Mandatory invoice details
The invoice must be drawn up on a form (paper or electronic).
- Designation of the serial number and date of issue of the invoice;
- Details of the identified taxpayer number, address and name;
- Address of the shipper and consignee, name;
- Payment and settlement document number;
- Name of supplies from shipment of goods or description of work performed, provision of services;
- The number of deliveries for shipment according to the invoice of goods or works, services;
- Price per unit of measurement excluding tax;
- Cost of goods or works, services;
- Excise tax amount;
- Tax rate;
- VAT amount;
- The sum of the total quantity of goods shipped;
- Country of origin;
- Customs declaration number.
The person authorized to do so may be authorized to sign the invoice by the relevant order. After the signature, you must indicate the surname and initials of the person who signed the document.
About the signature
The invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization (clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What if there is no chief accountant position on staff? Obviously, not indicating the signature of the chief accountant on the invoice due to the absence of such a position in the staffing table does not prevent tax authorities from identifying the seller and buyer of the transaction, the cost of goods, work, services, the rate and amount of tax (paragraph 2, clause 2, art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the absence of the signature of the chief accountant in such a situation should not be grounds for refusal to deduct VAT. A similar conclusion can be drawn from Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2013 No. 03-07-09/25296. Judicial practice confirms the legality of deducting VAT on an invoice in which there is no signature of the chief accountant, in the absence of such a position on the supplier’s staff (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated 04.12.11 No. A19-11133/08, FAS Moscow District dated 01.20.12 No. A40-144847/10-98-1227).
To minimize tax risks, the buyer can ask the seller to make an entry in the invoice indicating that she does not have the position of chief accountant.
Instead of the director and chief accountant, the invoice can be signed by a person authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization. Please note that the legislation does not provide for the obligation of the supplier to provide the buyer with a copy of the administrative document or power of attorney for the right to sign invoices by authorized persons. Therefore, the tax authority does not have the right to demand from the taxpayer-buyer a certified copy of these seller documents. Similar explanations are given by the Federal Tax Service in Letter No. ШС-37-3/8664 dated 08/09/2010.
And finally, we would like to draw your attention to the fact that in order to avoid tax risks, the signature on the invoice must be affixed personally. That is, it is not advisable for the supplier to sign by using a facsimile (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 01.06.2010 No. 03-07-09/33, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated 30.05.14 No. A32-2968/2012, Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 27.09 .2011 No. 4134/11). True, in judicial practice there are decisions made in favor of the legality of deducting VAT on the basis of invoices signed in facsimile. But most of the disputes were resolved in favor of the Federal Tax Service.
Invoice new in 2021
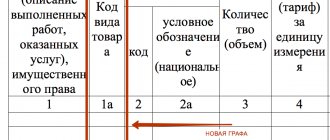
- A column “Identifier of government contract, agreement (agreement)” has appeared in the header - this field must be filled in if data is available;
- A “product type code” has appeared in the tabular section - it must be filled out if the document is sent to Belarus, Armenia, Kazakhstan or Kyrgyzstan;
- The word “registration” was added to the customs declaration column
- The field for signature of an individual entrepreneur has been supplemented with the words “or other authorized person”; now, with a power of attorney, he can sign a document representing the interests of the individual entrepreneur;
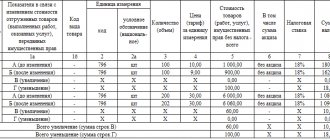
Sales invoice details
This account is used very often, and it requires a full set of details:
- Date and document number;
- Data of the buyer and seller (name, address, TIN);
- Shipper's address and name;
- Address and name of the consignee;
- Details of the payment and settlement document;
- Currency in which the document will be issued;
- Contract ID;
- Name of goods, works, services and indicate the code of the type of goods;
- Total amount of goods excluding VAT, excise tax amount, VAT rate and amount;
- Total amount including taxes;
- Country of origin of the goods;
- Signature of responsible persons;
The documents may be missing:
- Buyer's checkpoint;
- Seller's checkpoint;
- Data of the consignor and consignee, if it is not the goods that are sold;
- Details of the payment document if the advance is not received;
- Units of measurement – if the unit is not defined;
- Unit quantity and price – if the unit is not specified;
- Product code, if the product is imported to countries (EAEU);
The product name must be accurate
At the beginning of the article, we indicated errors that may deprive you of the right to deduct VAT on grounds that are completely legal from the Federal Tax Service.
So, the first mistake: an error that does not allow tax authorities to identify the name of a product (work, service, property right). If the invoice shows an incorrect title, then deduction will be made. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in Letter No. 03-03-06/1/47252 dated August 14, 2015 confirms that in such a situation the refusal to deduct is legal.
In addition, check that the name indicated on the invoice matches the name indicated in the primary document (delivery note, work completion certificate, etc.). If there is a difference in wording, even a court may not help here. For example, in the Resolution of the Twentieth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated November 28, 2011 No. 20AP-4364/11, the dispute was resolved in favor of the Federal Tax Service. The judges considered a situation where the invoice stated “garage repair work,” and the certificate of completion stated “railroad repair.” The arbitrators held that the contractor should have properly corrected the invoice or else the right to deduction would be lost.
