Sales costs are one of the main indicators that an enterprise must take into account to determine the price of a product. These expenses are recorded on accounting account 44 (sales expenses). In the article we will look at what is included in sales expenses, and also look at typical entries in tables and examples for account 44.
Composition of sales expenses
Selling expenses are the costs of an organization to purchase a product, as well as additional costs for its sale. The main items of selling expenses include costs for:
- maintenance and servicing of fixed assets that take part in the sales process (commercial equipment, retail premises, etc.);
- wages for employees who directly support the sales process;
- other representation and management expenses.
To record and analyze generalized information about the amounts of sales expenses, account 44 is used. Expenses are accumulated according to Dt 44, a decrease in the amount of costs is reflected according to Kt 44.
What typical wiring includes Dt 44 and Kt 44
Dt 44 Kt 44 is most often contained in the following postings:
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – debt to the supplier for services rendered;
- Dt 44 Kt 10 – the cost of materials is taken into account in expenses;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation;
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – wage costs;
- Dt 44 Kt 69 – expenses for contributions to extra-budgetary funds;
- Dt 44 Kt 71 – expenses for accountable persons;
- Dt 44 Kt 94 – expenses for shortages.
Kt 44 is used when writing off to account 90.
Let's look at a few examples using Dt 44 Kt 44 .
Example 1
An organization engaged in trading activities recorded in March:
- salaries for consultants and sales floor cashiers in the amount of 500,000 rubles;
- expenses for renting a sales area in the amount of 150,000 rubles;
- accrued depreciation on equipment in the hall - 200,000 rubles;
- advertising expenses – 450,000 rubles. (non-standardized for the purpose of calculating income tax).
For information on advertising expenses in tax accounting, see the publication “Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2015): questions and answers.”
In the accounting for March, these transactions were reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 44 Kt 70 – salary 500,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – rental services RUB 150,000;
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – advertising expenses 450,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 02 – depreciation 200,000 rub.
On March 31, the posting was made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 1,300,000. (writing off account 44).
Example 2
The trading organization reflected in its accounting for April on account 44 transportation expenses in the amount of 300,000 rubles. wiring Dt 44 Kt 60.
The balance on the account as of March 31 is 44 - 75,000 rubles.
The cost of goods sold for March is RUB 1,780,000.
The cost of the remaining goods as of March 31 is 360,000 rubles.
It is necessary to distribute transport costs.
To do this, we determine the average percentage of transport costs attributable to the balance of the goods:
(300 000 + 75 000) : (1 780 000 + 360 000) × 100% = 17,52%
The amount of transportation costs for the remaining goods is 360,000 × 17.52% = 63,072 rubles.
The amount of transportation expenses to be written off in April is 300,000 + 75,000 – 63,072 = 311,928 rubles.
On April 30, an entry will be made: Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – RUB 311,928.
For information on tax accounting registers, see the material “Maintaining analytical tax accounting registers (forms).”
Accounting for sales expenses on account 44
The costs of maintaining and servicing fixed assets (store premises, retail equipment) involved in the process of selling goods are one of the main components of sales costs. Let's look at typical transactions for accounting for these expenses:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 44 | 02 | Calculation of depreciation on fixed assets (buildings, premises, commercial equipment, vehicles, etc.) that are used by the organization in the sale of goods and products | Depreciation statement |
| 44 | 04 | Calculation of depreciation on intangible assets that are used by the organization in the sale of goods and products | Depreciation statement |
| 44 | 10, 60 | Reflection of the tenant's costs for renovation of the premises (shop, retail outlet, etc.) | Certificate of completion |
| 44 | 97 | Reflection of expenses for repairs of fixed assets used in the implementation process | Certificate of completion |
As a rule, the full functioning of the sales process is ensured by employees of the organization, whose job responsibilities are in one way or another related to the sale of goods (services). We are talking about salespeople at retail outlets, loaders, and delivery drivers, whose wages are included in sales expenses.
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 44 | Reflection of the amount of accrued wages of employees who provide the procedure for selling goods | Payroll sheet | |
| 44 | Reflection of the amount of sales expenses incurred by the accountable person | Advance report | |
| 44 | 69.1 | Calculation of the amount of insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance | Payroll sheet |
| 44 | 69.2 | Calculation of the amount of insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation on the salaries of employees who ensure the implementation process | Payroll sheet |
| 44 | 69.3 | Calculation of the amount of insurance contributions on the salaries of employees who provide the implementation process (compulsory health insurance) | Payroll sheet |
If the production of goods is carried out in-house, then selling expenses can be reflected in the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 44 | Attribution of the amount of production costs to the costs of selling goods | Production cost sheet | |
| 44 | Inclusion of the cost of products (works, services) of service industries into sales expenses | Production cost sheet |
The use of additional goods and materials in the sales process is recorded using the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Description | Document |
| 44 | 10 | Reflection of the cost of materials that were used in the process of selling goods | Packing list |
| 44 | 41 | Reflection of the cost of goods used in the process of selling goods | Packing list |
| 44 | Reflection of the cost of finished products that were used in the sale of goods | Packing list |
Features of writing off account 44
Expenses reflected in account 44 can relate to both fixed and variable costs and are written off to account 90 “Sales”.
