintaining children. Also, standard deductions are provided for persons with a special status (Heroes of Russia and the USSR, holders of the Order of Glory, etc.).
- Property. They provide for a reduction in the tax base for citizens who have purchased an apartment or other real estate.
- Social. Provided to provide benefits for amounts spent on full-time education in educational institutions for both the taxpayer himself and his children under the age of 24.
- Investment. They provide for preferential treatment for income received from transactions with securities and a number of other types of investment activities.
- Professional. These deductions can be used by persons engaged in private practice or entrepreneurial activities.
Deduction code 501 - decoding
Gifts given by an employer to its employees (including former employees who are retired due to age or disability) are eligible income tax deductions. Its maximum size is determined by clause 18 of Art. 217 of the Russian Tax Code and amounts to 4,000 rubles per year per taxpayer.
This deduction is reflected in the 2-NDFL certificate, as well as in accounting registers and other documents using code 501.
Calculation example
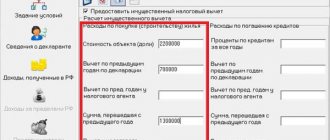
Let’s say a person at work was given a gift, the estimated value of which is 12,000 rubles. This amount must be reflected in the income part of the 2-NDFL certificate, and the amount of the due deduction (4000 rubles) must be indicated by code 501. The tax base in this situation is calculated as follows:
12,000 – 4000 = 8000 rubles
The deduction amount provided under code 501 is a fixed amount. This means that it does not depend on the value of the gift; it can be applied repeatedly during the year, but within the legally defined limit.
For example, if an employer gave an employee a gift in March in the amount of 2,000 rubles, in July - 1,500 rubles, and in December - 7,000 rubles, then the first and second amounts will be fully discounted, and from the third only the balance of 500 rubles can be deducted:
4000 – 2000 – 1500 = 500 rubles
Therefore, income tax withholding will only be made on the value of the gift made in December. The tax base in this case will be 6,500 rubles.
What is the 2-NDFL certificate used for?
As mentioned above, the provision of a 2-NDFL certificate is carried out by a tax agent. Earlier in the article we described what manipulations are carried out by the employing organization:
- issues income to the taxpayer;
- calculates and sends taxes to the budget;
- provides deductions.
Why do organizations fill out 2-NDFL certificates?
To display all the required transactions and transmit a report on them, use the form of the certificate in question established by the state.
The form itself was last updated by the government in December 2015. It was then that the use of a new sample of the required document came into force.
In addition to submitting reports to the Federal Tax Service, employees of the organization may need a 2-NDFL certificate for their own needs. To receive it, they must submit an application addressed to the head of the employing organization.
A document is submitted for verification by a tax agent if:
- he paid persons working for him funds that are subject to partial withholding in favor of the state budget through the calculation of personal income tax;
- it paid employees but was unable to withhold income taxes.
In the second case, the employing company has the obligation, no later than 60 days from the end of the current tax period, to notify employees of the Federal Tax Service about the absence of the required opportunity and, at the end of the year, to submit for verification the data in the completed 2-NDFL certificate.
Help 2-NDFL
When an employee comes to the accounting department and fills out an application for the certificate in question, he will most likely use it in the future for:
- provision at a new place of employment, in order to receive a standard or other type of deduction, since in order to issue the required funds it is necessary to take into account income paid since the beginning of the current taxation period, also taking into account funds issued by the previous employer;
- obtaining information that is then entered into the declaration form form 3-NDFL, which is submitted for verification to the tax office in certain situations;
- transfer to any other place where the certificate was required, for example, to a credit institution, to receive a cash loan.
Please pay attention to the following most important fact: a citizen who requests the issuance of a certificate should not report to accounting employees or even superiors about why he needed it. The employing organization does not have the right to refuse to issue a certificate without this information; this circumstance is determined by the Tax Code of our country.
According to the letter of the law, a certificate must be issued no later than three days from the moment the employee’s application is written and submitted for consideration. Weekends are not taken into account.