It happens that the invoice does not indicate a specific name, but only a link to the contract is given (for example, services under such and such a contract). We would like to immediately warn you that it is better not to allow such formulations. In practice, tax authorities often do not accept such invoices, believing that such design does not allow one to understand the exact name of the goods, works or services. Moreover, even a judicial review of the dispute does not guarantee a decision in your favor. For example, in the Resolution of the Ninth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated January 17, 2013 No. 09AP-38028/2012 in case No. A40-80881/12-91-445, what was important for the court (along with other circumstances) was the fact that the invoices in the column “ name of the product” did not disclose the types of services provided, but contained the general wording “services under a contract.” As a result, the dispute was resolved in favor of the inspection.
Although in arbitration practice one can also find decisions made in favor of companies (Resolutions of the Tenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated 04/09/12 No. 10AP-301/12 and FAS Moscow District dated 08/24/11 No. F05-8167/11). One of the main arguments is as follows: since the details of the contract are indicated in the invoice, nothing prevents the auditors from opening the contract and finding out the exact name.
What if information about goods (works, services) is provided in the invoice, but it is incomplete? This issue was considered by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in Letter No. 03-07-09/10 dated 05.10.11. The agency explained that if the invoice contains incomplete information about the goods, but the invoice does not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the above information, then such a document is not a basis for refusing to accept VAT amounts for deduction.
Dangerous invoice details
What not to miss:
| Invoice date | This data is needed in order to determine the deadline for paying the tax; you should not skip it, and even more so, make a mistake; |
| Full name or transaction name | Allows you to find a taxpayer in the database; |
| Buyer and seller address | You must specify: 1. If it is physical. person-place of registration 2. If this is a legal entity-place of registration The error will be the address of the parties' activities |
| TIN and checkpoint | The code allows you to find it in the database; without the code, the document will not be considered |
| Information about the sender and recipient of the cargo | If the seller and the buyer perform the task, then we make the note “THE SAME”; |
| Owner's signature | The signature must be signed by the entrepreneur himself; |
| Volume of goods and their cost | This data is needed to set up VAT calculations; |
| Product type | If the goods are taxed at different rates, then we register them separately; |
| Country of issue | It is necessary to register the country of the goods in order to establish the VAT payer; |
| Payment document details | So that during checks it is possible to compare the data in the invoice including primary documents (receipts, orders, checks); |
Name and TIN of the seller and buyer
Second error: the name of the seller and (or) buyer is missing or incorrectly indicated.
It happens that when issuing an invoice, the company made an inaccuracy in the name of the buyer. For example, capital letters are replaced with lowercase ones and vice versa, or extra symbols (dashes, commas) are added. If other mandatory details are correct and do not prevent tax authorities from identifying the counterparty, then the deduction on such an invoice is legal (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/02/12 No. 03-07-11/130 and dated 08/15/12 No. 03-07-09/117, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated January 16, 2006 No. KA-A40/13545-05).
An invoice in which the counterparty mistakenly indicated the letter “e” instead of “e” and vice versa will not be an obstacle to deducting VAT. Such conclusions can be drawn based on the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 06/08/11 No. 16-15/55909.
Is the absence or incorrect indication of the seller’s (or buyer’s) TIN a sufficient basis for “removing” the deduction? Practice shows that for inspectors this may be a reason to refuse a deduction.
However, if the supplier made a mistake in indicating the buyer’s TIN, or did not indicate his number at all, then such an error does not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the buyer, because it is he who is checking (Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated August 27, 2014 in case No. A32-11444/ 2012, FAS Moscow District dated April 27, 2011 No. KA-A40/2549-11 in case No. A40-160091/09-142-1315).
The same is true if the counterparty made a mistake in writing his TIN, and the error is in the nature of a clerical error or misprint (for example, an extra zero was added, or one digit was “doubled”). The Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District in its Resolution dated 04/08/2013 in case No. A14-7612/2011 noted that such a typo does not interfere with the identification of the seller. In the Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated December 30, 2014 No. F08-9625/2014 in case No. A32-26444/2012, the court considered that a typo in writing the TIN should not prevent the taxpayer from deducting VAT.
In other cases, the position of the courts is contradictory. For example, in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated July 23, 2012 in case No. A42-2345/2010, the court did not accept the indication in the invoice of an incorrect TIN of the seller as an argument for “withdrawal” of the deduction. The arbitrators noted that the company could not have known about the unreliability of the TIN. Resolution of the Eighteenth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated January 22, 2015 No. 18AP-15113/2014 in case No. A47-7539/2013 was also issued in favor of the companies. But there are also decisions with court conclusions that incorrect indication of the TIN in the invoice deprives the buyer of VAT deduction (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated April 5, 2012 No. A68-2733/11).
Secure invoice details
There are a number of safe details that will not entail a refusal by the tax office to deduct VAT:
| Additional details | You can include additional information in the document, for example: product number, price list number; |
| Units | It is necessary to indicate only if the product can be measured in any units; |
| Document Number | You can number invoices, as it is convenient for the organization; |