For information on accounting for direct and variable costs, see the article “How to calculate variable costs (examples, formula).”
Write-offs can be made in two ways:
- step by step,
- at one time.
In this case, phased write-off is carried out:
- by production organizations in the form of a monthly distribution of transport services and packaging costs between specific types of shipped products, taking into account their physical characteristics or other indicators;
- for trade organizations and intermediaries - distribution of transport costs taking into account products sold and their balance at the end of the month;
- for agricultural producers - distribution according to accounts 15 (“Procurement and acquisition of material assets”) and 11 (“Animals for growing and fattening”) of expenses for the procurement of agricultural raw materials.
Other expenses (not mentioned above) recorded on account 44 are written off monthly.
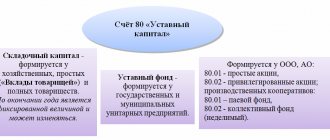
Account characteristics
In order to correctly make entries, you need to know exactly: is account 44 in accounting active or passive? The account is active, synthetic and collective. The latter means that the balance at the end of the period is written off to another account. For the entire month, the debit of account 44 records the enterprise's expenses for the sale of goods, which are reflected in the financial result accounts.
The debit balance in the balance sheet (item “Work in progress”) is indicated only if goods were not fully sold during the reporting period.
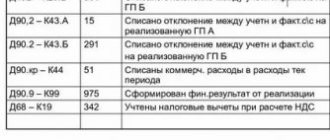
Calculations for income tax (PBU 18/02)
Permanent tax assets and liabilities.
The program analyzes NU data by type of PR accounting and identifies permanent differences between tax and accounting. accounting, their qualification as liabilities and assets.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities.
The program analyzes NU data by type of accounting BP, identifies temporary differences between tax and accounting. accounting, their qualification as settled and recognized deferred liabilities and assets.
Calculation of income tax.
When determining the amount of conditional expense or income for income tax, the program is based on the turnover in account 99.01 and the income tax rates specified in the information register “Income Tax Rates”.
Closing of the year
Balance reform.
In order to perform this operation, you must use documents that close December; in all other cases, this operation is not available. When it is carried out, all balances of subaccounts of accounts 90 and 91 / 99 / 99.01.1 are written off to the corresponding subaccounts 90.09 and 91.09 / 99.01.1 / 84.
Closing tax accounts.
In order to perform this operation in the same way as for the previous one, it is necessary to use documents that close December; in all other cases this operation is not available. When it is carried out, all balances of NU accounts that are not intended to reflect the value of assets are written off.
Need help creating a study plan? Specify a topic and receive a response in 15 minutes get help
Write-off of markup when using goods for your own needs
For example, if you used the goods for your own needs, then the markup should be written off by posting:
Debit 44 Credit 42-STORNO (with minus) - The trade margin is written off on the cost of goods spent for the trade organization’s own needs.
Example:
Condition:
The cost of goods at sales prices used for the trading organization’s own needs amounted to 30,000 rubles. The markup on these goods is 5,000 rubles.
Solution:
Debit 44 credit 41-30,000 rubles -Write off goods for own needs
Debit 44 Credit 42-5000 rubles - Trade mark-up written off (with minus)
Analytical accounts
Many expenses associated with the sale of goods are written off to account 44 in accounting. Subaccounts used for detailed reflection of information:
- 44.1 – opens to collect information on business expenses that are directly related to the process of selling goods or services;
- 44.2 - created to account for the costs of the implementation process, i.e. for the deduction of wages, social benefits, depreciation costs and other expenses;
- 44.3 – takes into account the amounts written off to the cost of sales (when using the partial write-off method).
In addition to analytical accounts of the first level, subaccounts of the second level can be used. They are used to reflect in more detail expenses for certain cost items; these can be accounting accounts:
- transportation costs;
- salary expenses;
- tax payments and social contributions;
- depreciation charges;
- entertainment and other expenses.
Account 44 in accounting has a different gradation of attributing costs to it depending on the direction of the company's activities.
Account 44 in accounting of agricultural enterprises
Organizations involved in the procurement and processing of agricultural products use account 44 to reflect expenses such as:
- transportation of goods;
- rental of premises;
- maintenance of buildings and necessary equipment;
- product storage;
- advertising and entertainment expenses;
- other expenses.