If a certificate is requested in the middle of the year, the employer fills it out based on the information already available at the moment.
If a company is not an employer, it is not required to make payroll payments and transfer income tax contributions to the state budget. This means that the organization is also not obliged to prepare, fill out and submit a tax return for verification.
In addition, exemption from this obligation is made in some other cases:
- if the company has paid income to employees, who must independently carry out the procedure for calculating income tax funds and transferring them to the state treasury;
- if such a payment of funds was made in favor of employees, which implies an independent transfer of their part to the treasury by the recipient;
- if income was issued in the form of cash, from which tax is not deducted in accordance with the letter of the law.
The certificate is filled out in accordance with the rules established “at the top”. The document consists of five sections, each of which implies specific information.
Table 1. Completing sections
| Order | Filling |
| 1 | First of all, data is entered on the employing organization that is filling out the required document. |
| 2 | Then indicate information about the employee receiving the funds. |
| 3 | Following is a list of income subject to income tax. |
| 4 | The fourth section lists the tax deductions provided to the employee. |
| 5 | In the fifth, they present the amount of tax that was calculated and the total income. |
Encodings in the certificate are used not only to indicate types of income and deductions. With their help, they also determine on what occasion the paper is provided for verification:
- in the column called “sign” the number 1 is entered if the paper is submitted for income tax that has been successfully transferred to the state treasury;
- The number 2 is entered in the same line if the tax was not withheld.
The transcript provided by the Federal Tax Service in the form of a list written in one of the orders issued by the service will help you understand all the encodings used for reference. You can view the full list by finding it among the attached documents on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
The rules governing the procedure for filling out the certificate are contained within the appendix of the relevant order. Every experienced accountant has an idea about them, since he was faced with filling out the required paper not only while studying at a higher educational institution, but also probably resorted to filling it out more than once in the process of work.
If you are just starting to work in the accounting field and are filling out a document for the first time, you should find a completed sample paper on the Internet and check it first. Be sure to pay attention to the edition from which year the sample you found was created.
The certificate was last updated in 2015, however, outdated certificate forms are still floating around the Internet
How is the right to a deduction under code 501 confirmed?
The provision of gifts to employees of an enterprise must be formalized in accordance with current legislation. Usually an order from the manager is issued, and the reasons for this may be:
- provisions of a collective agreement at a given enterprise or an employment contract with an employee;
- employee personal statement;
- a separate internal regulatory document defining the procedure for issuing gifts to employees of the enterprise.
To receive a tax deduction under code 501, no additional documents are required. Its provision is provided for by current federal legislation, as specified in paragraph 28 of Art. 217 of the Russian Tax Code.
Thus, if an employee of an enterprise received a gift, he will automatically be given a tax deduction in the amount of 4,000 rubles.
Why is it used in accounting practice?
Income code 2720 is used for the same purposes for which the system of codes for all taxes was invented:
- unity and unification of information;
- reducing accounting errors to a minimum;
- improving the quality of tax control.
With the advent of modern means of communication, including TCS, communication between inspectors and company accountants has led to frequent questions from the Federal Tax Service regarding submitted reports and the need for quick responses from payers. If uniform codes are used throughout accounting, then the accountant will easily satisfy the request of the inspection inspector.
For reference! Gifts are paid out of the company's profits after paying all taxes and do not participate in the formation of the financial result.
The gift transferred to the person must be reported to the Federal Tax Service through certificates 2 personal income tax and calculation 6 personal income tax. The certificate is submitted once a year, calculations are submitted after each quarter and at the end of the year (instead of the fourth quarter, calculations for the year are submitted).
Important! If an employee asks for an income form, the employer is obliged to do this within 3 days from the date of the request.
As a rule, the form is generated automatically in 1C, but if an accountant does not have the opportunity to prepare a report on time on a computer, he must fill out the template manually.
An employee can also receive his certificate online – in the taxpayer’s Personal Account, since the Federal Tax Service stores all documents submitted by tax agents in digital form.