If at the end of the month the products were not sold, the method of partial write-off of selling expenses can be used.
The procedure for reflecting expenses in case of incomplete sales
The following types of expenses are subject to write-off at the end of the reporting month:
- At manufacturing enterprises, they write off to account 90: the costs of packaging and transportation services. In this case, costs are divided between the types of goods shipped on a monthly basis based on weight, volume, production costs and other data.
- At agricultural enterprises, they write off to accounts 11 and 15: costs for the procurement of raw materials, poultry and livestock.
- In trade organizations, they write off to account 90: the costs of transport services, which are calculated as the difference between the costs of transporting goods already sold and balances in the warehouse. The operation is carried out at the end of each reporting period.
All other expenses for the sale of goods are included in their cost (Dt 90 Kt 44). The decision to apply partial or complete write-off of amounts from account 44 in case of incomplete sales remains with the management of the enterprise.
Postings to account 44
For a better understanding of the postings on account 44, we suggest solving the problem.
Conditions: Business expenses: wages - 120,000 rubles, insurance premiums - 36,240 rubles, depreciation of fixed assets - 11,000 rubles, transportation of goods - 21,000 rubles. The balance on account 44 at the beginning of the month was zero.
Postings:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Contents of operation |
| 44 | 02 | 11 000 | Depreciation of fixed assets |
| 44 | 70 | 120 000 | Remuneration of personnel |
| 44 | 69 | 36 240 | Insurance premiums |
| 44 | 76 | 21 000 | Fare |
| Total | 188 240 | ||
The accounting policy provides for the distribution of transportation costs between products sold during the month and the balance at the end of the month.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Yandex.Zen VKontakte Telegram
During the month, the company sold goods worth 560,000 rubles, including VAT 18% - 85,423.73 rubles. The cost of goods sold is 260,580 rubles, the balance of goods in the warehouse is 56,800 rubles.
Calculations:
- share of goods sold = 260,580 / (260,580 + 56,800) ×100 = 82.11%;
- amount of write-off of transportation costs = 21,000 × 82.11% = 17,243.10 rubles.
Consequently, the cost of goods is written off not 188,240, but 184,483.10 rubles.
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Contents of operation |
| 90.02 | 44 | 184 483,10 | Selling expenses are written off as the cost of goods (11,000 + 120,000 + 36,240 +17,243.10) |
The debit balance of account 44 at the end of the month will show the amount of RUB 3,756.90. (21,000 – 17,243.10).
Let's consider the financial result obtained by the company based on the above data:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Contents of operation |
| 62 | 90.01 | 560 000 | Revenue recognized |
| 90.03 | 19 | 85 423,73 | VAT on sales included (560,000 / 118 × 18) |
| 90.02 | 41 | 260 580 | The cost of goods sold is written off |
| 90.02 | 44 | 184 483,10 | Business expenses written off |
| 90.09 | 99 | 29 513,17 | Financial result recognized (560,000 – 85,423.73 –260,580 – 184,483.10) |
Write-off of markup when marking down goods
If you decide to mark down an item, you need to make a posting for the amount of the markdown REVERSE (with a minus):
Debit 41 Credit 42 REVERSE - Markdown of markup.
If the markdown led to a decrease in the cost of the goods, then the difference must be written off to 91 accounts:
Debit 91-2 Credit 41-For the difference in excess of markdown over actual cost.
Example 3 (easy task)
Condition:
CJSC "Tredax" Bought 10 calculators for 12000 (10*1200) Wh VAT 20%. At a surcharge of 30% excluding VAT. The cost of each teapot is 1000 (10,000/10). The total cost is 10,000 rubles.
Solution:
- Debit 41 Credit 60-10,000 rubles (12000/120*100) -Purchase of calculators.
- Debit 19 Credit 60-2000 rubles (12000/120*20) - VAT on purchase
- Debit 41 Credit 42-5600 rubles (10000*0.3+(10000+10000*0.3)*0.2)(Markup +(cost + markup)*20%) or (10000*1.3*1, 2-10000) - Reflects the markup on purchased goods. (comments on the last formula Cost * 1.3 (30% markup) * 1.2 (120% VAT) - Cost) This formula is difficult to understand, you need to re-read and comprehend.
Calculators were marked down by only 6,000 rubles (including VAT), each by 600 (including VAT)
- Debit 41 Credit 42-5600 rubles REVERSE (minus)
- Debit 91-2 Credit 41-400 rubles (6000-5600) - Write-off markdown exceeding the cost of goods (calculator).
ATTENTION: read VAT when marking down, since VAT was accepted for deduction more than sales VAT, VAT needs to be restored